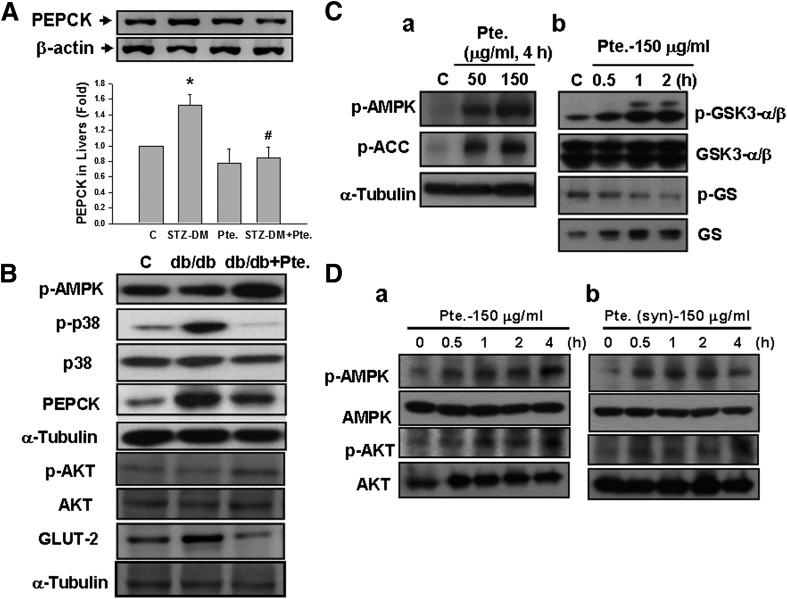
FIG. 7.
Effects of pterosin A on the liver gluconeogenesis–related signal proteins in diabetic mice (DM) and cultured liver cells. STZ-induced diabetic mice (A) and db/db diabetic mice (B) were orally treated with pterosin A (100 mg/kg) for 4 weeks. The protein expressions of liver gluconeogenesis–related signal proteins (PEPCK, phosphorylated AMPK, phosphorylated Akt, and phosphorylated p38) and GLUT-2 were determined by Western blotting. Phosphorylations of AMPK, Akt, ACC, GSK3-α/β, and GS in cultured H4-IIE (C) and HepG2 (D) liver cells treated with pterosin A (50–150 μg/mL) for 0.5–4 h were detected. Db: Pterosin A from a chemically synthesized source was used. A: Data are presented as mean ± SEM (n = 4). *P < 0.05 vs. control (C). #P < 0.05 vs. diabetic mice without pterosin A. B–D: Representative images of three independent experiments are shown.