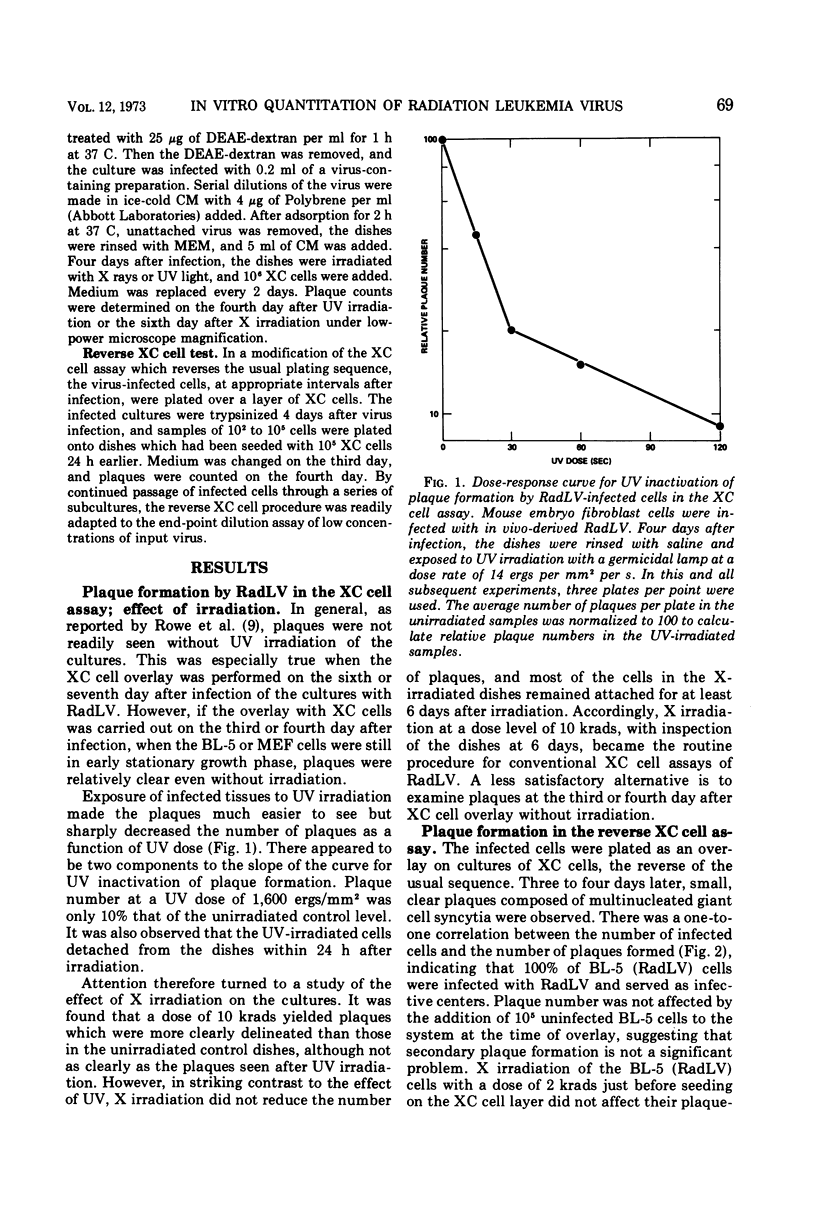
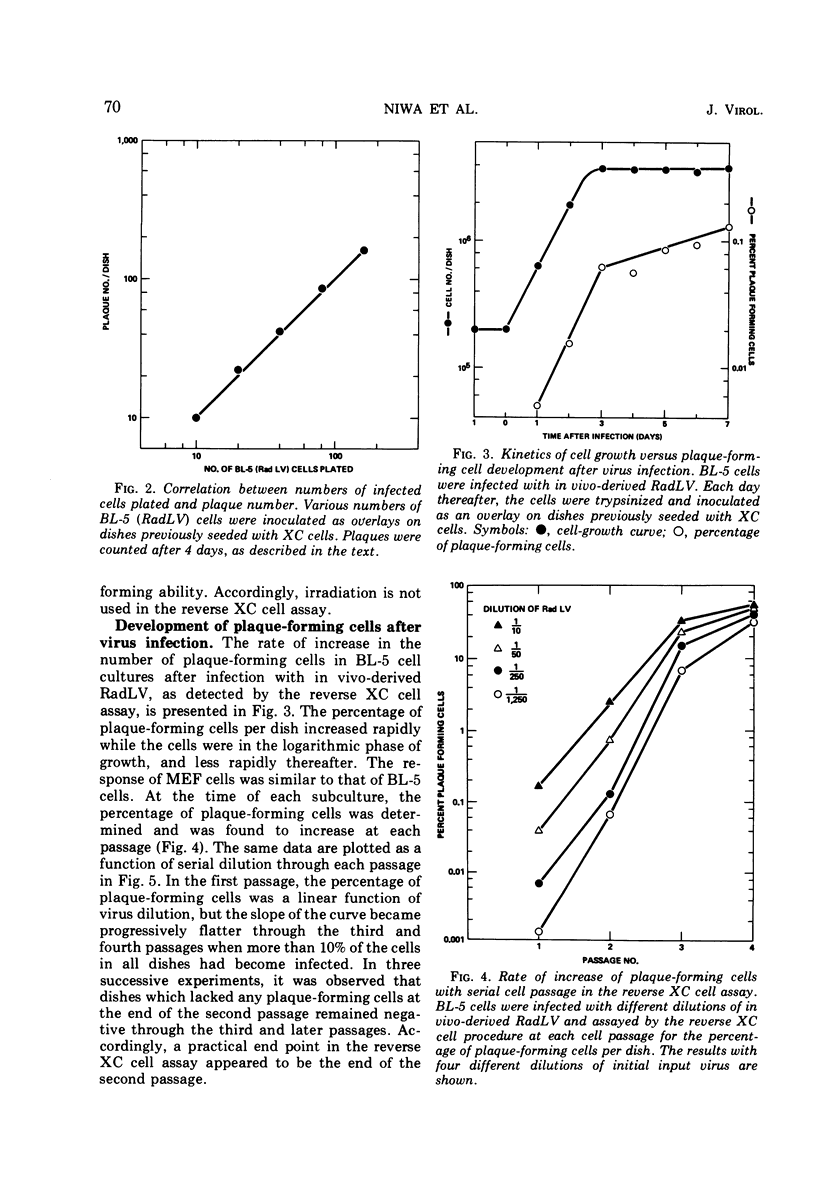
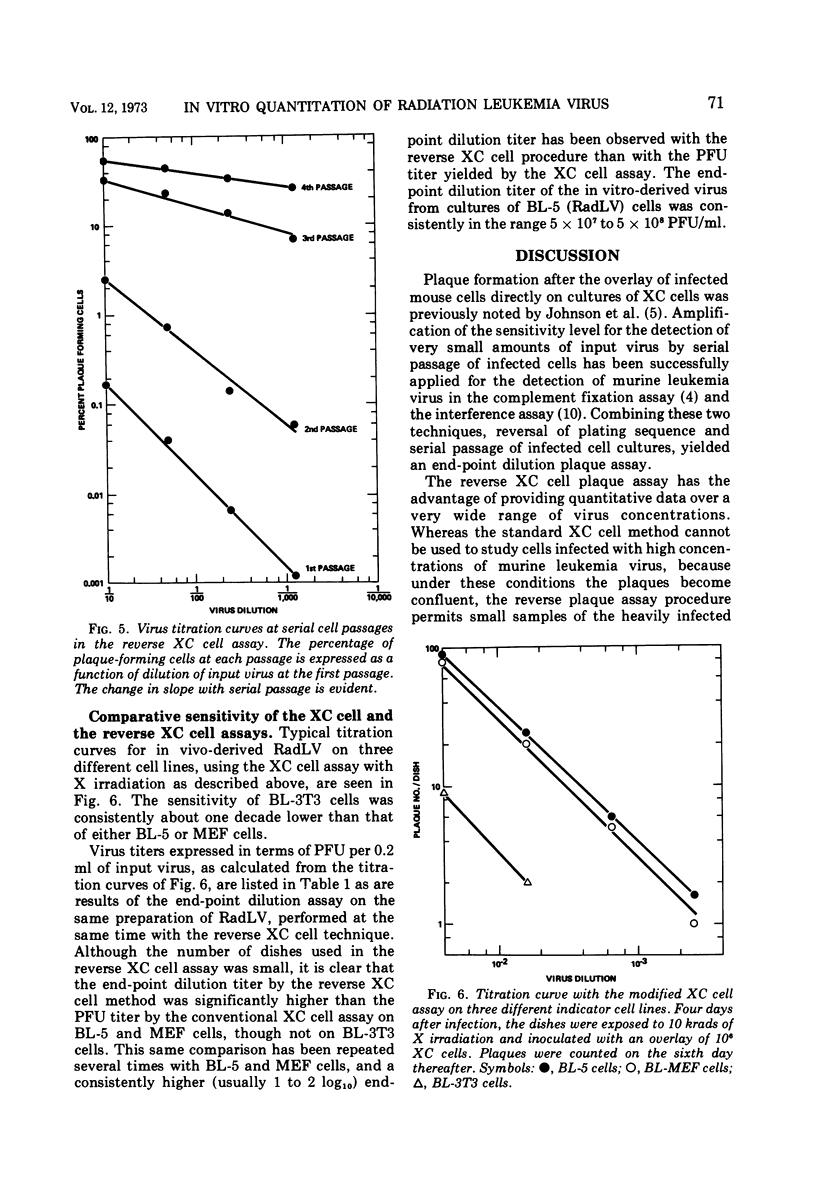
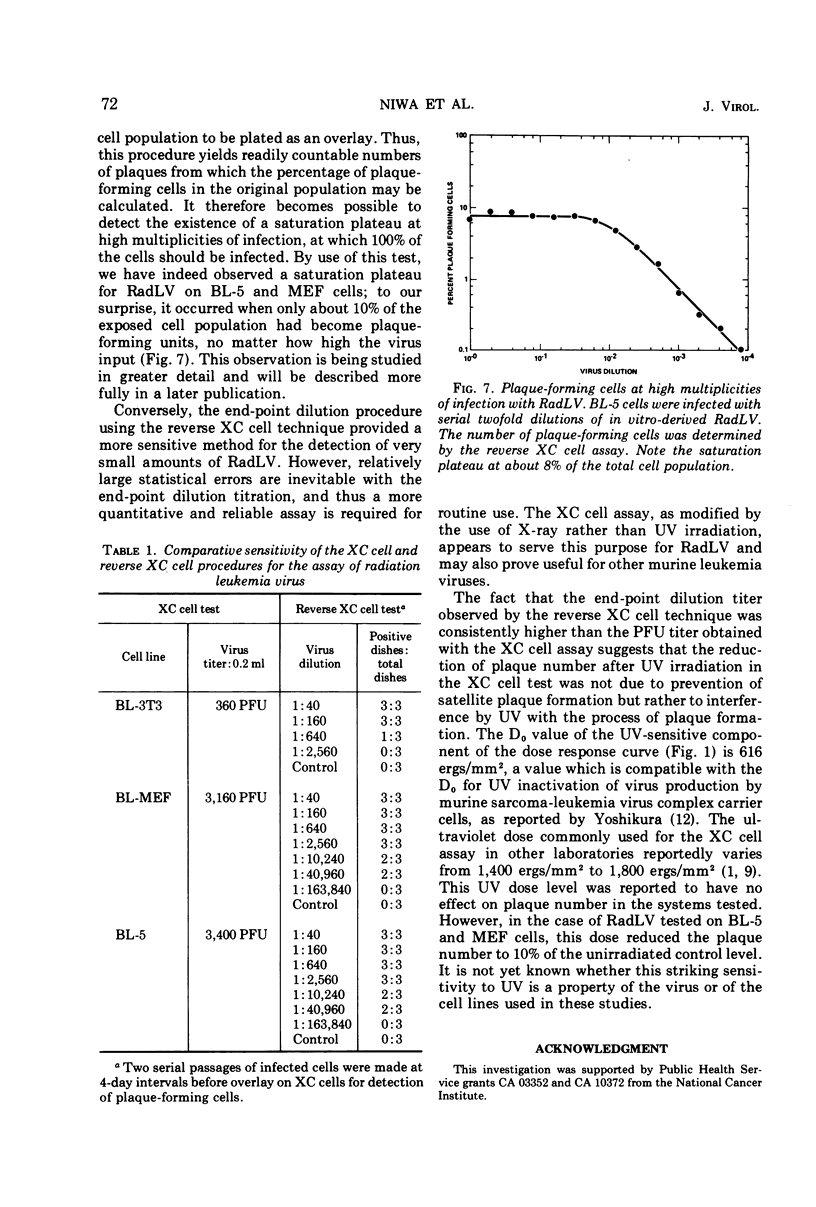
Abstract
A modification of the XC cell procedure for murine leukemia virus assay which yields quantitative data over a wide range of virus concentrations is described. By using serial passage of infected cell cultures and reversal of the plating sequence in the XC procedure, titers of radiation leukemia virus (RadLV) were obtained which were about 10-fold higher than those found by using the conventional assay. By using the modified procedure, it was observed that, even at high multiplicities of infection, less than 10% of the cells function as infective centers, although the proportion increases with serial passage. It was also observed that exposure of infected cells to UV light, which is commonly used to make plaques more visible in the conventional XC cell test, inhibits plaque formation in the RadLV system. Substitution of X irradiation for UV exposure improved plaque visibility without loss of sensitivity.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bass L. R., Turner W. Semi-micro XC cell assay technique for murine leukemia virus. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Jan;23(1):200–201. doi: 10.1128/am.23.1.200-201.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Declève A., Lieberman M., Hahn G. M., Kaplan H. S. Focus formation by a murine sarcoma leukemia virus complex. II. Quantitative aspects of the interaction between radiation leukemia virus and its murine sarcoma virus pseudotype in strain C57BL mouse embryo cells. J Virol. 1970 Apr;5(4):437–445. doi: 10.1128/jvi.5.4.437-445.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischinger P. J., O'Connor T. E. Radiation leukemia virus: quantitative tissue culture assay. Science. 1969 Jul 18;165(3890):306–309. doi: 10.1126/science.165.3890.306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartley J. W., Rowe W. P., Capps W. I., Huebner R. J. Complement fixation and tissue culture assays for mouse leukemia viruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 May;53(5):931–938. doi: 10.1073/pnas.53.5.931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson G. S., Friedman R. M., Pastan I. Analysis of the fusion of XC cells induced by homogenates of murine leukemia virus-infected cells and by purified murine leukemia virus. J Virol. 1971 Jun;7(6):753–758. doi: 10.1128/jvi.7.6.753-758.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan H. S. On the natural history of the murine leukemias: presidential address. Cancer Res. 1967 Aug;27(8):1325–1340. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIEBERMAN M., KAPLAN H. S. Leukemogenic activity of filtrates from radiation-induced lymphoid tumors of mice. Science. 1959 Aug 14;130(3372):387–388. doi: 10.1126/science.130.3372.387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieberman M., Niwa O., Declève A., Kaplan H. S. Continuous propagation of radiation leukemia virus on a C57BL mouse-embryo fibroblast line, with attenuation of leukemogenic activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Apr;70(4):1250–1253. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.4.1250. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe W. P., Pugh W. E., Hartley J. W. Plaque assay techniques for murine leukemia viruses. Virology. 1970 Dec;42(4):1136–1139. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90362-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarma P. S., Cheong M. P., Hartley J. W., Huebner R. J. A viral interference test for mouse leukemia viruses. Virology. 1967 Sep;33(1):180–184. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(67)90111-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TODARO G. J., GREEN H. Quantitative studies of the growth of mouse embryo cells in culture and their development into established lines. J Cell Biol. 1963 May;17:299–313. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.2.299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshikura H. Effect of 5-fluorouracil on ultraviolet inactivation of virus production by murine sarcoma-leukemia virus complex carrier cells. Virology. 1972 Apr;48(1):193–200. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90126-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



