Abstract
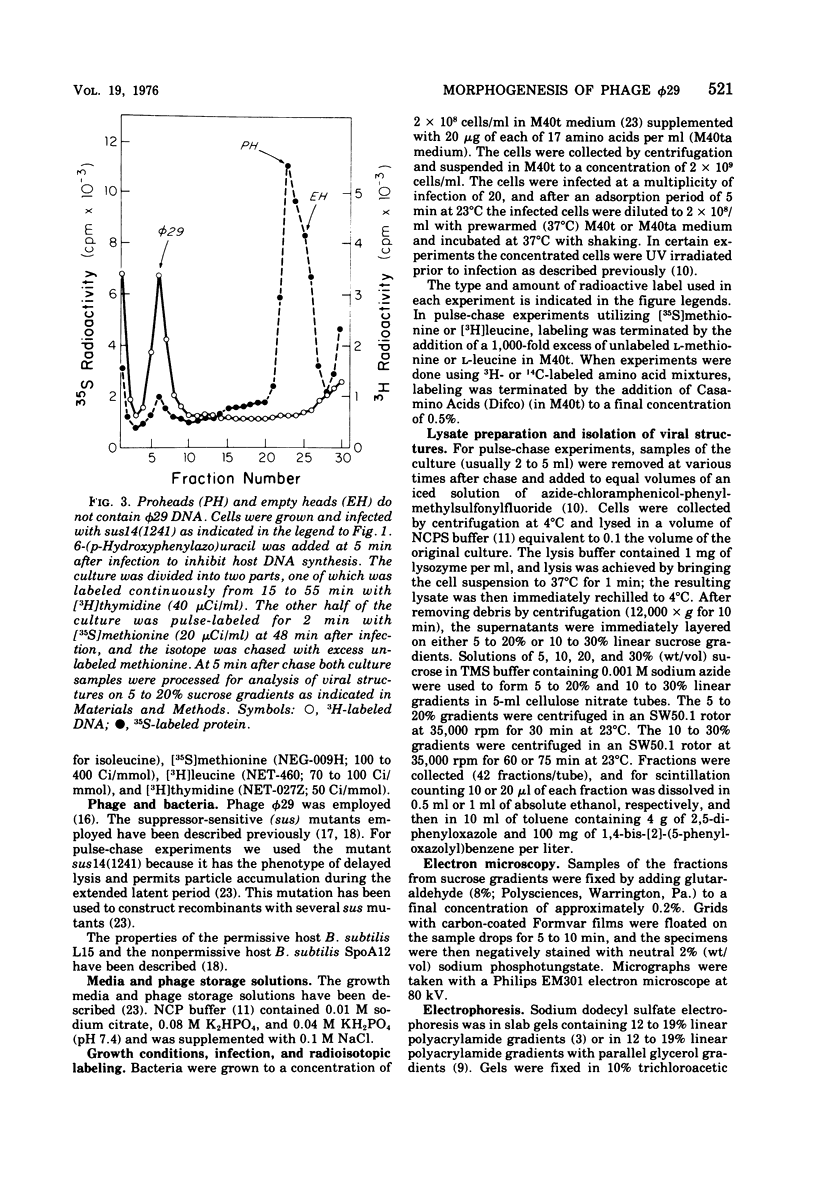
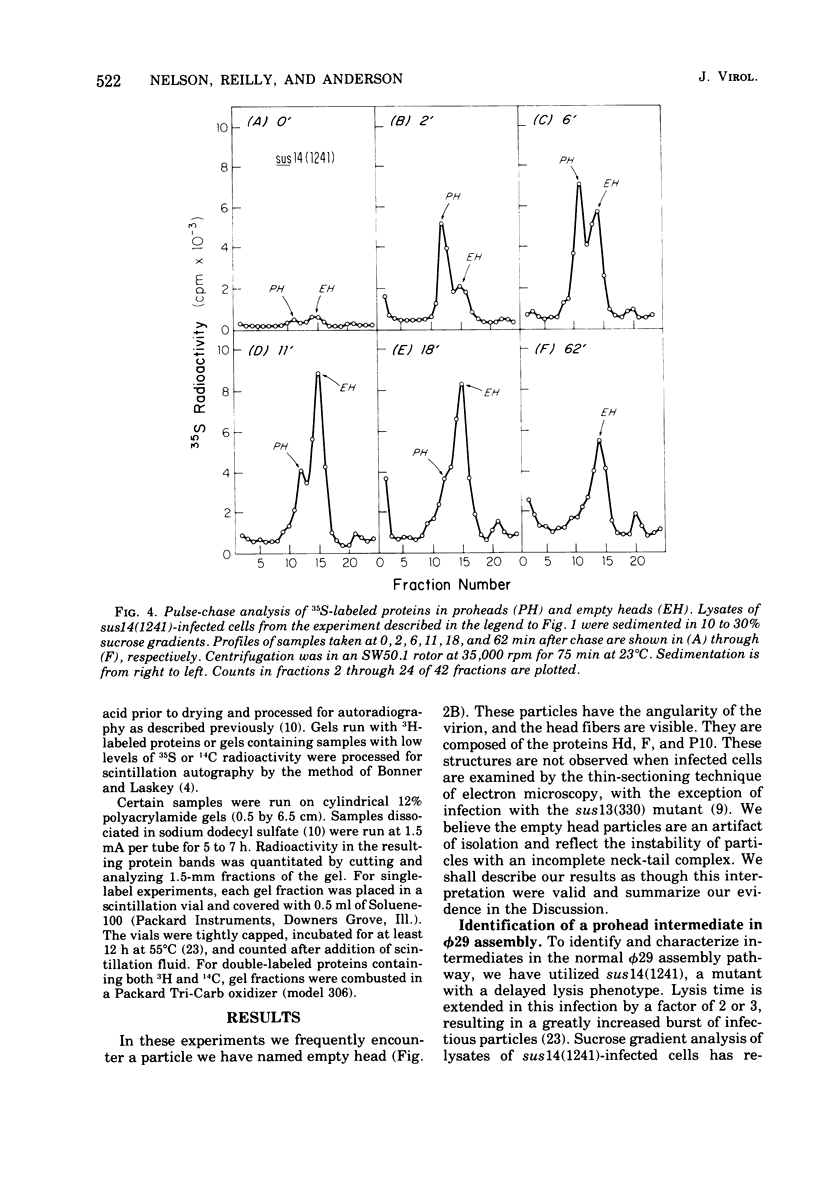
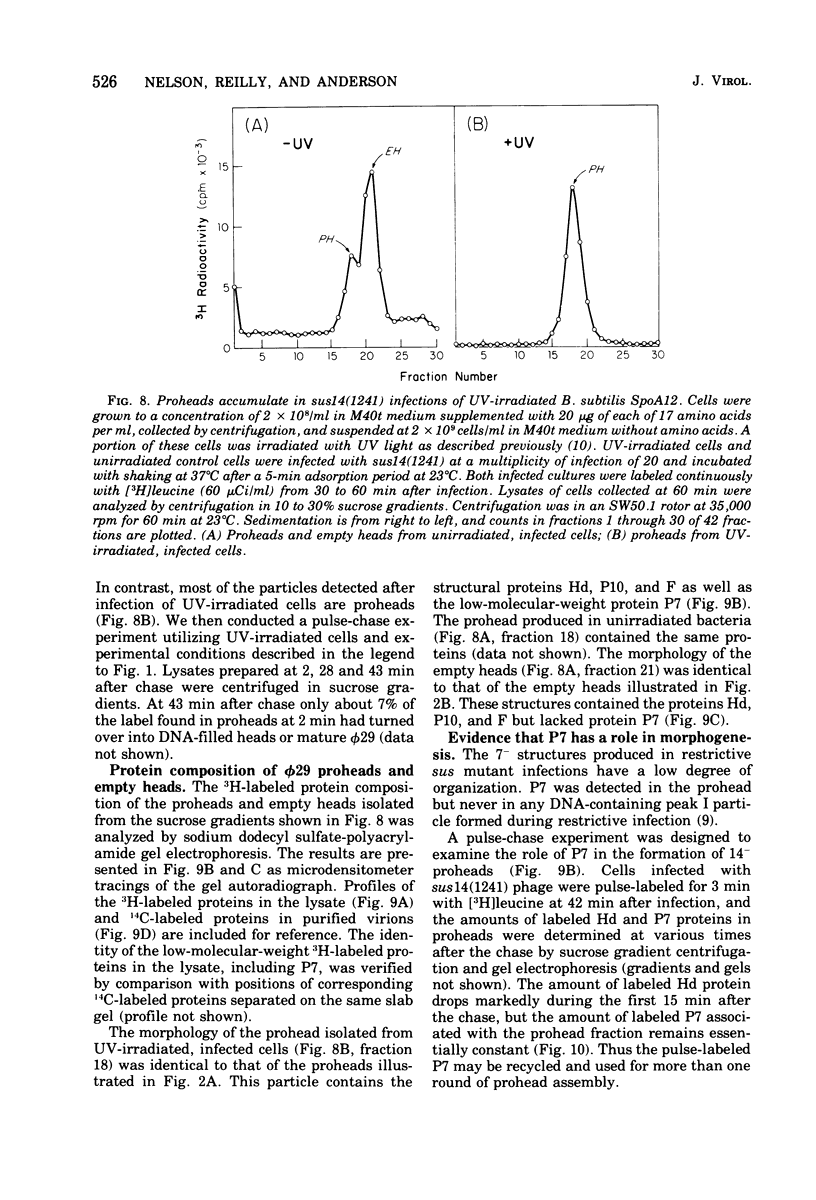
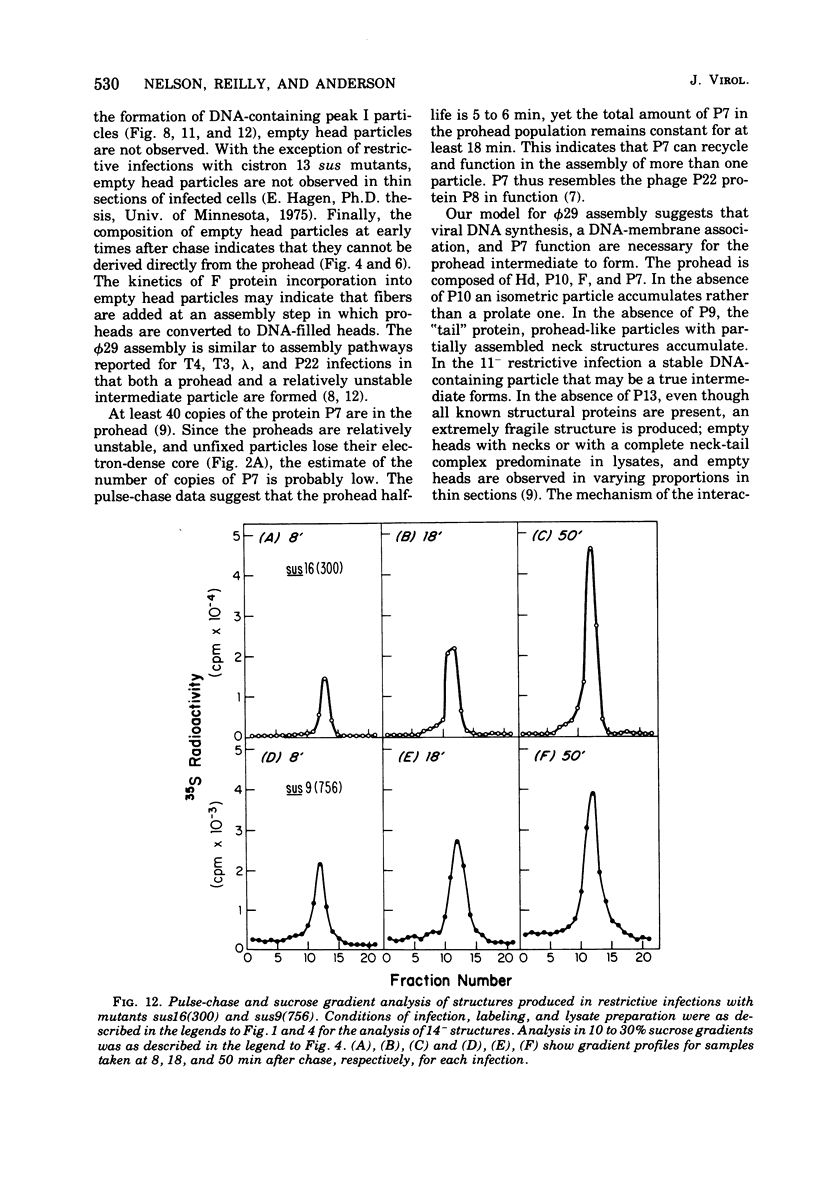
Three classes of particles have been identified in restrictive phi 29 suppressor-sensitive (sus) mutant infections of Bacillus subtilis, including DNA-containing heads or phage, prohead, and empty heads. Pulse-chase labeling experiments indicate that the prohead, the first particle assembled in 14-infected cells, is converted to DNA-filled heads and phi 29. In addition to the proteins Hd, P10, and F found in mature phi 29, the prohead contains a "core" protein P7 that exits as the prohead matures and appears to recycle during subsequent rounds of prohead assembly. Prohead-like structures accumulate in UV-irradiated cells and are present in restrictive infections with sus mutants of cistrons 9 and 16. Empty heads are observed only when infection results in the formation of DNA-containing particles; this and other evidence indicates that the empty heads are probably not true intermediates. Phage phi 29 assembly apparently occurs by a single pathway in which neck and tail components interact to stabilize the completed DNA-containing head.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson D. L., Hickman D. D., Reilly B. E. Structure of Bacillus subtilis bacteriophage phi 29 and the length of phi 29 deoxyribonucleic acid. J Bacteriol. 1966 May;91(5):2081–2089. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.5.2081-2089.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson D. L., Mosharrafa E. T. Physical and biological properties of phage phi 29 deoxyribonucleic acid. J Virol. 1968 Oct;2(10):1185–1190. doi: 10.1128/jvi.2.10.1185-1190.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson D. L., Reilly B. E. Analysis of bacteriophage phi 29 gene function: protein synthesis in suppressor-sensitive mutant infection of Bacillus subtilis. J Virol. 1974 Jan;13(1):211–221. doi: 10.1128/jvi.13.1.211-221.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrascosa J. L., Camacho A., Viñuela E., Salas M. A precursor of the neck appendage protein of B. subtilis phage phi 29. FEBS Lett. 1974 Aug 30;44(3):317–321. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrascosa J. L., Viñuela E., Salas M. Proteins induced in Bacillus subtilis infected with bacteriophage phi 29. Virology. 1973 Nov;56(1):291–299. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casjens S., King J. P22 morphogenesis. I: Catalytic scaffolding protein in capsid assembly. J Supramol Struct. 1974;2(2-4):202–224. doi: 10.1002/jss.400020215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casjens S., King J. Virus assembly. Annu Rev Biochem. 1975;44:555–611. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.44.070175.003011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagen E. W., Reilly B. E., Tosi M. E., Anderson D. L. Analysis of gene function of bacteriophage phi 29 of Bacillus subtilis: identification of cistrons essential for viral assembly. J Virol. 1976 Aug;19(2):501–517. doi: 10.1128/jvi.19.2.501-517.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawley L. A., Reilly B. E., Hagen E. W., Anderson D. L. Viral protein synthesis in bacteriophage phi 29-infected Bacillus subtilis. J Virol. 1973 Nov;12(5):1149–1159. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.5.1149-1159.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ivarie R. D., Pène J. J. Association of the Bacillus subtilis chromosome with the cell membrane: resolution of free and bound deoxyribonucleic acid on renografin gradients. J Bacteriol. 1970 Nov;104(2):839–850. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.2.839-850.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King J., Lenk E. V., Botstein D. Mechanism of head assembly and DNA encapsulation in Salmonella phage P22. II. Morphogenetic pathway. J Mol Biol. 1973 Nov 15;80(4):697–731. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90205-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Méndez E., Ramírez G., Salas M., Viñuela E. Structural proteins of bacteriophage phi 29. Virology. 1971 Sep;45(3):567–576. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90172-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Péne J. J., Murr P. C., Barrow-Carraway J. Synthesis of bacteriophage phi 29 proteins in Bacillus subtilis. J Virol. 1973 Jul;12(1):61–67. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.1.61-67.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REILLY B. E., SPIZIZEN J. BACTERIOPHAGE DEOXYRIBONUCLEATE INFECTION OF COMPETENT BACILLUS SUBTILIS. J Bacteriol. 1965 Mar;89:782–790. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.3.782-790.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reilly B. E., Tosi M. E., Anderson D. L. Genetic analysis of bacteriophage phi29 of Bacillus subtilis: mapping of the cistrons coding for structural proteins. J Virol. 1975 Oct;16(4):1010–1016. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.4.1010-1016.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reilly B. E., Zeece V. M., Anderson D. L. Genetic study of suppressor-sensitive mutants of the Bacillus subtilis bacteriophage phi 29. J Virol. 1973 May;11(5):756–760. doi: 10.1128/jvi.11.5.756-760.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubio V., Salas M., Viñuela E., Usobiaga P., Saiz J. L., Llopis J. F. Biophysical properties of bacteriophage phi29. Virology. 1974 Jan;57(1):112–121. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90112-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schachtele C. F., De Sain C. V., Hawley L. A., Anderson D. L. Transcription during the development of bacteriophage phi 29: production of host- and phi 29-specific ribonucleic acid. J Virol. 1972 Dec;10(6):1170–1178. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.6.1170-1178.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schachtele C. F., Reilly B. E., De Sain C. V., Whittington M. O., Anderson D. L. Selective replication of bacteriophage phi29 deoxyribonucleic acid in 6-(p-hydroxyphenylazo)-uracil-treated Bacillus subtilis. J Virol. 1973 Jan;11(1):153–155. doi: 10.1128/jvi.11.1.153-155.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tosi M. E., Reilly B. E., Anderson D. L. Morphogenesis of bacteriophage phi29 of Bacillus subtilis: cleavage and assembly of the neck appendage protein. J Virol. 1975 Nov;16(5):1282–1295. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.5.1282-1295.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tosi M., Anderson D. L. Antigenic properties of bacteriophage phi 29 structural proteins. J Virol. 1973 Dec;12(6):1548–1559. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.6.1548-1559.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]






