Abstract
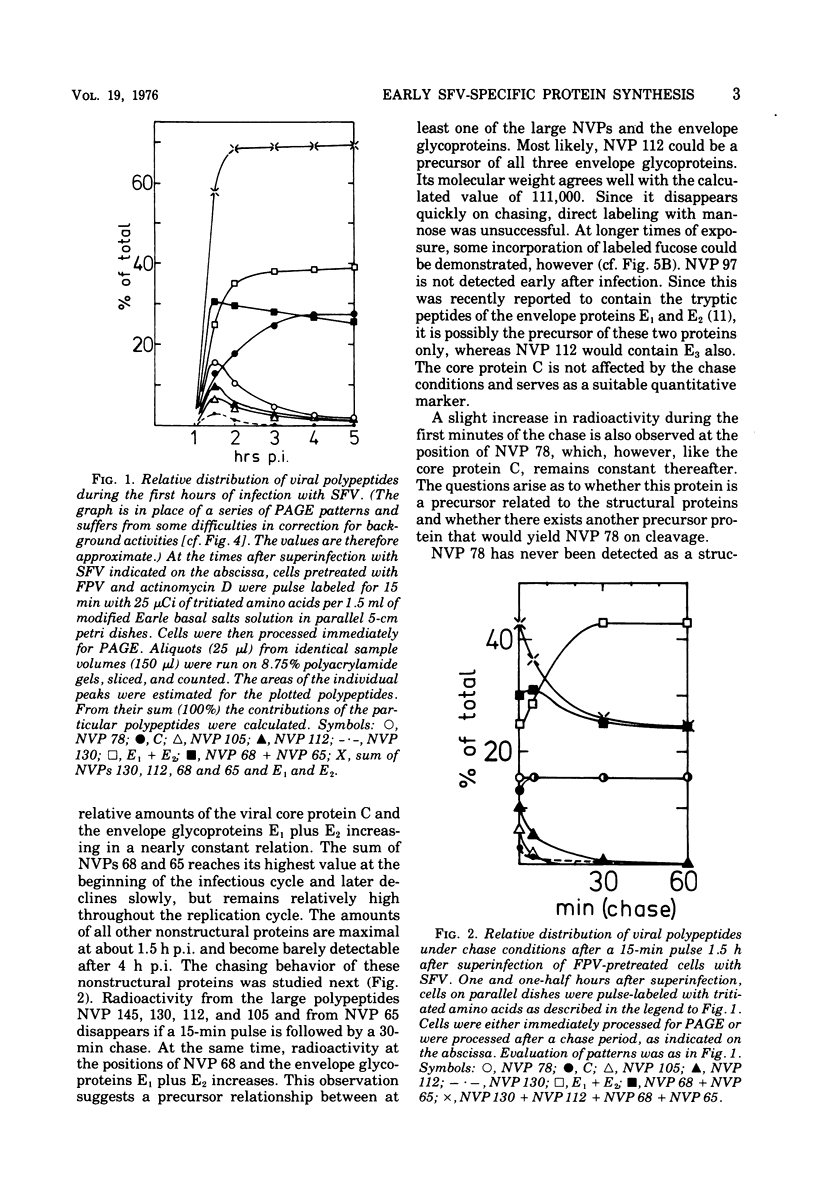
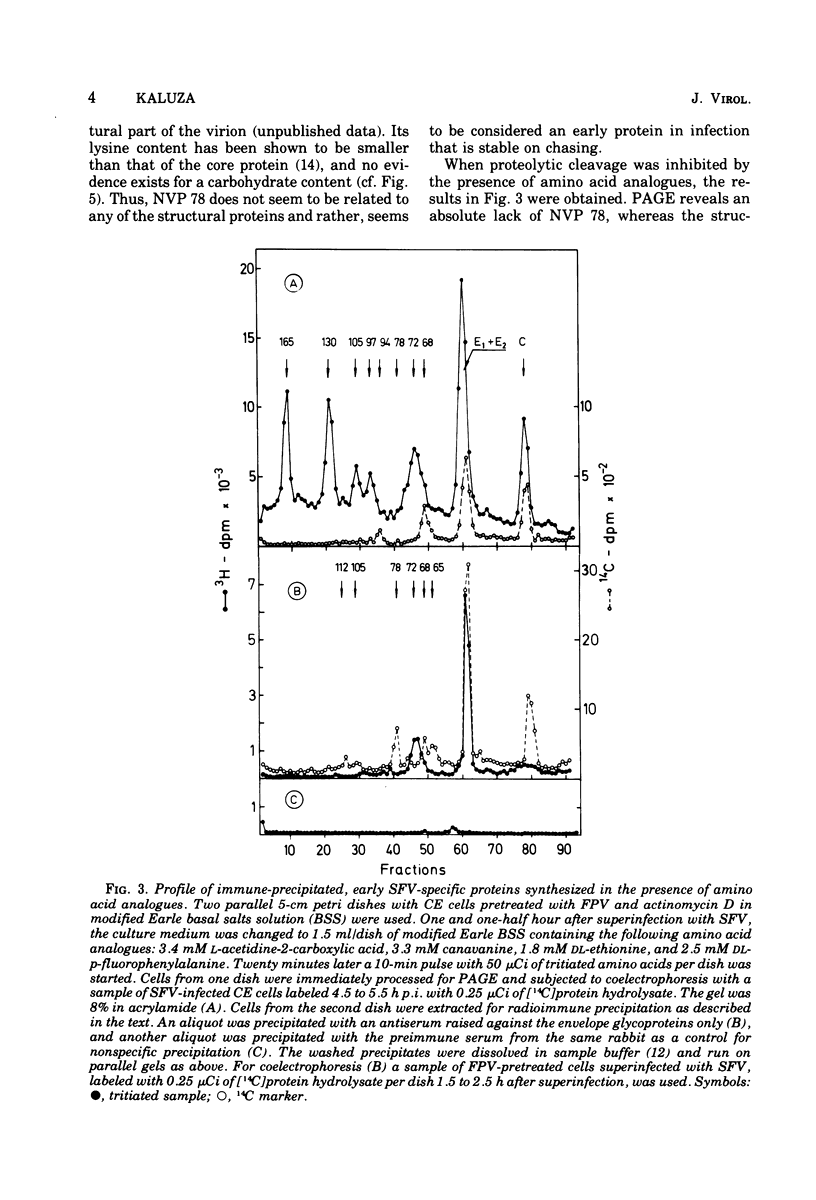
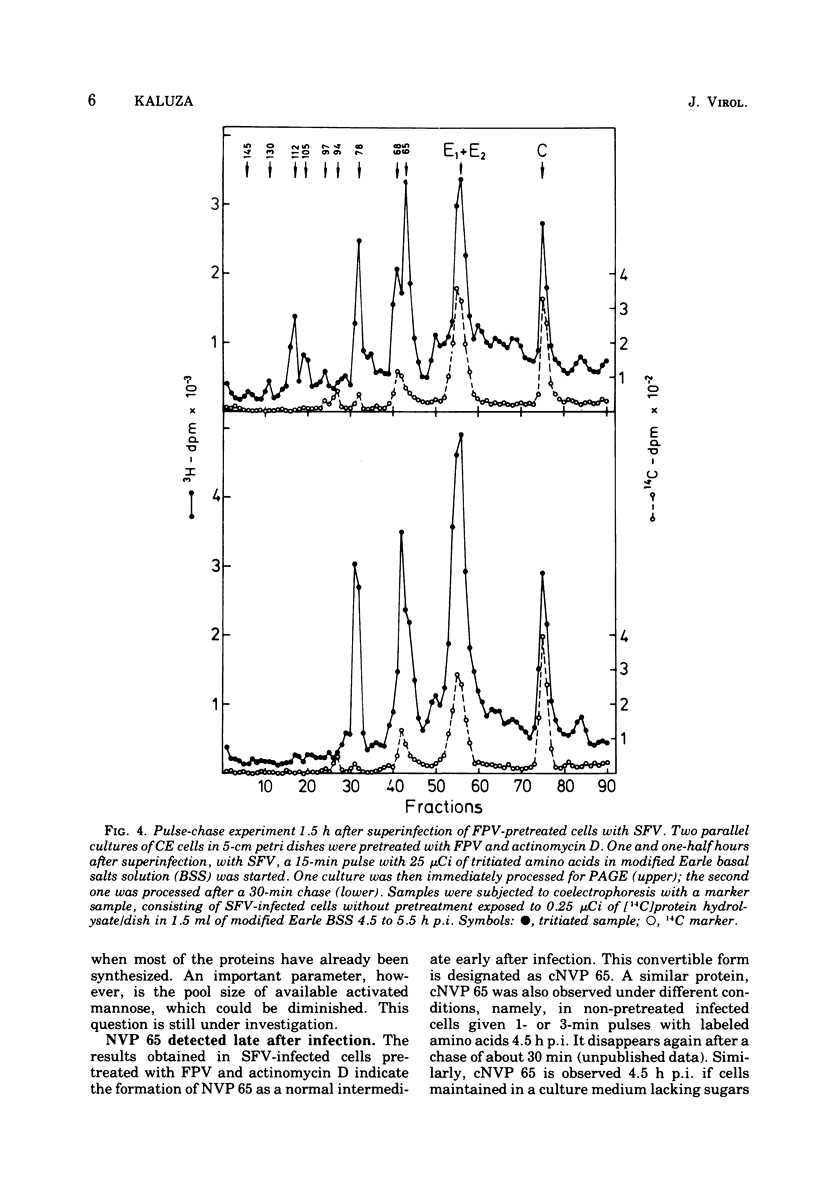
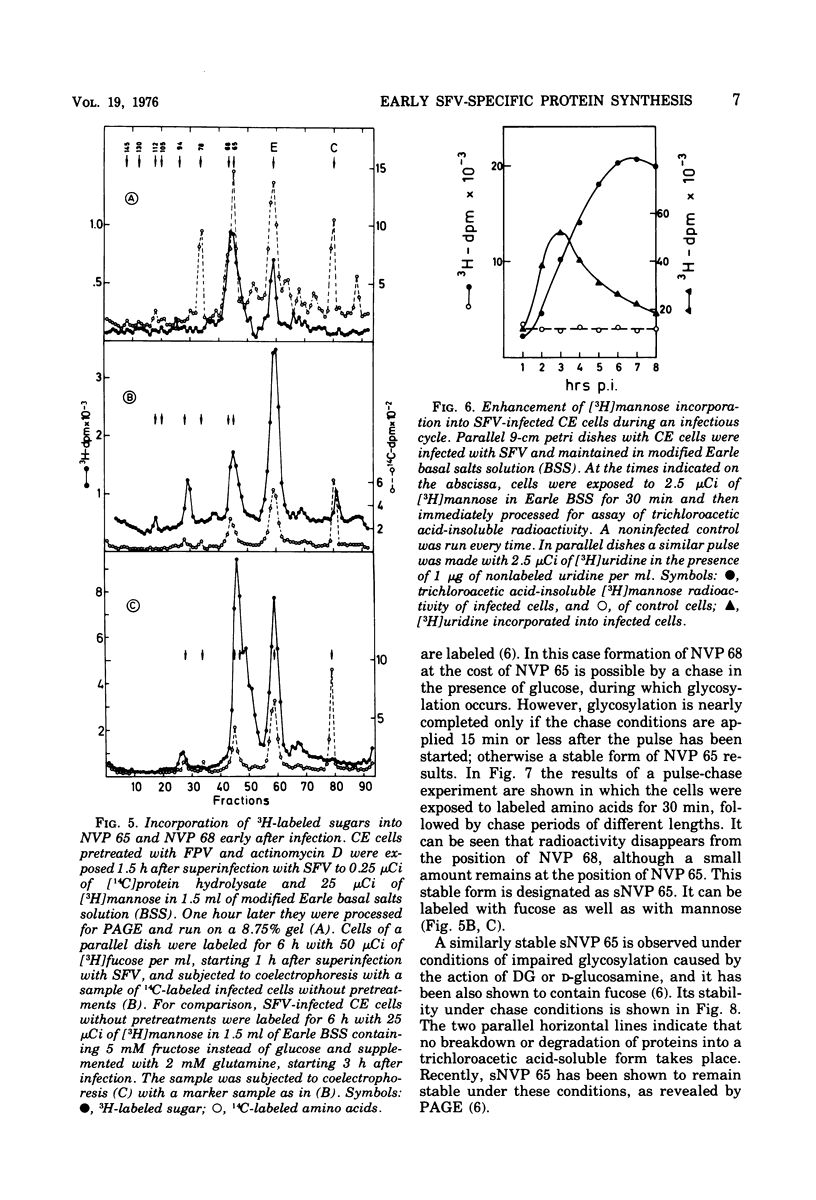
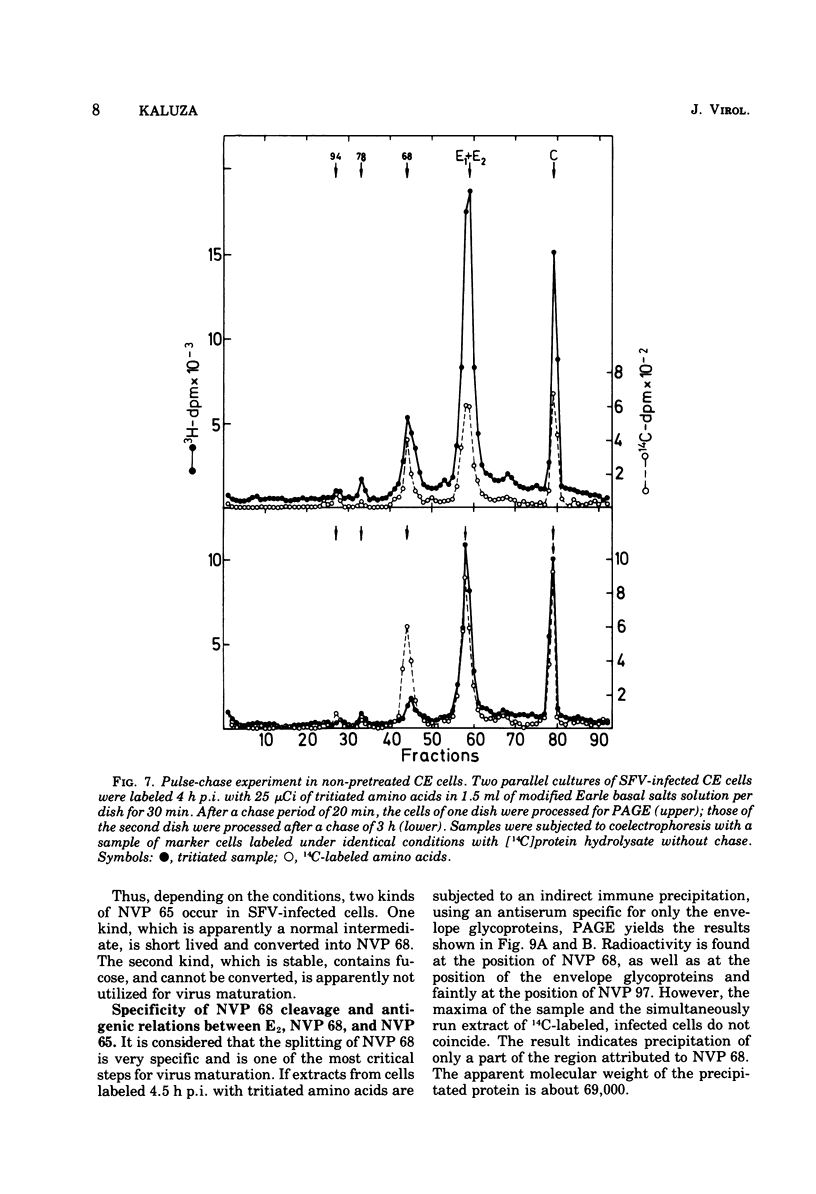
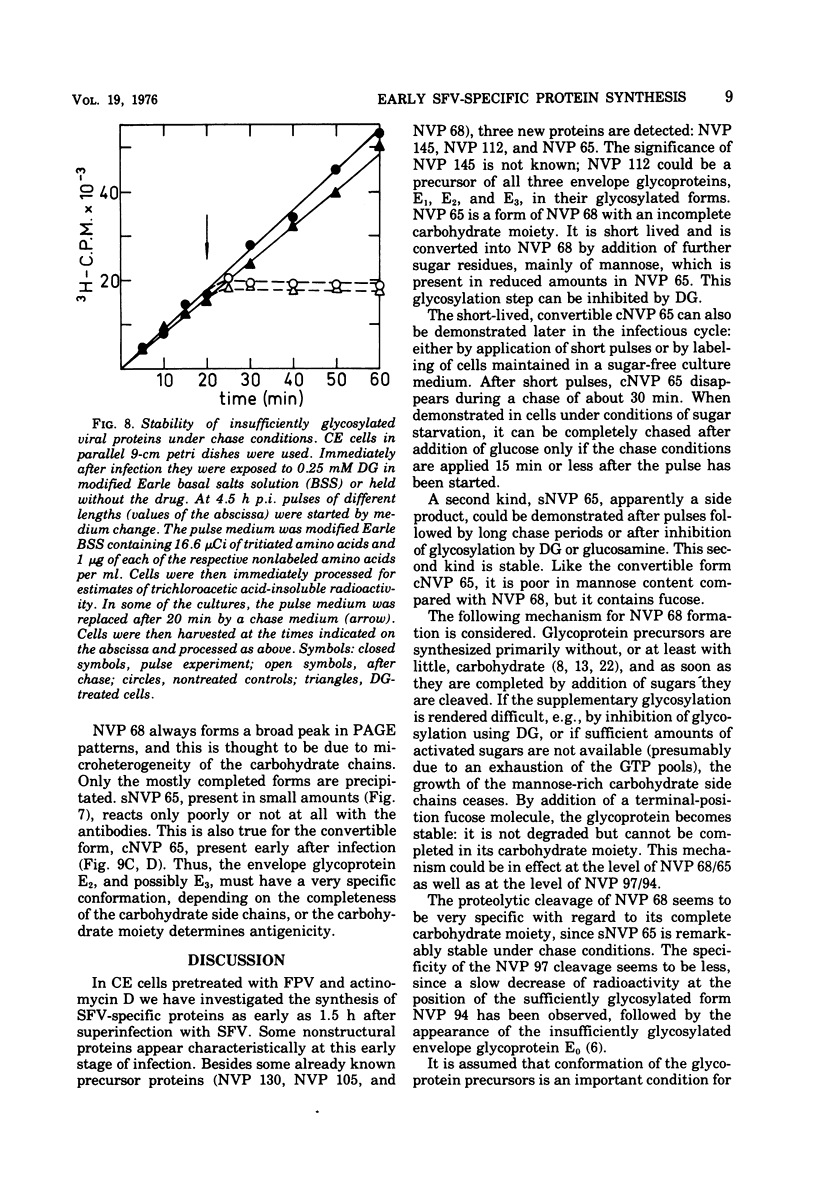
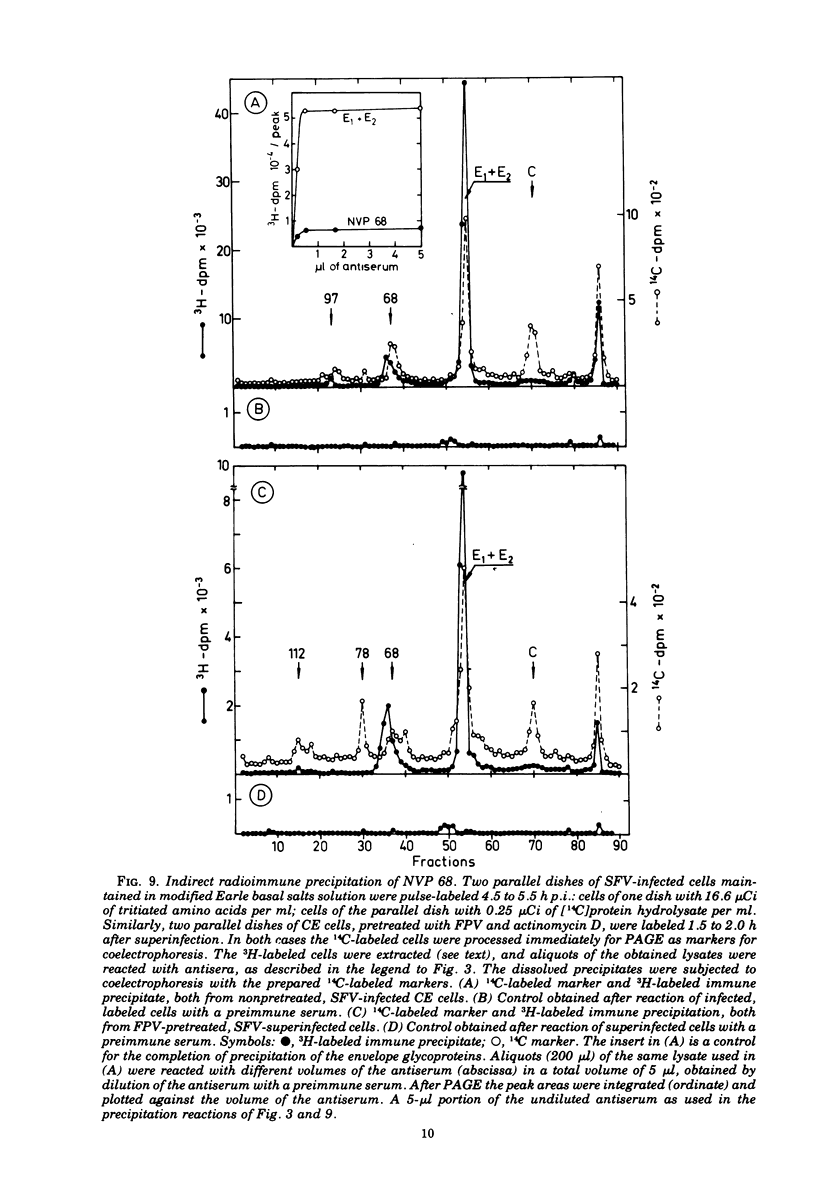
Cells preinfected with fowl plague virus followed by treatment with actinomycin D are a suitable system for studying early protein synthesis in cells infected with Semliki forest virus. One and one-half hours after superinfection, three new nonstructural proteins (NVP) were detected: NVP 145, NVP, 112, and NVP 65. They appeared in parallel with a low incorporation of mannose at the beginning of the infectious cycle. Behavior on chasing suggested a precursor relationship of NVP 112 to the envelope glycoproteins. Two kinds of NVP 65 are described, both of which are varieties of NVP 68 with an incomplete mannose content. One type, detected early after infection, was converted into NVP 68 by supplementary glycosylation. The second, late type was stable. It contains fucose and resembles the NVP 65 observed after impairment of glycosylation. The mechanism of NVP 68 glycosylation is discussed. The presence of the complete carbohydrate moiety is crucial for the cleavage of NVP 68 into the envelope proteins E2 and E3 and, thus, for virus maturation. Only the complete form of NVP 68 was precipitated by envelope-specific antisera. A large production of NVP 78 is a further feature of the early events in infected cells. It is not related to the structural proteins.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cancedda R., Villa-Komaroff L., Lodish H. F., Schlesinger M. Initiation sites for translation of sindbis virus 42S and 26S messenger RNAs. Cell. 1975 Oct;6(2):215–222. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90012-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garoff H., Simons K., Renkonen O. Isolation and characterization of the membrane proteins of Semliki Forest virus. Virology. 1974 Oct;61(2):493–504. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90285-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helenius A., Simons K. Solubilization of membranes by detergents. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Mar 25;415(1):29–79. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(75)90016-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson M. F., Baltimore D. Polypeptide cleavages in the formation of poliovirus proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Sep;61(1):77–84. doi: 10.1073/pnas.61.1.77. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaluza G. Effect of impaired glycosylation on the biosynthesis of Semliki forest virus glycoproteins. J Virol. 1975 Sep;16(3):602–612. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.3.602-612.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaluza G., Kraus A. A., Rott R. Inhibition of cellular protein synthesis by simultaneous pretreatment of host cells with fowl plague virus and actinomycin D: a method for studying early protein synthesis of several RNA viruses. J Virol. 1975 Jan;17(1):1–9. doi: 10.1128/jvi.17.1.1-9.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaluza G., Schmidt M. F., Scholtissek C. Effect of 2-deoxy-D-glucose on the multiplication of Semliki Forest virus and the reversal of the block by mannose. Virology. 1973 Jul;54(1):179–189. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90127-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaluza G., Scholtissek C., Rott R. Inhibition of the multiplication of enveloped RNA-viruses by glucosamine and 2-deoxy-D-glucose. J Gen Virol. 1972 Mar;14(3):251–259. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-14-3-251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keränen S., Käriäinen L. Proteins synthesized by Semliki Forest virus and its 16 temperature-sensitive mutants. J Virol. 1975 Aug;16(2):388–396. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.2.388-396.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Käriäinen L., Simons K., von Bonsdorff C. H. Studies in subviral components of Semliki Forest virus. Ann Med Exp Biol Fenn. 1969;47(4):235–248. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molnar J., Sy D. Attachment of glucosamine to protein at the ribosomal site of rat liver. Biochemistry. 1967 Jul;6(7):1941–1947. doi: 10.1021/bi00859a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morser M. J., Kennedy S. I., Burke D. C. Virus-specified polypeptides in cells infected with Semliki Forest virus. J Gen Virol. 1973 Oct;21:19–29. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-21-1-19. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osterrieth P. M., Calberg-Bacq C. M. Changes in morphology, infectivity and haemagglutinating activity of Semliki Forest virus produced by the treatment with caseinase C from Streptomyces albus G. J Gen Microbiol. 1966 Apr;43(1):19–30. doi: 10.1099/00221287-43-1-19. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russ G., Poláková K. The molecular weight determination of proteins and glycoproteins of RNA enveloped viruses by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis in SDS. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Dec 10;55(3):666–672. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)91196-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scholtissek C. Influence of glucosamine on the uptake of nucleosides by chick fibroblasts and on the incorporation into RNA. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Sep 14;277(3):459–465. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(72)90088-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sefton B. M., Burge B. W. Biosynthesis of the Sindbis virus carbohydrates. J Virol. 1973 Dec;12(6):1366–1374. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.6.1366-1374.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro A. L., Viñuela E., Maizel J. V., Jr Molecular weight estimation of polypeptide chains by electrophoresis in SDS-polyacrylamide gels. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1967 Sep 7;28(5):815–820. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(67)90391-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simons K., Keränen S., Käriänen L. Identification of a precursor for one of the Semliki forest virus membrane proteins. FEBS Lett. 1973 Jan 15;29(2):87–91. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80532-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiro R. G., Spiro M. J. Glycoprotein biosynthesis: studies on thyroglobulin. Characterization of a particulate precursor and radioisotope incorporation by thyroid slices and particle systems. J Biol Chem. 1966 Mar 25;241(6):1271–1282. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wengler G. Comparative studies on polyribosomal, nonpolyribosome-associated and viral 42 S RNA from BHK 21 cells infected with Semliki Forest virus. Virology. 1975 Jun;65(2):601–605. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90068-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wengler G., Wengler G. Studies on the polyribosome-associated RNA in BHK21 cells infected with Semliki Forest virus. Virology. 1974 May;59(1):21–35. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90202-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



