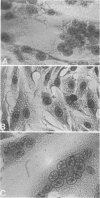
Abstract
Cell-free extracts prepared from herpes simplex virus-infected BHK-21 cells rapidly induced exogenous fusion when incubated with indicator monolayers of uninfected BHK-21 cells. Fusion was first observed at 1 h, and peak activity was reached by 4 h. Divalent cations were required for activity. Inhibition of indicator cell macromolecular synthesis, with metabolic inhibitors, failed to prevent formation of cell-free extract-induced polykaryocytes. Removal of virus particles from the cell-free extract by velocity sedimentation centrifugation did not affect cell-free extract exogenous fusion activity. Studies using molecular probes, namely, glycosidases, lectins, and antiserum (directed against either HSV envelope or capsid proteins), suggest that the factor(s) responsible for herpesvirus fusion is a fucosylated glycoprotein that is not a structural component of the virion.
Full text
PDF

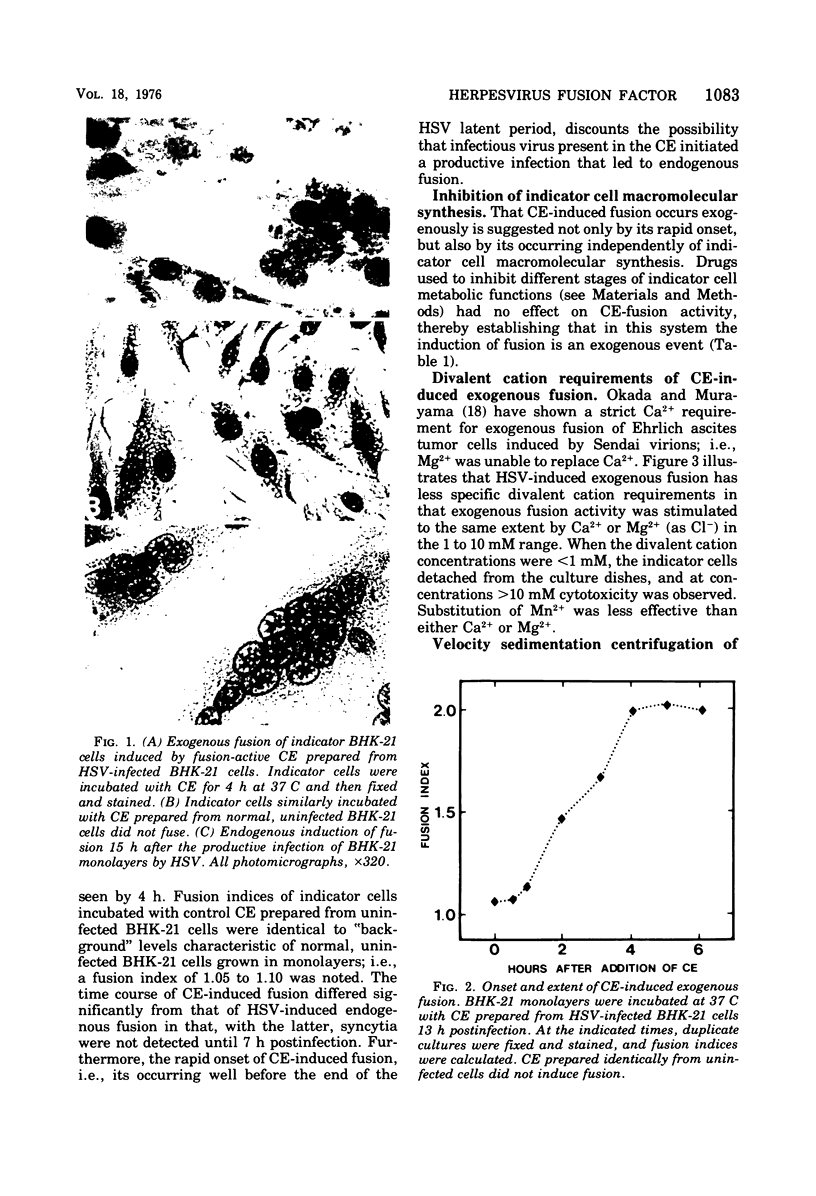
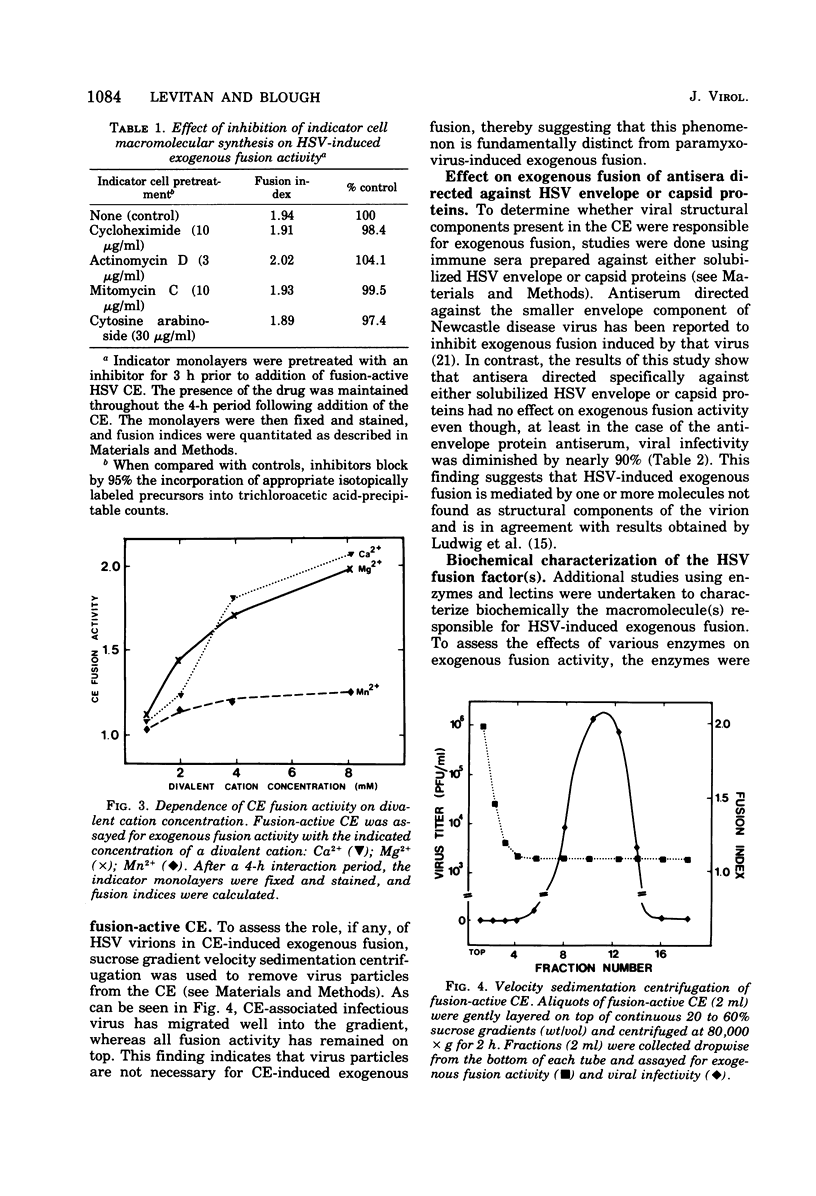
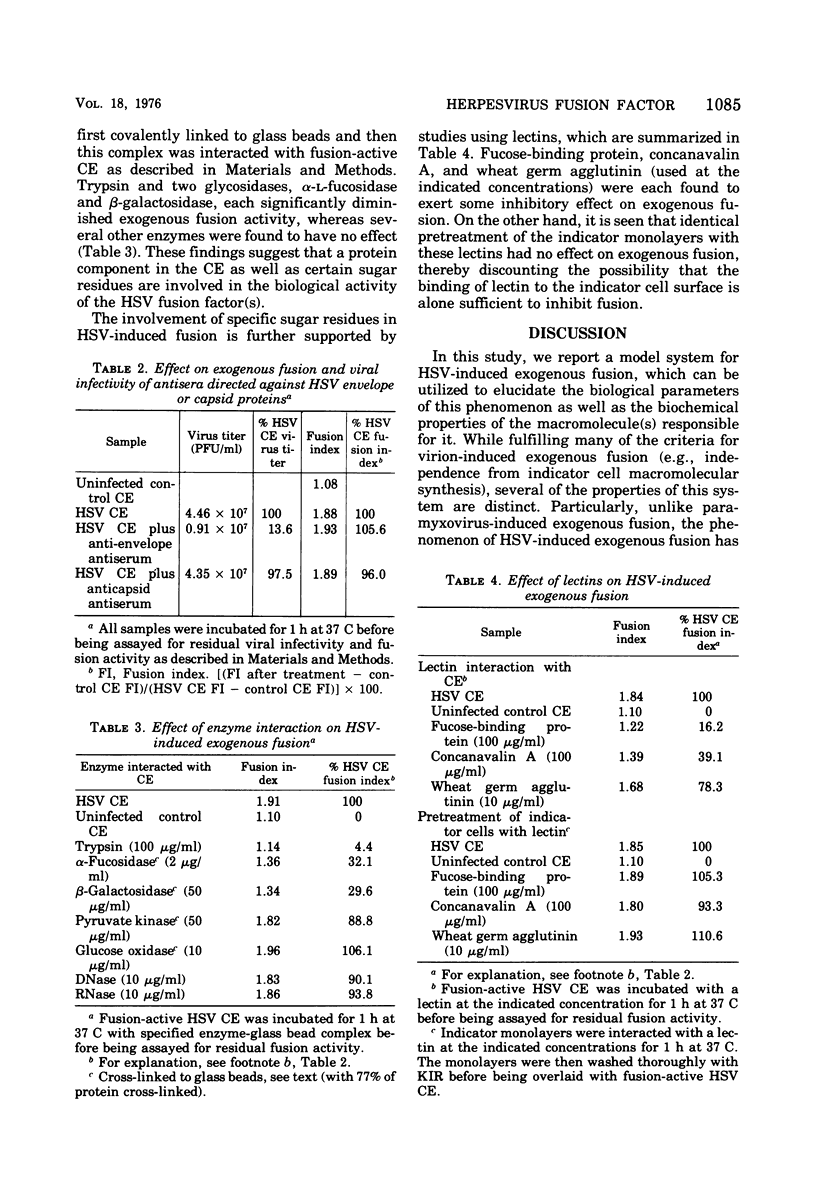


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bratt M. A., Gallaher W. R. Comparison of fusion from within and fusion from without by Newcastle disease virus. In Vitro. 1970 Jul-Aug;6(1):3–14. doi: 10.1007/BF02616129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen G. H., Vaughan R. K., Lawrence W. C. Deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis in synchronized mammalian KB cells infected with herpes simplex virus. J Virol. 1971 Jun;7(6):783–791. doi: 10.1128/jvi.7.6.783-791.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen G. H., Wilcox W. C. Soluble antigens of vaccinia-infected mammalian cells. I. Separation of virus-induced soluble antigens into two classes on the basis of physical characteristics. J Bacteriol. 1966 Sep;92(3):676–686. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.3.676-686.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DULBECCO R., VOGT M. Plaque formation and isolation of pure lines with poliomyelitis viruses. J Exp Med. 1954 Feb;99(2):167–182. doi: 10.1084/jem.99.2.167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ejercito P. M., Kieff E. D., Roizman B. Characterization of herpes simplex virus strains differing in their effects on social behaviour of infected cells. J Gen Virol. 1968 May;2(3):357–364. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-2-3-357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flanagan J. F. Virus-specific ribonucleic acid synthesis in KB cells infected with herpes simplex virus. J Virol. 1967 Jun;1(3):583–590. doi: 10.1128/jvi.1.3.583-590.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallaher W. R., Levitan D. B., Blough H. A. Effect of 2-deoxy-D-glucose on cell fusion induced by Newcastle disease and herpes simplex viruses. Virology. 1973 Sep;55(1):193–201. doi: 10.1016/s0042-6822(73)81021-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall W. W., Martin S. J. The biochemical and biological characteristics of the surface components of measles virus. J Gen Virol. 1974 Mar;22(3):363–374. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-22-3-363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homma M., Tamagawa S. Restoration of the fusion activity of L cell-borne Sendai virus by trypsin. J Gen Virol. 1973 Jun;19(3):423–426. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-19-3-423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hosaka Y., Shimizu Y. K. Artificial assembly of envelope particles of HVJ (Sendai virus). I. Assembly of hemolytic and fusion factors from envelopes solubilized by Nonidet P40. Virology. 1972 Sep;49(3):627–639. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90519-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOHN A. POLYKARYOCYTOSIS INDUCED BY NEWCASTLE DISEASE VIRUS IN MONOLAYERS OF ANIMAL CELLS. Virology. 1965 Jun;26:228–245. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(65)90050-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller J. M., Spear P. G., Roizman B. Proteins specified by herpes simplex virus. 3. Viruses differing in their effects on the social behavior of infected cells specify different membrane glycoproteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Apr;65(4):865–871. doi: 10.1073/pnas.65.4.865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludwig H., Becht H., Rott R. Inhibition of herpes virus-induced cell fusion by concanavalin A, antisera, and 2-deoxy-D-glucose. J Virol. 1974 Aug;14(2):307–314. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.2.307-314.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NII S., KAMAHORA J. Cytopathic changes induced by herpes simplex virus. Biken J. 1961 Dec;4:255–270. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okada Y., Murayama F. Requirement of calcium ions for the cell fusion reaction of animal cells by HVJ. Exp Cell Res. 1966 Nov-Dec;44(2):527–551. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(66)90458-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROIZMAN B. Polykaryocytosis. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1962;27:327–342. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1962.027.001.031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheid A., Choppin P. W. Identification of biological activities of paramyxovirus glycoproteins. Activation of cell fusion, hemolysis, and infectivity of proteolytic cleavage of an inactive precursor protein of Sendai virus. Virology. 1974 Feb;57(2):475–490. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90187-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seto J. T., Becht H., Rott R. Effect of specific antibodies on biological functions of the envelope components of Newcastle disease virus. Virology. 1974 Oct;61(2):354–360. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90273-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegert R., Falke D. Elektronenmikroskopische Untersuchungen über die Entwicklung des Herpesvirus hominis in Kulturzellen. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1966;19(2):230–249. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spear P. G. Membrane proteins specified by herpes simplex viruses. I. Identification of four glycoprotein precursors and their products in type 1-infected cells. J Virol. 1976 Mar;17(3):991–1008. doi: 10.1128/jvi.17.3.991-1008.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TREADWELL P. E., ROSS J. D. Effects of human adult and bovine fetal serum on colonial propagation of rabbit cells. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1962 Mar;28:679–697. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHEELER C. E., Jr BIOLOGIC COMPARISON OF A SYNCYTIAL AND A SMALL GIANT CELL-FORMING STRAIN OF HERPES SIMPLEX. J Immunol. 1964 Nov;93:749–756. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson D. H., Shedden W. I., Elliot A., Tetsuka T., Wildy P., Bourgaux-Ramoisy D., Gold E. Virus specific antigens in mammalian cells infected with herpes simplex virus. Immunology. 1966 Oct;11(4):399–408. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]