Abstract
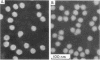
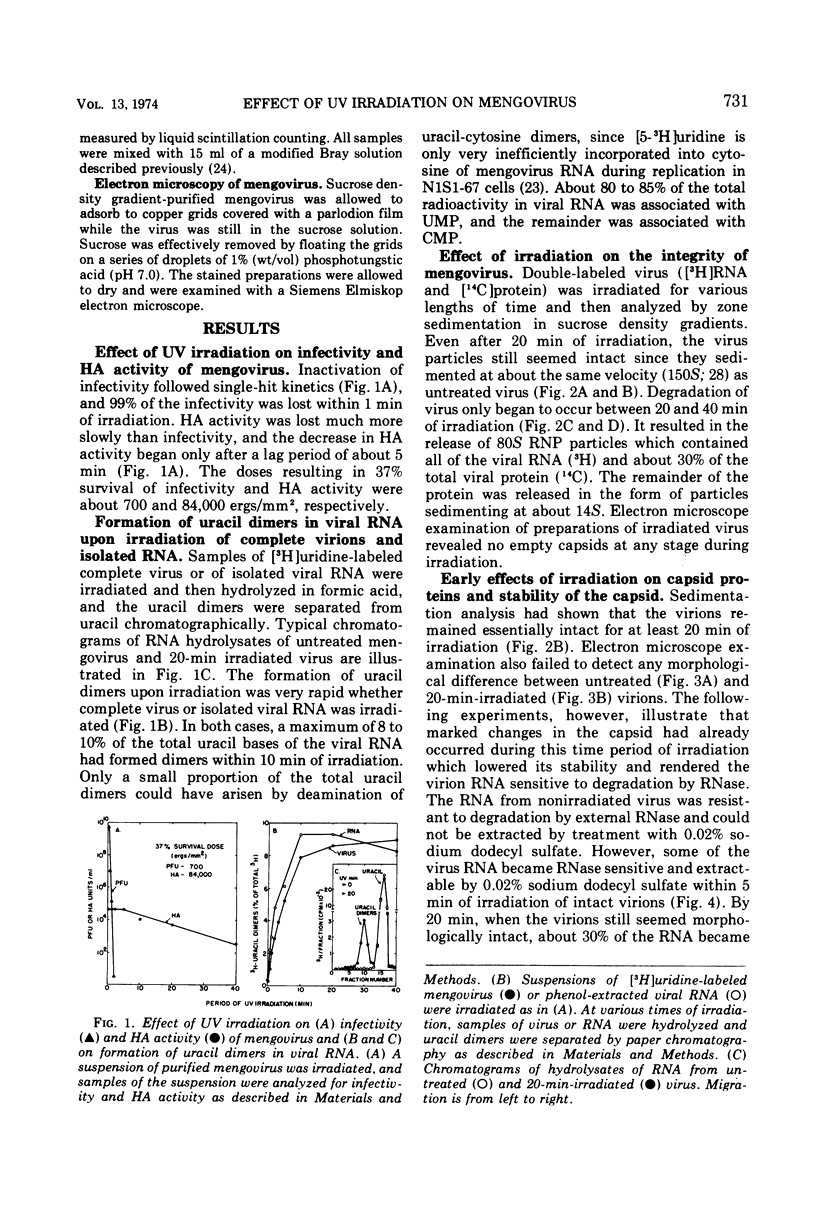
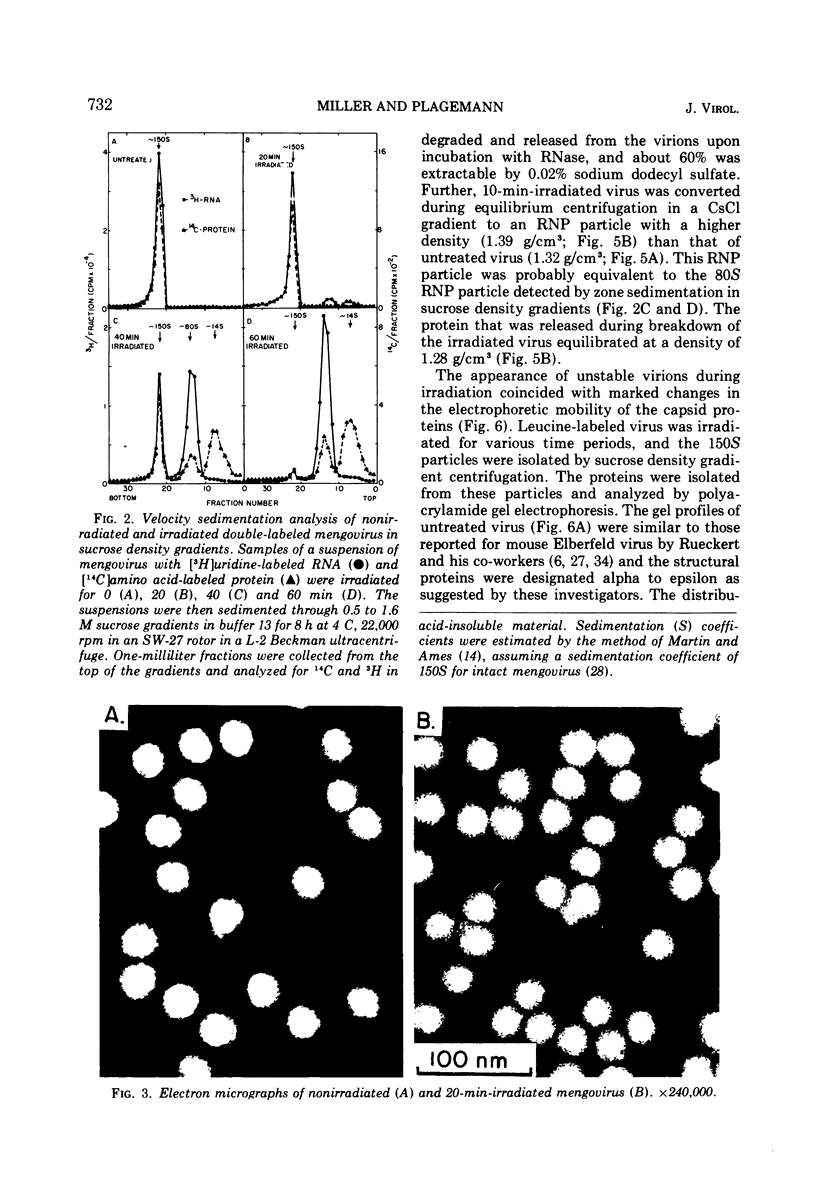
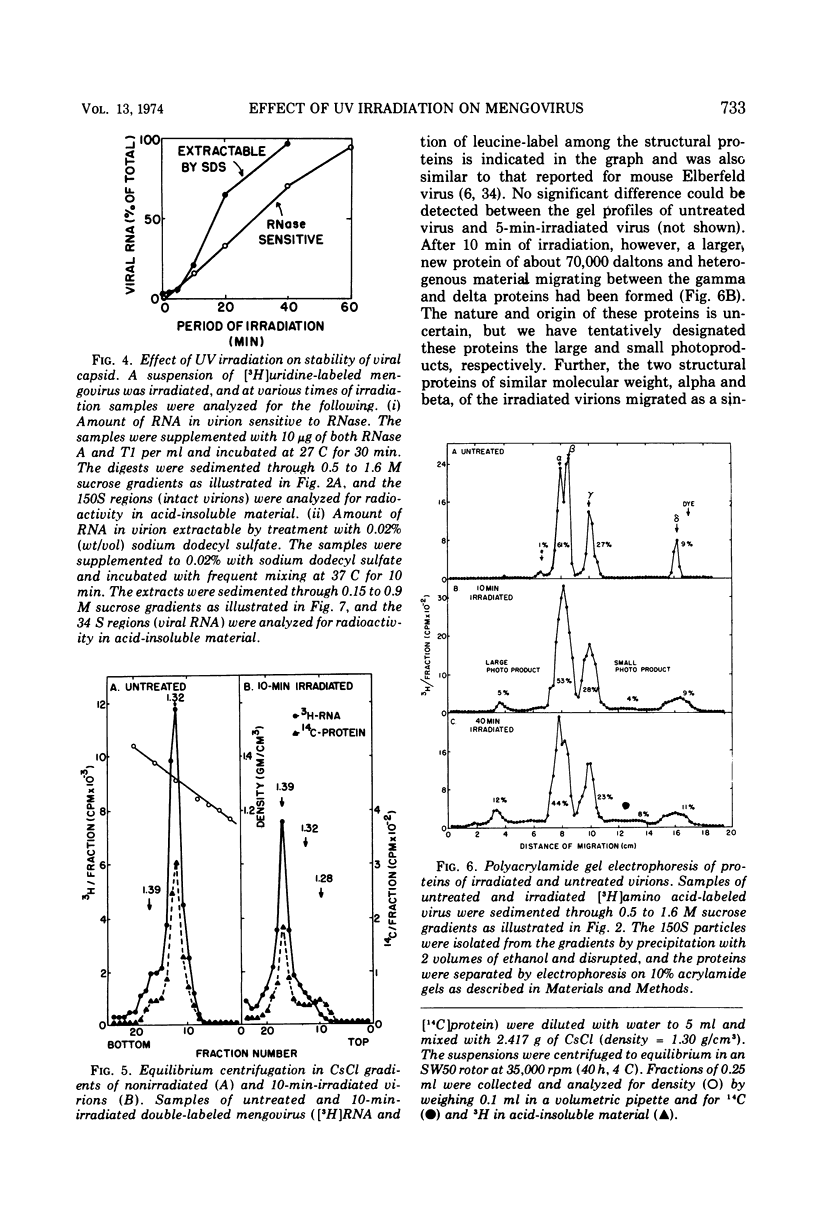
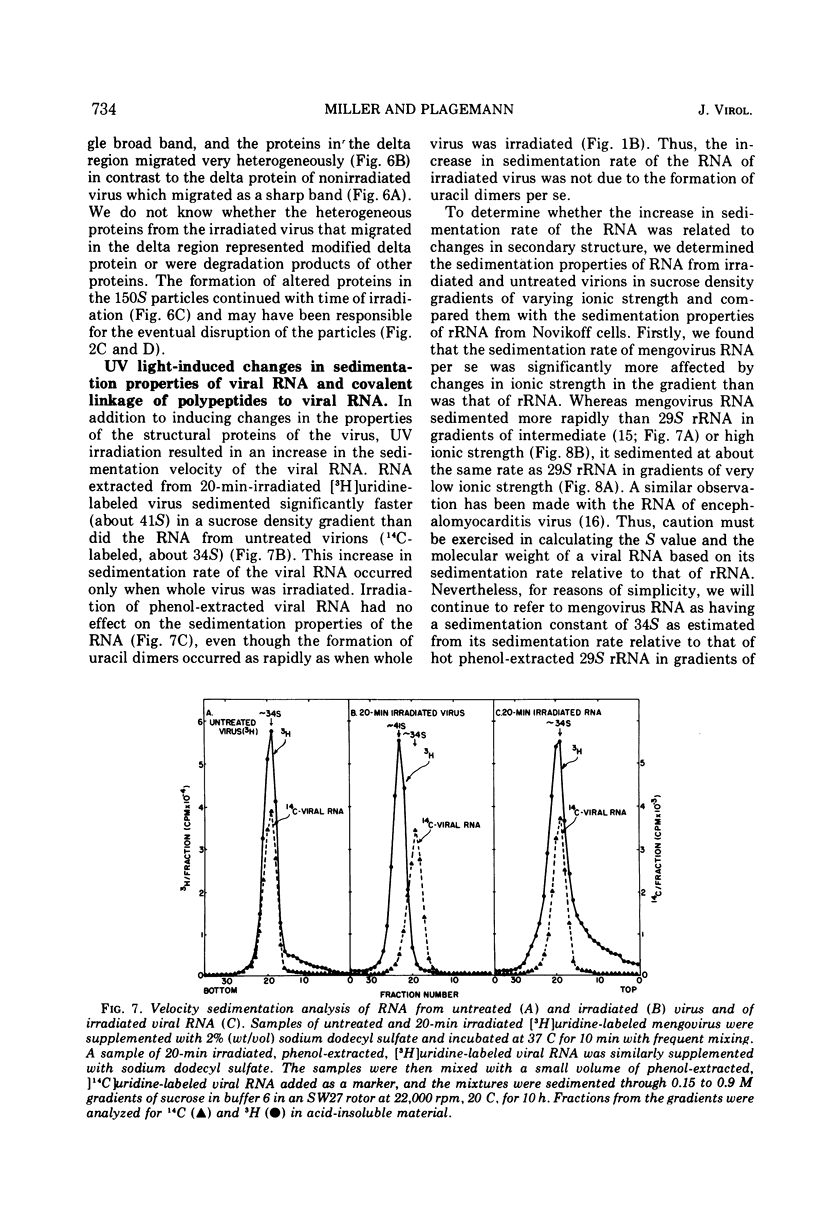
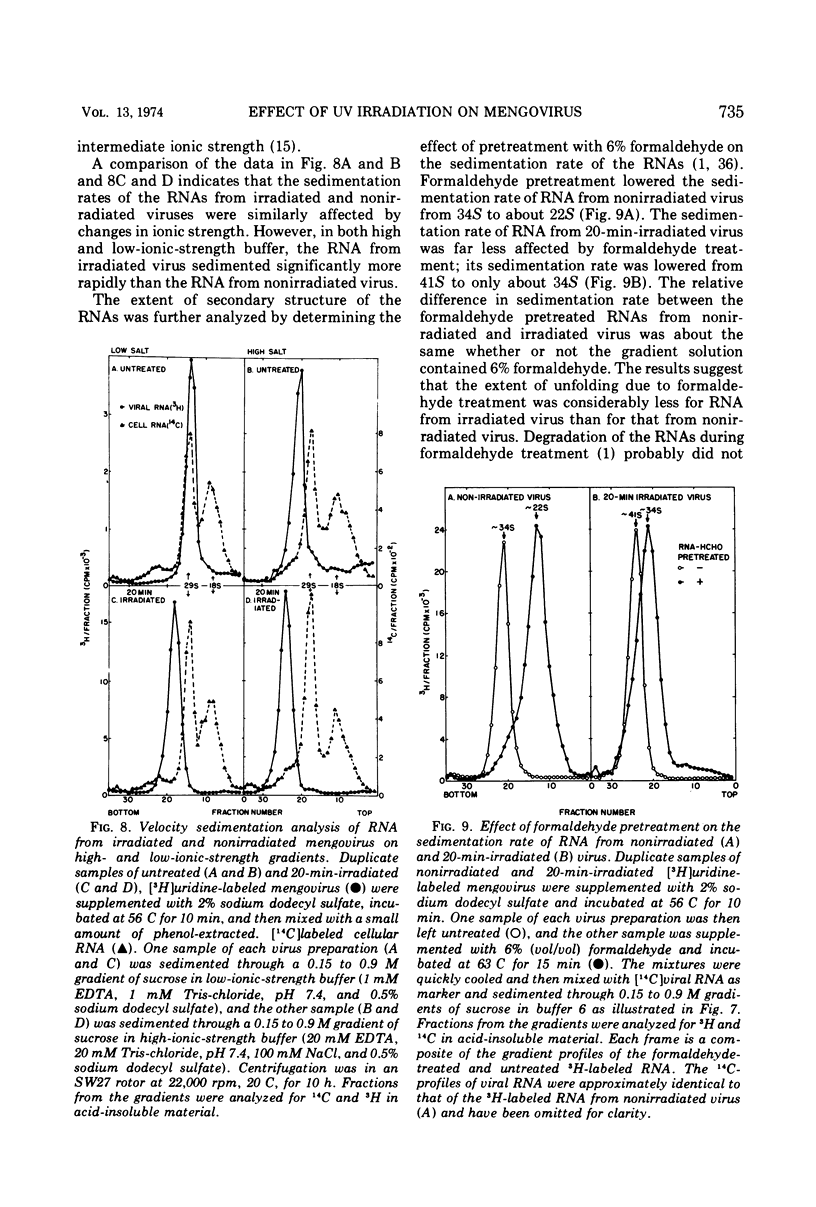
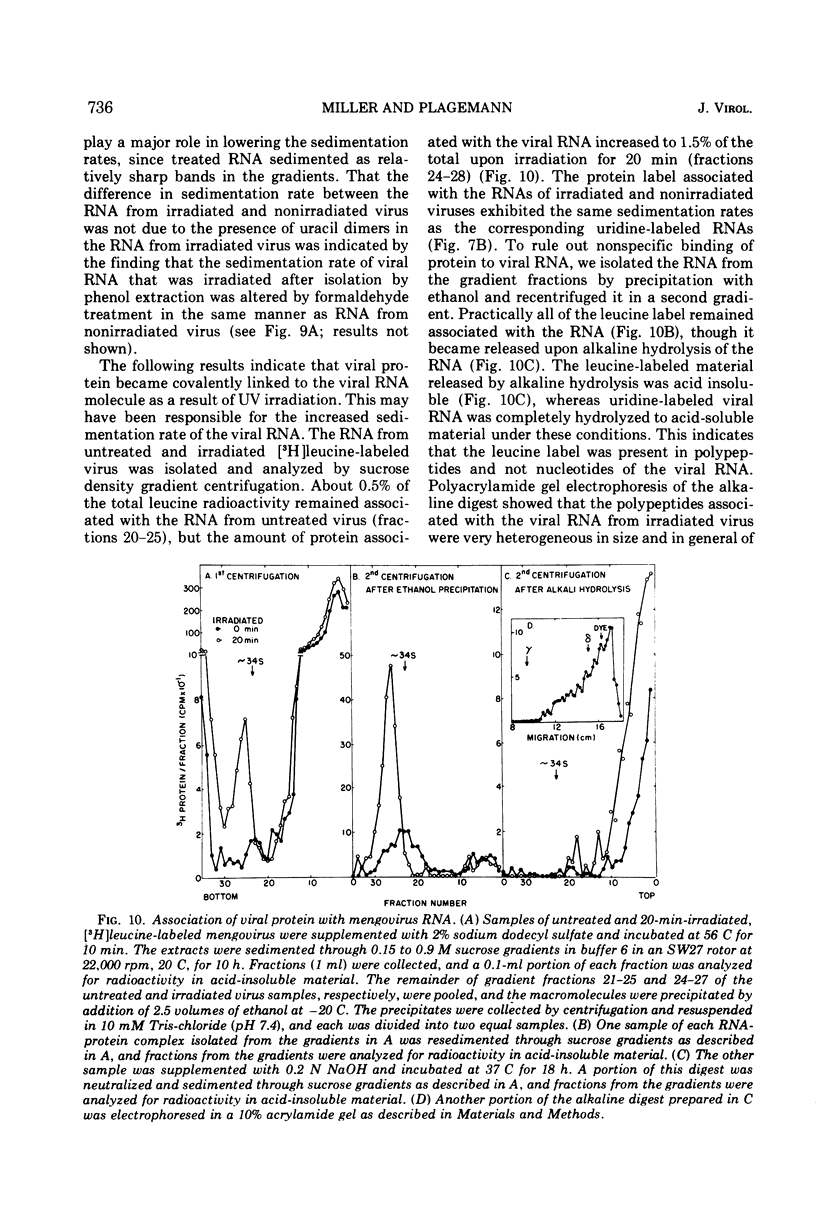
UV irradiation of purified mengovirus resulted in a very rapid inactivation of the infectivity of the virions (D37 [37% survival dose] = 700 ergs/mm2) which correlated in time with the formation of uracil dimers in the viral RNA. During the first 2 min of irradiation, an average of 1.7 uracil dimers were formed per PFU of virus inactivated. Hemagglutination activity of the virions began to decrease only after a lag period of about 5 min and at a much lower rate (D37 = 84,000 ergs/mm2). This decrease coincided in time with the appearance of altered proteins in the capsid and a structural change in the capsid. Although 10- to 20-min irradiated virions appeared intact in the electron microscope and sedimented at 150S in sucrose density gradients, the RNA of the virions became accessible to RNase and extractable by low concentrations of sodium dodecyl sulfate, and the virions broke down upon equilibrium centrifugation in CsCl gradients. During longer periods of irradiation (30 to 60 min), a progressively greater proportion of the virions were converted to 14S protein particles and 80S ribonucleoprotein particles composed of intact viral RNA and about 30% of the capsid proteins, alpha, beta, and gamma. Empty capsids were not detectable at any time during 60 min of irradiation, by which time disruption of the virions was complete. Irradiation of complete virions also resulted in an increased sedimentation rate of the viral RNA and in the covalent linkage to the viral RNA of about 1% of the total capsid protein in the form of heterogeneous low-molecular-weight polypeptides. The two observations seem to be causally related, since irradiation of isolated viral RNA did not result in an increase in sedimentation rate of the RNA, even though uracil dimer formation in viral RNA occurred at about the same rate and to the same extent whether intact virions or viral RNA were irradiated.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boedtker H. Dependence of the sedimentation coefficient on molecular weight of RNA after reaction with formaldehyde. J Mol Biol. 1968 Jul 14;35(1):61–70. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(68)80036-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boeyé A., Van Elsen A. Alkaline disruption of poliovirus: kinetics and purification of RNA-free particles. Virology. 1967 Oct;33(2):335–343. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(67)90152-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breindl M. VP 4, the D-reactive part of poliovirus. Virology. 1971 Dec;46(3):962–964. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90097-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowell R. L., Philipson L. Specific alterations of coxsackievirus B3 eluted from HeLa cells. J Virol. 1971 Oct;8(4):509–515. doi: 10.1128/jvi.8.4.509-515.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drzeniek R., Bilello P. Dissociation and reassociation of infectious poliovirus particles. Nat New Biol. 1972 Nov 22;240(99):118–122. doi: 10.1038/newbio240118a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunker A. K., Rueckert R. R. Fragments generated by pH dissociation of ME-virus and their relation to the structure of the virion. J Mol Biol. 1971 May 28;58(1):217–235. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90242-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goddard J., Streeter D., Weber C., Gordon M. P. tudies on the inactivation of tobacco mosaic virus by ultraviolet light. Photochem Photobiol. 1966 Feb;5:213–222. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.1966.tb05783.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinuma Y., Katagiri S., Fukuda M., Fukushi K., Watanabe Y. Kinetic studies on the thermal degradation of purified poliovirus. Biken J. 1965 Sep;8(3):143–153. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson M. F., Baltimore D. Morphogenesis of poliovirus. I. Association of the viral RNA with coat protein. J Mol Biol. 1968 Apr 28;33(2):369–378. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90195-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katagiri S., Hinuma Y., Ishida N. Biophysical properties of poliovirus particles irradiated with ultraviolet light. Virology. 1967 Jun;32(2):337–343. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(67)90282-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LE BOUVIER G. L. The modification of poliovirus antigens by heat and ultraviolet light. Lancet. 1955 Nov 12;269(6898):1013–1016. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(55)93435-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTIN R. G., AMES B. N. A method for determining the sedimentation behavior of enzymes: application to protein mixtures. J Biol Chem. 1961 May;236:1372–1379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. L., Plagemann P. G. Purification of mengovirus and identification of an A-rich segment in its ribonucleic acid. J Gen Virol. 1972 Dec;17(3):349–353. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-17-3-349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry R. P., La Torre J., Kelley D. E., Greenberg J. R. On the lability of poly(A) sequences during extraction of messenger RNA from polyribosomes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Mar 14;262(2):220–226. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(72)90236-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips B. A., Fennell R. Polypeptide composition of poliovirions, naturally occurring empty capsids, and 14S precursor particles. J Virol. 1973 Aug;12(2):291–299. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.2.291-299.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips B. A. In vitro assembly of polioviruses. I. Kinetics of the assembly of empty capsids and the role of extracts from infected cells. Virology. 1969 Dec;39(4):811–821. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90018-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips B. A., Summers D. F., Maizel J. V., Jr In vitro assembly of poliovirus-related particles. Virology. 1968 Jun;35(2):216–226. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(68)90262-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plagemann P. G. Mengovirus replication in Novikoff rat hepatoma and mouse L cells: effects on synthesis of host-cell macromolecules and virus-specific synthesis of ribonucleic acid. J Virol. 1968 May;2(5):461–473. doi: 10.1128/jvi.2.5.461-473.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plagemann P. G. Nucleotide pools of Novikoff rat hepatoma cells growing in suspension culture. II. Independent nucleotide pools for nucleic acid synthesis. J Cell Physiol. 1971 Apr;77(2):241–248. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040770213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plagemann P. G., Swim H. E. Replication of mengovirus. I. Effect on synthesis of macromolecules by host cell. J Bacteriol. 1966 Jun;91(6):2317–2326. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.6.2317-2326.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plagemann P. G., Swim H. E. Synthesis of ribonucleic acid by mengovirus-induced RNA polymerase in vitro: nature of products and of RNase-resistant intermediate. J Mol Biol. 1968 Jul 14;35(1):13–25. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(68)80034-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plagemann P. G. Temperature- and phenol-induced alterations in sedimentation rates of 29-S and 18-S ribosomal RNA's from Novikoff hepatoma cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Dec 14;224(2):451–457. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(70)90577-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROIZMAN B., MAYER M. M., ROANE P. R., Jr Immunochemical studies of poliovirus. IV. Alteration of the immunologic specificity of purified poliomyelitis virus by heat and ultraviolet light. J Immunol. 1959 Jan;82(1):19–25. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rueckert R. R., Dunker A. K., Stoltzfus C. M. The structure of mouse-Elberfeld virus: a model. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Mar;62(3):912–919. doi: 10.1073/pnas.62.3.912. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scraba D. G., Kay C. M., Colter J. S. Physico-chemical studies of three variants of Mengo virus and their constituent ribonucleates. J Mol Biol. 1967 May 28;26(1):67–79. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90261-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Setlow R. B., Carrier W. L. Pyrimidine dimers in ultraviolet-irradiated DNA's. J Mol Biol. 1966 May;17(1):237–254. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80105-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shea M. A., Plagemann P. G. Effects of elevated temperatures on mengovirus ribonucleic acid synthesis and virus production in Novikoff rat hepatoma cells. J Virol. 1971 Jan;7(1):144–154. doi: 10.1128/jvi.7.1.144-154.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith K. C., Meun D. H. Kinetics of the photochemical addition of [35S] cysteine to polynucleotides and nucleic acids. Biochemistry. 1968 Mar;7(3):1033–1037. doi: 10.1021/bi00843a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoltzfus C. M., Rueckert R. Capsid polypeptides of mouse Elberfeld virus. I. Amino acid compositions and molar ratios in the virion. J Virol. 1972 Sep;10(3):347–355. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.3.347-355.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subasinghe H. A., Loh P. C. Reovirus cytotoxicity: some properties of the UV-irradiated reovirus and its capsid proteins. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1972;39(1):172–189. doi: 10.1007/BF01241540. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tannock G. A., Gibbs A. J., Cooper P. D. A re-examination of the molecular weight of poliovirus RNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Jan 23;38(2):298–304. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90712-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]