Abstract
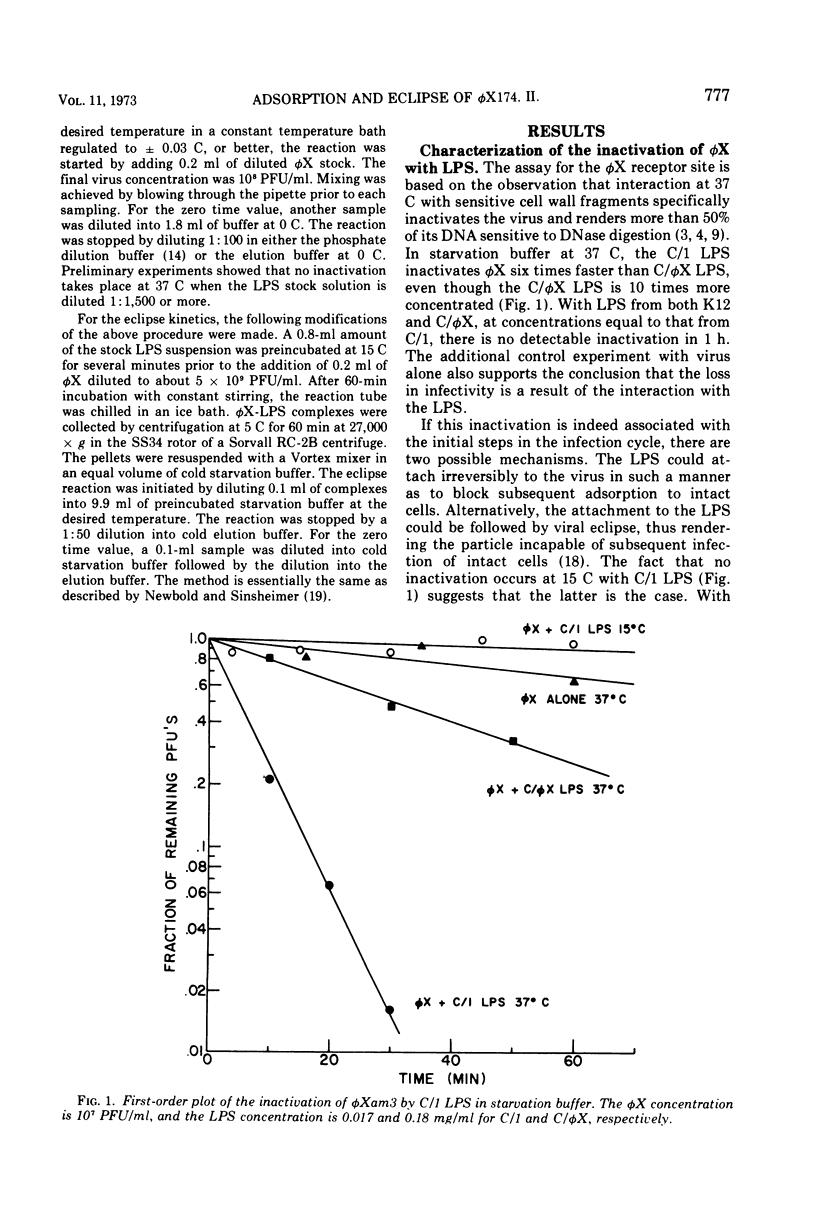
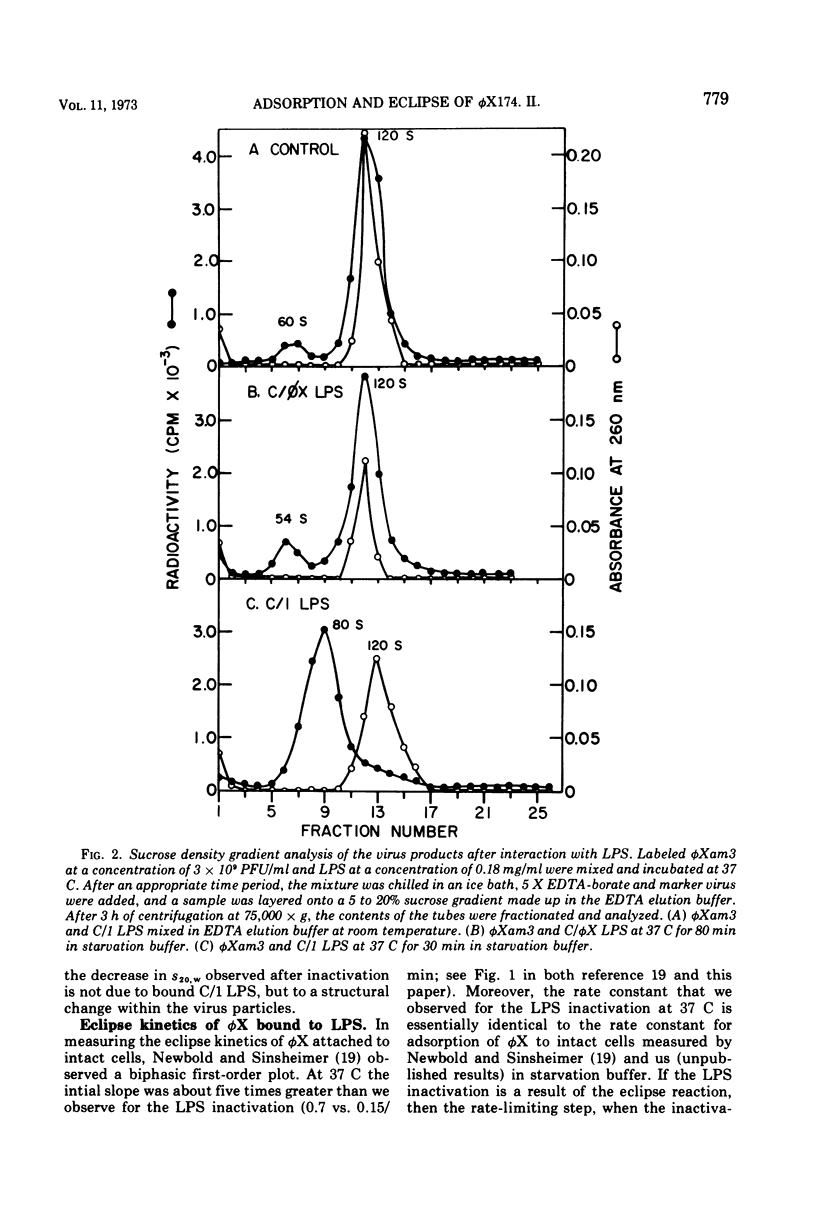
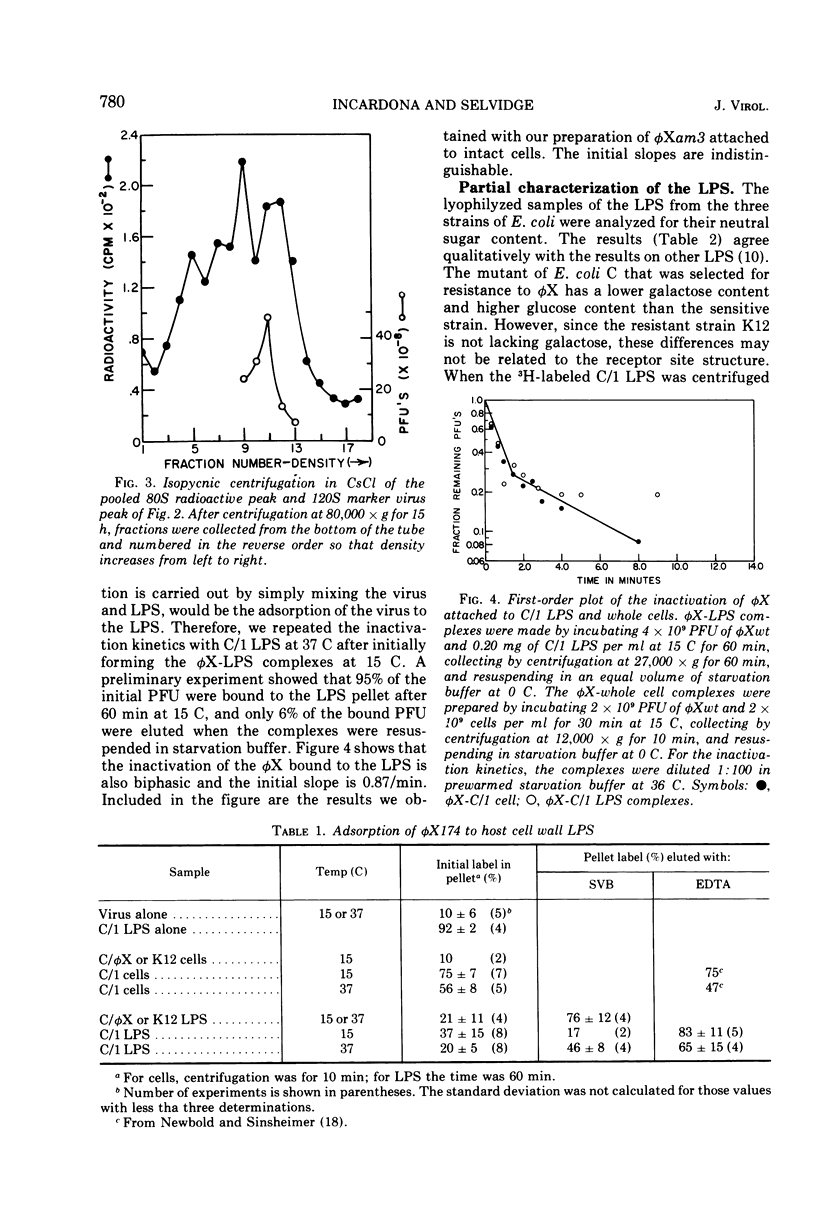
A mixture of aqueous phenol, choloroform, and ether extracts the lipopolysaccharides (LPS) from the φX174-sensitive strain, Escherichia coli C/1, and resistant strains, C/φX and K12. Interaction of the C/1 LPS with φX in a starvation buffer containing 10−3 M CaCl2 at 37 C, but not at 15 C, results in a first-order inactivation that is specific for C/1 LPS. After interaction for 60 min at 15 C, followed by centrifugation, 37 and 20% of a 14C-φX preparation are bound to the C/1 and C/φX LPS pellets, respectively. The results for intact cells are 75 and 10%. Supporting the conclusion that this represents specific attachment of φX to its receptor site in the LPS is the fact that EDTA-borate buffer is required to elute 85% of the 14C-φX from the C/1 LPS, whereas starvation buffer elutes the same amount from C/φX LPS. Moreover, 95% of the PFU are found in the C/1 LPS pellets as compared with 50% in the resistant strain LPS pellets. When the products of interaction between φX and LPS at 37 C are examined by sucrose density gradients in EDTA-borate, a single 60 to 90S peak is observed in the C/1 sample, and the single peak cosediments with the 120S marker φX in the C/φX sample. This change in S20, w is very similar to that reported for the eclipse of φX in vivo. If the inactivation at 37 C is carried out on φX-LPS complexes first formed at 15 C, the first-order kinetics are biphasic and nearly identical to that observed for the eclipse kinetics of φX attached to intact cells. Thus, the φX-LPS system is suitable for in vitro studies on the early events in φX infection.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bancroft J. B. The self-assembly of spherical plant viruses. Adv Virus Res. 1970;16:99–134. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3527(08)60022-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayer M. E., Starkey T. W. The adsorption of bacteriophage phi X174 and its interaction with Escherichia coli; a kinetic and morphological study. Virology. 1972 Jul;49(1):236–256. doi: 10.1016/s0042-6822(72)80026-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beswick F. M., Lunt M. R. Adsorption of bacteriophage phiX174 to isolated bacterial cell walls. J Gen Virol. 1972 Sep;16(3):381–390. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-16-3-381. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. T., MacKenzie J. M., Bayer M. E. Mode of host cell penetration by bacteriophage phi X174. J Virol. 1971 Jun;7(6):836–846. doi: 10.1128/jvi.7.6.836-846.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess A. B. Studies on the proteins of phi X174. II. The protein composition of the phi X coat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Oct;64(2):613–617. doi: 10.1073/pnas.64.2.613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler P. J., Klug A. Assembly of the particle of tobacco mosaic virus from RNA and disks of protein. Nat New Biol. 1971 Jan 13;229(2):47–50. doi: 10.1038/newbio229047a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CASPAR D. L., KLUG A. Physical principles in the construction of regular viruses. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1962;27:1–24. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1962.027.001.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edgell M. H., Hutchison C. A., 3rd, Sinsheimer R. L. The process of infection with bacteriophage phi-X174. 28. Removal of the spike proteins from the phage capsid. J Mol Biol. 1969 Jun 28;42(3):547–557. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90242-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FUJIMURA R., KAESBERG P. The adsorption of bacteriophage phi-X174 to its host. Biophys J. 1962 Nov;2:433–449. doi: 10.1016/s0006-3495(62)86866-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galanos C., Lüderitz O., Westphal O. A new method for the extraction of R lipopolysaccharides. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Jun;9(2):245–249. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb00601.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godson G. N. Characterization and synthesis of phi X174 proteins in ultraviolet-irradiated and unirradiated cells. J Mol Biol. 1971 May 14;57(3):541–553. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90108-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutchison C. A., 3rd, Sinsheimer R. L. The process of infection with bacteriophage phi-X174. X. Mutations in a phi-X Lysis gene. J Mol Biol. 1966 Jul;18(3):429–447. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80035-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Incardona N. L., Blonski R., Feeney W. Mechanism of adsorption and eclipse of bacteriophage phi X174. I. In vitro conformational change under conditions of eclipse. J Virol. 1972 Jan;9(1):96–101. doi: 10.1128/jvi.9.1.96-101.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Incardona N. L., Notarius H., Flanegan J. B. Measurement of temperature within the sample cell during sedimentation velocity experiments. Anal Biochem. 1971 Apr;40(2):267–280. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(71)90385-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehnhardt W. F., Winzler R. J. Determination of neutral sugars in glycoproteins by gas-liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr. 1968 May 7;34(4):471–479. doi: 10.1016/0021-9673(68)80091-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayol R. F., Sinsheimer R. L. Process of infection with bacteriophage phiX174. XXXVI. Measurement of virus-specific proteins during a normal cycle of infection. J Virol. 1970 Sep;6(3):310–319. doi: 10.1128/jvi.6.3.310-319.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newbold J. E., Sinsheimer R. L. Process of infection with bacteriophage phi-X174. XXXIV. Kinetic of the attachment and eclipse steps of the infection. J Virol. 1970 Apr;5(4):427–431. doi: 10.1128/jvi.5.4.427-431.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newbold J. E., Sinsheimer R. L. The process of infection with bacteriophage phiX174. XXXII. Early steps in the infection process: attachment, eclipse and DNA penetration. J Mol Biol. 1970 Apr 14;49(1):49–66. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90375-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiser M. M., Rothfield L. The reassociation of lipopolysaccharide, phospholipid, and transferase enzymes of the bacterial cell envelope. Isolation of binary and ternary complexes. J Biol Chem. 1968 Mar 25;243(6):1320–1328. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood W. B., Edgar R. S., King J., Lielausis I., Henninger M. Bacteriophage assembly. Fed Proc. 1968 Sep-Oct;27(5):1160–1166. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



