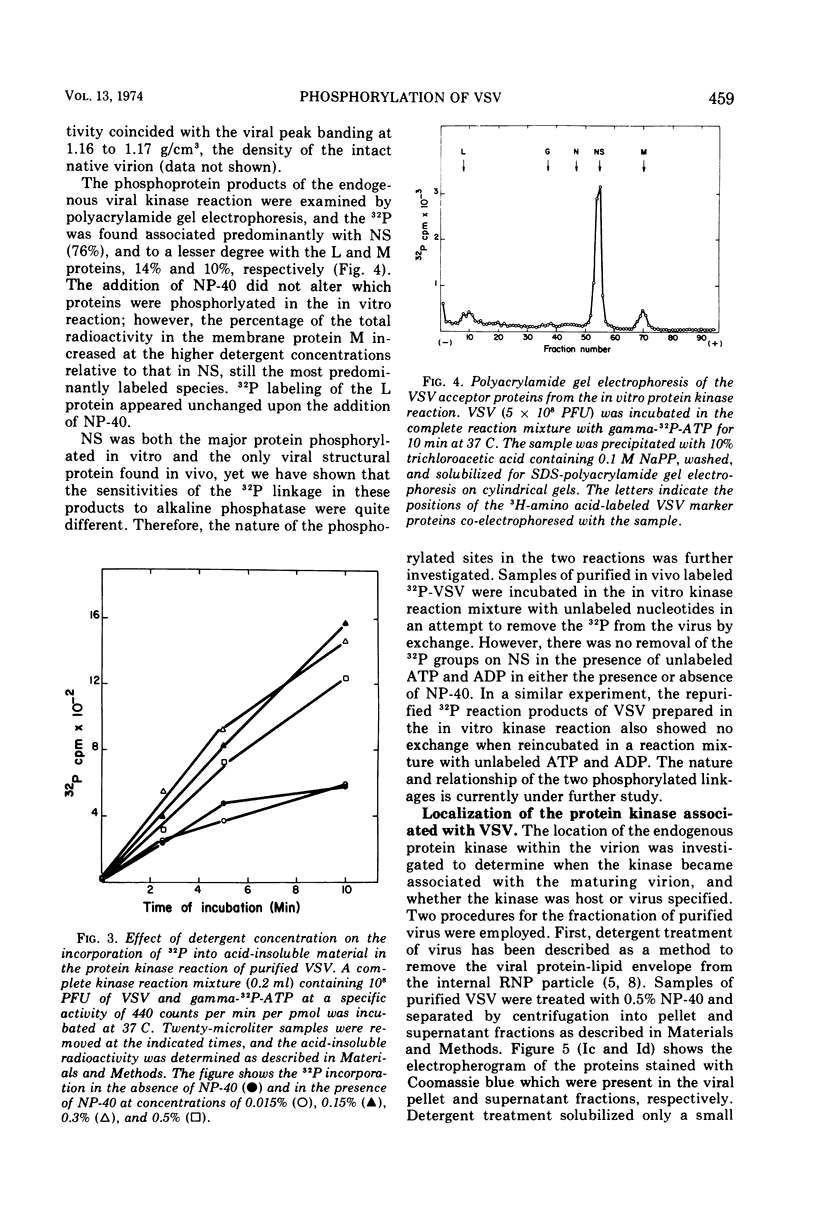
Abstract
The structural protein, NS, of purified vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV) is a phosphoprotein. In infected cells phosphorylated NS is found both free in the cytoplasm and as part of the viral ribonucleoprotein (RNP) complex containing both the 42S RNA and the structural proteins L, N, and NS, indicating that phosphorylation occurs as an early event in viral maturation. VSV contains an endogenous protein kinase activity, probably of host region, which catalyzes the in vitro phosphorylation of the viral proteins NS, M, and L, but not of N or G. The phosphorylated sites on NS appear to be different in the in vivo and in vitro reactions, and are differentially sensitive to alkaline phosphatase. After removal of the membrane components of purified VSV with a dextran-polyethylene glycol two-phase separation, the kinase activity remains tightly associated with the viral RNP. However, viral RNP isolated from infected cells shows only a small amount of kinase activity. The protein kinase enzyme appears to be a cellular contaminant of purified VSV because an activity from the uninfected cell extract can phosphorylate in vitro the dissociated viral proteins NS and M. The virion-associated activity may be derived either from the cytoplasm or the plasma membrane of the host cell since both of these cellular components contain protein kinase activity similar to that found in purified VSV.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atkinson P. H., Summers D. F. Purification and properties of HeLa cell plasma membranes. J Biol Chem. 1971 Aug 25;246(16):5162–5175. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baum S. G., Horwitz M. S., Maizel J. V., Jr Studies of the mechanism of enhancement of human adenovirus infection in monkey cells by simian virus 40. J Virol. 1972 Aug;10(2):211–219. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.2.211-219.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop D. H., Roy P. Dissociation of vesicular stomatitis virus and relation of the virion proteins to the viral transcriptase. J Virol. 1972 Aug;10(2):234–243. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.2.234-243.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cartwright B., Smale C. J., Brown F., Hull R. Model for vesicular stomatitis virus. J Virol. 1972 Aug;10(2):256–260. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.2.256-260.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cartwright B., Talbot P., Brown F. The proteins of biologically active sub-units of vesicular stomatitis virus. J Gen Virol. 1970 Jun;7(3):267–272. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-7-3-267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen G. H., Atkinson P. H., Summers D. F. Interactions of vesicular stomatitis virus structural proteins with HeLa plasma membranes. Nat New Biol. 1971 May 26;231(21):121–123. doi: 10.1038/newbio231121a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- David A. E. Assembly of the vesicular stomatitis virus envelope: incorporation of viral polypeptides into the host plasma membrane. J Mol Biol. 1973 May 5;76(1):135–148. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90085-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downer D. N., Rogers H. W., Randall C. C. Endogenous protein kinase and phosphate acceptor proteins in vaccinia virus. Virology. 1973 Mar;52(1):13–21. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90393-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gravell M., Cromeans T. L. Viron-associated protein kinase and its involvement in nongenetic reactivation of frog polyhedral cytoplasmic deoxyribovirus. Virology. 1972 Jun;48(3):847–851. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90167-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grubman M. J., Summers D. F. In vitro protein-synthesizing activity of vesicular stomatitis virus-infected cell extracts. J Virol. 1973 Aug;12(2):265–274. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.2.265-274.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatanaka M., Twiddy E., Gilden R. V. Protein kinase associated with RNA tumor viruses and other budding RNA viruses. Virology. 1972 Feb;47(2):536–538. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90297-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hecht T. T., Summers D. F. Effect of vesicular stomatitis virus infection on the histocompatibility antigen of L cells. J Virol. 1972 Oct;10(4):578–585. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.4.578-585.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howatson A. F. Vesicular stomatitis and related viruses. Adv Virus Res. 1970;16:195–256. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3527(08)60024-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hultquist D. E., Moyer R. W., Boyer P. D. The preparation and characterization of 1-phosphohistidine and 3-phosphohistidine. Biochemistry. 1966 Jan;5(1):322–331. doi: 10.1021/bi00865a041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kabat D. Phosphorylation of ribosomal proteins in rabbit reticulocytes. A cell-free system with ribosomal protein kinase activity. Biochemistry. 1971 Jan 19;10(2):197–203. doi: 10.1021/bi00778a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kang C. Y., Prevec L. Proteins of vesicular stomatitis virus. 3. Intracellular synthesis and extracellular appearance of virus-specific proteins. Virology. 1971 Dec;46(3):678–690. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90070-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krebs E. G. Protein kinases. Curr Top Cell Regul. 1972;5:99–133. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mudd J. A., Summers D. F. Protein synthesis in vesicular stomatitis virus-infected HeLa cells. Virology. 1970 Oct;42(2):328–340. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90277-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paoletti E., Moss B. Protein kinase and specific phosphate acceptor proteins associated with vaccinia virus cores. J Virol. 1972 Sep;10(3):417–424. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.3.417-424.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randall C. C., Rogers H. W., Downer D. N., Gentry G. A. Protein kinase activity in equine herpesvirus. J Virol. 1972 Feb;9(2):216–222. doi: 10.1128/jvi.9.2.216-222.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosemond H., Moss B. Phosphoprotein component of vaccinia virions. J Virol. 1973 Jun;11(6):961–970. doi: 10.1128/jvi.11.6.961-970.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy P., Bishop D. H. Nucleoside triphosphate phosphotransferase. A new enzyme activity of oncogenic and non-oncogenic "budding" viruses. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Apr 14;235(1):191–206. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(71)90047-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubenstein A. S., Gravell M., Darlington R. Protein kinase in enveloped herpes simplex virions. Virology. 1972 Oct;50(1):287–290. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90374-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin C. S., Erlichman J., Rosen O. M. Cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinase of human erythrocyte membranes. J Biol Chem. 1972 Oct 10;247(19):6135–6139. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell W. C., Shekel J. J., Machado R., Pereira H. G. Phosphorylated polypeptides in adenovirus-infected cells. Virology. 1972 Dec;50(3):931–934. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90450-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silberstein H., August J. T. Phosphorylation of animal virus proteins by a virion protein kinase. J Virol. 1973 Sep;12(3):511–522. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.3.511-522.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sokol F., Clark H. F. Phosphoproteins, structural components of rhabdoviruses. Virology. 1973 Mar;52(1):246–263. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90413-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stampfer M., Baltimore D. Identification of the vesicular stomatitis virus large protein as a unique viral protein. J Virol. 1973 Apr;11(4):520–526. doi: 10.1128/jvi.11.4.520-526.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strand M., August J. T. Protein kinase and phosphate acceptor proteins in Rauscher murine leukaemia virus. Nat New Biol. 1971 Sep 29;233(39):137–140. doi: 10.1038/newbio233137a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan K. B., Sokol F. Structural proteins of simian virus 40: phosphoproteins. J Virol. 1972 Nov;10(5):985–994. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.5.985-994.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tao M., Doerfler W. Phosphorylation of adenovirus polypeptides. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Jun 9;27(3):448–452. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb01859.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trauch J. A., Mumby M., Traut R. R. Phosphorylation of ribosomal proteins by substrate-specific protein kinases from rabbit reticulocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Feb;70(2):373–376. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.2.373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner R. R., Kiley M. P., Snyder R. M., Schnaitman C. A. Cytoplasmic compartmentalization of the protein and ribonucleic acid species of vesicular stomatitis virus. J Virol. 1972 Apr;9(4):672–683. doi: 10.1128/jvi.9.4.672-683.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner R. R., Prevec L., Brown F., Summers D. F., Sokol F., MacLeod R. Classification of rhabdovirus proteins: a proposal. J Virol. 1972 Dec;10(6):1228–1230. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.6.1228-1230.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner R. R., Schnaitman T. C., Snyder R. M., Schnaitman C. A. Protein composition of the structural components of vesicular stomatitis virus. J Virol. 1969 Jun;3(6):611–618. doi: 10.1128/jvi.3.6.611-618.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner R. R., Snyder R. M., Yamazaki S. Proteins of vesicular stomatitis virus: kinetics and cellular sites of synthesis. J Virol. 1970 May;5(5):548–558. doi: 10.1128/jvi.5.5.548-558.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





