Abstract
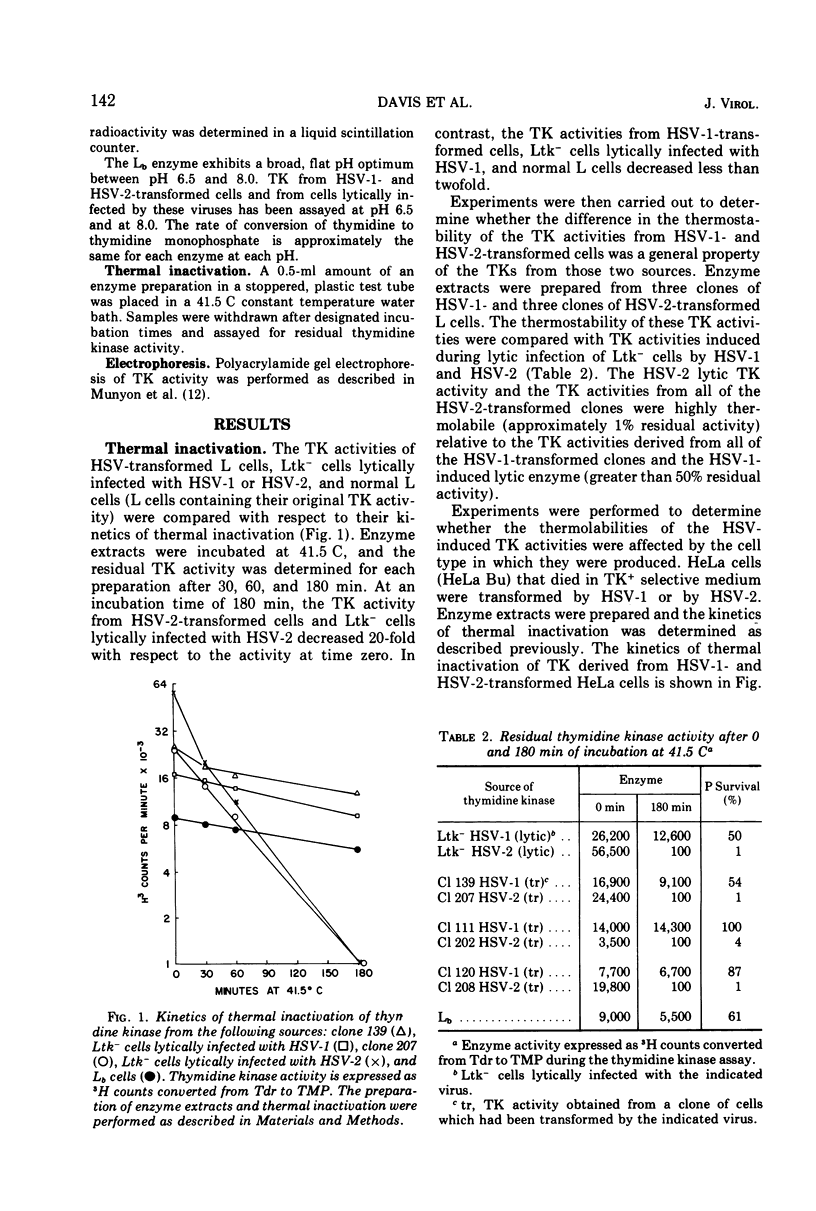
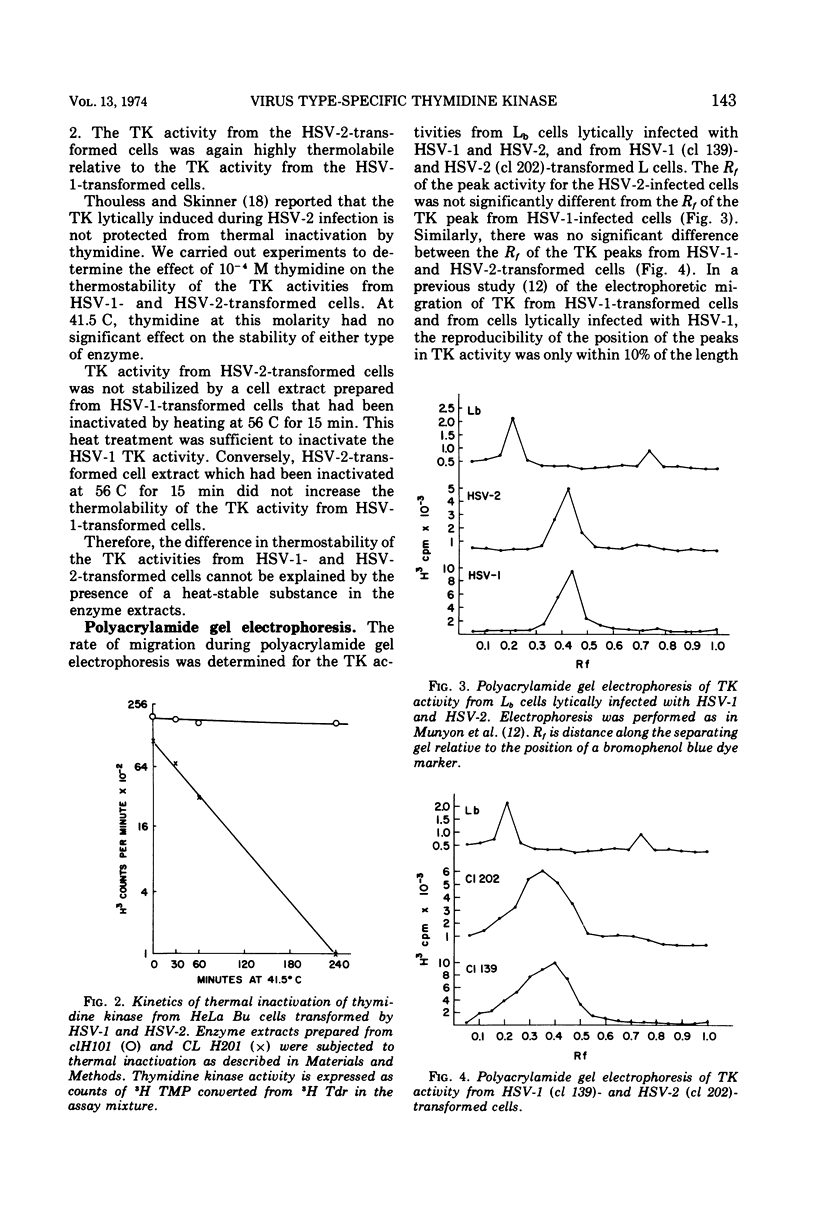
Transformation of mouse cells (Ltk−) and human cells (HeLa Bu) from a thymidine kinase (TK)-minus to a TK+ phenotype (herpes simplex virus [HSV]-transformed cells) has been induced by infection with ultraviolet-irradiated HSV type 2 (HSV-2), as well as by HSV type 1 (HSV-1). Medium containing methotrexate, thymidine, adenine, guanosine, and glycine was used to select for cells able to utilize exogenous thymidine. We have determined the kinetics of thermal inactivation of TK from cells lytically infected with HSV-1 or HSV-2 and from HSV-1- and HSV-2-transformed cells. Three hours of incubation at 41 C produces a 20-fold decrease in the TK activity of cell extracts from HSV-2-transformed cells and Ltk− cells lytically infected with HSV-2. The same conditions produce only a twofold decrease in the TK activities from HSV-1-transformed cells and cells lytically infected with HSV-1. This finding supports the hypothesis that an HSV structural gene coding for TK has been incorporated in the HSV-transformed cells.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Buchan A., Watson D. H., Dubbs D. R., Kit S. Serological study of a mutant of herpesvirus unable to stimulate thymidine kinase. J Virol. 1970 Jun;5(6):817–818. doi: 10.1128/jvi.5.6.817-818.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchan A., Watson D. H. The immunological specificity of thymidine kinases in cells infected by viruses of the herpes group. J Gen Virol. 1969 Apr;4(3):461–463. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-4-3-461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson R. L., Adelstein S. J., Oxman M. N. Herpes simplex virus as a source of thymidine kinase for thymidine kinase-deficient mouse cells: suppression and reactivation of the viral enzyme. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jul;70(7):1912–1916. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.7.1912. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duff R., Rapp F. Oncogenic transformation of hamster cells after exposure to herpes simplex virus type 2. Nat New Biol. 1971 Sep 8;233(36):48–50. doi: 10.1038/newbio233048a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duff R., Rapp F. Properties of hamster embryo fibroblasts transformed in vitro after exposure to ultraviolet-irradiated herpes simplex virus type 2. J Virol. 1971 Oct;8(4):469–477. doi: 10.1128/jvi.8.4.469-477.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EAGLE H. Amino acid metabolism in mammalian cell cultures. Science. 1959 Aug 21;130(3373):432–437. doi: 10.1126/science.130.3373.432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frenkel N., Roizman B., Cassai E., Nahmias A. A DNA fragment of Herpes simplex 2 and its transcription in human cervical cancer tissue. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Dec;69(12):3784–3789. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.12.3784. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIT S., DUBBS D. R., PIEKARSKI L. J., HSU T. C. DELETION OF THYMIDINE KINASE ACTIVITY FROM L CELLS RESISTANT TO BROMODEOXYURIDINE. Exp Cell Res. 1963 Aug;31:297–312. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(63)90007-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kit S., Dubbs D. R., Frearson P. M. HeLa cells resistant to bromodeoxyuridine and deficient in thymidine kinase activity. Int J Cancer. 1966 Jan;1(1):19–30. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910010105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klemperer H. G., Haynes G. R., Shedden W. I., Watson D. H. A virus-specific thymidine kinase in BHK-21 cells infected with herpes simplex virus. Virology. 1967 Jan;31(1):120–128. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(67)90015-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kutinová L., Vonka V., Broucek J. Increased oncogenicity and synthesis of herpesvirus antigens in hamster cells exposed to herpes simplex type-2 virus. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1973 Mar;50(3):759–766. doi: 10.1093/jnci/50.3.759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowry S. P., Bresnick E., Rawls W. E. Differences in thymidine kinase-inducing ability of herpesvirus types 1 and 2. Virology. 1971 Dec;46(3):958–961. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90096-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munyon W., Buchsbaum R., Paoletti E., Mann J., Kraiselburd E., Davis D. Electrophoresis of thymidine kinase activity synthesized by cells transformed by herpes simplex virus. Virology. 1972 Sep;49(3):683–689. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90525-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munyon W., Kraiselburd E., Davis D., Mann J. Transfer of thymidine kinase to thymidine kinaseless L cells by infection with ultraviolet-irradiated herpes simplex virus. J Virol. 1971 Jun;7(6):813–820. doi: 10.1128/jvi.7.6.813-820.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Royston I., Aurelian L. Immunofluorescent detection of herpesvirus antigens in exfoliated cells from human cervical carcinoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Sep;67(1):204–212. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.1.204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thouless M. E. Serological properties of thymidine kinase produced in cells infected with type 1 or type 2 herpes virus. J Gen Virol. 1972 Dec;17(3):307–315. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-17-3-307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thouless M. E., Skinner G. R. Differences in the properties of thymidine kinase produced in cells infected with type 1 and type 2 herpes virus. J Gen Virol. 1971 Aug;12(2):195–197. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-12-2-195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



