Abstract
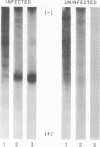
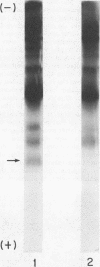
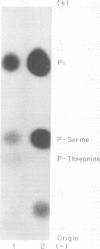
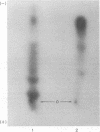
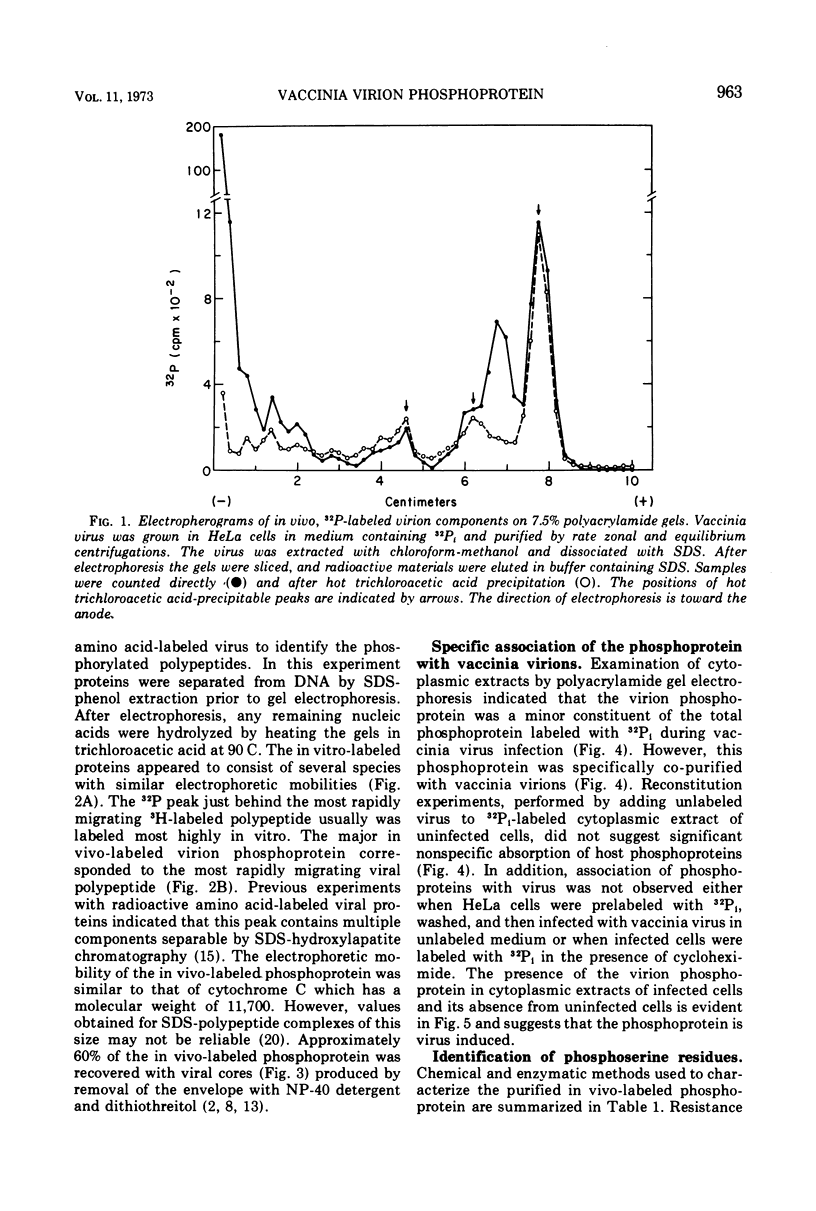
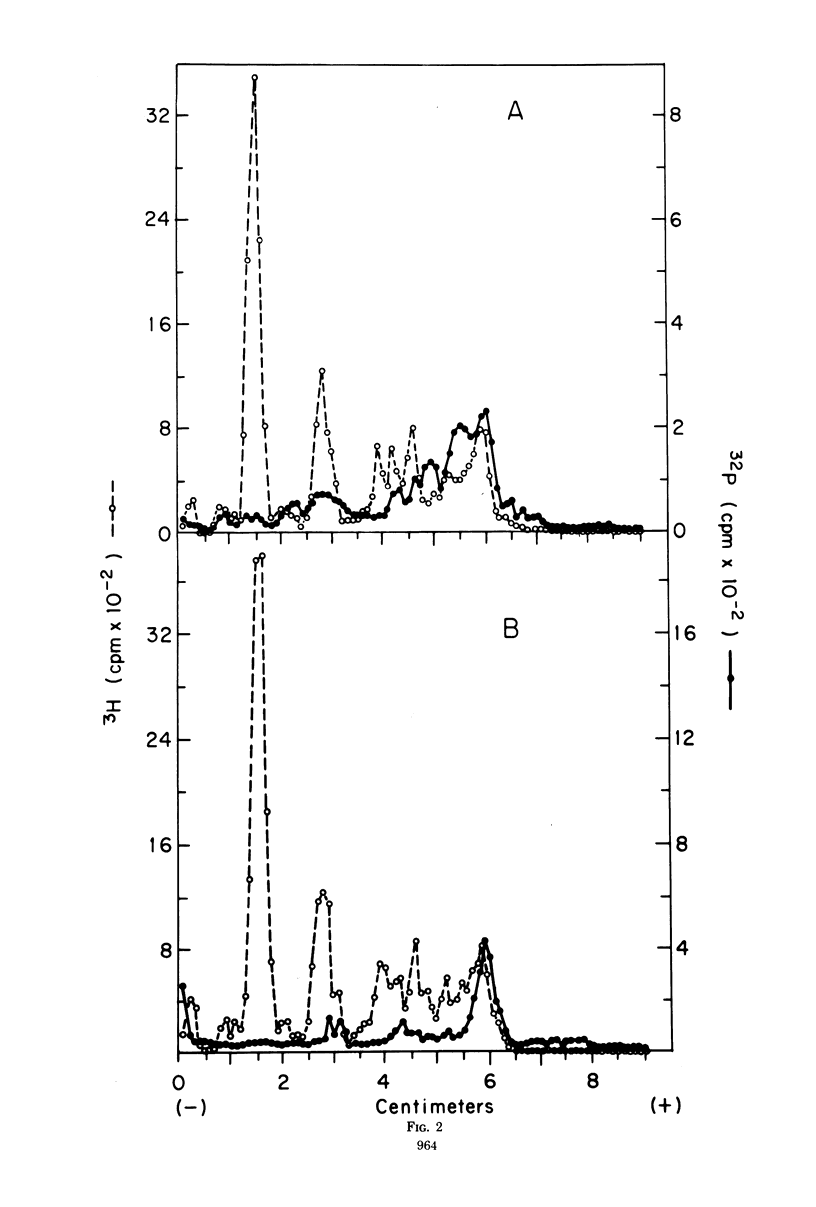
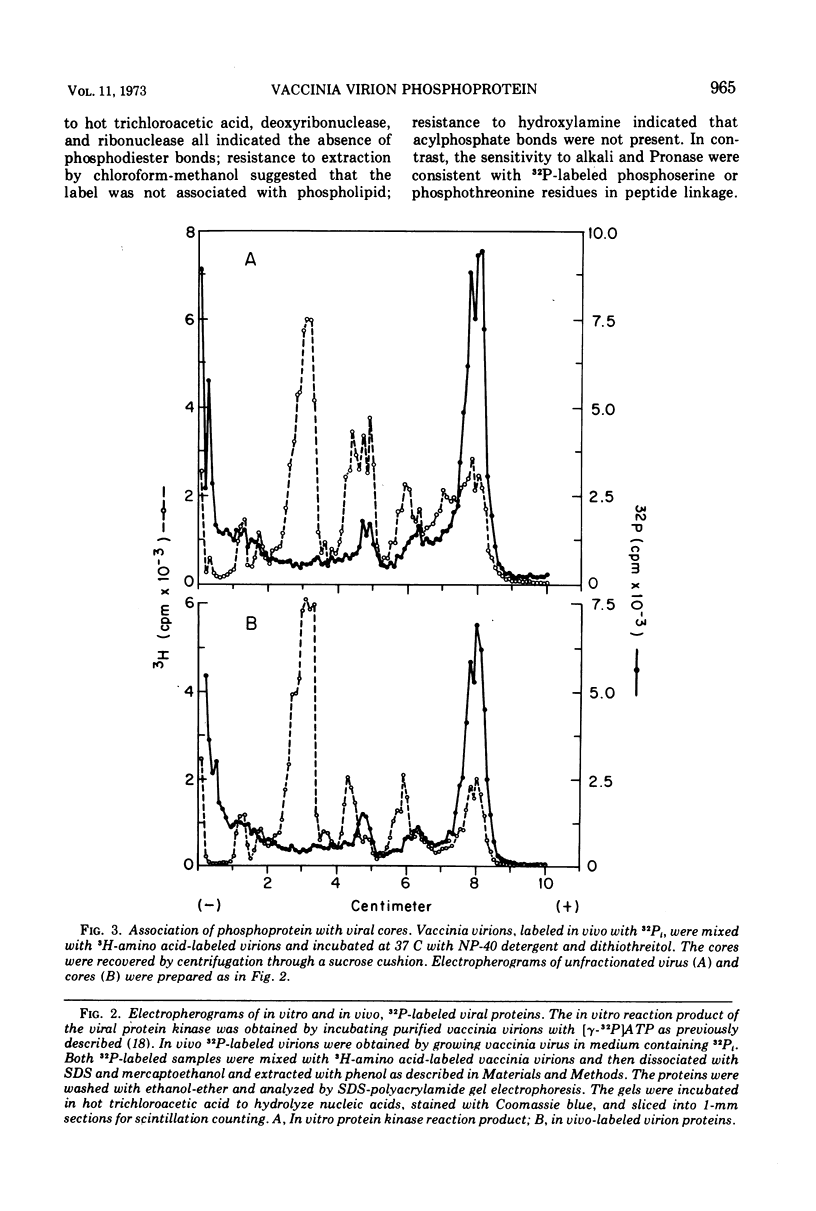
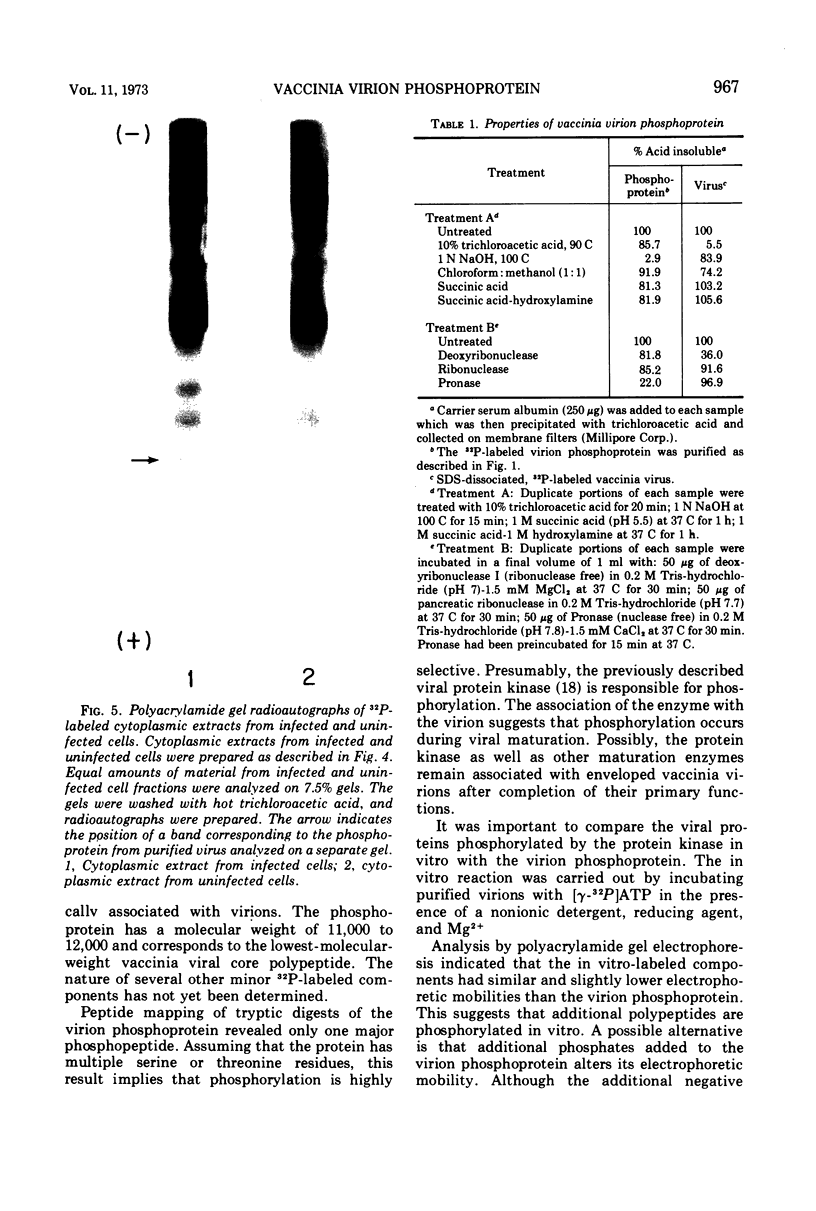
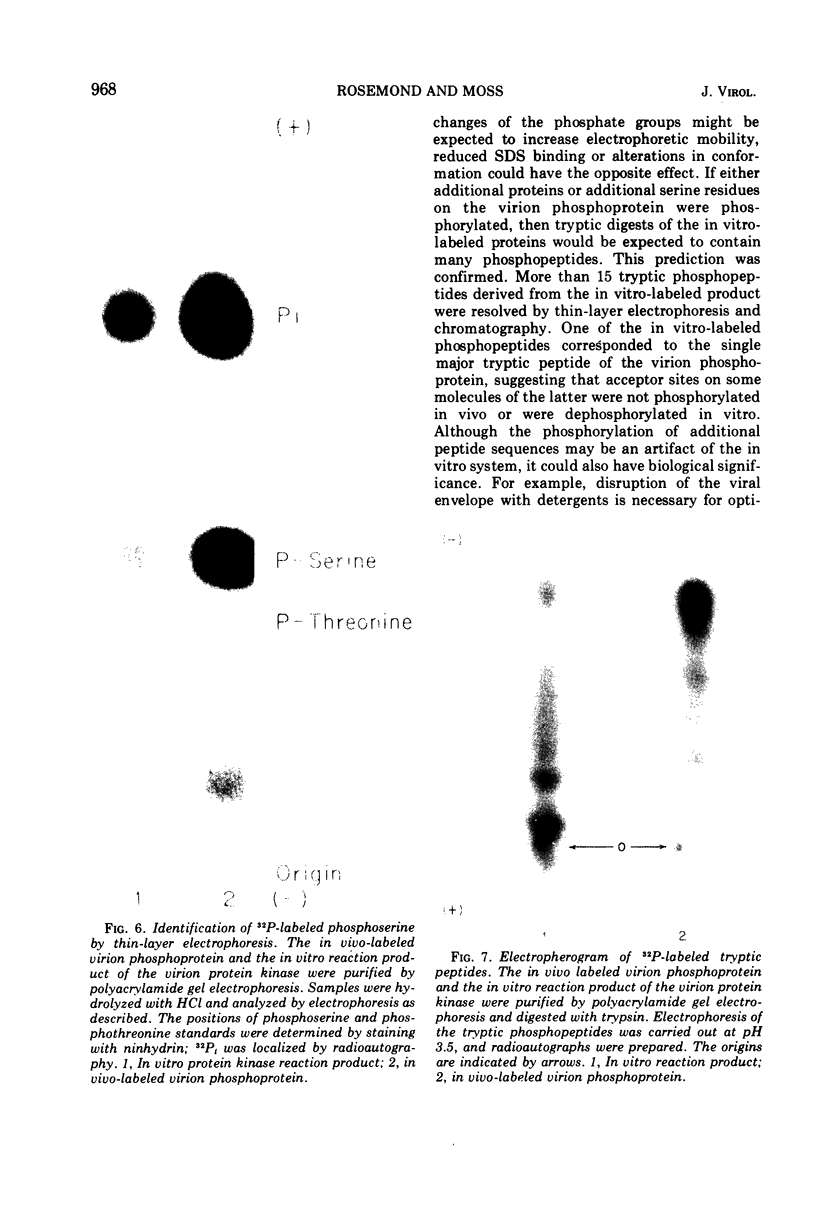
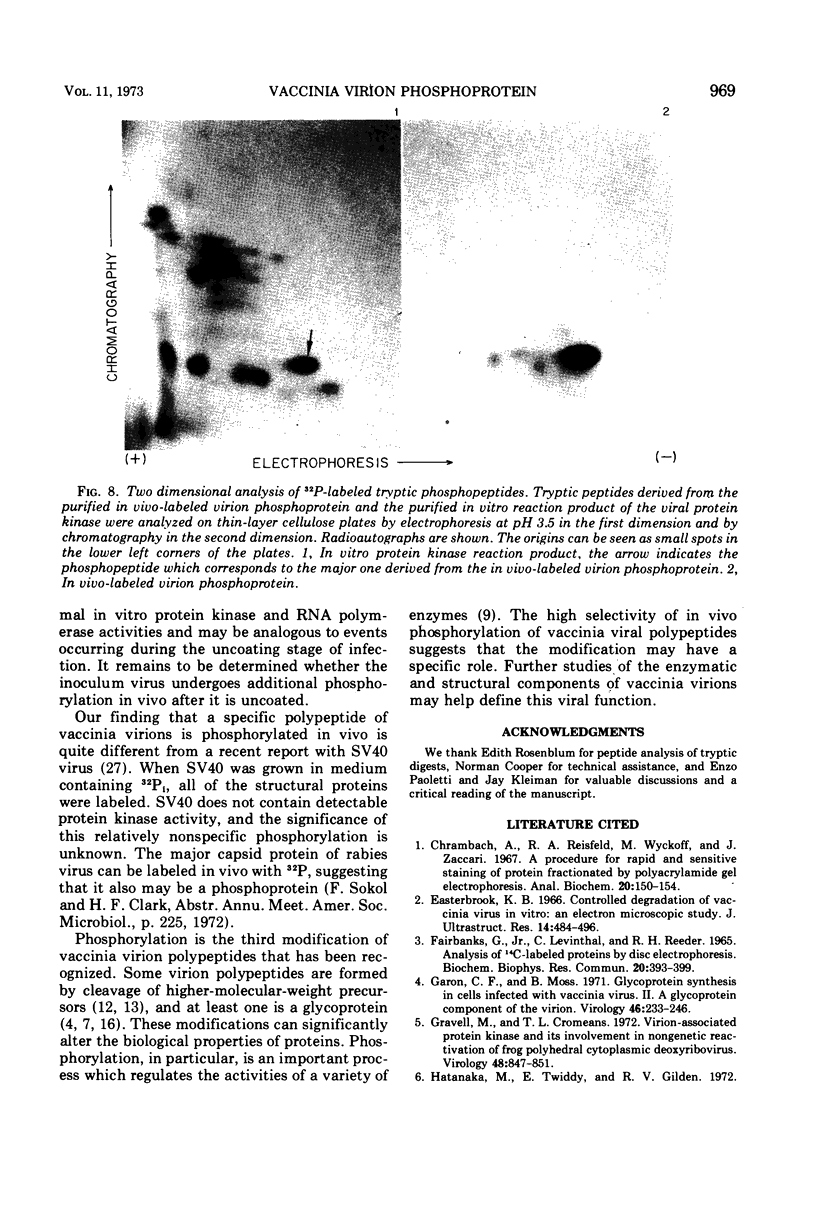
The recent discovery of a protein kinase activity in vaccinia virions led us to search for a viral protein which is phosphorylated in vivo. Vaccinia virus was radioactively labeled by infecting cells in the presence of 32P1. A phosphoprotein was isolated from purified delipidated virions by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. The phosphoprotein appeared to be a specific viral component induced after infection. More than 60% of the phosphoprotein was associated with viral cores. The electrophoretic mobility of the protein suggested that it has a molecular weight of 11,000 to 12,000. Phosphoserine was liberated by acid hydrolysis and identified by electrophoresis with known standards. Tryptic digests of the purified phosphoprotein were analyzed by two-dimensional electrophoresis and chromatography on thin-layer cellulose plates, and a single major phosphopeptide was resolved. The high selectivity of phosphorylation suggested that the process has a specific function.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chrambach A., Reisfeld R. A., Wyckoff M., Zaccari J. A procedure for rapid and sensitive staining of protein fractionated by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1967 Jul;20(1):150–154. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(67)90272-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Easterbrook K. B. Controlled degradation of vaccinia virions in vitro: an electron microscopic study. J Ultrastruct Res. 1966 Mar;14(5):484–496. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(66)80077-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairbanks G., Jr, Levinthal C., Reeder R. H. Analysis of C14-labeled proteins by disc electrophoresis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1965 Aug 16;20(4):393–399. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(65)90589-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garon C. F., Moss B. Glycoprotein synthesis in cells infected with vaccinia virus. II. A glycoprotein component of the virion. Virology. 1971 Nov;46(2):233–246. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90026-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gravell M., Cromeans T. L. Viron-associated protein kinase and its involvement in nongenetic reactivation of frog polyhedral cytoplasmic deoxyribovirus. Virology. 1972 Jun;48(3):847–851. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90167-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatanaka M., Twiddy E., Gilden R. V. Protein kinase associated with RNA tumor viruses and other budding RNA viruses. Virology. 1972 Feb;47(2):536–538. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90297-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holowczak J. A. Glycopeptides of vaccinia virus. I. Preliminary characterization and hexosamine content. Virology. 1970 Sep;42(1):87–99. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90241-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holzer H., Duntze W. Metabolic regulation by chemical modification of enzymes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1971;40:345–374. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.40.070171.002021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOKLIK W. K. THE INTRACELLULAR UNCOATING OF POXVIRUS DNA. II. THE MOLECULAR BASIS OF THE UNCOATING PROCESS. J Mol Biol. 1964 Feb;8:277–288. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(64)80137-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOKLIK W. K. The preparation and characteristics of highly purified radioactively labelled poxvirus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Aug 20;61:290–301. doi: 10.1016/0926-6550(62)90091-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz E., Moss B. Formation of a vaccinia virus structural polypeptide from a higher molecular weight precursor: inhibition by rifampicin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Jul;66(3):677–684. doi: 10.1073/pnas.66.3.677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz E., Moss B. Vaccinia virus structural polypeptide derived from a high-molecular-weight precursor: formation and integration into virus particles. J Virol. 1970 Dec;6(6):717–726. doi: 10.1128/jvi.6.6.717-726.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss B., Rosenblum E. N., Garon C. F. Glycoprotein synthesis in cells infected with vaccinia virus. I. Non-virion glycoproteins. Virology. 1971 Nov;46(2):221–232. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90025-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss B., Rosenblum E. N. Hydroxylapatite chromatography of protein-sodium dodecyl sulfate complexes. A new method for the separation of polypeptide subunits. J Biol Chem. 1972 Aug 25;247(16):5194–5198. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss B., Salzman N. P. Sequential protein synthesis following vaccinia virus infection. J Virol. 1968 Oct;2(10):1016–1027. doi: 10.1128/jvi.2.10.1016-1027.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paoletti E., Moss B. Protein kinase and specific phosphate acceptor proteins associated with vaccinia virus cores. J Virol. 1972 Sep;10(3):417–424. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.3.417-424.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randall C. C., Rogers H. W., Downer D. N., Gentry G. A. Protein kinase activity in equine herpesvirus. J Virol. 1972 Feb;9(2):216–222. doi: 10.1128/jvi.9.2.216-222.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds J. A., Tanford C. The gross conformation of protein-sodium dodecyl sulfate complexes. J Biol Chem. 1970 Oct 10;245(19):5161–5165. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubenstein A. S., Gravell M., Darlington R. Protein kinase in enveloped herpes simplex virions. Virology. 1972 Oct;50(1):287–290. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90374-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHWARTZ J. H., LIPMANN F. Phosphate incorporation into alkaline phosphatase of E. coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1961 Dec 15;47:1996–2005. doi: 10.1073/pnas.47.12.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarov I., Joklik W. K. Studies on the nature and location of the capsid polypeptides of vaccinia virions. Virology. 1972 Nov;50(2):579–592. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90409-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro A. L., Viñuela E., Maizel J. V., Jr Molecular weight estimation of polypeptide chains by electrophoresis in SDS-polyacrylamide gels. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1967 Sep 7;28(5):815–820. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(67)90391-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strand M., August J. T. Protein kinase and phosphate acceptor proteins in Rauscher murine leukaemia virus. Nat New Biol. 1971 Sep 29;233(39):137–140. doi: 10.1038/newbio233137a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan K. B., Sokol F. Structural proteins of simian virus 40: phosphoproteins. J Virol. 1972 Nov;10(5):985–994. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.5.985-994.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]