Abstract
Synovial cysts of the lumbar spine are an uncommon cause of back and radicular pain. These cysts most frequently present as back pain, followed by chronic progressive radiculopathy or gradual onset of symptoms secondary to spinal canal compromise. Although less common, they can also present with acute spinal cord or root compression symptoms. We report of a case in which hemorrhaging into a right L2-3 facet synovial cyst caused an acute onset of back pain and radiculopathy, requiring surgical excision.
Keywords: Lumbar spine, Synovial cyst, Hemorrhage
INTRODUCTION
Intraspinal juxtafacet cysts (commonly, synovial or ganglion cyst) can be an uncommon cause of lower and radicular pain, neurogenic claudication, and cauda equina syndrome2,9,10,13). Spinal synovial cysts generally arise from a degenerated facet joint and often presenting as a gradual onset of back pain and potentially, chronic progressive radiculopathy. However, their pathogenesis is debatable11). Hemorrhage into juxtafacet cysts is a much less common occurrence, and patients may present with acute onset of symptoms3,13). We describe a case in which hemorrhage into a right L2-3 facet synovial cyst caused acute back pain and radiculopathy and required surgical excision.
CASE REPORT
A 72-year-old-woman with a past history of hypertension presented to the clinic with acute back pain radiating to the anterior surface of the right thigh and leg. There was no history of a previous traumatic event or history of anticoagulation treatment. She denied any bowel or bladder incontinence. On neurologic examination, muscle power and sensation were intact. The right straight-leg-raise test elicited pain in the leg at 30° which was exacerbated further by ankle dorsiflexion. Routine biochemical and hematological tests were within normal limit. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) revealed the presence of a cystic formation in the right L2-L3 facet joint with arthritis compressing the L3 right root and the dural sac (Fig. 1). In addition, the MRI displayed a hyperintense abnormality on T1-weighted images and hypointense on T2-weighted images consistent with hemorrhage. No connection with the intervertebral disc was identified. Surgical excision was perfomed 2 days after admission. The posterior elements from L1 to L3 were exposed and right L2-L3 laminectomy and facetectomy were performed. A brownish mass was found in continuity with the right L2-L3 facet joint adherent to the dural sac. The extradural hematoma was visualized and evacuated, effectively decompressing the right 2 nerve root and sacral sac. Histological examination of the surgical specimen revealed a synovial cyst with hematoma. Microscopically, there was a synovial cyst with synovial cell lining, neovascularization, hemosiderin microdeposits, and blood (Fig. 2). On postoperative day 1, the patient was able to walk independently. Recovery was uneventful except for an episode of slight pain in the right leg. One month after the operation, the patient had no symptoms in her lower back and leg.
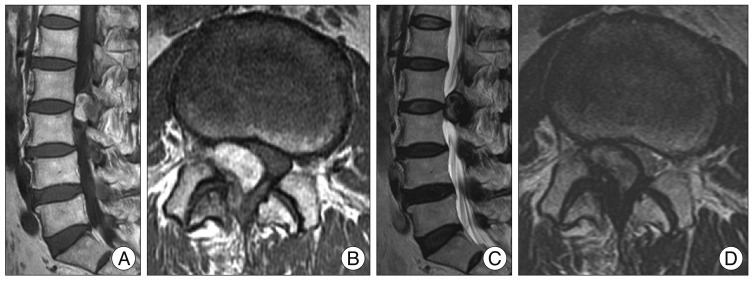
Fig. 1.
Magnetic resonance images are showing the presence of a cystic mass in the right L2-L3 facet joint with arthritis compressing the L3 right root and the dural sac. There are showing a hyperintense on T1-weighted image (A and B) and hypointense on T2-weighted image (C and D) consistent with hemorrhage.
Fig. 2.
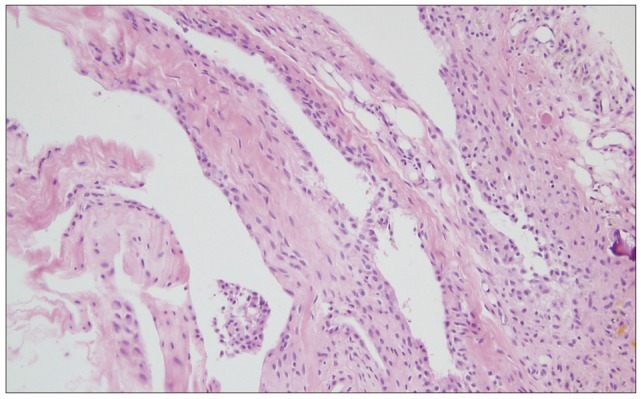
Histological appearance of the hemorrhagic synovial cyst showing synovial cell lining, fibroconnective tissue with widespread hemorrhage, neoangiogenesis, and hemosiderin microdeposits (hematoxylin-eosin stain, ×200).
DISCUSSION
Synovial or ganglion cysts usually present in the joints of the extremities13). Spinal synovial cyst can be defined as a soft tissue mass located extradurally along the medial border of a degenerated facet joint, especially L4-5 level1,4,8,11,12). These cysts are filled with clear or xanthochromic fluid and have a synovial-like epithelial lining with a demonstrable connection to a joint capsule3,11). If the synovial cell lining and the communication with a joint capsule are absent, the cyst is classified as ganglion11).
Intraspinal synovial cysts are rare but have been documented with increasing frequency because of the improvement of neuroradiological imagings4). An MRI is considered a good modality for diagnosis. On MRI, cysts appear as well-circumscribed, epidural mass lesions that are hypo- and hyper-intense on T1 and T2 weighted images, respectfully. Bleeding into a synovial cyst may cause a sudden expansion of the cyst leading to compression of the epidural space result in root compression symptoms. Hemorrhage into a synovial cyst results in an acute increase in pain and radicular symptoms, including neurological deficits12). Hemorrhagic presentation can be caused by anticoagulation treatment, trauma, disc herniation, vascular anomaly, and neoangiogenesis in the cyst4). In addition, high vascularization of the cyst can cause hemorrhage in spite of minor trauma or just spinal instability. Synovial cyst hemorrhagic events in some cases can occur despite the absence of trauma or coagulopathy13). As a result, other yet to be determined risk factors for synovial cyst hemorrhage occurrence exist prompting the need for more studies.
The treatments for synovial cysts either involve conservative modalities or surgical treatment. Non-hemorrhagic synovial cysts are occasionally treated by percutaneous aspiration with successful resolution of symptom6). The injection of corticosteroid agents into the facet joint may be an treatment option. Despite conservative treatment, recurrence of cyst with symptoms is frequently occurs6). The natural history of spinal synovial cysts is unknown, but spontaneous remissions of a synovial cyst on follow up imaging with improved symptoms have been reported5). Surgical excision with decompression is the primary treatment for lumbar hemorrhagic synovial cysts. Few cases with acute symptoms require emergency surgery. However, pain can be treated with steroid injections and bed rest in substantial number of patients. Immediate diagnosis and appropriate surgical excision can produce good outcome4,7,11,12).
We report of a case in which hemorrhage into a right L2-3 facet synovial cyst causing an acute back pain and radiculopathy. Treatment by resection of the cyst and evacuation of the hematoma led to complete neurological recovery.
CONCLUSION
Synovial cysts of the lumbar spine are an uncommon cause of back and radicular pain. Rarely, these cysts can go through hemorrhagic transformation by trauma, anti-coagulopathic state, or for unknown reasons. Hemorrhage into a cyst is an uncommon occurrence that can lead to acute symptom. In most cases, surgery is the treatment of choice for symptomatic hemorrhagic synovial cysts. Surgery involving the evacuation of the hematoma and/or cyst can result in complete resolution of acute symptoms and neurologic deficit.
References
- 1.Arantes M, Silva RS, Romão H, Resende M, Moniz P, Honavar M, et al. Spontaneous hemorrhage in a lumbar ganglion cyst. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2008;33:E521–E524. doi: 10.1097/BRS.0b013e31817b6206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Bandiera S, Campanacci L, De Iure F, Bertoni F, Picci P, Boriani S. Hemorrhagic synovial lumbar cyst : a case report and review of the literature. Chir Organi Mov. 1999;84:197–203. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Banning CS, Thorell WE, Leibrock LG. Patient outcome after resection of lumbar juxtafacet cysts. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2001;26:969–972. doi: 10.1097/00007632-200104150-00024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Cicuendez M, Alen JF, Ramos A, Lobato RD, Lagares A. Spontaneous hemorrhage into a lumbar synovial cyst. Eur Spine J. 2010;19(Suppl 2):S190–S192. doi: 10.1007/s00586-010-1332-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Hsu KY, Zucherman JF, Shea WJ, Jeffrey RA. Lumbar intraspinal synovial and ganglion cysts (facet cysts). Ten-year experience in evaluation and treatment. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 1995;20:80–89. doi: 10.1097/00007632-199501000-00015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Imai K, Nakamura K, Inokuchi K, Oda H. Aspiration of intraspinal synovial cyst : recurrence after temporal improvement. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 1998;118:103–105. doi: 10.1007/s004020050323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Kaneko K, Inoue Y. Haemorrhagic lumbar synovial cyst. A cause of acute radiculopathy. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2000;82:583–584. doi: 10.1302/0301-620x.82b4.10444. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Kim HS, Ju CI, Kim SW. Foraminal synovial cyst associated with ankylosing spondylitis. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2011;50:54–56. doi: 10.3340/jkns.2011.50.1.54. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Onofrio BM, Mih AD. Synovial cysts of the spine. Neurosurgery. 1988;22:642–647. doi: 10.1227/00006123-198804000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Pendleton B, Carl B, Pollay M. Spinal extradural benign synovial or ganglion cyst : case report and review of the literature. Neurosurgery. 1983;13:322–326. doi: 10.1227/00006123-198309000-00021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Ramieri A, Domenicucci M, Seferi A, Paolini S, Petrozza V, Delfini R. Lumbar hemorrhagic synovial cysts : diagnosis, pathogenesis, and treatment. Report of 3 cases. Surg Neurol. 2006;65:385–390. doi: 10.1016/j.surneu.2005.07.073. discussion 390. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Wait SD, Jones FD, Lonser RR, Lee KS. Symptomatic epidural hematoma caused by lumbar synovial cyst rupture : report of two cases and review of the literature. Neurosurgery. 2005;56:E1157. discussion E1157. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Xu R, Solakoglu C, Maleki Z, McGirt MJ, Gokaslan ZL, Bydon A. Hemorrhagic synovial cyst : the possible role of initial trauma and subsequent microtrauma in its pathogenesis : case report. Neurosurgery. 2011;68:E858–E865. doi: 10.1227/NEU.0b013e3182080127. discussion E865. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]