Abstract
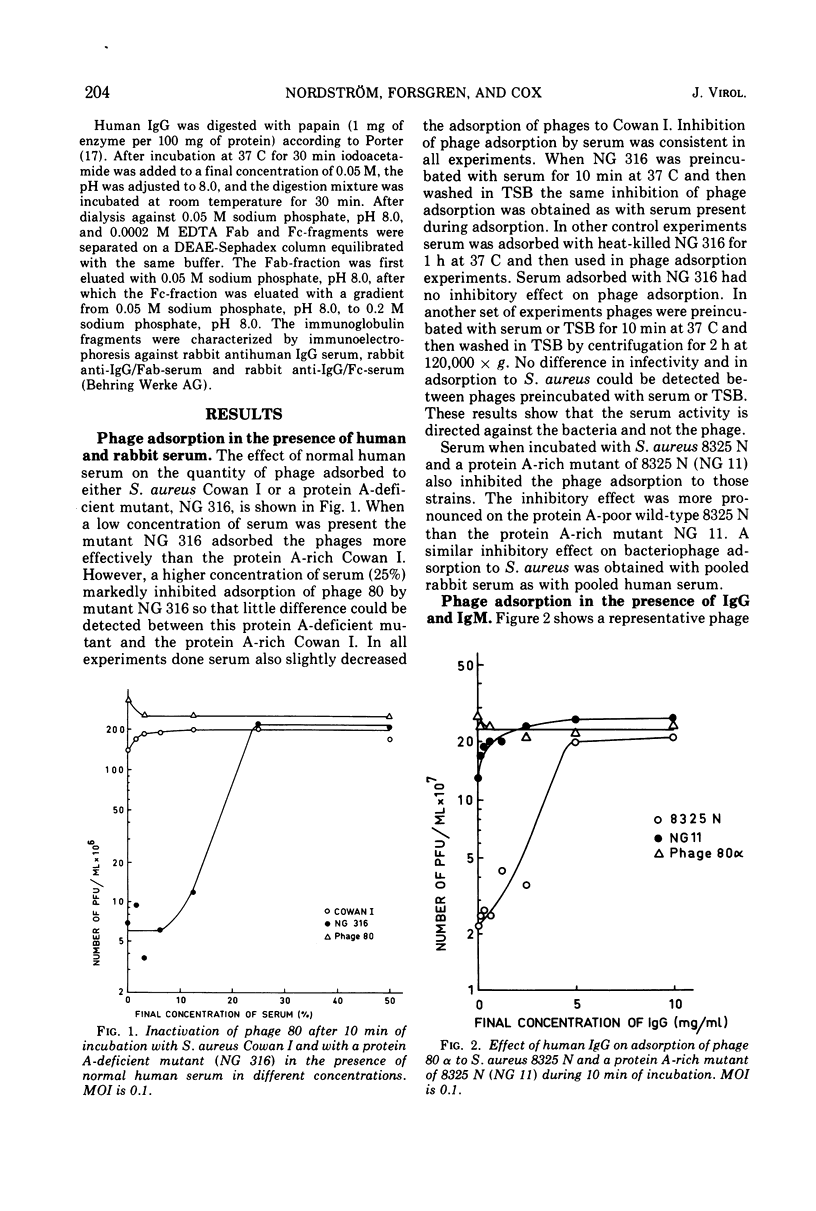
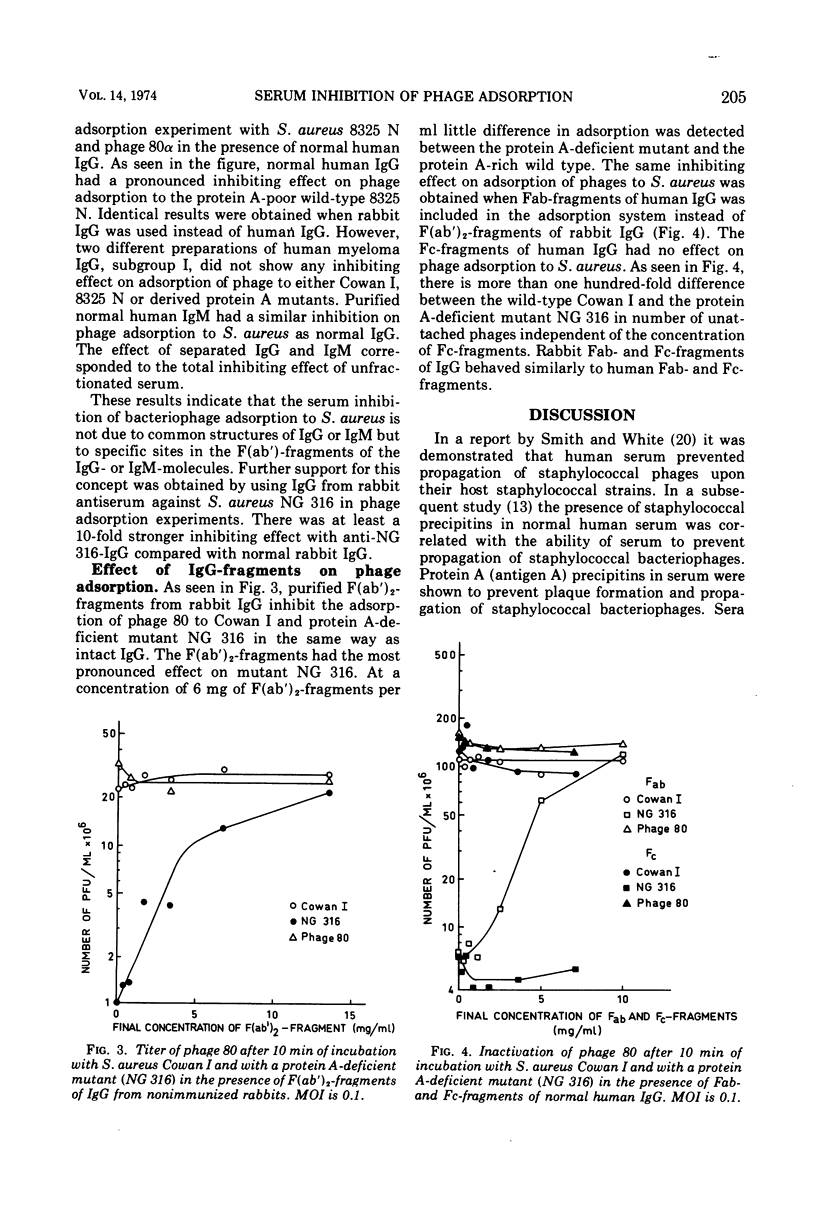
Normal human and rabbit sera when incubated with Staphylococcus aureus inhibit the adsorption of bacteriophages. The bacteriophage adsorption was also inhibited by separated normal immunoglobulin M (IgM), F(ab′)2, and Fab-fragments of IgG. No inhibition was obtained with myeloma IgG or Fc-fragments of normal human and rabbit IgG. The results indicate that the serum inhibition of bacteriophage adsorption to S. aureus is not due to a binding of IgG to protein A on the surface of S. aureus.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cerottini J. C., Fitch F. Complement-fixing ability and antibody activity of rabbit F(ab')2 antibody. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1968;34(2):188–200. doi: 10.1159/000230109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatterjee A. N. Use of bacteriophage-resistant mutants to study the nature of the bacteriophage receptor site of Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1969 May;98(2):519–527. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.2.519-527.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coyette J., Ghuysen J. M. Structure of the cell wall of Staphylococcus aureus, strain Copenhagen. IX. Teichoic acid and phage adsorption. Biochemistry. 1968 Jun;7(6):2385–2389. doi: 10.1021/bi00846a048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EKSTEDT R. D. The effect of coagulase on the antibacterial activity of normal human serum against selected strains of Micrococcus pyogenes. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1956 Aug 31;65(3):119–131. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1956.tb36630.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsgren A., Forsum U. Agglutination of Staphylococcus aureus by rabbit sera. Infect Immun. 1972 Apr;5(4):524–530. doi: 10.1128/iai.5.4.524-530.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsgren A., Nordström K., Philipson L., Sjöquist J. Protein A mutants of Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1971 Jul;107(1):245–250. doi: 10.1128/jb.107.1.245-250.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsgren A., Sjöquist J. "Protein A" from S. aureus. I. Pseudo-immune reaction with human gamma-globulin. J Immunol. 1966 Dec;97(6):822–827. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsum U. Agglutination and immunofluorescence studies on surface antigens of S. aureus. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1973 Jun;81(3):314–320. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1973.tb02209.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsum U. Characterization of FITC-labelled F(ab')2 fragments of IgG and a rapid technique for the separation of optimally labelled fragments. J Immunol Methods. 1973 Jan;2(2):183–195. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(73)90015-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JUERGENS W. G., SANDERSON A. R., STROMINGER J. L. Chemical basis for an immunological specificity of a strain of Staphylococcus aureus. J Exp Med. 1963 Jun 1;117:925–935. doi: 10.1084/jem.117.6.925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James A. M., Brewer J. E. A protein component of the cell surface of Staphylococcus aureus. Biochem J. 1968 Jun;108(2):257–262. doi: 10.1042/bj1080257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lind I., Mansa B. Further investigation of specific and non-specific adsorption of serum globulins to Staphylococcus aureus. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1968;73(4):637–645. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1968.tb03221.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin R. R., White A. Prevention of staphylococcal bacteriophage activity by antigen A precipitins in human sera. J Bacteriol. 1968 Jun;95(6):2177–2181. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.6.2177-2181.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NISONOFF A. ENZYMATIC DIGESTION OF RABBIT GAMMA GLOBULIN AND ANTIBODY AND CHROMATOGRAPHY OF DIGESTION PRODUCTS. Methods Med Res. 1964;10:134–141. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nickerson D. S., White J. G., Kronvali G., Williams R. C., Jr, Quie P. G. Indirect visualization of Staphylococcus aureus protein A. J Exp Med. 1970 May 1;131(5):1039–1047. doi: 10.1084/jem.131.5.1039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordström K., Forsgren A. Effect of protein A on adsorption of bacteriophages to Staphylococcus aureus. J Virol. 1974 Aug;14(2):198–202. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.2.198-202.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PORTER R. R. The hydrolysis of rabbit y-globulin and antibodies with crystalline papain. Biochem J. 1959 Sep;73:119–126. doi: 10.1042/bj0730119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw D. R., Chatterjee A. N. O-Acetyl groups as a component of the bacteriophage receptor on Staphylococcus aureus cell walls. J Bacteriol. 1971 Oct;108(1):584–585. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.1.584-585.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sjöquist J., Movitz J., Johansson I. B., Hjelm H. Localization of protein A in the bacteria. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Oct 17;30(1):190–194. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb02086.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J., White A. EFFECT OF HUMAN SERA ON THE PROPAGATION OF STAPHYLOCOCCAL BACTERIOPHAGES. J Bacteriol. 1960 Dec;80(6):741–743. doi: 10.1128/jb.80.6.741-743.1960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Virgilio A R., González P C., Munoz S N., Mendoza G S. Ability of Staphylococcus aureus Cells to Bind Normal Human Immunoglobulin G. Infect Immun. 1970 Sep;2(3):342–344. doi: 10.1128/iai.2.3.342-344.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


