Abstract
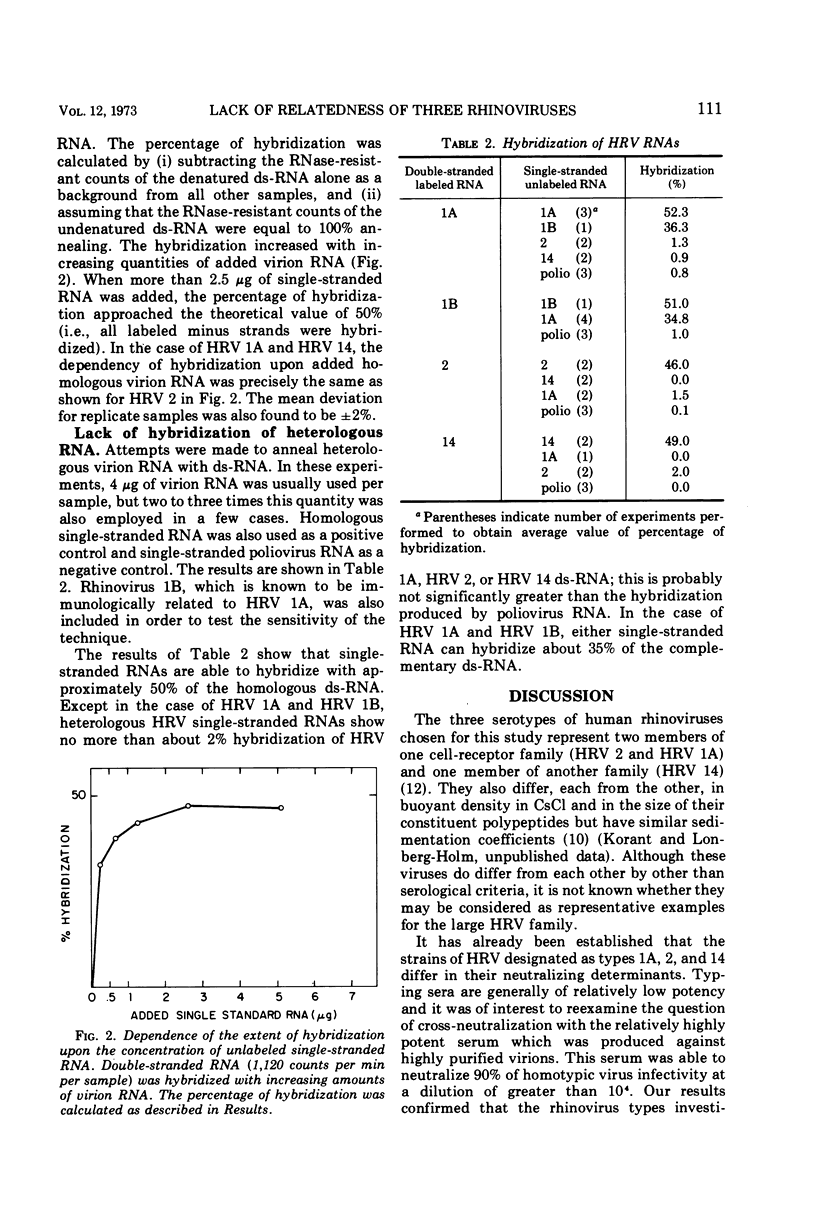
The possible genomic homologies between three serotypes of human rhinoviruses (HRV 1A, HRV 2, and HRV 14) were investigated. First we confirmed that these viruses were unrelated by the criterion of the absence of common antigenic determinants on the surfaces of the native virions, as detected by cross-neutralization of complementfixation. RNA-RNA hybridization was then examined with purified, highly radioactive, double-stranded, replicative-form RNA and excess single-stranded virion RNA. Single-stranded RNA showed 100% homology with the minus strand from the replicative-form RNA of the same type of virus. HRV 1A, HRV 2, and HRV 14 showed low intertypic homologies; these were not significantly greater than those found between the rhinoviruses and polivirus, which were used as a negative control. The immunological relationship and the RNA homology between HRV 1A and HRV 1B were also examined by the above techniques. It was confirmed that HRV 1A and HRV 1B share some surface determinants and it was also found that HRV 1B RNA shares 70% homology with HRV 1A RNA.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BROWN F., CARTWRIGHT B., NEWMAN J. F. FURTHER STUDIES OF THE EARLY ANTIBODY IN THE SEA OF CATTLE AND GUINEA PIGS INFECTED WITH FOOT-AND-MOUTH DISEASE VIRUS. J Immunol. 1964 Sep;93:397–402. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
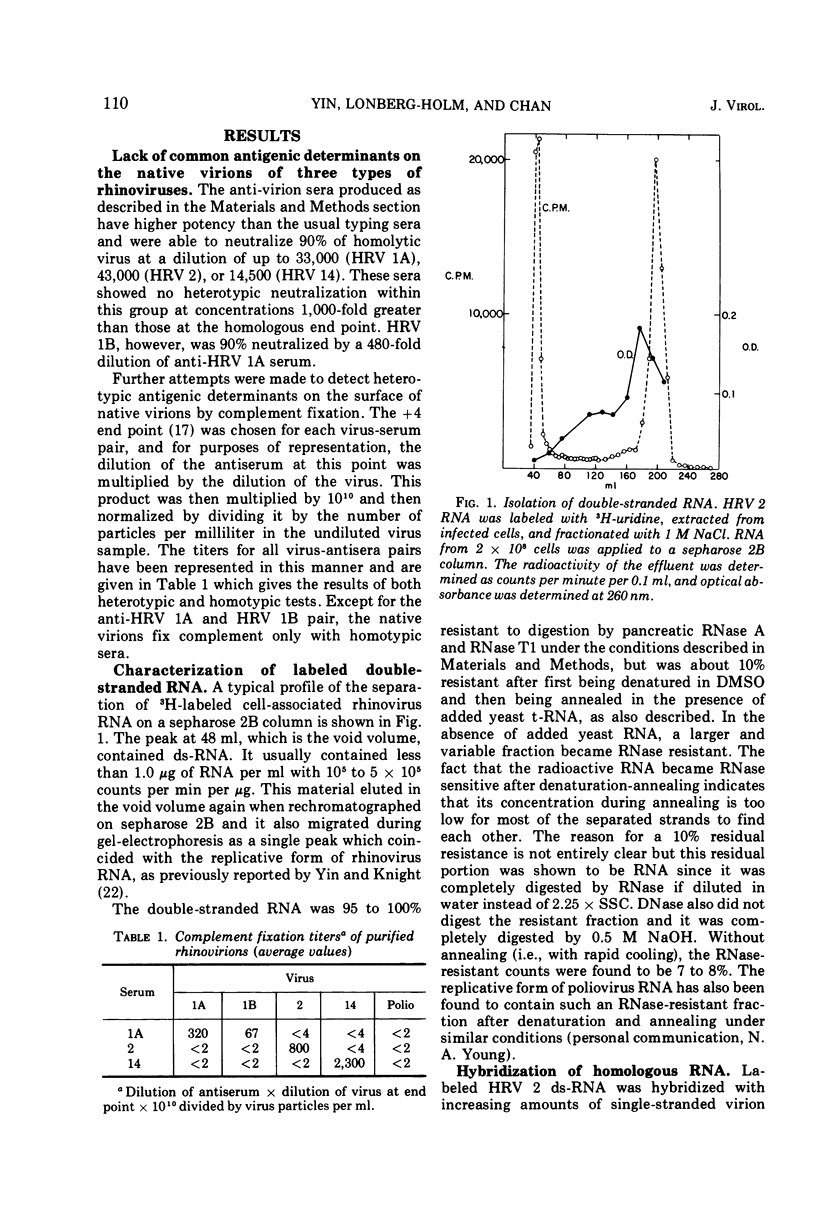
- Bishop J. M., Koch G. Purification and characterization of poliovirus-induced infectious double-stranded ribonucleic acid. J Biol Chem. 1967 Apr 25;242(8):1736–1743. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown F., Newman J. F., Stott E. J. Molecular weight of rhinovirus ribonucleic acid. J Gen Virol. 1970 Aug;8(2):145–148. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-8-2-145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan S. P., Maca R. D., Levine P. H., Ting R. C. Immunologic studies of human breast cancer. I. Serum reactivity against a lymphoid cell line (Belev) derived from a breast cancer patient as detected by complement-fixation test. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1971 Sep;47(3):511–517. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dans P. E., Forsyth B. R., Chanock R. M. Density of infectious virus and complement-fixing antigens of two rhinovirus strains. J Bacteriol. 1966 Apr;91(4):1605–1611. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.4.1605-1611.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietzschold B., Kaaden O. R., Tokui T., Böhm H. O. Polynucleotide sequence homologies among the RNAs of foot-and-mouth disease virus types A, C and O. J Gen Virol. 1971 Oct;13(1):1–7. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-13-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korant B. D., Lonberg-Holm K., Noble J., Stasny J. T. Naturally occurring and artificially produced components of three rhinoviruses. Virology. 1972 Apr;48(1):71–86. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90115-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LE BOUVIER G. L. The modification of poliovirus antigens by heat and ultraviolet light. Lancet. 1955 Nov 12;269(6898):1013–1016. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(55)93435-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lonberg-Holm K., Korant B. D. Early interaction of rhinoviruses with host cells. J Virol. 1972 Jan;9(1):29–40. doi: 10.1128/jvi.9.1.29-40.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lonberg-Holm K., Yin F. H. Antigenic determinants of infective and inactivated human rhinovirus type 2. J Virol. 1973 Jul;12(1):114–123. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.1.114-123.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nair C. N., Lonberg-Holm K. K. Infectivity and sedimentation of rhinovirus ribonucleic acid. J Virol. 1971 Feb;7(2):278–280. doi: 10.1128/jvi.7.2.278-280.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noble J., Lonberg-Holm K. Interactions of components of human rhinovirus type 2 with Hela cells. Virology. 1973 Feb;51(2):270–278. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90427-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oberg B., Philipson L. Replication of poliovirus RNA studied by gel filtration and electrophoresis. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Dec;11(2):305–315. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb00774.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHMIDT N. J., LENNETTE E. H. Modification of the homotypic specificity of poliomyelitis complement-fixing antigens by heat. J Exp Med. 1956 Jul 1;104(1):99–120. doi: 10.1084/jem.104.1.99. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scholtissek C., Rott R. Hybridization studies with influenza virus RNA. Virology. 1969 Nov;39(3):400–407. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90088-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stott E. J., Killington R. A. Rhinoviruses. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1972;26:503–524. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.26.100172.002443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yin F. H., Knight E., Jr In vivo and in vitro synthesis of human rhinovirus type 2 ribonucleic acid. J Virol. 1972 Jul;10(1):93–98. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.1.93-98.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young N. A., Hoyer B. H., Martin M. A. Polynucleotide sequence homologies among polioviruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Oct;61(2):548–555. doi: 10.1073/pnas.61.2.548. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



