Abstract
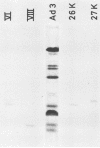
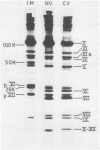
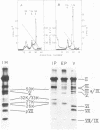
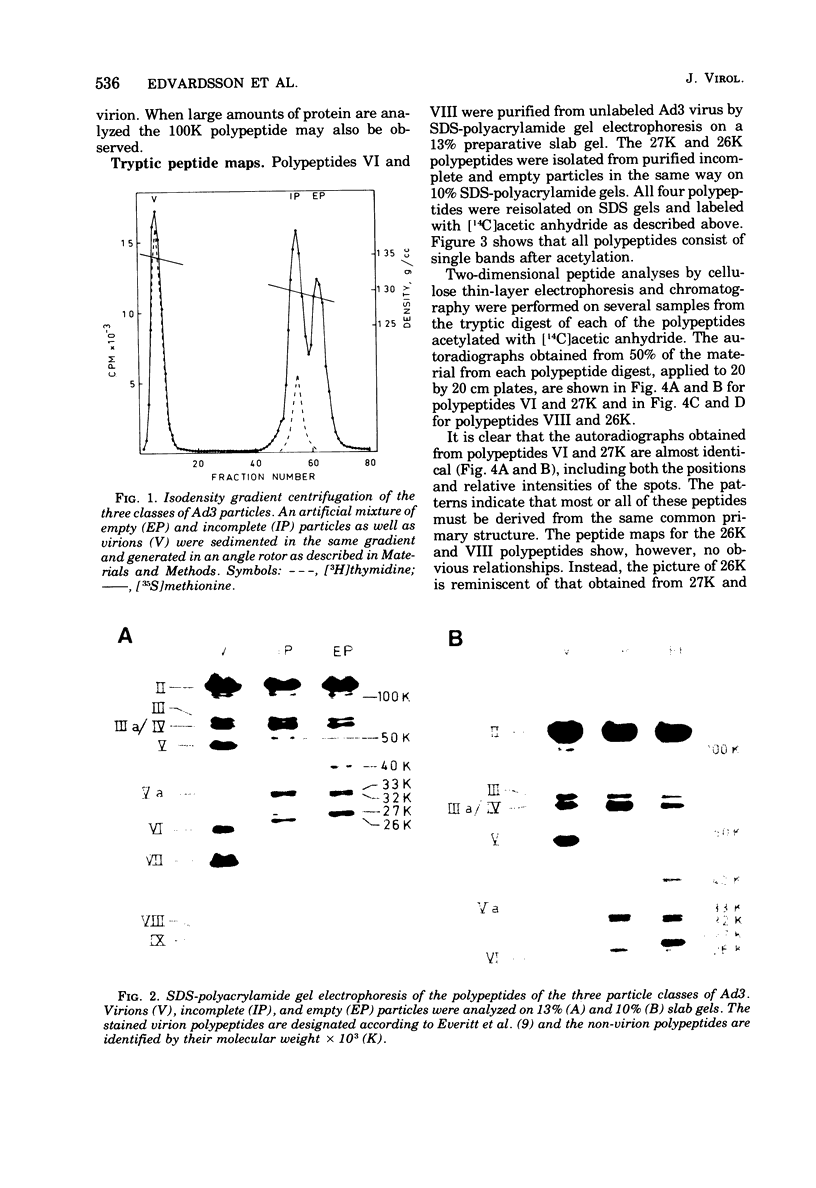
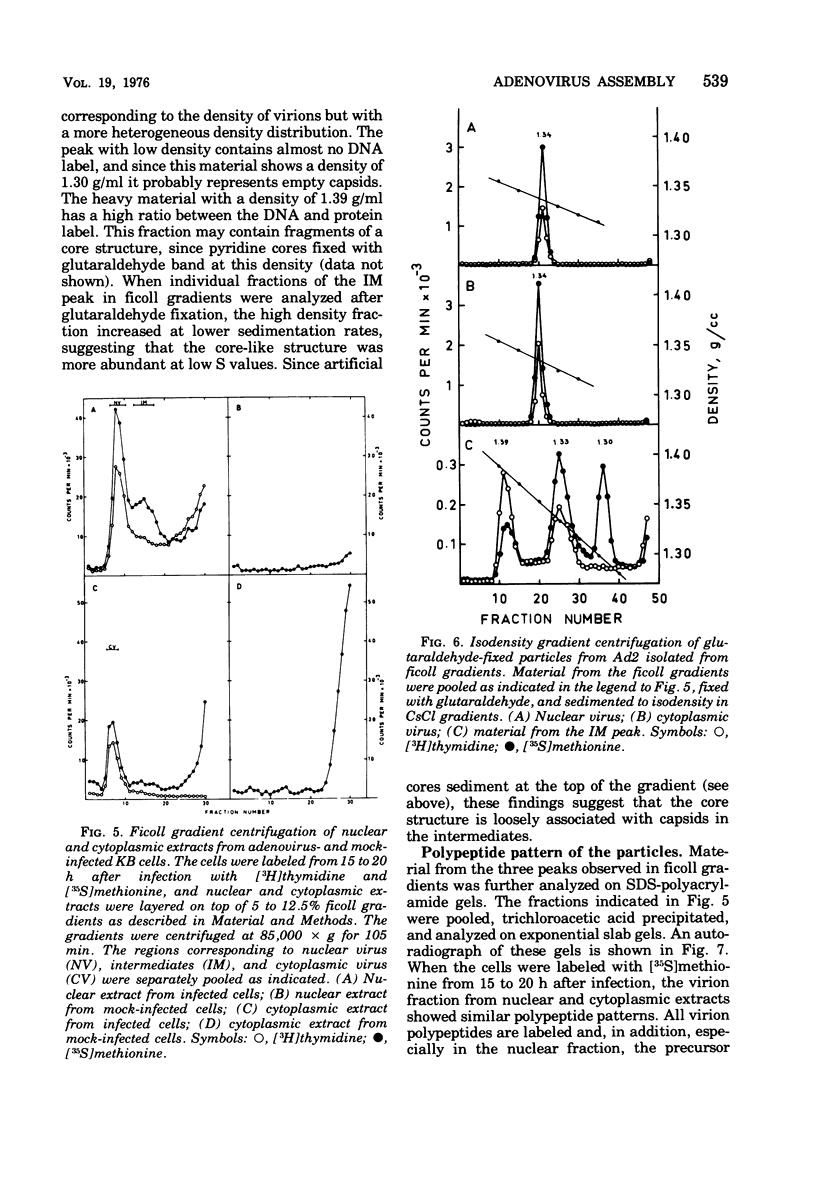
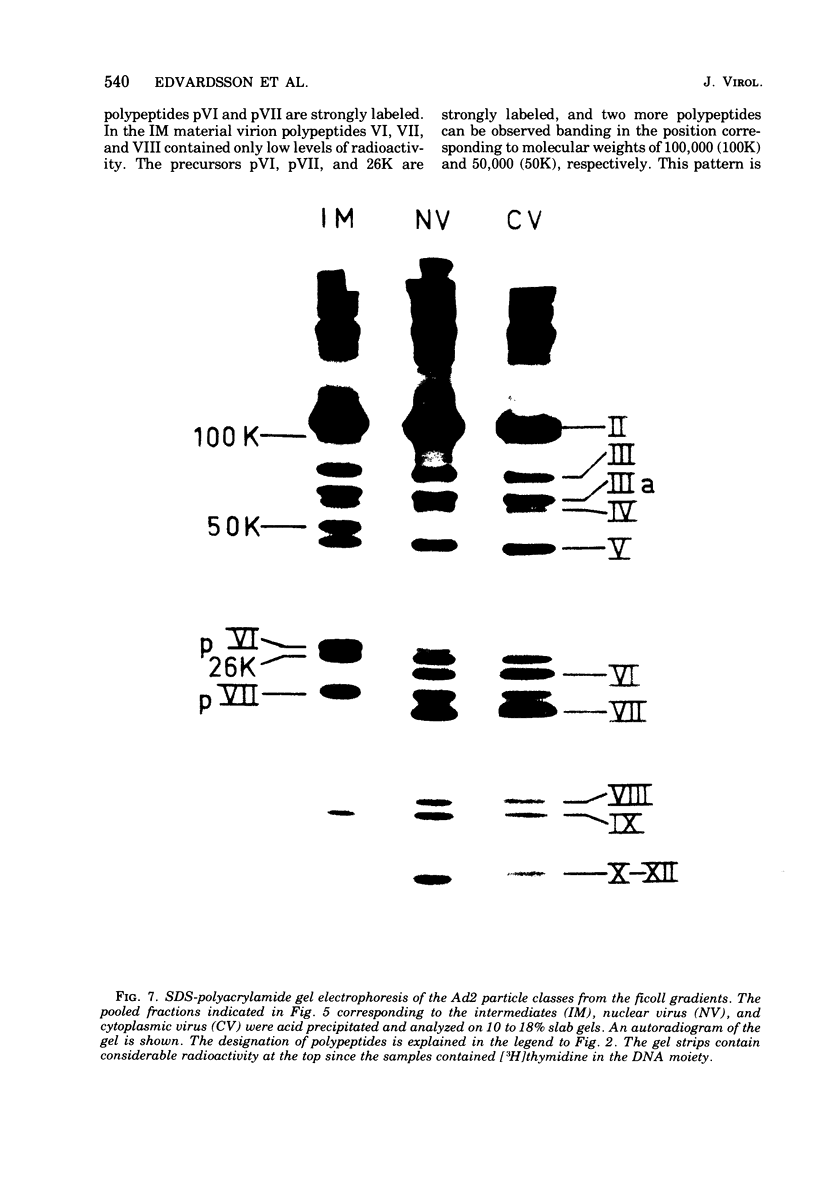
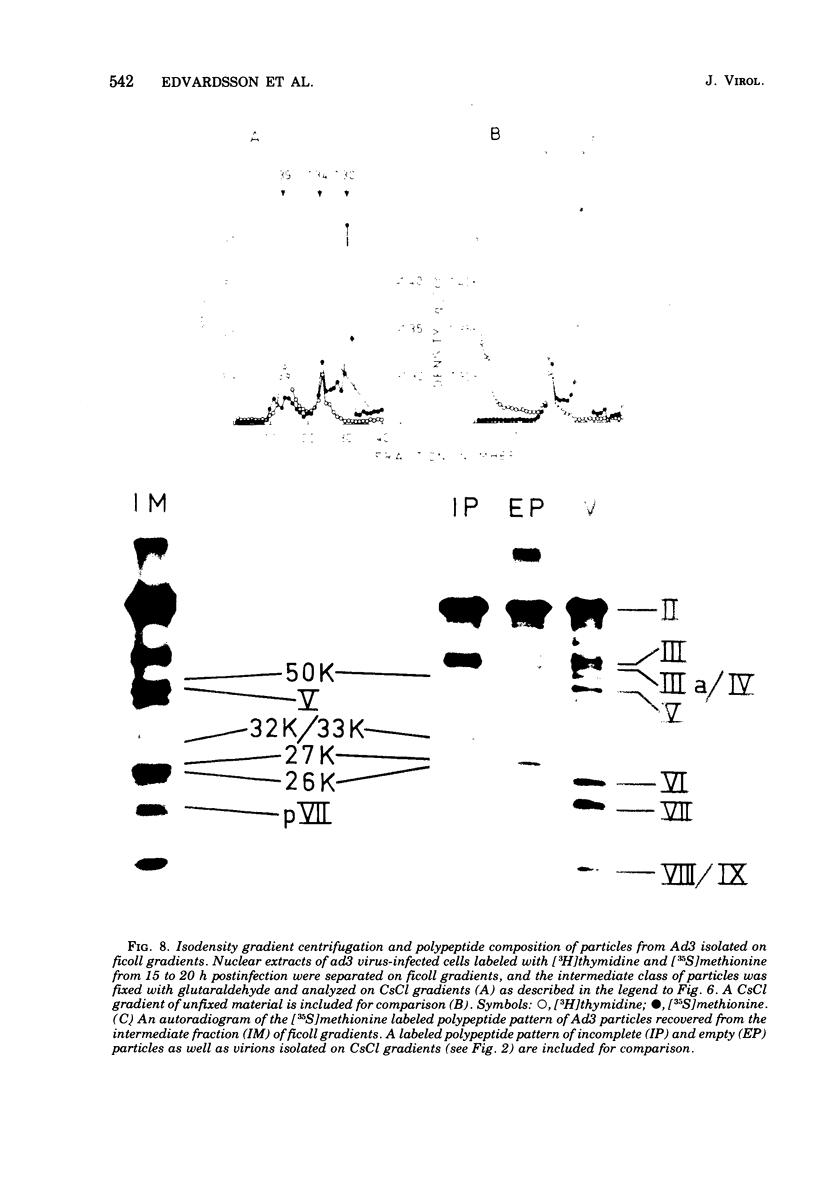
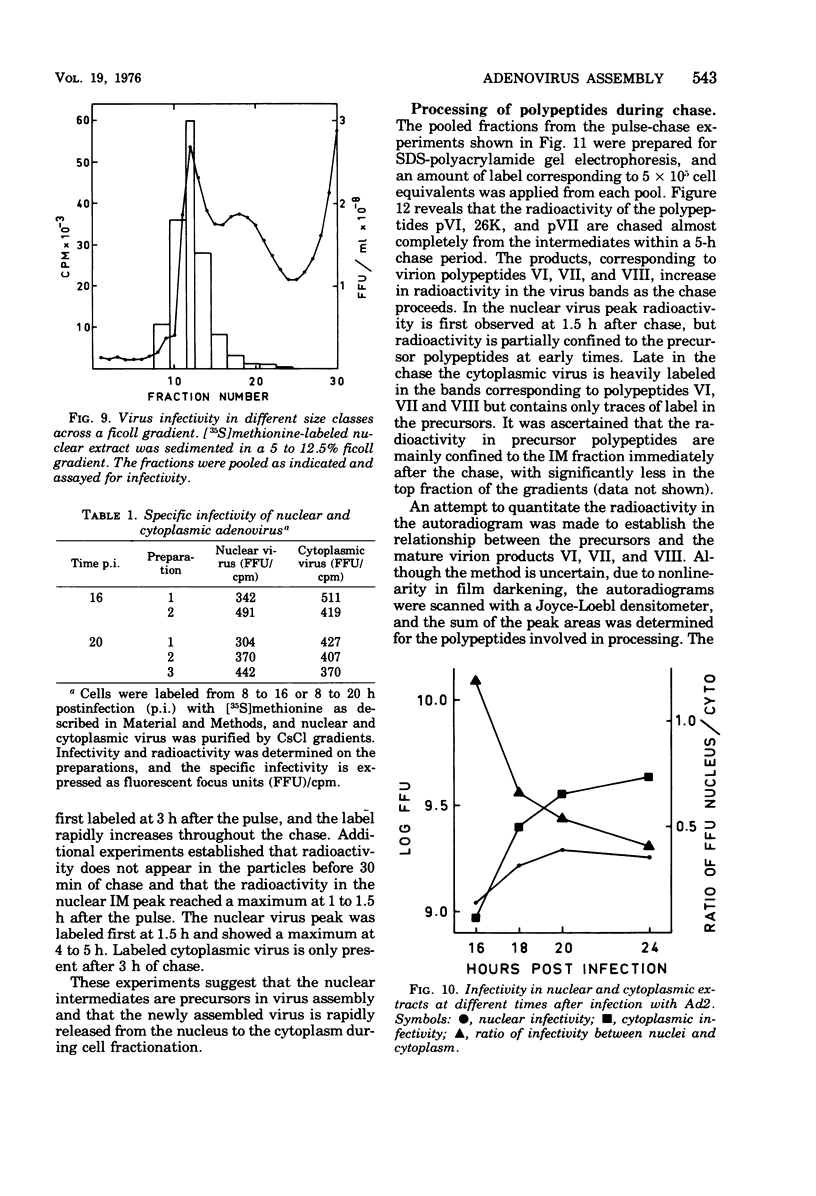
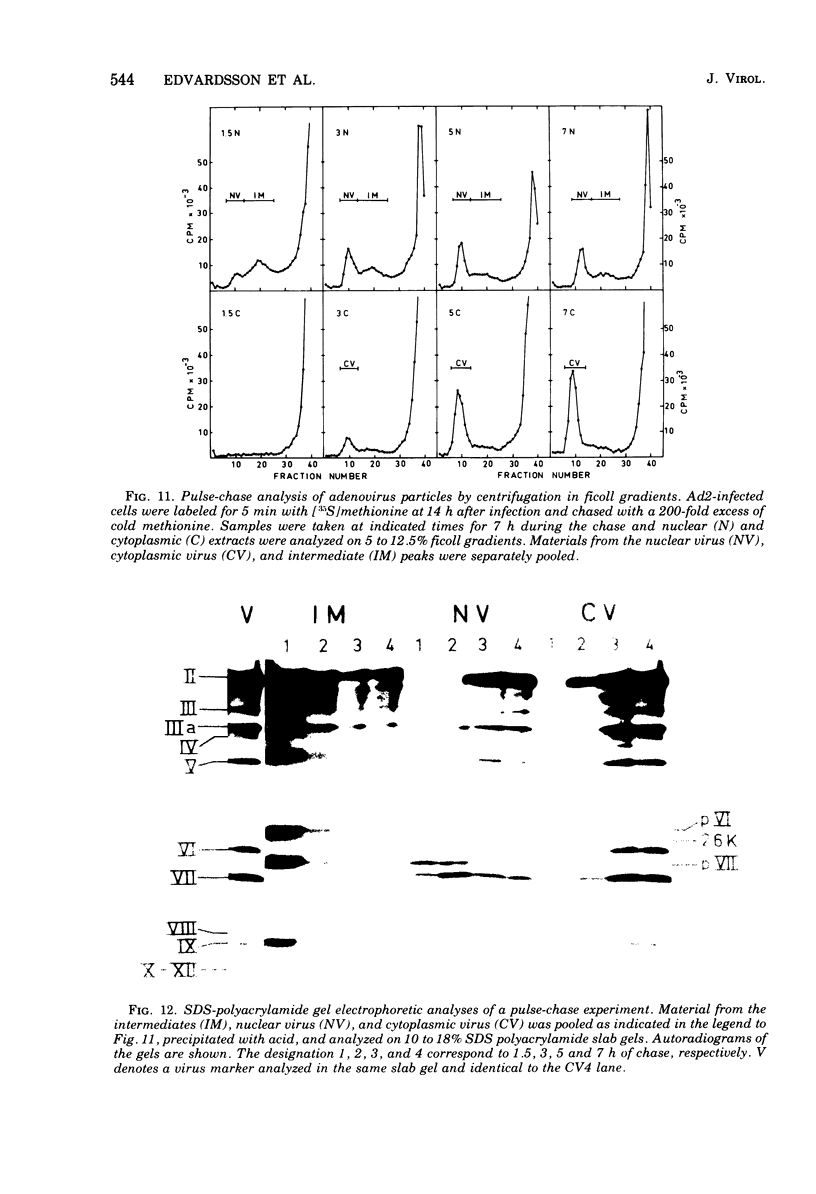
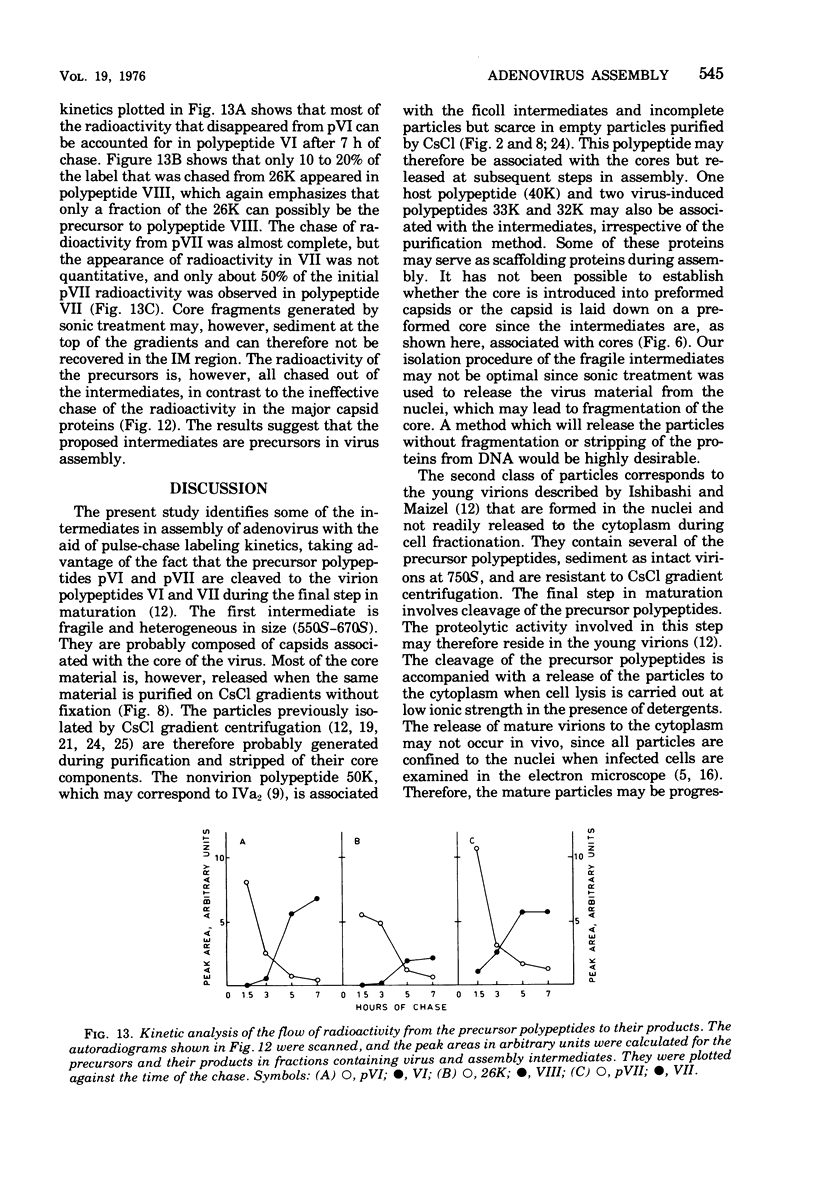
Three intermediates in adenovirus assembly have been defined; nuclear intermediates, young virions, and mature virions. The nuclear intermediates are fragile and heterogenous in size (550S-670S) and withstand separation on ficoll gradients but fall apart upon CsCl gradient centrifugation unless prefixed with glutaraldehyde. They contain both capsid and core structures, and the core structures are preferentially released during purification in CsCl. The precursor polypeptides pVI and pVII are present in the intermediates without any corresponding mature polypeptide. The young virions (Ishibashi and Maizel, 1974) are stable and preferentially confined to the nuclei after cell fractionation. They contain both uncleaved precursor polypeptides and their cleavage products. The mature virions accumulate in the cytoplasm during cell fractionation and contain the final mature polypeptides. Pulse-chase labeling kinetics, focusing on the precursor polypeptides, suggest that these three classes participate in assembly of adenovirus. Tryptic peptide maps establish that polypeptide pVI is the precursor of polypeptide VI, but only a small fraction of polypeptide 26K can in vivo account for polypeptide VIII.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson C. W., Baum P. R., Gesteland R. F. Processing of adenovirus 2-induced proteins. J Virol. 1973 Aug;12(2):241–252. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.2.241-252.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson C. W., Lewis J. B., Atkins J. F., Gesteland R. F. Cell-free synthesis of adenovirus 2 proteins programmed by fractionated messenger RNA: a comparison of polypeptide products and messenger RNA lengths. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jul;71(7):2756–2760. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.7.2756. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baltimore D., Huang A. S. Isopycnic separation of subcellular components from poliovirus-infected and normal HeLa cells. Science. 1968 Nov 1;162(3853):572–574. doi: 10.1126/science.162.3853.572. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulanger P. A., Torpier G., Rimsky A. Crystallographic study of intranuclear adenovirus type 5 crystals. Intervirology. 1974;2(1):56–62. doi: 10.1159/000149406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burlingham B. T., Brown D. T., Doerfler W. Incomplete particles of adenovirus. I. Characteristics of the DNA associated with incomplete adenovirions of types 2 and 12. Virology. 1974 Aug;60(2):419–430. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90336-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuatrecasas P. Properties of the insulin receptor isolated from liver and fat cell membranes. J Biol Chem. 1972 Apr 10;247(7):1980–1991. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EAGLE H. Amino acid metabolism in mammalian cell cultures. Science. 1959 Aug 21;130(3373):432–437. doi: 10.1126/science.130.3373.432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Everitt E., Sundquist B., Pettersson U., Philipson L. Structural proteins of adenoviruses. X. Isolation and topography of low molecular weight antigens from the virion of adenovirus type 2. Virology. 1973 Mar;52(1):130–147. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90404-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Everitt E., Sundquist B., Philipson L. Mechanism of the arginine requirement for adenovirus synthesis. I. Synthesis of structural proteins. J Virol. 1971 Nov;8(5):742–753. doi: 10.1128/jvi.8.5.742-753.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREEN M. Studies on the biosynthesis of viral DNA. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1962;27:219–235. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1962.027.001.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishibashi M., Maizel J. V., Jr The polypeptides of adenovirus. V. Young virions, structural intermediate between top components and aged virions. Virology. 1974 Feb;57(2):409–424. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90181-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORGAN C., GODMAN G. C., ROSE H. M., HOWE C., HUANG J. S. Electron microscopic and histochemical studies of an unusual crystalline protein occurring in cells infected by type 5 adenovirus. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1957 May 25;3(3):505–508. doi: 10.1083/jcb.3.3.505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maizel J. V., Jr, White D. O., Scharff M. D. The polypeptides of adenovirus. II. Soluble proteins, cores, top components and the structure of the virion. Virology. 1968 Sep;36(1):126–136. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(68)90122-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGuire J. C., Pène J. J., Barrow-Carraway J. Gene expression during the development of bacteriophage phi 29. 3. Analysis of viral-specific protein synthesis with suppressible mutants. J Virol. 1974 Mar;13(3):690–698. doi: 10.1128/jvi.13.3.690-698.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oberg B., Saborio J., Persson T., Everitt E., Philipson L. Identification of the in vitro translation products of adenovirus mRNA by immunoprecipitation. J Virol. 1975 Jan;15(1):199–207. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.1.199-207.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prage L., Höglund S., Philipson L. Structural proteins of adenoviruses. 8. Characterization of incomplete particles of adenovirus type 3. Virology. 1972 Sep;49(3):745–757. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90531-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prage L., Pettersson U., Höglund S., Lonberg-Holm K., Philipson L. Structural proteins of adenoviruses. IV. Sequential degradation of the adenovirus type 2 virion. Virology. 1970 Oct;42(2):341–358. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90278-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenwirth B., Tjia S., Westphal M., Doerfler W. Incomplete particles of adenovirus. II. Kinetics of formation and polypeptide composition of adenovirus type 2. Virology. 1974 Aug;60(2):431–437. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90337-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russel W. C., Newman C., Williams J. F. Characterization of temperature-sensitive mutants of adenovirus type 5--serology. J Gen Virol. 1972 Dec;17(3):265–279. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-17-3-265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH K. O. STUDIES ON ADENOVIRUS-12. I. QUANTITATIVE CORRELATIONS BETWEEN SOME PHYSICAL, ANTIGENIC AND INFECTIOUS PROPERTIES. J Immunol. 1965 Jun;94:976–989. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundquist B., Everitt E., Philipson L., Hoglund S. Assembly of adenoviruses. J Virol. 1973 Mar;11(3):449–459. doi: 10.1128/jvi.11.3.449-459.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wadell G., Hammarskjöld M. L., Varsanyi T. Incomplete virus particles of adenovirus type 16. J Gen Virol. 1973 Sep;20(3):287–302. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-20-3-287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber J. Genetic analysis of adenovirus type 2 III. Temperature sensitivity of processing viral proteins. J Virol. 1976 Feb;17(2):462–471. doi: 10.1128/jvi.17.2.462-471.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White D. O., Scharff M. D., Maizel J. V., Jr The polypeptides of adenovirus. 3. Synthesis in infected cells. Virology. 1969 Jul;38(3):395–406. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90152-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. F., Gharpure M., Ustacelebi S., McDonald S. Isolation of temperature-sensitive mutants of adenovirus type 5. J Gen Virol. 1971 May;11(2):95–101. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-11-2-95. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winters W. D., Russell W. C. Studies on the assembly of adenovirus in vitro. J Gen Virol. 1971 Feb;10(2):181–194. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-10-2-181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]