Abstract
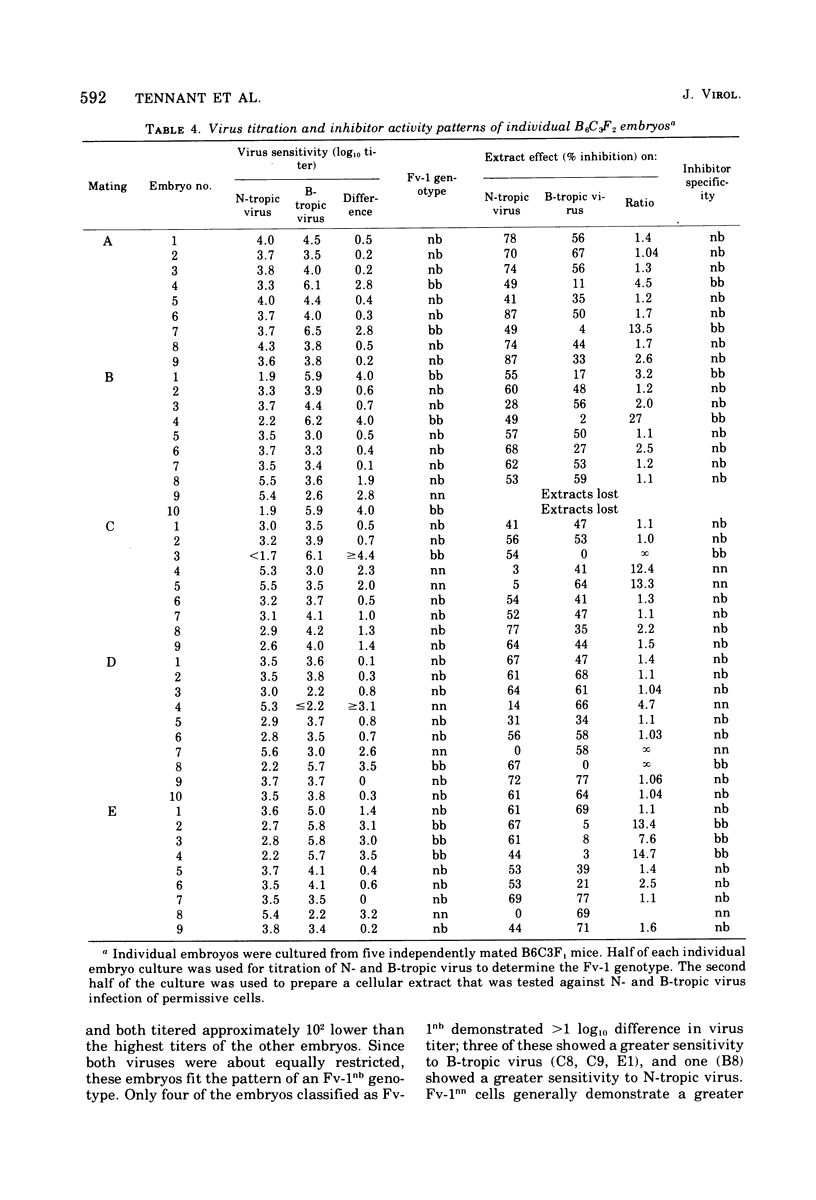
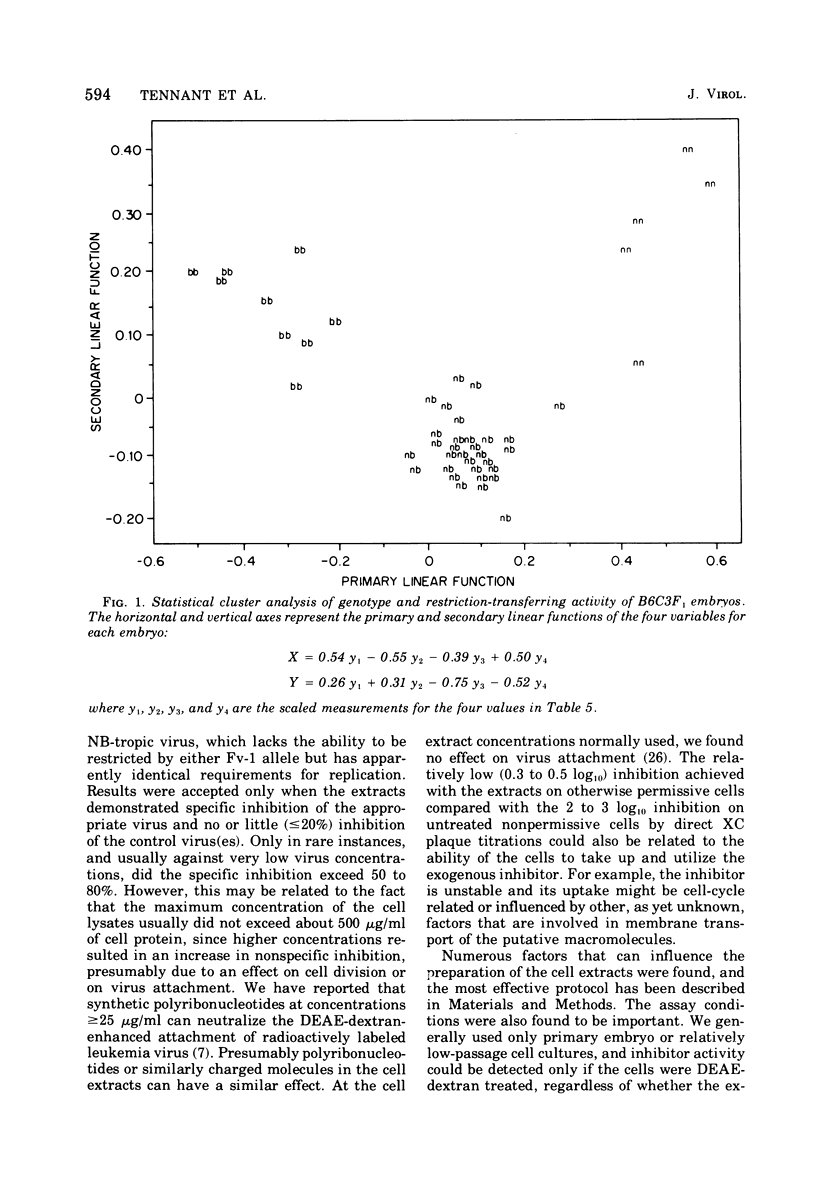
Extracts of mouse cells have been shown to transfer to N- or B-trophic host range types of mouse leukemia viruses. The genetic specificity of the inhibition was tested in two ways: (i) by correlating the Fv-1 genotype of a number of mouse strains with the restriction-transferring activity of extracts of the respective embryo cell cultures, and (ii) by correlating the Fv-1 genotype of BLC3F2 (C57BL/6 female [Fv-1bb] by C3H male [Fv-1nn] parental strains) mouse embryos, which segregate the Fv-1 alleles in a 12:1 ratio, with the inhibitor activity of extracts of the cells from each embryo. Five independent matings, totaling 45 individual embryos, were tested. Each embryo was cultured, and the Fv-1 genotype was determined independently by titration of N- and B-tropic viruses; the extracts of replicate secondary cultures were tested for their effect on infection of permissive cells by N- and B-tropic viruses. The specific-restriction-transferring activity of the embryos was found to segregate with the appropriate Fv-1 genotype. These res-lts confirm the suggestion that the inhibitor of the leukemia virus host range types in the cellular extracts is a product of the Fv-1 locus.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aaronson S. A., Todaro G. J. Development of 3T3-like lines from Balb-c mouse embryo cultures: transformation susceptibility to SV40. J Cell Physiol. 1968 Oct;72(2):141–148. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040720208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DULBECCO R., VOGT M. One-step growth curve of Western equine encephalomyelitis virus on chicken embryo cells grown in vitro and analysis of virus yields from single cells. J Exp Med. 1954 Feb;99(2):183–199. doi: 10.1084/jem.99.2.183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Declève A., Niwa O., Gelmann E., Kaplan H. S. Replication kinetics of N- and B-tropic murine leukemia viruses on permissive and nonpermissive cells in vitro. Virology. 1975 Jun;65(2):320–332. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90038-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartley J. W., Rowe W. P. Clonal cells lines from a feral mouse embryo which lack host-range restrictions for murine leukemia viruses. Virology. 1975 May;65(1):128–134. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90013-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartley J. W., Rowe W. P., Huebner R. J. Host-range restrictions of murine leukemia viruses in mouse embryo cell cultures. J Virol. 1970 Feb;5(2):221–225. doi: 10.1128/jvi.5.2.221-225.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang A. S., Besmer P., Chu L., Baltimore D. Growth of pseudotypes of vesicular stomatitis virus with N-tropic murine leukemia virus coats in cells resistant to N-tropic viruses. J Virol. 1973 Sep;12(3):659–662. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.3.659-662.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ihle J. N., Kenney F. T., Tennant R. W. Evidence for a stable intermediate in leukemia virus activation in AKR mouse embryo cells. J Virol. 1974 Sep;14(3):451–456. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.3.451-456.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jainchill J. L., Aaronson S. A., Todaro G. J. Murine sarcoma and leukemia viruses: assay using clonal lines of contact-inhibited mouse cells. J Virol. 1969 Nov;4(5):549–553. doi: 10.1128/jvi.4.5.549-553.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jolicoeur P., Baltimore D. Effect of Fv-1 gene product on synthesis of N-tropic and B-tropic murine leukemia viral RNA. Cell. 1976 Jan;7(1):33–39. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90252-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jolicoeur P., Baltimore D. Effect of the Fv-1 locus on the titration of murine leukemia viruses. J Virol. 1975 Dec;16(6):1593–1598. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.6.1593-1598.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krontiris T. G., Soeiro R., Fields B. N. Host restriction of Friend leukemia virus. Role of the viral outer coat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Sep;70(9):2549–2553. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.9.2549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lilly F. Fv-2: identification and location of a second gene governing the spleen focus response to Friend leukemia virus in mice. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1970 Jul;45(1):163–169. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ODAKA T., EDAKA T., YAMAMOTTO T. Inheritance of susceptibility to Friend mouse leukemia virus. Jpn J Exp Med. 1962 Oct;32:405–413. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pincus T., Hartley J. W., Rowe W. P. A major genetic locus affecting resistance to infection with murine leukemia viruses. I. Tissue culture studies of naturally occurring viruses. J Exp Med. 1971 Jun 1;133(6):1219–1233. doi: 10.1084/jem.133.6.1219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pincus T., Hartley J. W., Rowe W. P. A major genetic locus affecting resistance to infection with murine leukemia viruses. IV. Dose-response relationships in Fv-1-sensitive and resistant cell cultures. Virology. 1975 Jun;65(2):333–342. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90039-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pincus T., Rowe W. P., Lilly F. A major genetic locus affecting resistance to infection with murine leukemia viruses. II. Apparent identity to a major locus described for resistance to friend murine leukemia virus. J Exp Med. 1971 Jun 1;133(6):1234–1241. doi: 10.1084/jem.133.6.1234. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rein A., Kashmiri S. V., Bassin R. H., Gerwin B. L., Duran-Troise G. Phenotypic mixing between N- and B-tropic murine leukemia viruses: infectious particles with dual sensitivity to Fv-1 restriction. Cell. 1976 Mar;7(3):373–379. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90166-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe W. P., Hartley J. W., Lander M. R., Pugh W. E., Teich N. Noninfectious AKR mouse embryo cell lines in which each cell has the capacity to be activated to produce infectious murine leukemia virus. Virology. 1971 Dec;46(3):866–876. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90087-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe W. P., Pugh W. E., Hartley J. W. Plaque assay techniques for murine leukemia viruses. Virology. 1970 Dec;42(4):1136–1139. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90362-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sveda M. M., Fields B. N., Soeiro R. Host restriction of friend leukemia virus; fate of input virion RNA. Cell. 1974 Aug;2(4):271–277. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(74)90021-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TENNANT J. R. Derivation of a murine lymphoid leukemia virus. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1962 Jun;28:1291–1303. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tennant R. W., Farrelly J. G., Ihle J. N., Pal B. C., Kenney F. T., Brown A. Effects of polyadenylic acids on functions of murine RNA tumor viruses. J Virol. 1973 Dec;12(6):1216–1225. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.6.1216-1225.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tennant R. W., Myer F. E., McGrath L. Effect of the Fv-1 gene on leukemia virus in mouse cell heterokaryons. Int J Cancer. 1974 Oct 15;14(4):504–513. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910140410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tennant R. W., Schluter B., Yang W., Brown A. Reciprocal inhibition of mouse leukemia virus infection by Fv-1 allele cell extracts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Oct;71(10):4241–4245. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.10.4241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshikura H. Requirement of cellular DNA synthesis for the growth of Friend leukemia virus. Exp Cell Res. 1968 Oct;52(2):445–450. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(68)90486-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


