Abstract
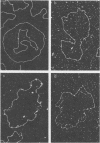
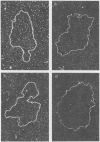
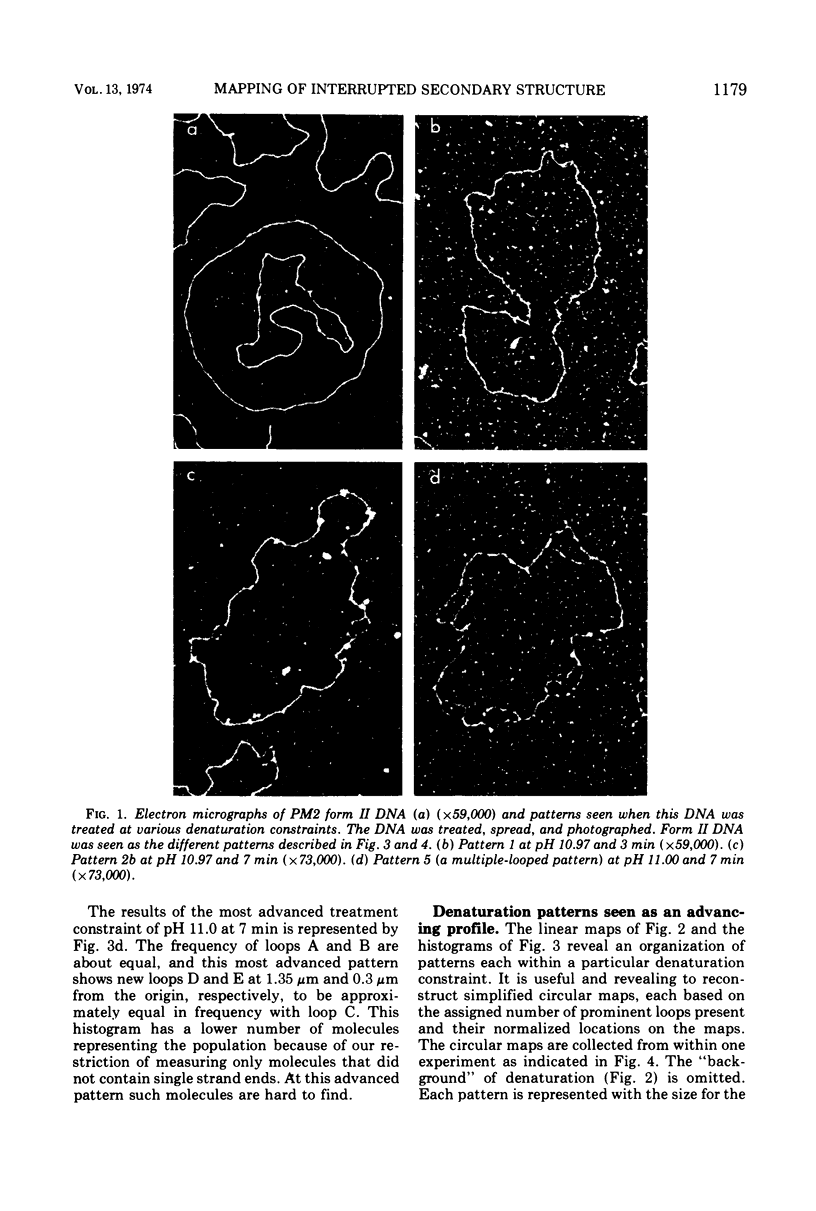
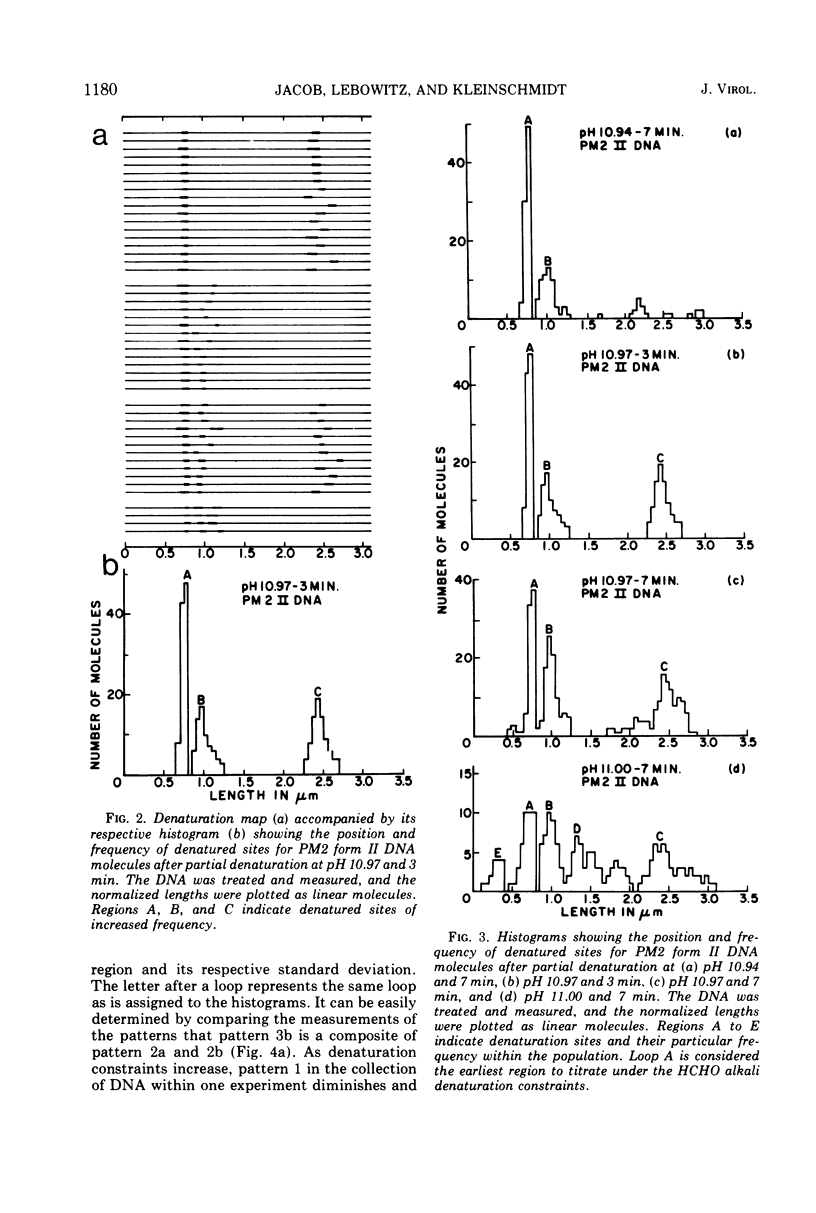
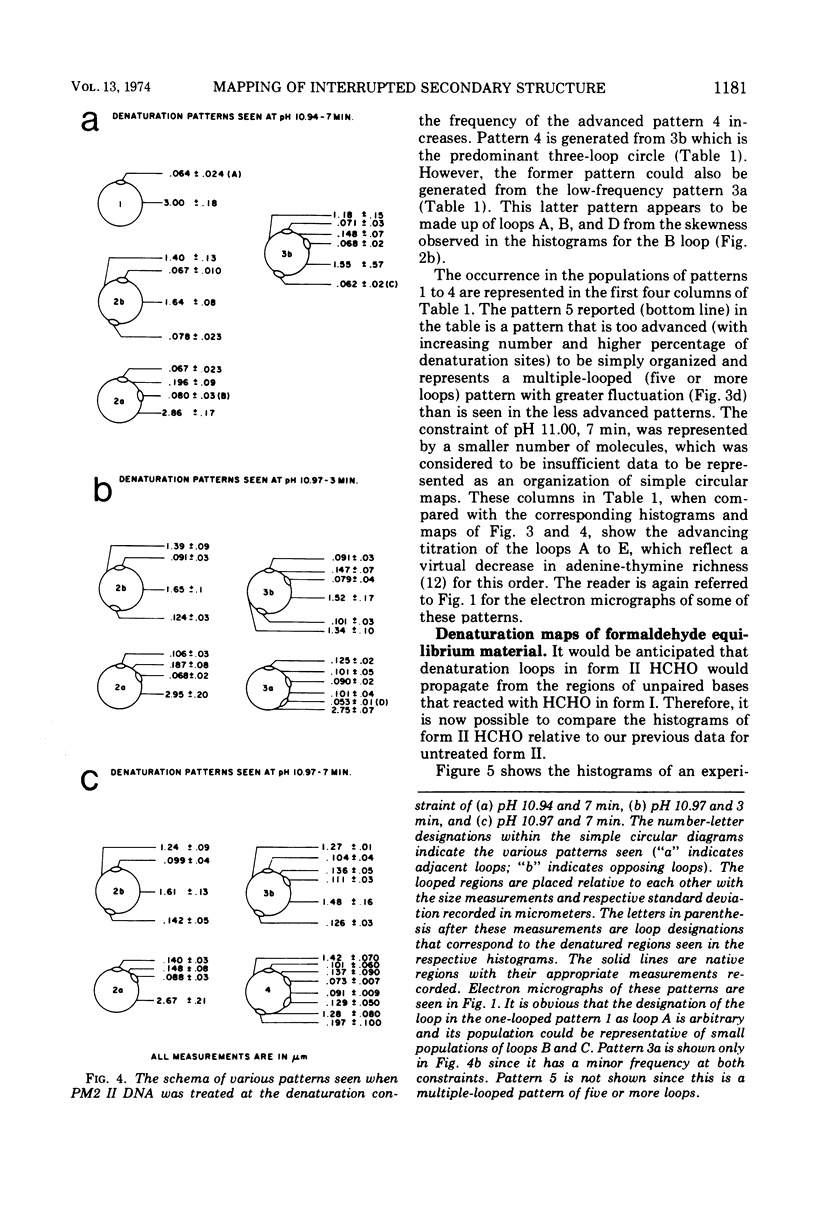
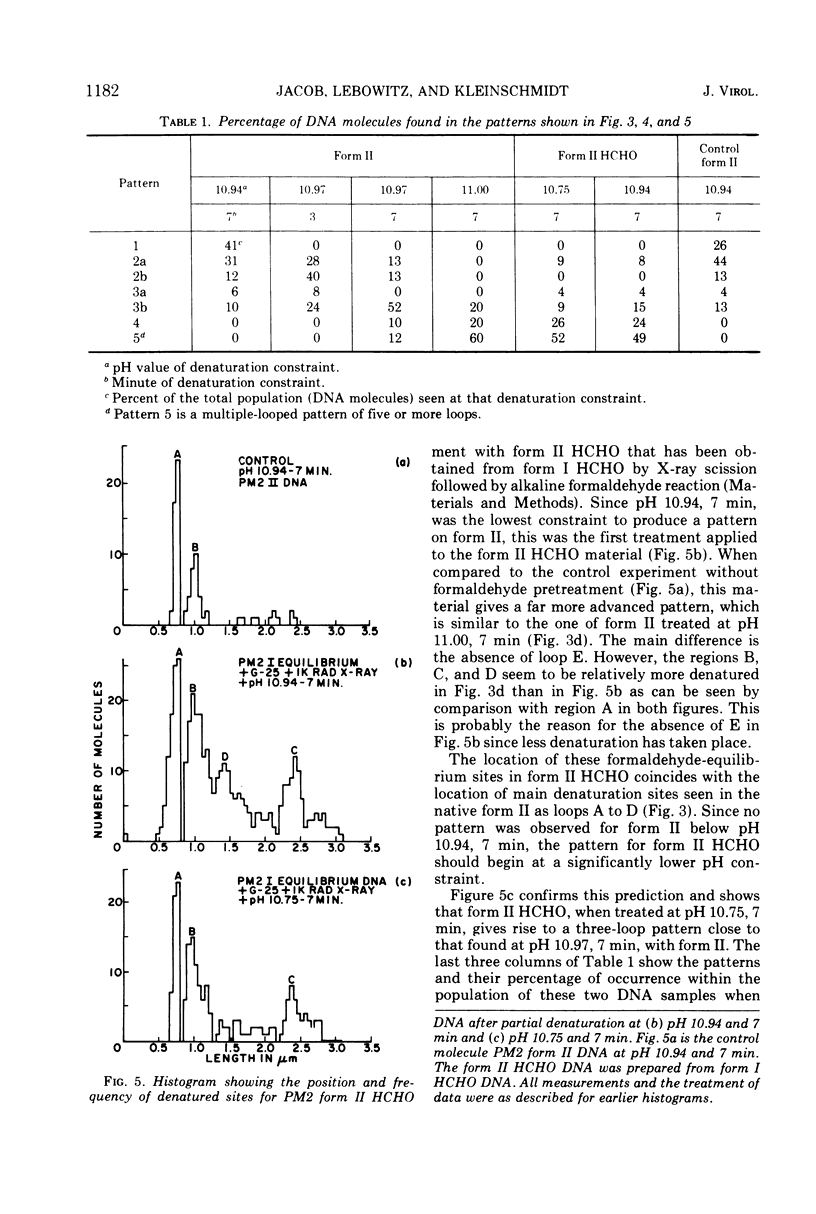
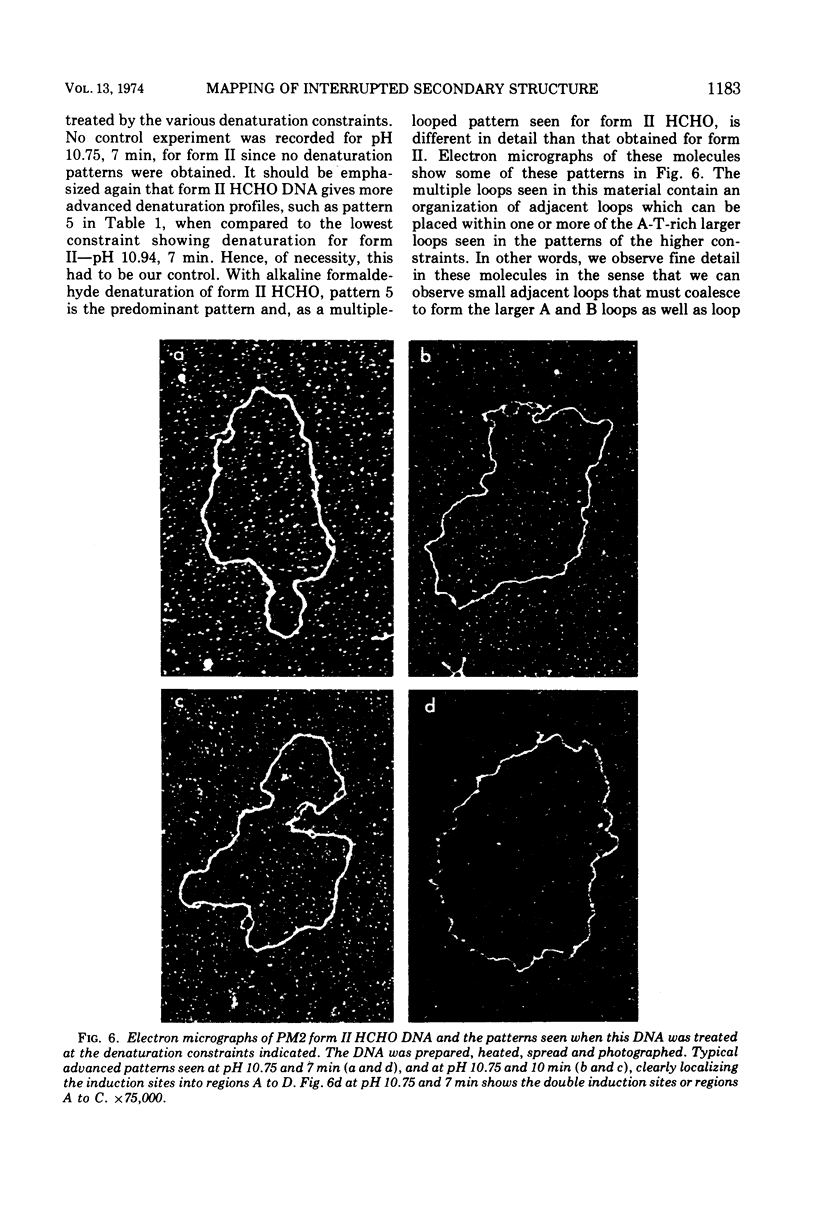
Previous studies with HCHO have revealed a reaction with superhelical DNA that strongly suggests that this DNA consists of small regions of interrupted secondary structure. To map these sites in PM2 DNA, the following set of experiments was performed using electron microscopy. (i) A denaturation map of nicked form II was obtained using Inman's alkaline-HCHO conditions. (ii) The superhelical form I was reacted with HCHO at 30 C until equilibrium was achieved at the interrupted sites (3.6% reactivity). The excess HCHO was removed rapidly and X-ray treatment was employed to nick these prereacted molecules. These form II molecules containing HCHO (form II HCHO) were also subjected to denaturation mapping. It would be expected that the HCHO-unpaired regions would serve as induction sites for the propagation of melting. Hence, depending on the location of the induction sites; we would anticipate either the creation of new regions of melting or a normal denaturation map shifted to lower pH values. Comparison of the development of progressive denaturation of form II and form II HCHO reveals that the latter is the case. The denaturation maps of form II are highly organized patterns of adenine-thymine (AT)-rich regions, with a total of five regions at extreme pH conditions. There are six highly organized regions for form II HCHO, i.e., smaller adjacent loops, at low denaturation conditions where no denaturation is seen for form II. These coalesce into the pattern for form II containing four of five A-T-rich regions observed for form II. Hence we conclude that the regions of altered hydrogen bonding in superhelical PM2 DNA are four to six in number and they map in the A-T-rich regions of the DNA.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beard P., Morrow J. F., Berg P. Cleavage of circular, superhelical simian virus 40 DNA to a linear duplex by S1 nuclease. J Virol. 1973 Dec;12(6):1303–1313. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.6.1303-1313.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beerman T. A., Lebowitz J. Further analysis of the altered secondary structure of superhelical DNA. Sensitivity to methylmercuric hydroxide a chemical probe for unpaired bases. J Mol Biol. 1973 Sep 25;79(3):451–470. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90398-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean W. W., Lebowitz J. Partial alteration of secondary structure in native superhelical DNA. Nat New Biol. 1971 May 5;231(18):5–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Espejo R. T., Canelo E. S. Properties of bacteriophage PM2: a lipid-containing bacterial virus. Virology. 1968 Apr;34(4):738–747. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(68)90094-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Espejo R. T., Canelo E. S., Sinsheimer R. L. DNA of bacteriophage PM2: a closed circular double-stranded molecule. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Aug;63(4):1164–1168. doi: 10.1073/pnas.63.4.1164. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inman R. B. A denaturation map of the lambda phage DNA molecule determined by electron microscopy. J Mol Biol. 1966 Jul;18(3):464–476. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80037-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inman R. B. Denaturation maps of the left and right sides of the lambda DNA molecule determined by electron microscopy. J Mol Biol. 1967 Aug 28;28(1):103–116. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(67)80081-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inman R. B., Schnös M. Partial denaturation of thymine- and 5-bromouracil-containing lambda DNA in alkali. J Mol Biol. 1970 Apr 14;49(1):93–98. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90378-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato A. C., Bartok K., Fraser M. J., Denhardt D. T. Sensitivity of superhelical DNA to a single-strand specific endonuclease. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Apr 21;308(7):68–78. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(73)90123-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazurkin Y. S., Frank-Kamenetskii M. D., Trifonov E. N. Melting of DNA: its study and application as a research method. Biopolymers. 1970 Nov;9(11):1253–1306. doi: 10.1002/bip.1970.360091102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PRINTZ M. P., VONHIPPEL P. H. HYDROGEN EXCHANGE STUDIES OF DNA STRUCTURE. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Feb;53:363–370. doi: 10.1073/pnas.53.2.363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]