Abstract
Background
Glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) is characterized by an aggressive clinical course, therapeutic resistance, and striking molecular heterogeneity. GBM-derived brain tumor stem cells (BTSCs) closely model this molecular heterogeneity and likely have a key role in tumor recurrence and therapeutic resistance. Emerging evidence indicates that Janus kinase (JAK)2/signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT)3 is an important mediator of tumor cell survival, growth, and invasion in a large group of GBM. Here, we used a large set of molecularly heterogeneous BTSCs to evaluate the translational potential of JAK2/STAT3 therapeutics.
Methods
BTSCs were cultured from GBM patients and MGMT promoter methylation, and the mutation statuses of EGFR, PTEN, and TP53 were determined. Endogenous JAK2/STAT3 activity was assessed in human GBM tissue, BTSCs, and orthotopic xenografts by immunohistochemistry and Western blotting. STAT3 short hairpin (sh)RNA, cucurbitacin-I, and WP1066 were used to inhibit JAK2/STAT3 activity in vitro and in vivo.
Results
The JAK2/STAT3 pathway was demonstrated to be highly activated in human GBM, molecularly heterogeneous BTSCs derived from these tumors, and BTSC xenografts. STAT3 shRNA knockdown or cucurbitacin-I and WP1066 administration resulted in on-target JAK2/STAT3 inhibition and dramatically reduced BTSC survival regardless of endogenous MGMT promoter methylation or EGFR, PTEN, and TP53 mutational status. BTSC orthotopic xenografts maintained the high levels of activated JAK2/STAT3 seen in their parent human tumors. Intraperitoneal WP1066 reduced intratumoral JAK2/STAT3 activity and prolonged animal survival.
Conclusion
Our study demonstrates the in vitro and in vivo efficacy of on-target JAK2/STAT3 inhibition in heterogeneous BTSC lines that closely emulate the genomic and tumorigenic characteristics of human GBM.
Keywords: JAK2/STAT3, brain tumor stem cells, glioblastoma, molecular therapeutics
Glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) is a devastating disease that is notoriously resistant to current therapies, leading to dismal patient outcomes and a median survival of just 14.6 months.1 As such, translation of our rapidly expanding knowledge of the molecular biology of GBM together with the growing repertoire of molecular-based chemotherapeutics now available has the potential to dramatically improve patient outcomes.
Signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT)3 signaling has recently come to the forefront of the glioma literature as a common pathway downstream of paracrine leukemia inhibitory factor, interleukin-6, or erythropoietin signaling in GBM.2–4 Recent transcriptional profiling and signaling network analyses have also identified STAT3 and CCAAT (cytidine-cytidine-adenosine-adenosine-thymidine)-enhancer-binding proteins β as 2 key master transcription factors underlying the mesenchymal subtype of GBM.5 Consequently, STAT3 has become a therapeutic target of significant interest in glioma, and a number of small-molecule inhibitors of the STAT3' upstream regulator Janus kinase (JAK)2 are currently in early preclinical investigation in GBM. Inhibition of JAK2 with AG490 or its more potent second-generation analog WP1066 has demonstrated efficacy in reducing survival and proliferation of U87 and U251 glioma cells in vitro and decreasing tumorigenicity of U87 in subcutaneous xenografts.6,7
JAK2/STAT3 blockade has also demonstrated promise as an adjuvant for other therapeutics. Concurrent inhibition of JAK2/STAT3 with cucurbitacin-I (JSI-124) and blockade of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) with Iressa has been recently reported to potently induce apoptosis in GBM cell lines and sensitize them to temozolomide.8 Emerging evidence suggests that high levels of STAT3 activation are also present within brain tumor stem cells (BTSCs), and STAT3 inhibition has been reported to decrease the self-renewal survival and resistance to temozolomide of glioma stemlike cells in vitro.2–4,9,10 Thus, there is strong evidence in the glioma literature for the crucial role of STAT3 in human GBM, and JAK2-targeted therapeutics have yielded promising results against GBM cell lines in vitro. However, the true translational potential of JAK2/STAT3 therapeutics for GBM remained an unanswered question, as these drugs had yet to be thoroughly investigated in a model that accounted for the molecular heterogeneity of human GBM and assessed on-target efficacy in intracranial humanlike GBM tumors in vivo.
BTSCs have been postulated to be at the root of the disease initiation, recurrence, and therapeutic resistance that is characteristic of GBM. BTSCs isolated from human GBM tumors capture the molecular heterogeneity and mutation spectrum that are characteristic of the disease.11,12 BTSCs also initiate orthotopic xenograft tumors in nonobese diabetic/severe combined immunodeficient (NOD SCID) mice that emulate the phenotypic and molecular characteristics of their parent human tumors, hence making them the most relevant model currently available for preclinical evaluation of novel GBM therapeutics. Our group has successfully established a large collection of BTSC lines from glioma patients that display the molecular heterogeneity of the disease,13 including rare lines endogenously expressing isocitrate dehydrogenase (IDH1)R132H, differential MGMT promoter methylation status, and mutations in common targets such as PTEN, TP53, and EGFR variant III (unpublished), amongst others.14–16
Here, we use a large panel of patient-derived GBM BTSCs to investigate whether JAK2/STAT3 is (i) a clinically relevant signaling pathway whose activity is crucial in molecularly diverse BTSCs and (ii) amenable to therapeutic targeting in vivo in orthotopic humanlike GBM xenografts. We demonstrate that JAK2/STAT3 signaling is a key driver for proliferation in GBM BTSCs and that on-target inhibition of this pathway results in decreased BTSC survival in vitro and slows disease progression in vivo.
Materials and Methods
Brain Tumor Sphere Culture
GBM BTSCs were cultured from a series of tumor specimens (Table 1) obtained following informed consent from adult GBM patients during their operative procedure as previously described13 and approval by the University of Calgary Ethics Review Board. Briefly, BTSC cultures were initiated in defined culture serum-free medium (SFM) and gave rise to nonadherent spheres after 7–21 days in culture. Primary tumor spheres were expanded for several passages and then cryopreserved in 10% dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO; Sigma-Aldrich) in SFM until use in experiments. Human fetal neural stem cells were also cultured as previously described17 and induced to differentiate into astrocytes by addition of 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS) and removal of epidermal growth factor, fibroblast growth factor 2, and heparan sulfate.
Table 1.
Identification of a molecularly heterogeneous panel of BTSCs
| Sample No. | Diagnosis | Age, y | Sex | MGMT Status | EGFR Status | PTEN Status | TP53 Status | IDH1 Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 41 | GBM-r | 49 | M | U | wt | wt | wt | wt |
| 75 | GBM | 74 | M | U | wt | wt | wt | wt |
| 12 | GBM-r | 59 | M | U | wt | Frameshift Del codon 328 | wt | wt |
| 30 | GBM | 67 | M | U | wt | N49I | wt | wt |
| 48 | GBM | 68 | M | M | G598V | wt | wt | wt |
| 53 | GBM | 59 | M | M | G598V | wt | F113L | wt |
| 63 | GBM | 59 | F | M | vIII | wt | wt | wt |
| 68 | GBM | 59 | M | U | vIII | wt | wt | wt |
| 73 | GBM | 52 | M | M | vIII | Ins intron 5 | V272L, R273H | wt |
| 147 | GBM-r | 56 | M | U | vIII | Frameshift Ins codon 174 | P278S | wt |
Abbreviations, GBM-r, sample obtained at recurrence following initiation of radiation and temozolomide; M, methylated MGMT promoter; U, unmethylated MGMT promoter; wt, wild type; vIII, variant III; Del, deletion; Ins, insertion.
BTSC Characterization
BTSCs were plated on glass coverslips coated with poly-l-ornithine (Sigma-Aldrich) in SFM or SFM + 1% FBS for 7 days before fixation with 4% paraformaldehyde. Triple label immunostaining was performed for glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) (rabbit anti-GFAP, 1:400; Biomedical Technologies), β-III-tubulin (1:1000; Sigma), and oligodendrocyte marker O4 (1:20; Chemicon), as previously described.13 Cells were also double labeled with mouse anti-human nestin (1:100; Chemicon) and rabbit anti-Ki67 (1:250; Novacastra) in 10% normal donkey serum in phosphate buffered saline (PBS) with 0.3% Triton X-100 (Sigma-Aldrich). Staining was visualized with fluorescein isothiocyanate-conjugated donkey anti-mouse and rhodamine-conjugated donkey anti-rabbit secondary antibodies (1:200; Jackson ImmunoResearch) in PBS. Nuclei were counterstained with Hoechst 33258 (1:500; Sigma-Aldrich). BTSCs were also dissociated to single cells with Accumax (Innovative Cell Technologies) and stained with CD15-fluorescein (Miltenyi Bitotec) and CD133-phycoerythrin (Miltenyi Bitotec) as previously described.13
cDNA and DNA Sequencing
Genomic DNA sequencing of exon 4 of IDH1 and cDNA sequencing of the open reading frames of EGFR, phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN), and tumor protein (TP)53 were performed as previously described.14,18,19
MGMT Promoter Methylation Assay
Five hundred nanograms of DNA were bisulfite-converted with the Epitect Bisulfite Kit (Qiagen) according to the manufacturer's instructions. Two microliters of each Epitect product were used for methylation-specific (MS-)PCR determination of MGMT promoter methylation as previously described.20 Thermocycling conditions for MGMT MS-PCR included initial denaturation at 95°C for 10 min, then 35 cycles of 95°C for 45 s denaturation, 45 s annealing, 72°C for 45 s extension, and a final 10-min extension at 72°C. The annealing temperatures were 61°C for MGMT methylated MS-PCR and 58°C for MGMT unmethylated MS-PCR.
Western Blotting
BTSC spheres were lysed in modified radioimmunoprecipitation assay buffer supplemented with Complete Mini protease (Roche) and Halt phosphatase (Thermo Scientific) inhibitor cocktails. For protein analysis following drug treatment, BTSC spheres were dissociated to single cells, and 1 × 106 cells were treated with cucurbitacin-I (Tocris Bioscience), WP1066 (Sigma-Aldrich), or vehicle (DMSO) for 2 h, 24 h, or 72 h. Fifteen micrograms of protein were loaded on 7.5% or 10% sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS PAGE) gels and transblotted to nitrocellulose membranes. Blots were stained with the following antibodies: phospho-STAT3 Y705 (1:1000; Cell Signaling Technology), phospho-STAT3 S727 (1:1000; Cell Signaling Technology), STAT3 (1:1000; Santa Cruz Biotechnology), Bcl-xL (1:1000; Cell Signaling Technology), cyclin D1 (1:1000; Cell Signaling Technology), poly-ADP ribose polymerase (PARP) (1:1000; Cell Signaling Technology), and actin (1:2500; Santa Cruz Biotechnology). Horseradish peroxidase–conjugated secondary antibodies (donkey anti-mouse, donkey anti-goat, and goat anti-rabbit; Calbiochem) were used at 1:6000. Bands were visualized with the ECL Plus Western Blotting Detection System and Hyperfilm (Amersham).
BTSC Growth Assays
Dissociated BTSC spheres were seeded at 1500 cells/well in 96-well plates and treated with cucurbitacin-I (Tocris Biosciences), WP1066 (Sigma), or vehicle (DMSO) 1 day after plating. Cell viability following drug treatment was assessed 8 days later using the Invitrogen alamarBlue assay according to the manufacturer's instructions. Drug sensitivity was assessed using the neurosphere assay, in which 500–2500 cells were seeded per well in 96-well plates and treated with cucurbitacin-I, WP1066, or DMSO and the number of spheres counted 14–28 days later. All culture experiments were performed in triplicate with a minimum of 3 wells per condition.
Flow Cytometry
BTSC spheres were dissociated to single cells, plated at 2.5 × 105 cells/5 mL round-bottom tube in 0.5-mL media and treated with cucurbitacin-I, WP1066, or DMSO for 72 h. Cell clusters were then dissociated to single cells with Accumax and stained with Annexin V–fluorescein (Roche), fixed with ice-cold methanol, permeabilized with 0.3% Triton-X100, and stained with proliferating cell nuclear antigen–phycoerythrin (R&D Systems) to detect apoptotic and proliferating cells, respectively.
STAT3 Knockdown Using Lentiviral ShRNA
Pre-made lentiviral STAT3 small hairpin (sh)RNA constructs (cat #V3LHS_376018 and #V2LHS_88502) were purchased from Thermo Scientific, and lentiviral helper plasmids (pCMV-dR8.2 and pCMV-VSVG; cat #8455 and #8454) were purchased from Addgene. A nontargeting construct from Thermo Scientific (cat #RHS4346) was used as a control. Lentiviral stocks were prepared following the manufacturer's protocol. Briefly, 4.5 × 106 293METR cells were plated in T-150 flasks. Cells were cotransfected with 2.3 μg shRNA constructs together with 4.7 μg pCMVdR8.2 and 2 μg pCMV-VSV-G helper constructs. Viral particles were harvested from the culture media 48 h and 72 h after transfection and were concentrated by centrifugation at 26 000 rpm for 90 min at 4°C. BTSC73 cells were infected with the viral stocks at different dilutions, ranging from 1:20 to 1:5. For sphere assays, 500 cells were seeded per well in 96-well plates and transduced with nontargeting or STAT3 shRNA lentiviral particles, and the number of spheres was counted after 14 days. For western blots, 5 × 105 BTSC73 cells were transduced with control or STAT3 shRNA lentiviral particles and processed 6 days later for SDS PAGE followed by immunoblotting for STAT3 as described above.
Intracranial BTSC Xenografts
BTSC spheres from 3 different cell lines (BTSC30, −73, and −147) were dissociated to single-cell suspensions, and 2 × 105 cells (BTSC30 and −73) and 1 × 105 cells (BTSC147) were stereotactically implanted into the right striata of 6- to 8-week-old NOD SCID mice as previously described.13 For in vivo inhibition of JAK2, mice were randomized to vehicle or treatment cohorts 7 days after cell implantation. WP1066 (20 mg/kg) or vehicle (1:9 DMSO:PEG300; Sigma-Aldrich) was injected thrice weekly for 4 weeks. Three vehicle- and 3 WP1066-treated mice from each BTSC line were euthanized by transcardiac perfusion of 4% paraformaldehyde on day 15, 2hr after receiving the fourth injection for confirmation of in vivo inhibition of JAK2/STAT3 activity. Brains were removed, fixed in formalin, and prepared for histology and immunohistochemistry. An additional 3 vehicle- and 3 WP1066-treated mice were euthanized by transcardiac perfusion on day 35, 2 hr after receiving the final injection to assess tumor cell apoptosis. For Kaplan–Meier survival studies, 2 cohorts of 10 vehicle and 10 WP1066 animals completed the full course of 12 injections and were allowed to survive until significant weight loss or presentation of neurological symptoms necessitated euthanasia. Necropsy and cranial dissection were performed to confirm presence of tumor in all animals.
Immunohistochemistry
Patient tumor and xenograft specimens were immediately fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde upon receipt and processed for cryosectioning according to standard protocols. Tumor and xenograft sections were immunostained for phospho-JAK2 Y1007/1008 (1:50; Millipore), phospho-STAT3 Y705 (1:50; Cell Signaling Technology), phospho-STAT3 S727 (1:50; Cell Signaling Technology), human nucleolin (1:1000; Millipore), and human nuclear antigen (1:20; Chemicon). Staining was visualized with Vectastain Elite mouse immunoglobulin (Ig)G or rabbit IgG ABC kits (Vector Laboratories) and DAB (3,3′-diaminobenzidine) substrate (Sigma-Aldrich), followed by hematoxylin counterstaining. Xenograft tumor cells undergoing apoptosis were detected with the ApopTag Plus Peroxidase In Situ Apoptosis Detection Kit (Chemicon International) according to the manufacturer's instructions. The percentage of apoptotic cells is expressed as the average of independent quantifications by 2 blinded observers counting 10 randomly selected 40× fields of view containing xenograft tumor cells in each vehicle or WP1066-treated animal.
Statistical Analysis
In figures 2-5, error bars represent SEMs and asterisks denote statistically significant differences determined by Student t-tests or ANOVA and Tukey multiple comparison tests (α = 0.05). Statistically significant differences in median survival were determined by a log-rank test using GraphPad Prism.
Results
JAK2/STAT3 Signaling Is Activated in Human GBM, BTSC Lines, and BTSC Xenografts
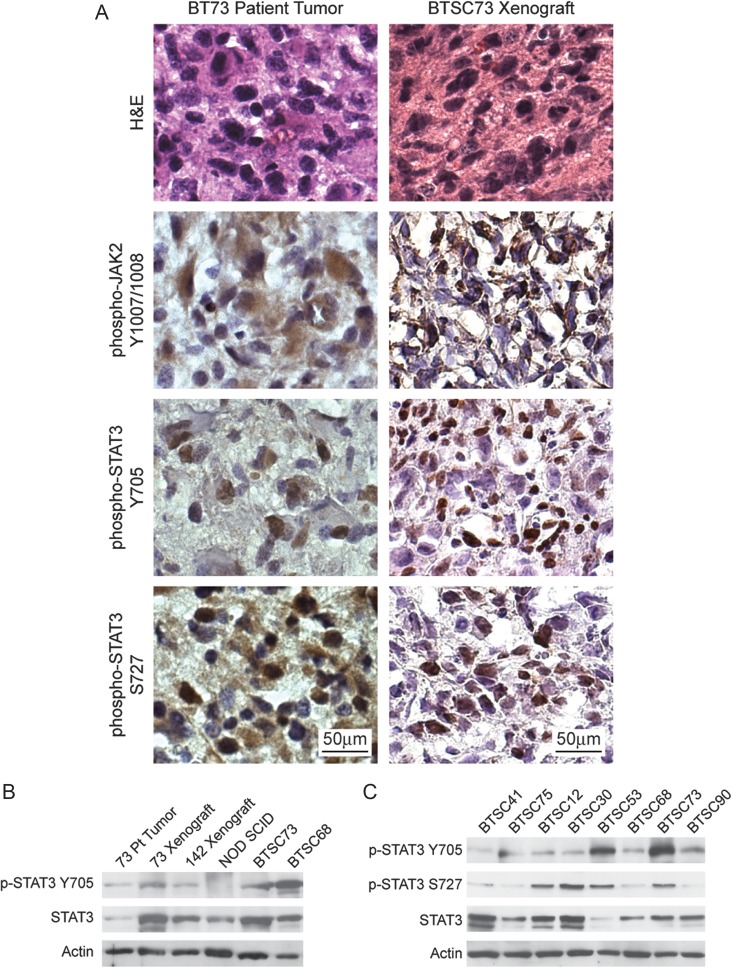
To investigate the role of JAK2/STAT3 signaling in GBM and BTSC biology, we asked whether the JAK2/STAT3 pathway was active in a set of molecularly diverse human GBM tumors and the BTSCs derived from them. We used immunohistochemistry with phospho-specific antibodies to look at the presence of activated JAK2 and STAT3 in human tissues, BTSCs, and tumors from orthotopic xenografts. We found strong staining of the cell membrane for phosphorylated Y1007/1008 JAK2 and staining of the nucleus for phosphorylated Y705 and S727 STAT3 (Fig. 1A) in neoplastic cells throughout patient GBM tumor specimens. Cells expressing neural progenitor markers (Supplementary Table 1) and displaying BTSC multipotency characteristics (Supplementary Fig. 1) that were cultured from human GBMs also retained the high levels of JAK2/STAT3 activity present in their corresponding patient tumors. Western blotting for STAT3 revealed detectable phosphorylation of Y705 and S727 of STAT3 (Fig. 1B and C) in a large panel of BTSC cultures with diverse mutational profiles (Table 1). Moreover, JAK2 and STAT3 phosphorylations were retained in orthotopic xenograft tumors initiated from BTSC lines (Fig. 1A and B). Taken together, these results indicate that activation of the JAK2/STAT3 pathway is a common feature of human GBM that is faithfully modeled by BTSC cultures and xenograft tumors.
Fig. 1.
Human GBM, BTSC cell lines, and BTSC xenograft tumors have endogenous activation of JAK2/STAT3. (A) Immunohistochemical staining showing robust phosphorylation of JAK2 and STAT3 in neoplastic cells of patient tumor 73. Strong phosphorylation of JAK2 and STAT3 were also detectable in tumor but not host cells of BTSC73 xenografts. (B) Phosphorylation of the Y705 residue of STAT3 was detectable in lysates of tumor tissue from patient 73 as well as in BTSC73 xenografts and BTSC73 cells, but not in the normal NOD SCID mouse brain. (C) High levels of STAT3 expression and phosphorylation of both tyrosine 705 and serine 727 were present in a diverse set of BTSC lines.
On-target Inhibition of JAK2/STAT3 Signaling With Cucurbitacin-I and WP1066 Decreases Survival and Proliferation of Molecularly Diverse BTSCs In Vitro
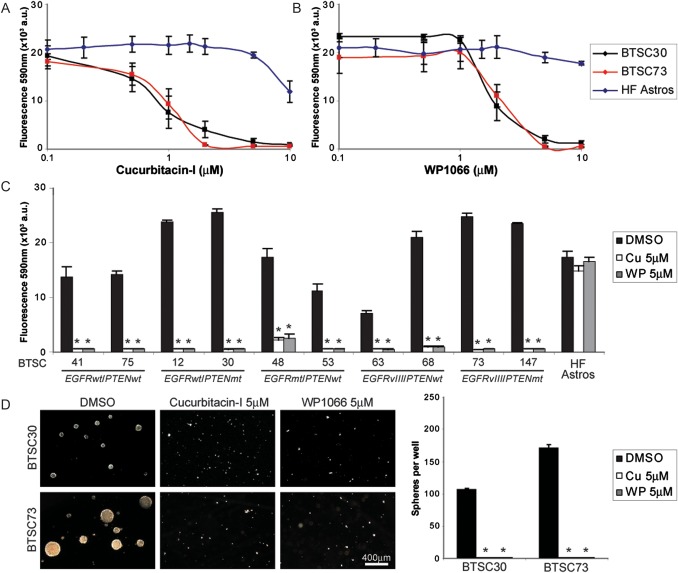
Given the high level of JAK2/STAT3 signaling in GBM, BTSC cell lines, and BTSC xenografts, we next asked whether inhibition of JAK2/STAT3 signaling would result in decreased survival and proliferation in BTSCs. We found that inhibition of STAT3 signaling with the JAK2/STAT3 inhibitors cucurbitacin-I and WP1066 reduced cell viability in a dose-dependent manner (Fig. 2A and B). Both drugs showed broad efficacy against all BTSC lines and achieved dramatic reductions in cell viability after 8 days of treatment (Fig. 2C). However, both cucurbitacin-I and WP1066 had minimal effects on human fetal astrocytes, suggesting that STAT3 signaling is not a key factor for survival in these nonneoplastic brain cells. Similarly, in both BTSC30 and -73, treatment with a single 5-μM dose of either cucurbitacin-I or WP1066 completely inhibited sphere production, with only single cells or small cell clusters remaining after 14–21 days (Fig. 2D).
Fig. 2.
Cucurbitacin-I and WP1066 dramatically inhibit growth of BTSCs with diverse mutational profiles. (A and B) Cucurbitacin-I and WP1066 reduced cell viability in BTSC30 and -73 in a dose-dependent manner. (C) Cucurbitacin-I and WP1066 dramatically reduced alamarBlue conversion in all BTSC lines but not human fetal astrocytes (HF Astros) (* denotes P < .01 vs DMSO, Tukey's multiple comparison test). (D) Cucurbitacin-I and WP1066 completely abolished sphere formation in both BTSC30 and -73 (* denotes P < .01 vs DMSO, Tukey's multiple comparison test). Abbreviations: wt, wild type; mt, mutation; vIII, variant III.
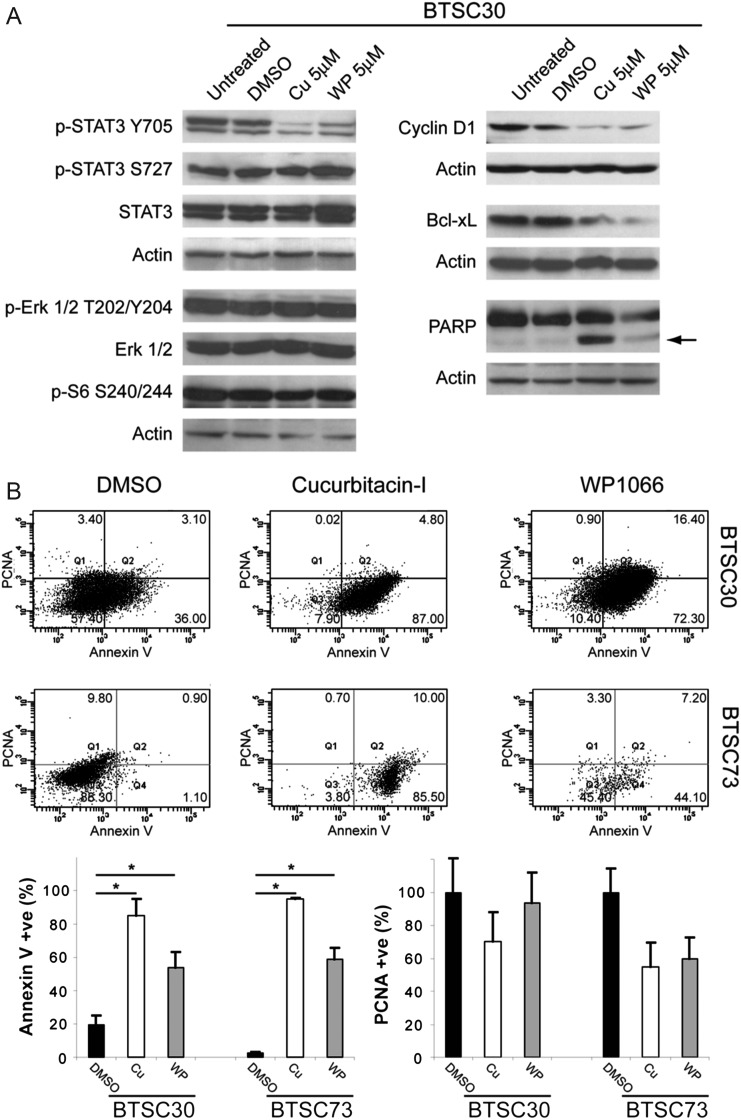
Downstream STAT3 signaling was effectively and specifically inhibited by cucurbitacin-I and WP1066. Both drugs decreased phosphorylation of STAT3 on Y705 and downregulated the pro-proliferative and anti-apoptotic STAT3 target genes cyclin D1 and Bcl-xL (Fig. 3A). No effects were observed on the levels of phospho-S727 STAT3, phospho-Erk1/2, or phospho-S6, which are not catalyzed by JAK2, thus confirming the specificity of both drugs for JAK2/STAT3 and lack of significant off-target effects on other signaling pathways. Cucurbitacin-I and WP1066 also robustly induced apoptosis, as evidenced by increased cleavage of PARP (Fig. 3A) and Annexin V staining (Fig. 3B). Taken together, these results show that JAK2/STAT3 inhibition with cucurbitacin-I and WP1066 potently induces apoptosis and is broadly effective against BTSCs with diverse mutational profiles.
Fig. 3.
Cucurbitacin-I and WP1066 inhibit STAT3 phosphorylation and induce apoptosis in BTSCs. (A) Cucurbitacin-I and WP1066 reduced phosphorylation of tyrosine 705 of STAT3 in BTSC30 but did not affect phosphorylation of Erk1/2 or S6. Inhibition of STAT3 with both agents also reduced levels of the STAT3 target genes cyclin D1 and Bcl-xL and increased levels of the apoptotic marker cleaved PARP (arrow) after 72 h. (B) Cucurbitacin-I and WP1066 dramatically increased the percentage of cells labeling with the apoptotic marker Annexin V in both BTSC30 and -73 (*P < .05 vs DMSO, Tukey's multiple comparison test); no significant changes in the percentage of proliferating cells expressing proliferating cell nuclear antigen were observed.
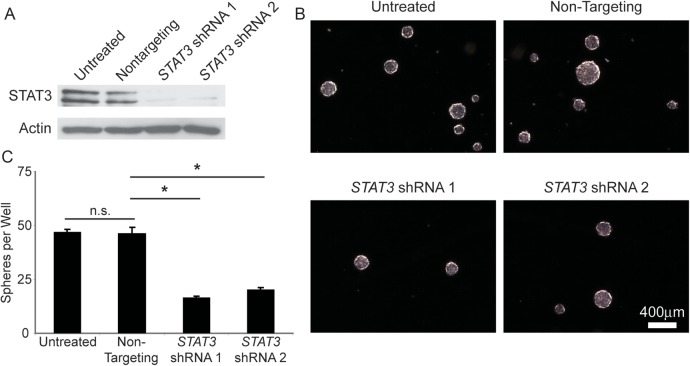
ShRNA Knockdown of STAT3 Is Sufficient to Decrease BTSC Growth In Vitro
We asked whether STAT3 activation through JAK2 was an integral signaling pathway in GBM and whether STAT3 knockdown would replicate the effects seen by chemical inhibition of JAK2/STAT3 signaling. To this effect we transduced BTSCs with lentiviruses engineered to deliver 2 different shRNA sequences targeted against STAT3. After 6 days, both STAT3 shRNAs dramatically decreased the level of STAT3 protein compared with untransduced and nontargeting vector controls (Fig. 4A), thus demonstrating robust STAT3 knockdown. Moreover, after 14 days, both STAT3 knockdown cultures generated significantly fewer spheres (P < .05) compared with nontargeting or untransduced controls (Fig. 4B and C). These data demonstrate that STAT3 has a crucial role in BTSC survival and proliferation in vitro.
Fig. 4.
STAT3 shRNA knockdown decreases BTSC sphere growth. (A) Transduction of BTSCs with lentiviruses expressing 2 different shRNA sequences targeted against STAT3 dramatically reduced the levels of STAT3 protein after 6 days compared with nontargeting shRNA or untransduced control BTSCs. (B and C) STAT3 shRNA cultures generated significantly fewer spheres compared with corresponding nontargeting shRNA or untransduced control BTSCs (P < .05, Tukey's multiple comparison test). Abbreviation: n.s., nonsignificant.
Systemic Treatment With WP1066 Specifically Inhibits Intracranial JAK2/STAT3 Signaling In Vivo and Prolongs Animal Survival
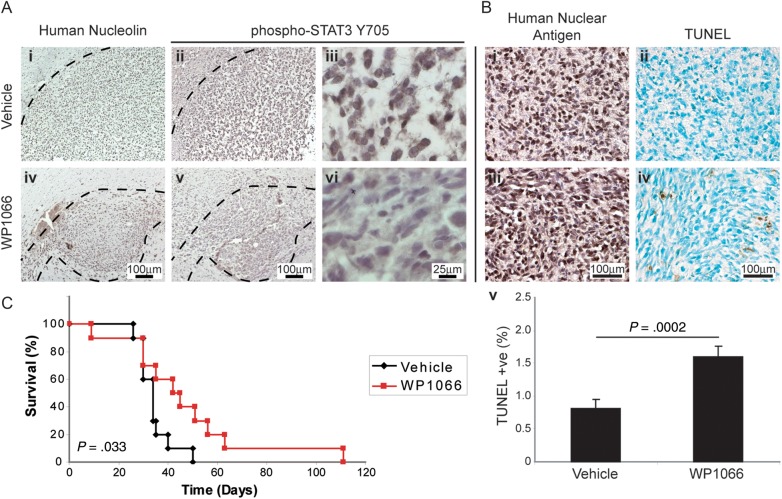
As we and others2–10 have observed the activation of the STAT3 pathway in human GBM tumors, we asked whether orthotopic xenografts of BTSCs in NOD SCID mice would respond to JAK2/STAT3 inhibition in vivo. We found that in brain sections of animals systemically treated with intraperitoneal injections of WP1066, there were dramatically decreased levels of phospho-Y705 STAT3 in BTSC30, -73, and -147 xenograft tumor cells by immunostaining (Fig. 5A), thus confirming in vivo on-target JAK2/STAT3 blockade. WP1066 administration also significantly increased the percentage of cells positive for staining by terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase 2′-deoxyuridine 5′-triphosphate nick end labeling (TUNEL; P = .0002; Fig. 5B) after 4 weeks of thrice-weekly injections, demonstrating apoptosis of tumor cells in vivo. This treatment regimen also significantly slowed progression of tumor growth in the treatment cohort, with an increase in median survival from 34 to 43 days on Kaplan–Meier analysis (P = .033; Fig. 5C). Together, these data demonstrate that JAK2/STAT3 signaling plays a vital role in tumor growth and progression in vivo, and JAK2/STAT3 may be an amenable target for GBM therapy by decreasing BTSC survival.
Fig. 5.
Systemic administration of WP1066 inhibits growth of intracranial BTSC73 xenografts. (A) STAT3 phosphorylation was dramatically reduced in BTSC xenografts after administration of WP1066 ([i, iv] human-specific nucleolin immunostaining in vehicle- and WP1066-treated mice; [ii, iii] phospho-STAT3 Y705 staining in vehicle- and [v, vi] WP1066-treated mice). (B) The percentage of TUNEL staining apoptotic cells was also significantly increased in WP1066-treated mice (P = .0002, Student's t-test). (C) A course of 4 weeks of thrice-weekly injections of WP1066 increased median survival of BTSC73 xenograft mice from 34 to 43 days (P = .033, log-rank test).
Discussion
GBM is a devastating disease for which effective treatment has remained elusive. Disease initiation, recurrence, and resistance to existing therapeutic modalities may be in large part due to BTSCs. JAK2/STAT3 has garnered significant interest as a key driver of tumor cell survival, proliferation, and invasion in GBM2–10 that may be particularly important in BTSCs and thus exploitable for novel GBM therapeutic strategies targeting BTSCs.2–4,9,10 However, the translational potential of JAK2/STAT3 inhibitors had yet to be thoroughly evaluated in a preclinical model that spanned the molecular heterogeneity of the disease. Moreover, the role of STAT3 across the spectrum of GBM was unclear and appeared to be possibly contextual, based on the presence of other mutations. While STAT3 has been reported to be a master transcription factor in the mesenchymal subtype of GBM5 and a direct effector for the EGFR variant III mutant protein,21 it has also been reported to be a tumor suppressor in PTEN-deficient mouse glioma models.21
Our study demonstrates the efficacy of on-target JAK2/STAT3 inhibition in heterogeneous BTSC lines, which closely emulate the genomic and tumorigenic characteristics of human GBM. All of the BTSC lines tested here were sensitive to JAK2/STAT3 inhibition regardless of the mutational status of EGFR, PTEN, or TP53, implying that STAT3 signaling consistently has a pro-tumorigenic role and is a common feature of BTSCs that evolve from diverse mutational combinations. Moreover, BTSC lines isolated from recurrent, highly temozolomide-resistant GBMs lacking MGMT promoter methylation demonstrated significant JAK2/STAT3 sensitivity in this study. Our data support the premise that STAT3 is a key pro-oncogenic player in GBM and BTSCs notwithstanding the particular molecular aberrations present in any one tumor or cell line.
We show here that JAK2/STAT3 signaling is essential for survival, proliferation, and tumorigenicity in GBM BTSCs and that targeting the JAK2/STAT3 pathway results in tumor cell apoptosis and improved xenograft animal survival outcomes. Sai et al10 have recently reported that the novel JAK2/STAT3 inhibitor WP1193 inhibits glioma stemlike cell proliferation, neurosphere formation, and stem cell marker expression in vitro. The results presented here thus validate the potency of JAK2/STAT3 inhibitors against BTSCs in vitro and demonstrate their in vivo efficacy against intracranial, humanlike xenograft tumors from multiple BTSC lines. The low levels of STAT3 activity and tolerance for JAK2/STAT3 inhibition in human fetal or murine astrocyte cultures that we and others8 have observed suggest that JAK2/STAT3 is an amenable molecular target with relatively few side effects on nonneoplastic glia. Systemic WP1066 administration was well tolerated, achieved effective on-target inhibition of intracranial STAT3 activity, and significantly prolonged animal survival time in our xenograft model.
Nonetheless, JAK2 inhibitors are not without the potential for significant hematopoietic side effects due to the important role of JAK2 in erythropoietin and thrombopoietin signaling, and clinical trials of JAK2 inhibitors have reported therapy-related anemia and thrombocytopenia (reviewed by Verstovsek22). As in most other chemotherapy protocols, vigilant monitoring and management of any hematopoietic or other side effects will thus be essential for any potential use of JAK2 inhibitors in treatment of human neuro-oncology. However, we did not observe significant therapy-related adverse events in the WP1066 cohort in our xenograft study, suggesting that therapeutically relevant intracranial concentrations of WP1066 can be achieved without producing dramatic side effects. Moreover, our results together with a growing body of recent evidence gathered using a variety of different small-molecule STAT3 inhibitors6–10,23 demonstrate that STAT3 signaling is crucial for the survival, proliferation, and tumorigenicity of BTSCs both in vitro and in vivo and provide strong rationale for use of JAK2/STAT3 inhibitors in GBM treatment. The sensitivity of BTSCs to JAK2/STAT3 inhibition is particularly of consequence because tumor initiation, recurrence, and especially therapeutic resistance may be in large part due to BTSCs. JAK2/STAT3 inhibition therefore has the potential to be broadly effective in treatment of GBM and may be particularly well suited as a salvage strategy for patients who have failed radiotherapy and temozolomide therapy.
Supplementary Material
Funding
This work was supported by an Alberta Cancer Foundation grant to S. W. and J. G. C. and Alberta Heritage Foundation for Medical Research Studentship, Fellowship, and Scientist Awards to O. S., J. K., and S. W., respectively.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Rozina Hassam, Dorothea Livingstone, and Orsolya Cseh for technical help, and Andrea Ramirez and Carmen Binding for help with mouse xenografts and monitoring. The patient samples were obtained through the Calgary Brain Tumour and Tissue Bank, generously supported by funds from the Clark H. Smith Family.
Conflict of interest statement. None declared.
References
- 1.Stupp R, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, et al. Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N Engl J Med. 2005;352:987–996. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa043330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Peñuelas S, Anido J, Prieto-Sánchez RM, et al. TGF-beta increases glioma-initiating cell self-renewal through the induction of LIF in human glioblastoma. Cancer Cell. 2009;15:315–327. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2009.02.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Wang H, Lathia JD, Wu Q, et al. Targeting interleukin 6 signaling suppresses glioma stem cell survival and tumor growth. Stem Cells. 2009;27:2393–2404. doi: 10.1002/stem.188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Cao Y, Lathia JD, Eyler CE, et al. Erythropoietin receptor signaling through STAT3 is required for glioma stem cell maintenance. Genes Cancer. 2010;1:50–61. doi: 10.1177/1947601909356352. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Carro MS, Lim WK, Alvarez MJ, et al. The transcriptional network for mesenchymal transformation of brain tumours. Nature. 2010;463:318–325. doi: 10.1038/nature08712. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Rahaman SO, Harbor PC, Chernova O, Barnett GH, Vogelbaum MA, Haque SJ. Inhibition of constitutively active Stat3 suppresses proliferation and induces apoptosis in glioblastoma multiforme cells. Oncogene. 2002;21:8404–8413. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1206047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Iwamaru A, Szymanski S, Iwado E, et al. A novel inhibitor of the STAT3 pathway induces apoptosis in malignant glioma cells both in vitro and in vivo. Oncogene. 2007;26:2435–2444. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1210031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Lo HW, Cao X, Zhu H, Ali-Osman F. Constitutively activated STAT3 frequently coexpresses with epidermal growth factor receptor in high-grade gliomas and targeting STAT3 sensitizes them to Iressa and alkylators. Clin Cancer Res. 2008;14:6042–6054. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-07-4923. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Villalva C, Martin-Lannerée S, Cortes U, et al. STAT3 is essential for the maintenance of neurosphere-initiating tumor cells in patients with glioblastomas: a potential for targeted therapy? Int J Cancer. 2011;128:826–838. doi: 10.1002/ijc.25416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Sai K, Wang S, Balasubramaniyan V, et al. Induction of cell-cycle arrest and apoptosis in glioblastoma stem-like cells by WP1193, a novel small molecule inhibitor of the JAK2/STAT3 pathway. J Neurooncol. 2012;107:487–501. doi: 10.1007/s11060-011-0786-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Lee J, Kotliarova S, Kotliarov Y, et al. Tumor stem cells derived from glioblastomas cultured in bFGF and EGF more closely mirror the phenotype and genotype of primary tumors than do serum-cultured cell lines. Cancer Cell. 2006;9:391–403. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2006.03.030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Piccirillo SG, Combi R, Cajola L, et al. Distinct pools of cancer stem-like cells coexist within human glioblastomas and display different tumorigenicity and independent genomic evolution. Oncogene. 2009;28:1807–1811. doi: 10.1038/onc.2009.27. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Kelly JJ, Stechishin O, Chojnacki A, et al. Proliferation of human glioblastoma stem cells occurs independently of exogenous mitogens. Stem Cells. 2009;27:1722–1733. doi: 10.1002/stem.98. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Luchman HA, Stechishin OD, Dang NH, et al. An in vivo patient-derived model of endogenous IDH1-mutant glioma. Neuro Oncol. 2012;14:184–191. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/nor207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Kelly JJ, Blough MD, Stechishin OD, et al. Oligodendroglioma cell lines containing t(1;19)(q10;p10) Neuro Oncol. 2010;12:745–755. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/noq031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Blough MD, Westgate MR, Beauchamp D, et al. Sensitivity to temozolomide in brain tumor initiating cells. Neuro Oncol. 2010;12:756–760. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/noq032. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Chojnacki A, Kelly JJ, Hader W, Weiss S. Distinctions between fetal and adult human platelet-derived growth factor-responsive neural precursors. Ann Neurol. 2008;64:127–142. doi: 10.1002/ana.21421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Parsons DW, Jones S, Zhang X, et al. An integrated genomic analysis of human glioblastoma multiforme. Science. 2008;321:1807–1812. doi: 10.1126/science.1164382. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Kato H, Kato S, Kumabe T, et al. Functional evaluation of p53 and PTEN gene mutations in gliomas. Clin Cancer Res. 2000;6:3937–3943. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Hegi ME, Diserens AC, Gorlia T, et al. MGMT gene silencing and benefit from temozolomide in glioblastoma. N Engl J Med. 2005;352:997–1003. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa043331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.de la Iglesia N, Konopka G, Puram SV, et al. Identification of a PTEN-regulated STAT3 brain tumor suppressor pathway. Genes Dev. 2008;22:449–462. doi: 10.1101/gad.1606508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Verstovsek S. Janus-activated kinase 2 inhibitors: a new era of targeted therapies providing significant clinical benefit for Philadelphia chromosome-negative myeloproliferative neoplasms. J Clin Oncol. 2011;29:781–783. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2010.33.4508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Gu J, Li G, Sun T, et al. Blockage of the STAT3 signaling pathway with a decoy oligonucleotide suppresses growth of human malignant glioma cells. J Neurooncol. 2008;89:9–17. doi: 10.1007/s11060-008-9590-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.