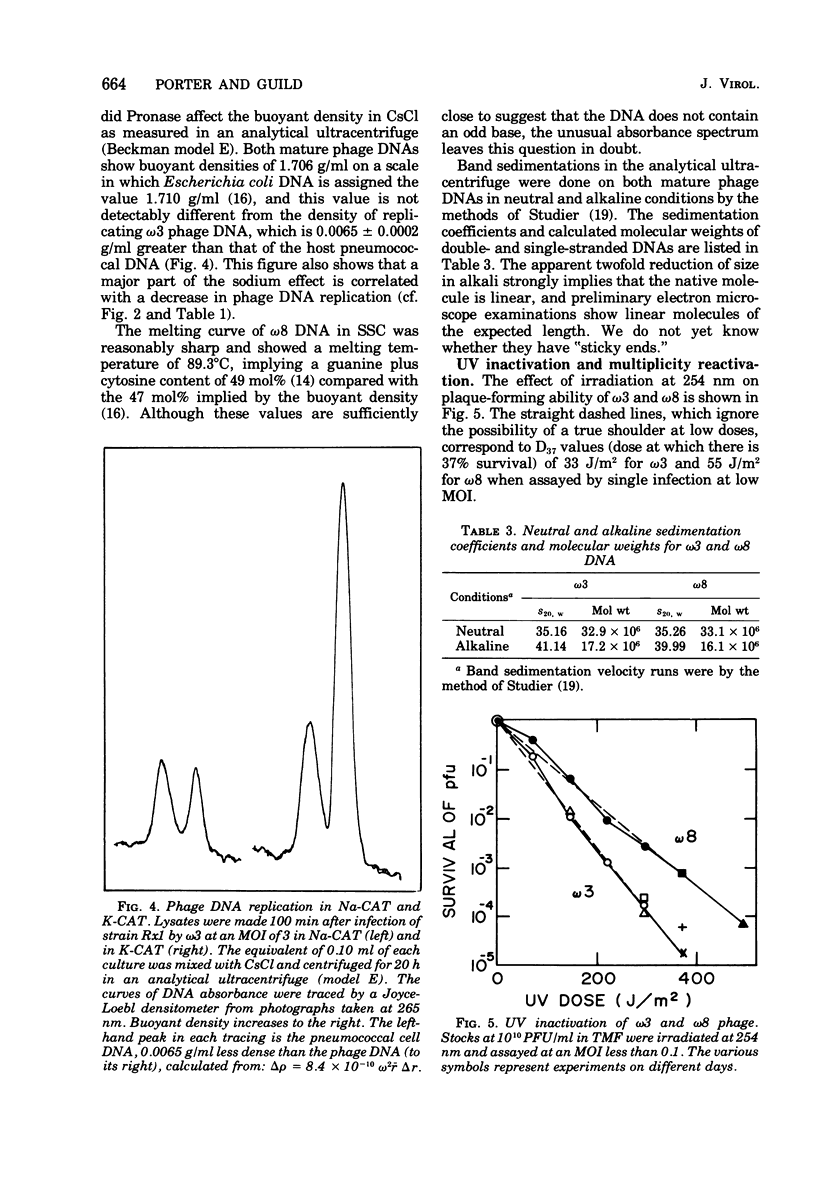
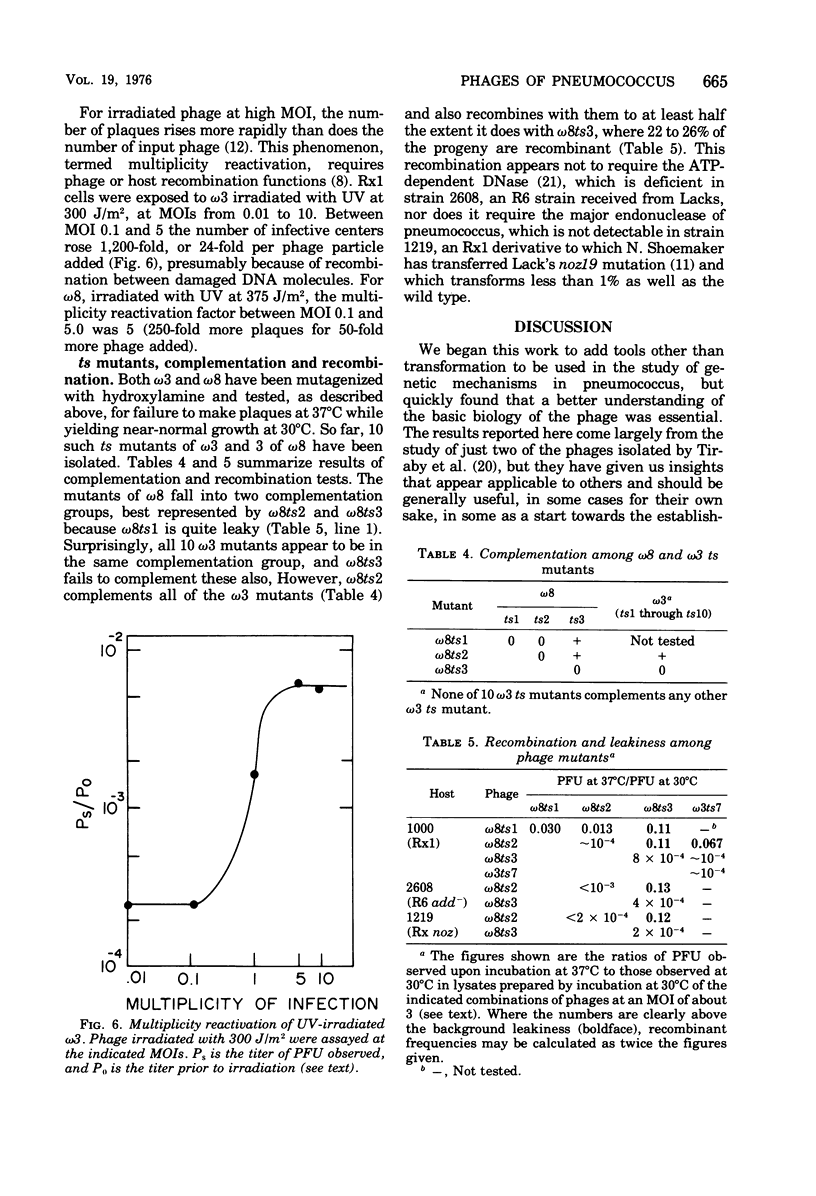
Abstract
The growth of pneumococcal phages at high cell and phage densities is enhanced strongly by the substitution of potassium for sodium in the medium. Initial titers of 2 X 10(10) to 4 X 10(10) PFU/ml are readily obtained, and concentrated stocks are stable in a storage buffer described here. The mechanism of the cation effect is obscure. Phages omega3 and omega8 each have linear double-stranded DNA of 33 X 10(6) daltons per particle, with an apparent guanine plus cytosine content of 47 to 49 mol%, as determined by buoyancy and melting temperature, but with an unusual absorbance spectrum. Efficiency of plating is high if sufficient time is allowed for a relatively slow adsorption, which differs several-fold in rate between the two phages. Morphologically, these and other pneumococcal phages are similar to coliphage lambda but with a longer tail and tail fiber. Upon UV inactivation, omega3 and omega8 have D37 values of 33 and 55 J/m2, respectively, and each shows multiplicity reactivation. A total of 13 ts mutants have been isolated from the two phages, representing only two complementation groups; complementation and recombination occur between omega3 and omega8 mutants. Both phages provoke high-titer antisera with extensive cross-reactivity against a number of newly isolated pneumococcal phages.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- EDGAR R. S., DENHARDT G. H., EPSTEIN R. H. A COMPARATIVE GENETIC STUDY OF CONDITIONAL LETHAL MUTATIONS OF BACTERIOPHAGE T4D. Genetics. 1964 Apr;49:635–648. doi: 10.1093/genetics/49.4.635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EDGAR R. S., LIELAUSIS I. TEMPERATURE-SENSITIVE MUTANTS OF BACTERIOPHAGE T4D: THEIR ISOLATION AND GENETIC CHARACTERIZATION. Genetics. 1964 Apr;49:649–662. doi: 10.1093/genetics/49.4.649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GAREN A. Physiological effects of rII mutations in bacteriophage T4. Virology. 1961 Jun;14:151–163. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(61)90190-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall D. H., Tessman I. T4 mutants unable to induce deoxycytidylate deaminase activity. Virology. 1966 Jun;29(2):339–345. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(66)90041-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huskey R. J. Multiplicity reactivation as a test for recombination function. Science. 1969 Apr 18;164(3877):319–320. doi: 10.1126/science.164.3877.319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacks S., Greenberg B., Neuberger M. Identification of a deoxyribonuclease implicated in genetic transformation of Diplococcus pneumoniae. J Bacteriol. 1975 Jul;123(1):222–232. doi: 10.1128/jb.123.1.222-232.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luria S. E., Dulbecco R. Genetic Recombinations Leading to Production of Active Bacteriophage from Ultraviolet Inactivated Bacteriophage Particles. Genetics. 1949 Mar;34(2):93–125. doi: 10.1093/genetics/34.2.93. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARMUR J., DOTY P. Determination of the base composition of deoxyribonucleic acid from its thermal denaturation temperature. J Mol Biol. 1962 Jul;5:109–118. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(62)80066-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mcdonnell M., Lain R., Tomasz A. "Diplophage": a bacteriophage of Diplococcus pneumoniae. Virology. 1975 Feb;63(2):577–582. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90329-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. A., Guild W. R. Structure of deoxyribonucleic acid on the cell surface during uptake by pneumococcus. J Bacteriol. 1973 Sep;115(3):1055–1062. doi: 10.1128/jb.115.3.1055-1062.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHILDKRAUT C. L., MARMUR J., DOTY P. Determination of the base composition of deoxyribonucleic acid from its buoyant density in CsCl. J Mol Biol. 1962 Jun;4:430–443. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(62)80100-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STUDIER F. W. SEDIMENTATION STUDIES OF THE SIZE AND SHAPE OF DNA. J Mol Biol. 1965 Feb;11:373–390. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80064-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sekiguchi M. Studies on the physiological defect in rII mutants of bacteriophage T4. J Mol Biol. 1966 Apr;16(2):503–522. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80188-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoemaker N. B., Guild W. R. Destruction of low efficiency markers is a slow process occurring at a heteroduplex stage of transformation. Mol Gen Genet. 1974;128(4):283–290. doi: 10.1007/BF00268516. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tiraby J. G., Tiraby E., Fox M. S. Pneumococcal bacteriophages. Virology. 1975 Dec;68(2):566–569. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90300-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vovis G. F., Buttin G. An ATP-dependent deoxyribonuclease from diplococcus pneumoniae. I. Partial purification and some biochemical properties. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Nov 12;224(1):29–41. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(70)90617-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilcox K. W., Smith H. O. Isolation and characterization of mutants of Haemophilus influenzae deficient in an adenosine 5'-triphosphate-dependent deoxyribonuclease activity. J Bacteriol. 1975 May;122(2):443–453. doi: 10.1128/jb.122.2.443-453.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto K. R., Alberts B. M., Benzinger R., Lawhorne L., Treiber G. Rapid bacteriophage sedimentation in the presence of polyethylene glycol and its application to large-scale virus purification. Virology. 1970 Mar;40(3):734–744. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90218-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]