Abstract
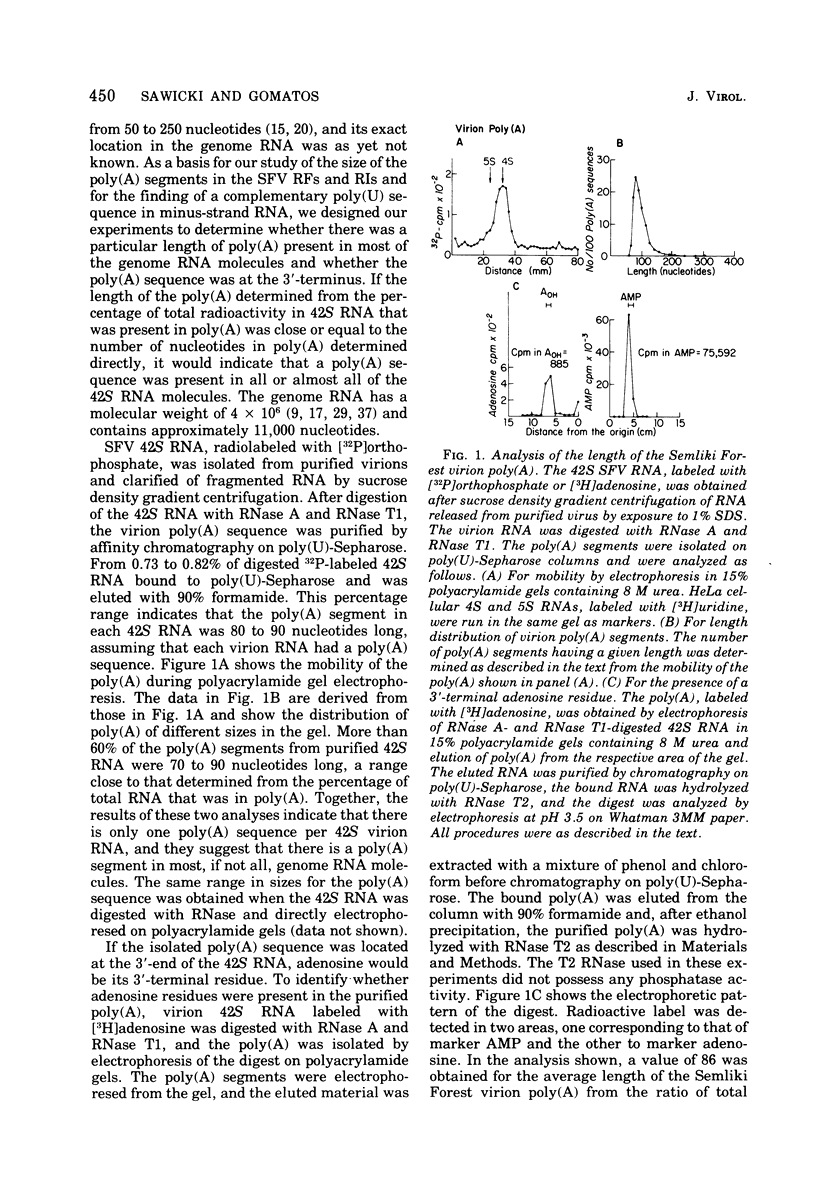
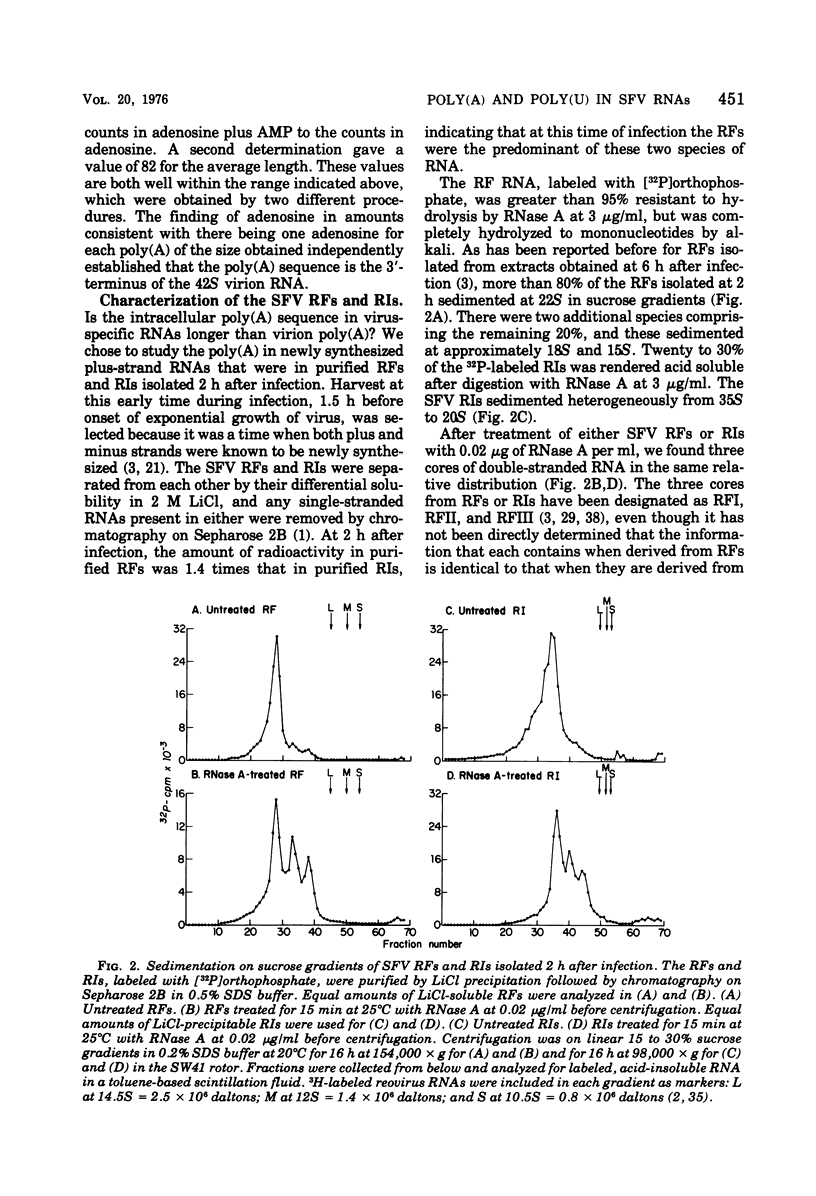
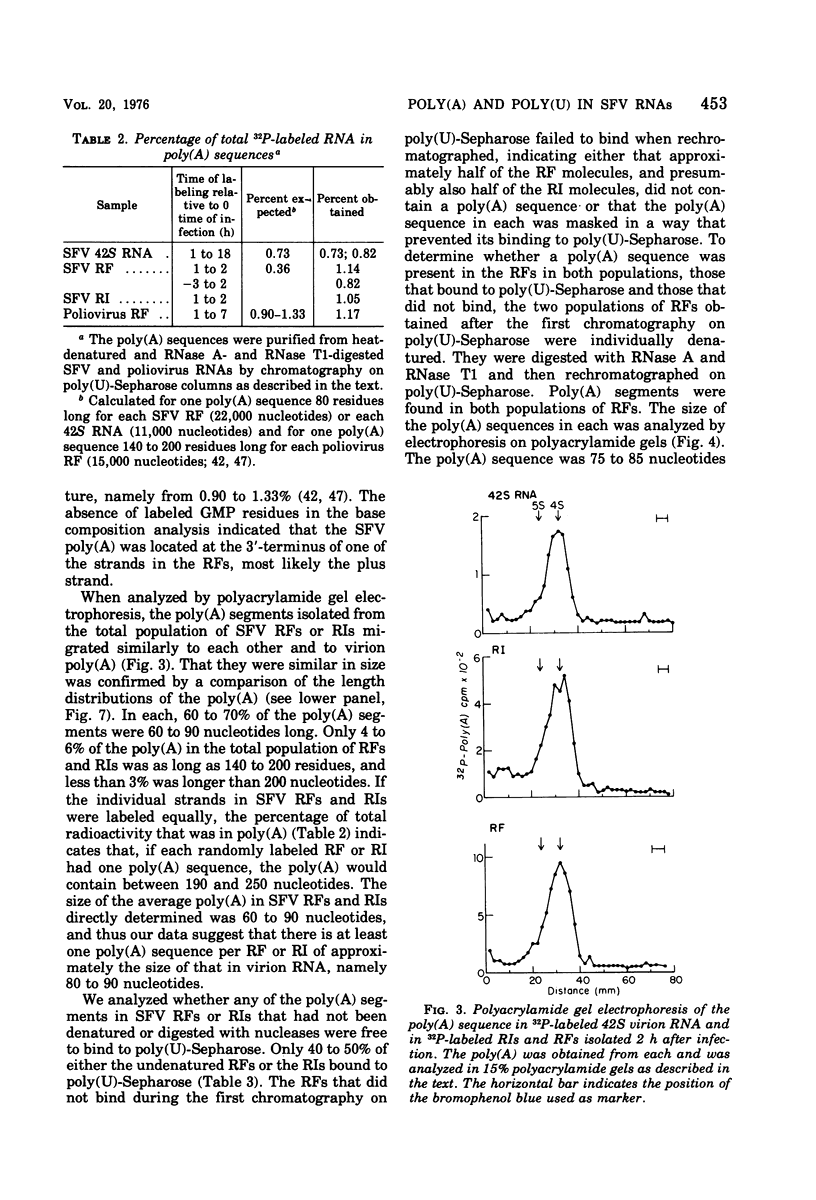
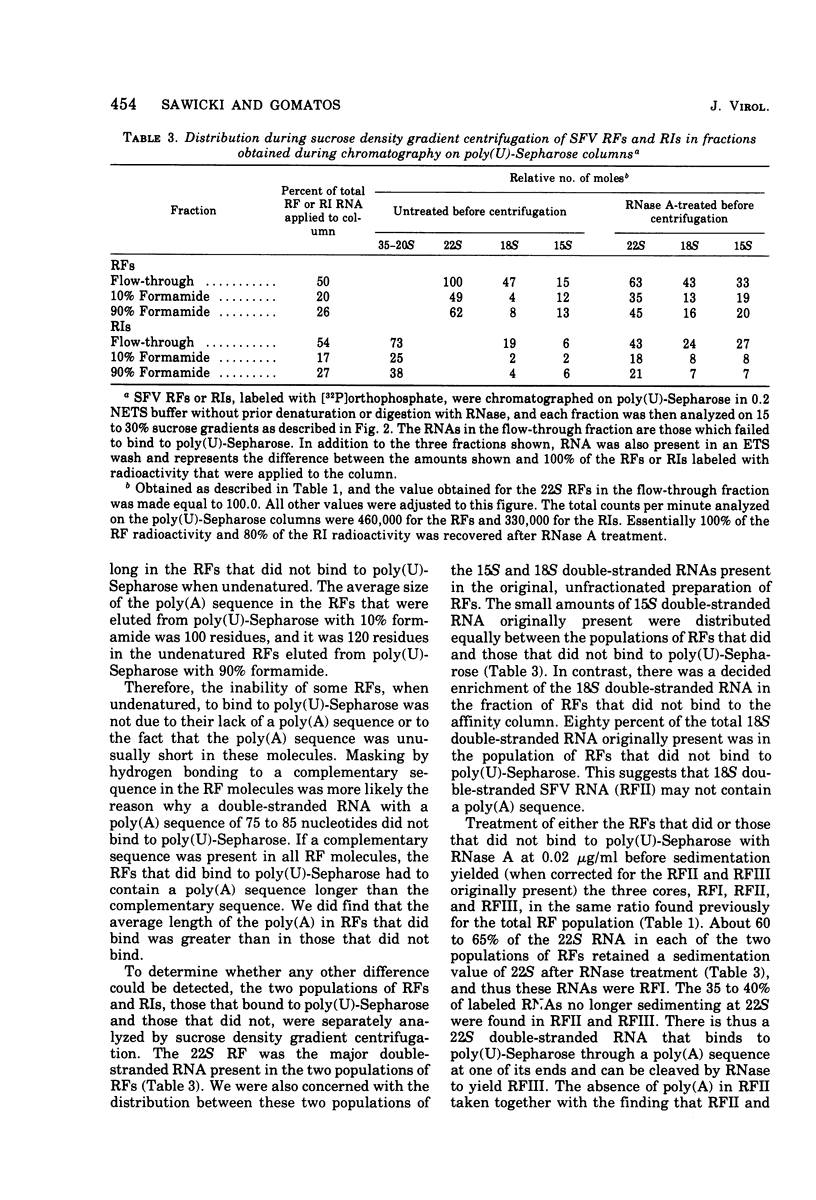
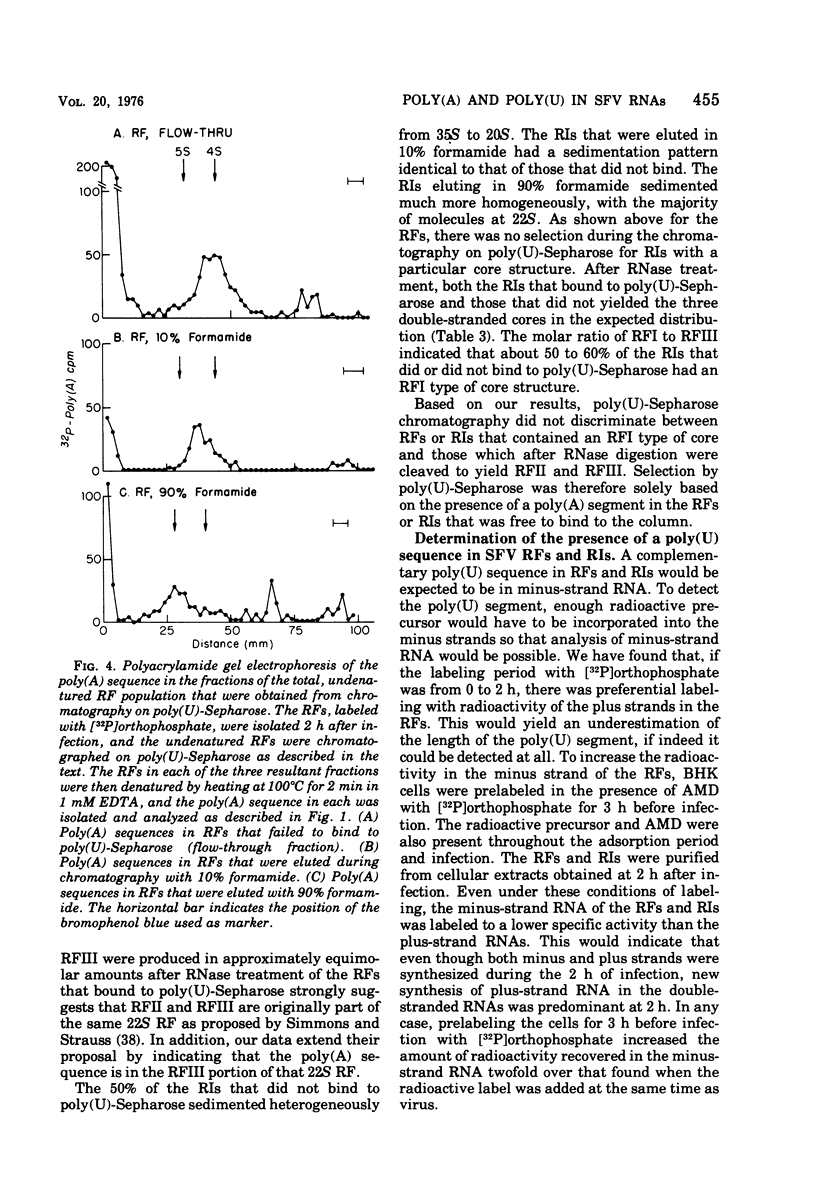
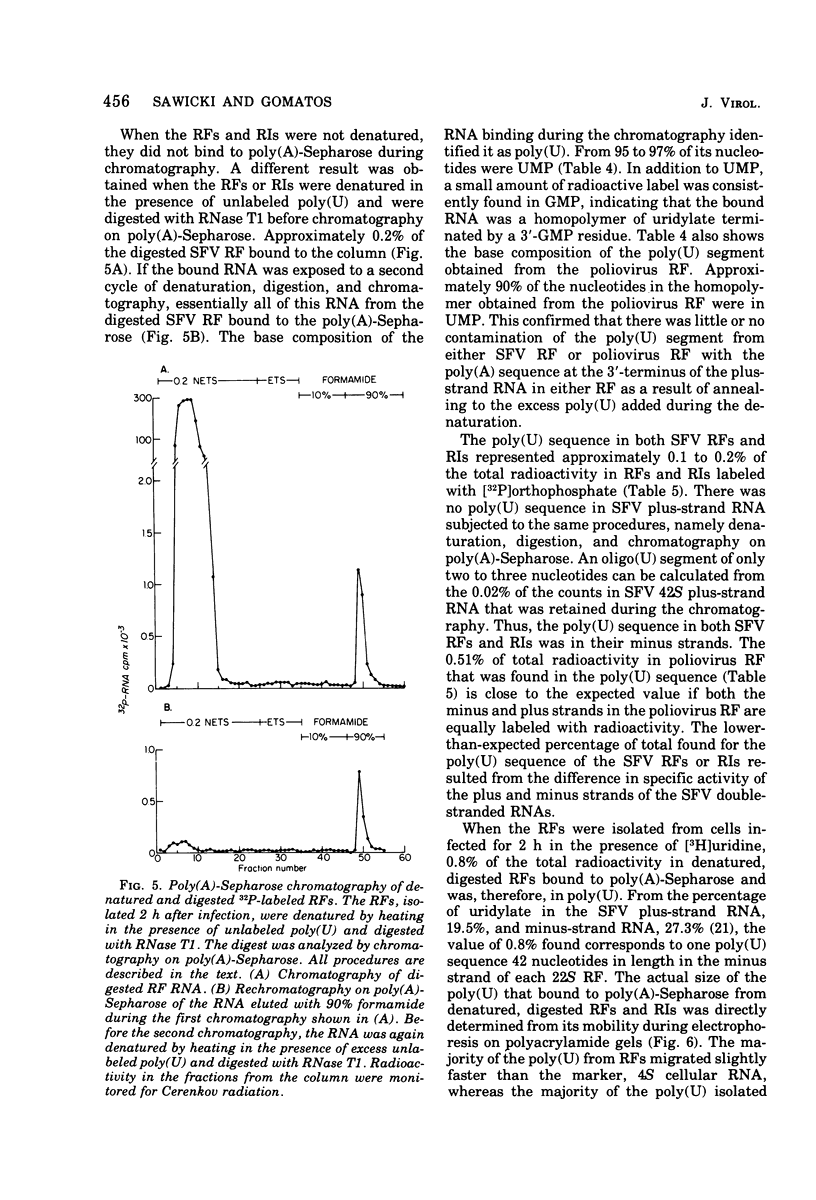
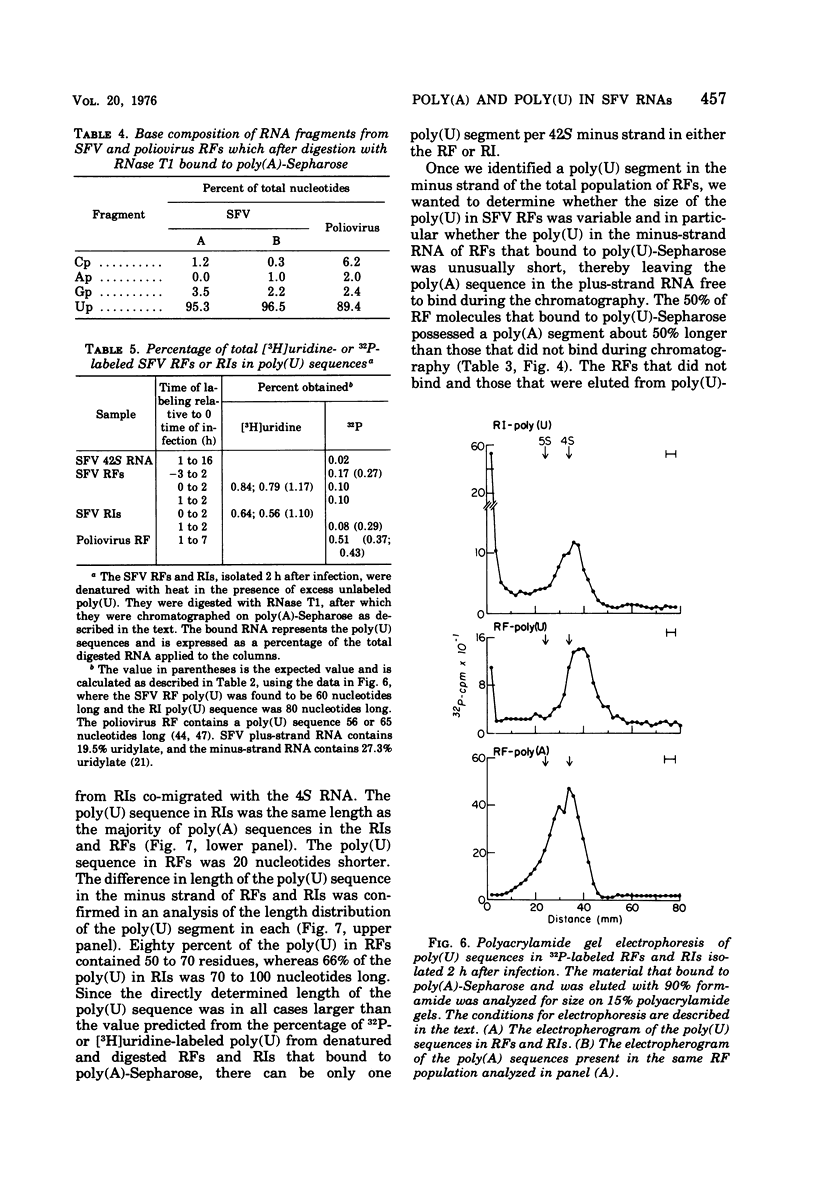
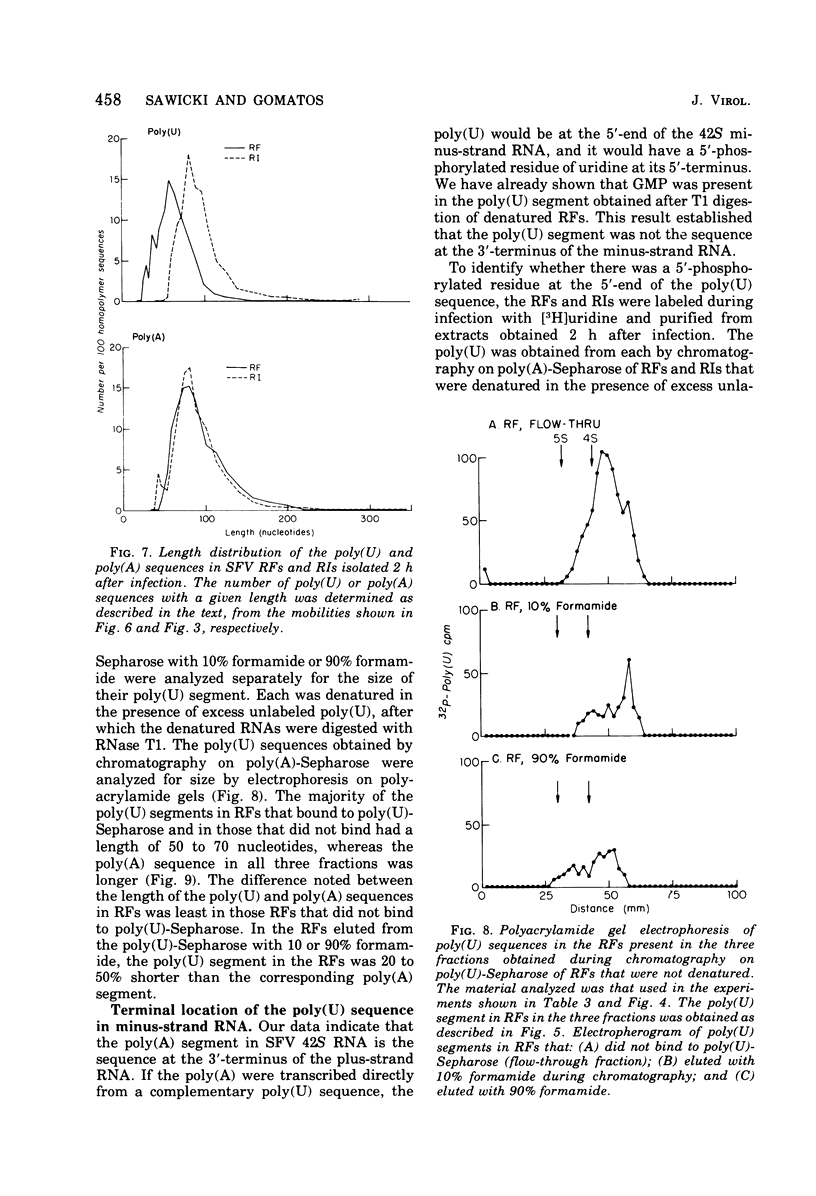
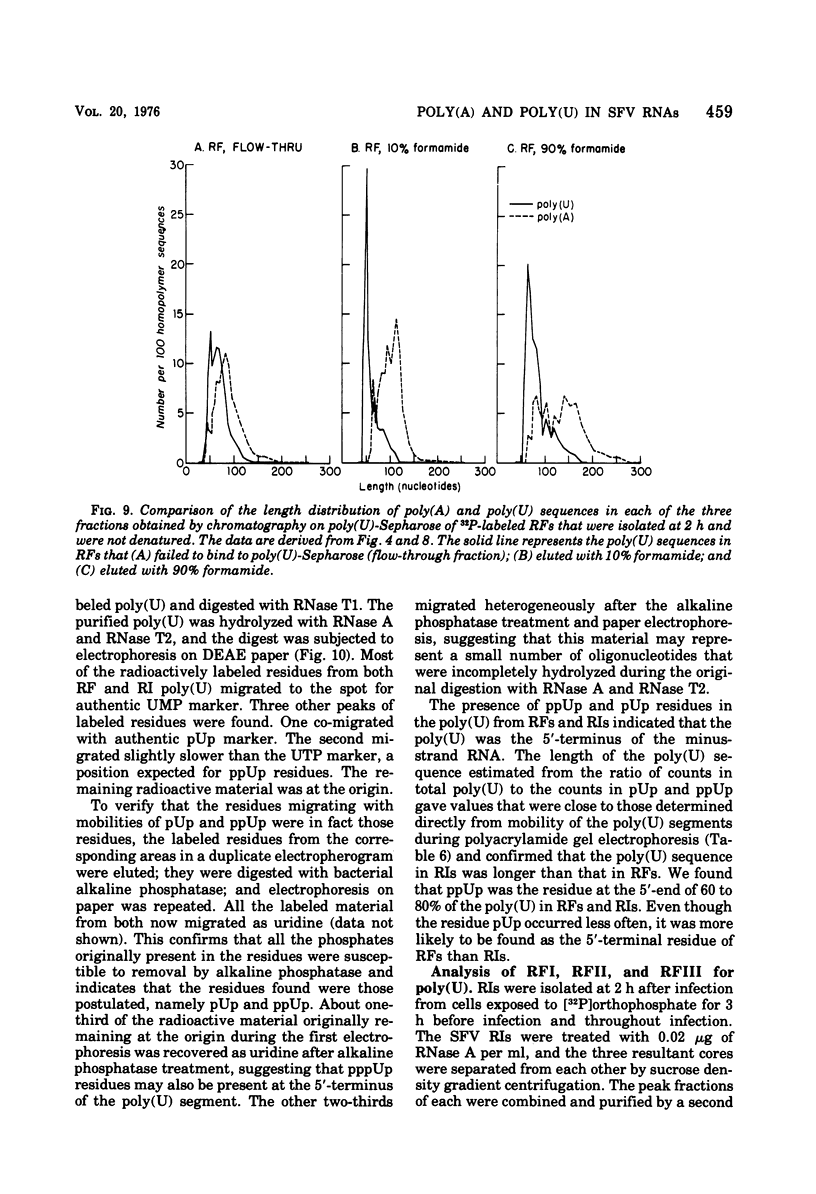
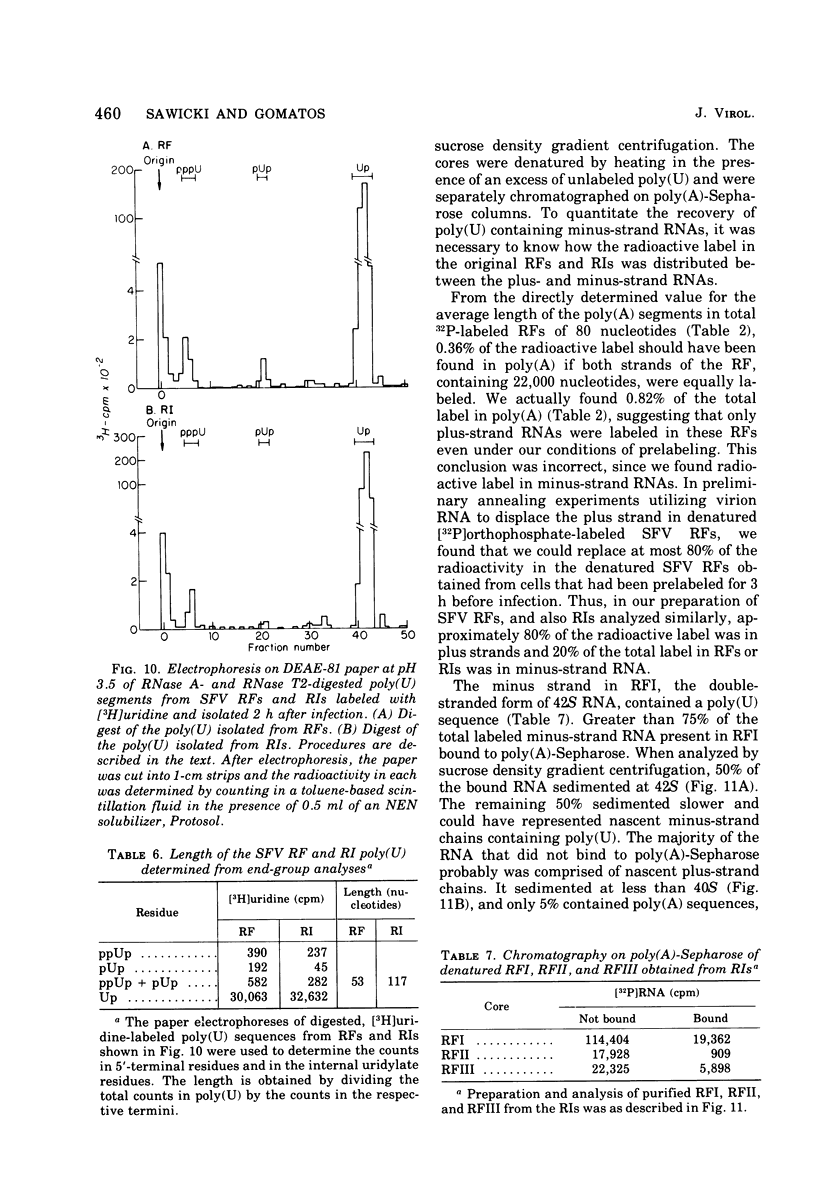
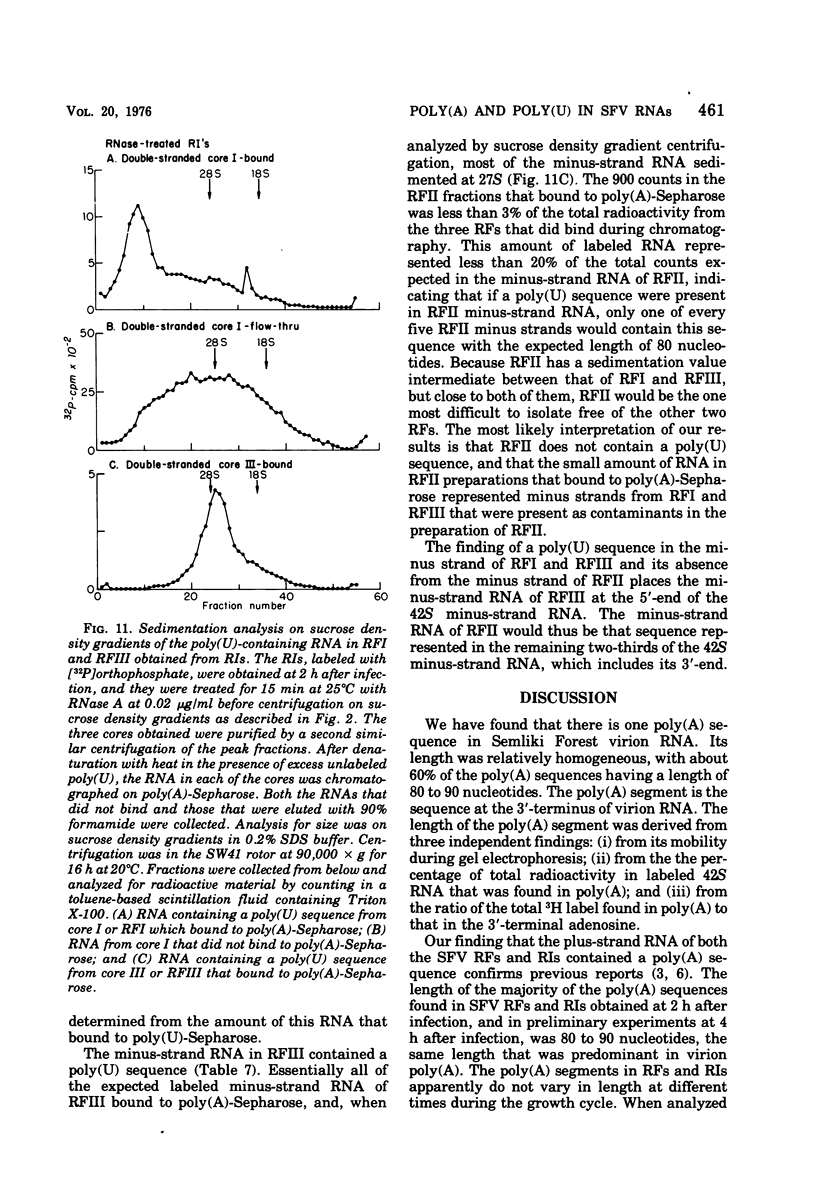
The 42S RNA from Semliki Forest virus contains a polyadenylate [poly(A)] sequence that is 80 to 90 residues long and is the 3'-terminus of the virion RNA. A poly(A) sequence of the same length was found in the plus strand of the replicative forms (RFs) and replicative intermediates (RIs) isolated 2 h after infection. In addition, both RFs and RIs contained a polyuridylate [poly(U)] sequence. No poly(U) was found in virion RNA, and thus the poly(U) sequence is in minus-strand RNA. The poly(U) from RFs was on the average 60 residues long, whereas that isolated from the RIs was 80 residues long. Poly(U) sequences isolated from RFs and RIs by digestion with RNase T1 contained 5'-phosphorylated pUp and ppUp residues, indicating that the poly(U) sequence was the 5'-terminus of the minus-strand RNA. The poly(U) sequence in RFs or RIs was free to bind to poly(A)-Sepharose only after denaturation of the RNAs, indicating that the poly(U) was hydrogen bonded to the poly(A) at the 3'-terminus of the plus-strand RNA in these molecules. When treated with 0.02 mug of RNase A per ml, both RFs and RIs yielded the same distribution of the three cores, RFI, RFII, and RFIII. The minus-strand RNA of both RFI and RFIII contained a poly(U) sequence. That from RFII did not. It is known that RFI is the double-stranded form of the 42S plus-strand RNA and that RFIII is the experimetnally derived double-stranded form of 26S mRNA. The poly(A) sequences in each are most likely transcribed directly from the poly(U) at the 5'-end of the 42S minus-strand RNA. The 26S mRNA thus represents the nucleotide sequence in that one-third of the 42S plus-strand RNA that includes its 3'-terminus.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baltimore D. Structure of the poliovirus replicative intermediate RNA. J Mol Biol. 1968 Mar 14;32(2):359–368. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90015-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellamy A. R., Shapiro L., August J. T., Joklik W. K. Studies on reovirus RNA. I. Characterization of reovirus genome RNA. J Mol Biol. 1967 Oct 14;29(1):1–17. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90177-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruton C. J., Kennedy S. I. Semliki Forest virus intracellular RNA: properties of the multi-stranded RNA species and kinetics of positive and negative strand synthesis. J Gen Virol. 1975 Jul;28(1):111–127. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-28-1-111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHAMBERLIN M., BERG P. MECHANISM OF RNA POLYMERASE ACTION: CHARACTERIZATION OF THE DNA-DEPENDENT SYNTHESIS OF POLYADENYLIC ACID. J Mol Biol. 1964 May;8:708–726. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(64)80120-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cancedda R., Villa-Komaroff L., Lodish H. F., Schlesinger M. Initiation sites for translation of sindbis virus 42S and 26S messenger RNAs. Cell. 1975 Oct;6(2):215–222. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90012-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clegg J. C., Kennedy S. I. Initiation of synthesis of the structural proteins of Semliki Forest virus. J Mol Biol. 1975 Oct 5;97(4):401–411. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80050-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clegg J. C., Kennedy S. I. Polyadenylic acid sequences in the virus RNA species of cells infected with Semliki Forest Virus. J Gen Virol. 1974 Mar;22(3):331–345. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-22-3-331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DULBECCO R., VOGT M. Plaque formation and isolation of pure lines with poliomyelitis viruses. J Exp Med. 1954 Feb;99(2):167–182. doi: 10.1084/jem.99.2.167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diez J., Brawerman G. Elongation of the polyadenylate segment of messenger RNA in the cytoplasm of mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Oct;71(10):4091–4095. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.10.4091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobos P., Faulkner P. Molecular weight of Sindbis virus ribonucleic acid as measured by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Virol. 1970 Jul;6(1):145–147. doi: 10.1128/jvi.6.1.145-147.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donaghue T. P., Faulkner P. Characterisation of the 3'-terminus of Sindbis virion RNA. Nat New Biol. 1973 Dec 12;246(154):168–170. doi: 10.1038/newbio246168a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorsch-Häsler K., Yogo Y., Wimmer E. Replication of picornaviruses. I. Evidence from in vitro RNA synthesis that poly(A) of the poliovirus genome is genetically coded. J Virol. 1975 Dec;16(6):1512–1517. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.6.1512-1517.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EAGLE H. Amino acid metabolism in mammalian cell cultures. Science. 1959 Aug 21;130(3373):432–437. doi: 10.1126/science.130.3373.432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eaton B. T., Donaghue T. P., Faulkner P. Presence of poly (A) in the polyribosome-associated RNA of Sindbis-infected BHK cells. Nat New Biol. 1972 Jul 26;238(82):109–111. doi: 10.1038/newbio238109a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eaton B. T., Faulkner P. Heterogeneity in the poly(A) content of the genome of Sindbis virus. Virology. 1972 Dec;50(3):865–873. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90440-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez-Munoz R., Darnell J. E. Structural difference between the 5' termini of viral and cellular mRNA in poliovirus-infected cells: possible basis for the inhibition of host protein synthesis. J Virol. 1976 May;18(2):719–726. doi: 10.1128/jvi.18.2.719-726.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman R. M., Levy H. B., Carter W. B. Replication of semliki forest virus: three forms of viral RNA produced during infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Aug;56(2):440–446. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.2.440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu M. T., Kung H. J., Davidson N. An electron microscope study of Sindbis virus RNA. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1974;38:943–950. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.038.01.096. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston R. E., Bose H. R. An adenylate-rich segment in the virion RNA of Sindbis virus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Jan 31;46(2):712–718. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(72)80198-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaariainen L., Gomatos P. J. A kinetic analysis of the synthesis in BHK 21 cells of RNAs specific for Semliki Forest virus. J Gen Virol. 1969 Sep;5(2):251–265. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-5-2-251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy S. I. Isolation and identification of the virus-specified RNA species found on membrane-bound polyribosomes of chick embryo cells infected with Semliki Forest virus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Sep 5;48(5):1254–1258. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90846-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lachmi B. E., Glanville N., Keränen S., Läriäinen L. Tryptic peptide analysis on nonstructural and structural precursor proteins from Semliki Forest virus mutant-infected cells. J Virol. 1975 Dec;16(6):1615–1629. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.6.1615-1629.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lachmi B. E., Käriäinen L. Sequential translation of nonstructural proteins in cells infected with a Semliki Forest virus mutant. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jun;73(6):1936–1940. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.6.1936. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin J. G., Friedman R. M. Analysis of arbovirus ribonucleic acid forms by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Virol. 1971 Apr;7(4):504–514. doi: 10.1128/jvi.7.4.504-514.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MANDEL B. THE EXTRACTION OF RIBONUCLEIC ACID FROM POLIOVIRUS BY TREATMENT WITH SODIUM DODECYL SULFATE. Virology. 1964 Mar;22:360–367. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(64)90026-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcus S. L., Modak M. J., Cavalieri L. F. Purification of avian myeloblastosis virus DNA polymerase by affinity chromatography on polycytidylate-agarose. J Virol. 1974 Oct;14(4):853–859. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.4.853-859.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall S., Gillespie D. Poly U tracts absent from viral RNA. Nat New Biol. 1972 Nov 8;240(97):43–45. doi: 10.1038/newbio240043a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin B. A., Burke D. C. The replication of Semliki Forest virus. J Gen Virol. 1974 Jul;24(1):45–66. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-24-1-45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel M. R., Gomatos P. J. Semliki forest virus-specific RNAs synthesized in vitro by enzyme from infected BHK cells. J Virol. 1973 Jun;11(6):900–914. doi: 10.1128/jvi.11.6.900-914.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mowshowitz D. Identification of polysomal RNA in BHK cells infected by sindbis virus. J Virol. 1973 Apr;11(4):535–543. doi: 10.1128/jvi.11.4.535-543.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peacock A. C., Dingman C. W. Resolution of multiple ribonucleic acid species by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Biochemistry. 1967 Jun;6(6):1818–1827. doi: 10.1021/bi00858a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosemond H., Sreevalsan T. Viral RNAs associated with ribosomes in Sindbis virus-infected HeLa cells. J Virol. 1973 Mar;11(3):399–415. doi: 10.1128/jvi.11.3.399-415.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STUDIER F. W. SEDIMENTATION STUDIES OF THE SIZE AND SHAPE OF DNA. J Mol Biol. 1965 Feb;11:373–390. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80064-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shatkin A. J., Sipe J. D., Loh P. Separation of ten reovirus genome segments by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Virol. 1968 Oct;2(10):986–991. doi: 10.1128/jvi.2.10.986-991.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shih D. S., Kaesberg P. Translation of brome mosaic viral ribonucleic acid in a cell-free system derived from wheat embryo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jun;70(6):1799–1803. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.6.1799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmons D. T., Strauss J. H. Replication of Sindbis virus. I. Relative size and genetic content of 26 s and 49 s RNA. J Mol Biol. 1972 Nov 28;71(3):599–613. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmons D. T., Strauss J. H. Replication of Sindbis virus. II. Multiple forms of double-stranded RNA isolated from infected cells. J Mol Biol. 1972 Nov 28;71(3):615–631. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(72)80027-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmons D. T., Strauss J. H. Replication of Sindbis virus. V. Polyribosomes and mRNA in infected cells. J Virol. 1974 Sep;14(3):552–559. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.3.552-559.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmons D. T., Strauss J. H. Translation of Sindbis virus 26 S RNA and 49 S RNA in lysates of rabbit reticulocytes. J Mol Biol. 1974 Jun 25;86(2):397–409. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90027-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonnabend J. A., Martin E. M., Mécs E. Viral specific RNAs in infected cells. Nature. 1967 Jan 28;213(5074):365–367. doi: 10.1038/213365a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector D. H., Baltimore D. Polyadenylic acid on poliovirus RNA IV. Poly(U) in replicative intermediate and double-stranded RNA. Virology. 1975 Oct;67(2):498–505. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90450-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector D. H., Baltimore D. Polyadenylic acid on poliovirus RNA. II. poly(A) on intracellular RNAs. J Virol. 1975 Jun;15(6):1418–1431. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.6.1418-1431.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector D. H., Baltimore D. Polyadenylic acid on poliovirus RNA. III. In vitro addition of polyadenylic acid to poliovirus RNAs. J Virol. 1975 Jun;15(6):1432–1439. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.6.1432-1439.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wengler G., Beato M., Hackemack B. A. Translation of 26 S virus-specific RNA from Semliki Forest virus-infected cells in vitro. Virology. 1974 Sep;61(1):120–128. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90247-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yogo Y., Wimmer E. Poly (A) and poly (U) in poliovirus double stranded RNA. Nat New Biol. 1973 Apr 11;242(119):171–174. doi: 10.1038/newbio242171a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yogo Y., Wimmer E. Sequence studies of poliovirus RNA. III. Polyuridylic acid and polyadenylic acid as components of the purified poliovirus replicative intermediate. J Mol Biol. 1975 Mar 5;92(3):467–477. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90292-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



