Abstract
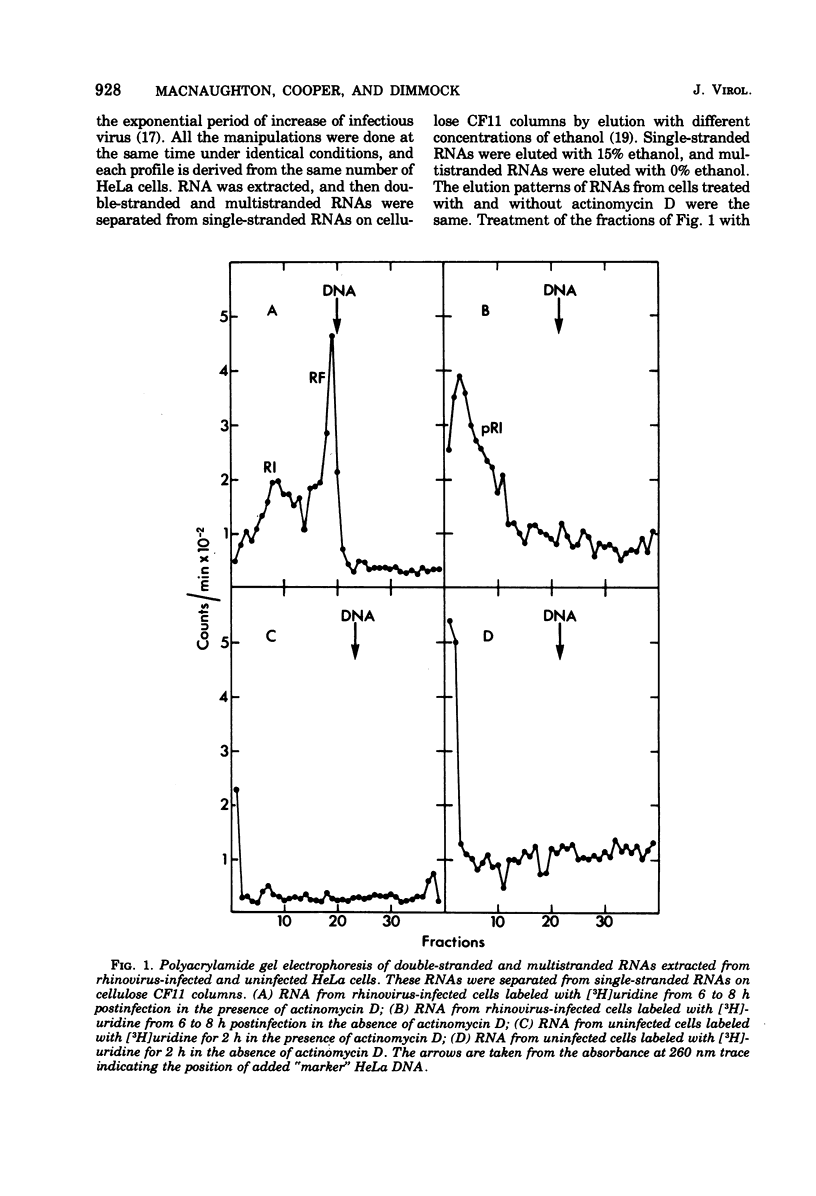
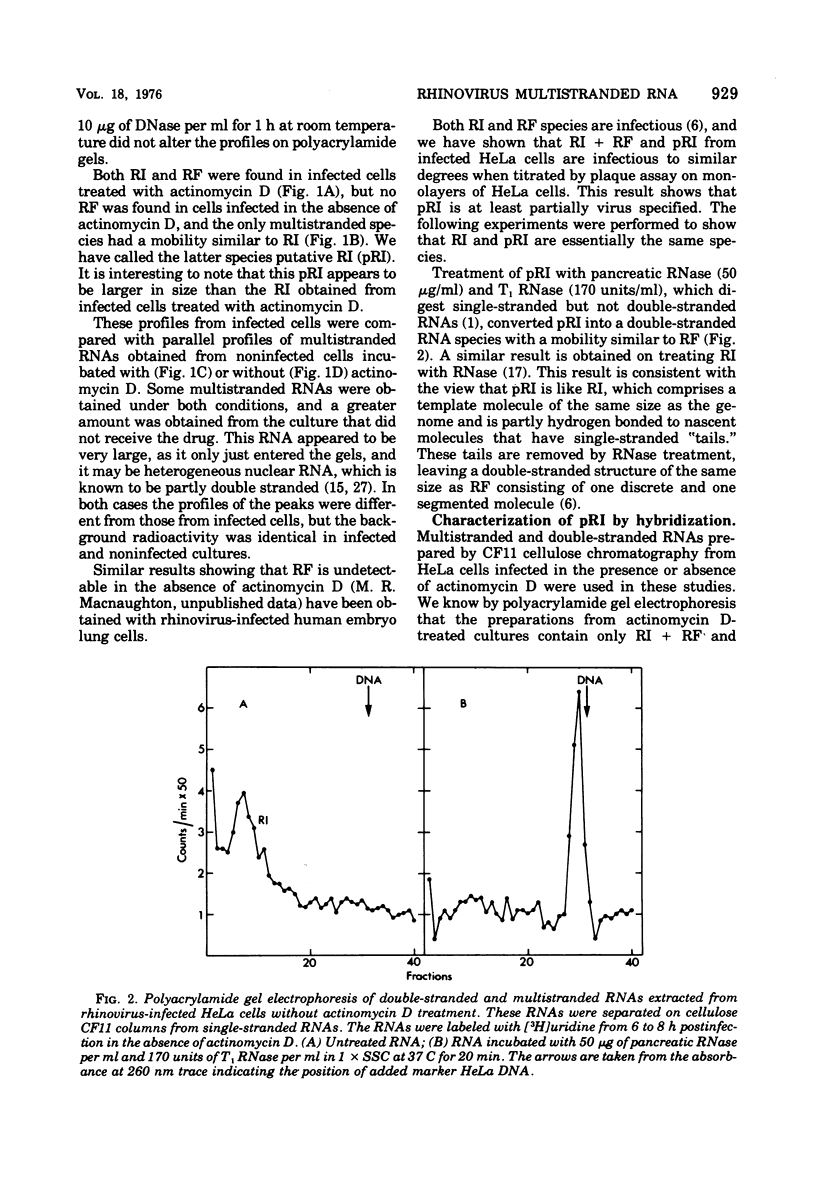
The multistranded and double-stranded RNAs synthesized in HeLa cells infected with rhinovirus in the presence and in the absence of actinomycin D have been characterized by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and hybridization studies. The replicative form is only found in infected cells treated with actinomycin D, whereas the replicative intermediate is found in both the presence and the absence of the drug. The significance of these results is discussed.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Avery R. J. The subcellular localization of virus-specific RNA in influenza virus-infected cells. J Gen Virol. 1974 Jul;24(1):77–88. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-24-1-77. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baltimore D., Girard M. An intermediate in the synthesis of poliovirus RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Aug;56(2):741–748. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.2.741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baltimore D. Structure of the poliovirus replicative intermediate RNA. J Mol Biol. 1968 Mar 14;32(2):359–368. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90015-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bechet J. M. Isolation of the minus strand of encephalomyocarditis virus RNA. Virology. 1972 Jun;48(3):855–857. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90169-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Best M., Evans B., Bishop J. M. Double-stranded replication form of poliovirus RNA: phenotype of heterozygous molecules. Virology. 1972 Mar;47(3):592–603. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90548-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cordell-Stewart B., Taylor M. W. Effect of viral double-stranded RNA on protein synthesis in intact cells. J Virol. 1973 Feb;11(2):232–237. doi: 10.1128/jvi.11.2.232-237.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrenfeld E., Hunt T. Double-stranded poliovirus RNA inhibits initiation of protein synthesis by reticulocyte lysates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 May;68(5):1075–1078. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.5.1075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franklin R. M. Purification and properties of the replicative intermediate of the RNA bacteriophage R17. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Jun;55(6):1504–1511. doi: 10.1073/pnas.55.6.1504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garwes D. J., Wright P. J., Cooper P. D. Poliovirus temperature-sensitivie mutants defective in cytopathic effects are also defective in synthesis of double-stranded RNA. J Gen Virol. 1975 Apr;27(1):45–59. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-27-1-45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girard M. In vitro synthesis of poliovirus ribonucleic acid: role of the replicative intermediate. J Virol. 1969 Apr;3(4):376–384. doi: 10.1128/jvi.3.4.376-384.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grado C., Fischer S., Contreras G. The inhibition by actinomycin D of poliovirus multiplication HEp 2 cells. Virology. 1965 Dec;27(4):623–625. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(65)90189-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Hunt T., Jackson R. J., Robertson H. D. The characteristics of inhibition of protein synthesis by double-stranded ribonucleic acid in reticulocyte lysates. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jan 25;250(2):409–417. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jelinek W., Darnell J. E. Double-stranded regions in heterogeneous nuclear RNA from Hela cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Sep;69(9):2537–2541. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.9.2537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr I. M., Brown R. E., Tovell D. R. Characterization of the polypeptides formed in response to encephalomyocarditis virus ribonucleic acid in a cell-free system from mouse ascites tumor cells. J Virol. 1972 Jul;10(1):73–81. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.1.73-81.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koliais S. I., Dimmock N. J. Replication of rhinovirus RNA. J Gen Virol. 1973 Jul;20(1):1–15. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-20-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loening U. E. The fractionation of high-molecular-weight ribonucleic acid by polyacrylamide-gel electrophoresis. Biochem J. 1967 Jan;102(1):251–257. doi: 10.1042/bj1020251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macnaughton M. R., Dimmock N. J. Polyadenylic acid sequences in rhinovirus RNA species from infected human diploid cells. J Virol. 1975 Sep;16(3):745–748. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.3.745-748.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin B. A., Burke D. C. The replication of Semliki Forest virus. J Gen Virol. 1974 Jul;24(1):45–66. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-24-1-45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell W. R., Tershak D. R. The synthesis of complementary ribonucleic acid during infection with LSc poliovirus. Virology. 1973 Jul;54(1):290–293. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90140-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noble J., Levintow L. Dynamics of poliovirus-specific RNA synthesis and the effects of inhibitors of virus replication. Virology. 1970 Mar;40(3):634–642. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90208-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oberg B. F., Shatkin A. J. Initiation of picornavirus protein synthesis in ascites cell extracts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Dec;69(12):3589–3593. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.12.3589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oberg B., Philipson L. Replicative structures of poliovirus RNA in vivo. J Mol Biol. 1971 Jun 28;58(3):725–737. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90036-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plagemann P. G., Swim H. E. Synthesis of ribonucleic acid by mengovirus-induced RNA polymerase in vitro: nature of products and of RNase-resistant intermediate. J Mol Biol. 1968 Jul 14;35(1):13–25. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(68)80034-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy P., Bishop D. H. Isolation and properties of poliovirus minus strand ribonucleic acid. J Virol. 1970 Nov;6(5):604–609. doi: 10.1128/jvi.6.5.604-609.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryskov A. P., Farashyan V. R., Georgiev G. P. Ribonuclease-stable base sequences specific exclusively for giant dRNA. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Apr 12;262(4):568–572. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(72)90502-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaffer F. L., Gordon M. Differential inhibitory effects of actinomycin D among strains of poliovirus. J Bacteriol. 1966 Jun;91(6):2309–2316. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.6.2309-2316.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith A. E. The initiation of protein synthesis directed by the RNA from encephalomyocarditis virus. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Mar 1;33(2):301–313. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02684.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart W. E., 2nd, De Clercq E. Relationship of cytotoxicity and interferon-inducing activity of polyriboinosinic acid. Polyribocytidylic acid to the molecular weights of the homopolymers. J Gen Virol. 1974 Apr;23(1):83–89. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-23-1-83. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stott E. J., Heath G. F. Factors affecting the growth of Rhinovirus 2 in suspension cultures of L132 cells. J Gen Virol. 1970 Jan;6(1):15–24. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-6-1-15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tytell A. A., Lampson G. P., Field A. K., Hilleman M. R. Inducers of interferon and host resistance. 3. Double-stranded RNA from reovirus type 3 virions (reo 3-RNA). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Oct;58(4):1719–1722. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.4.1719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



