Abstract
Healthcare systems in many low income countries have evolved to provide services for acute, infections and are poorly structured for the provision of chronic, non-communicable diseases which are increasingly common. Epilepsy is a common chronic neurologic condition and antiepileptic drugs are affordable, but the epilepsy treatment gap remains >90% in most African countries. The World Health Organization has recently released evidence-based guidelines for epilepsy care provision at the primary care level. Based upon these guidelines, we estimated all direct costs associated with epilepsy care provision as well as the cost of healthcare worker training and social marketing. We developed a model for epilepsy care delivery primarily by primary healthcare workers. We then used a variety of sources to develop cost estimates for the actual implementation and maintenance of this program being as comprehensive as possible to include all costs incurred within the health sector. Key sensitivity analyses were completed to better understand how changes in costs for individual aspects of care impact the overall cost of care delivery. Even after including the costs of healthcare worker retraining, social marketing and capital expenditures, epilepsy care can be provided at less than $25.00 per person with epilepsy per year. This is substantially less than for drugs alone for other common chronic conditions. Implementation of epilepsy care guidelines for patients receiving care at the primary care level is a cost effective approach to decreasing the epilepsy treatment gap in high gap, low income countries.
Key words: epilepsy, treatment gap, cost, Africa.
Introduction
Evidence-based clinical guideline recommendations for the management of epilepsy at the primary health care level have recently been released by the World Health Organization (WHO) as part of an essential care package for such conditions in the Mental Health Gap Action Programme (mhGAP).1 For mhGAP guidelines to reduce the epilepsy treatment gap in a high gap country like Zambia, healthcare workers will need further training. Once appropriate primary health care level services are in place, epilepsy-associated stigma and misinformation will need to be addressed to encourage people with epilepsy (PWE) and their families to seek medical services.2 We undertook a study to determine the cost of implementing a national epilepsy care program aimed at using these guidelines to scale up epilepsy care and decrease the treatment gap in a low income, high gap country. We have used data from Zambia but the health system structure and infrastructural costs of Zambia are fairly typical of the region and may offer important insights relevant to other sub-Saharan African countries.
Materials and Methods
Zambia ranks among the poorest countries in the world and has an epilepsy treatment gap of >90%.3–5 To address the overall cost of implementing an epilepsy care program using the mhGAP evidence-based guidelines and thus decreasing the epilepsy treatment gap in this high gap, low income country, we developed a model of how such care might be delivered in Zambia if primary healthcare workers could provide the bulk of care. We estimated the cost of this epilepsy care model including optimal referral patterns and an explicit delineation of feasible services to be made available at the primary, secondary and tertiary levels (Figure 1). We then used a variety of sources to develop cost estimates for the actual implementation and maintenance of this program. To assure a realistic cost estimate, we attempted to develop a relatively comprehensive list of all potential direct costs including drug distribution (not just purchase price of antiepileptic drugs, AEDs), marginal capital expenditures, primary healthcare worker training, and social marketing programs to increase healthcare seeking among PWE. Given the uncertain nature of many of the estimates, a number of sensitivity analyses were conducted to determine which program items/activities, when subject to reasonable variability, would substantially change the overall program cost (Table 1).6–8 Costs were estimated in US Dollars with the appropriate conversion based upon global exchange rates in December 2010. We assessed costs separately for each level of healthcare delivery: primary, secondary and tertiary. Costs for each level that were explicitly included in our costing assessment included: drug purchasing and distribution, personnel costs for healthcare workers, diagnostic tests, proportionate use of healthcare facilities through capital expenditures for the healthcare facility including depreciation costs, the costs of (re)training non-physician healthcare workers, and the costs associated with an annual social marketing campaign. Cost estimates were based upon actual costs from the Ministry of Health budget and/or published costs of antiepileptic drugs for bulk purchase during the time of the assessment.
Figure 1.
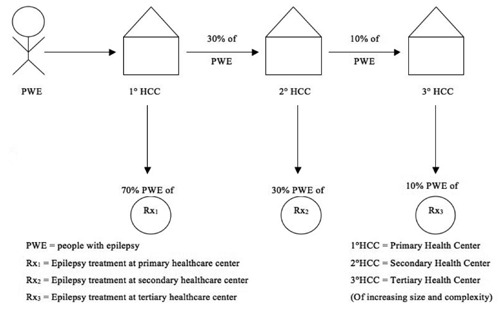
Flow of patients through proposed health model.
Table 1. Cost estimate sources and sensitivity analysis.
| Estimate | Source | Description/adaptation | Sensitivity analysis |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of people with epilepsy requiring treatment | Previously conducted door-to-door survey5 | Extrapolated findings and assumed no treatment offered to individuals seizure free for more than 1 year off treatment | We assessed a 10% reduction in number of PWE in urban vs. rural region (survey data is from rural) |
| Labor costs: primary and Secondary levels | Reports from Ministry of Health6,7 | Marginal costs of labor | We assessed a 20% increase in staffing costs |
| Labor costs: tertiary level | Estimated based upon costs for specialist consultant time + nurse time | Assumed new patient requires 30 minutes and follow-up 15 minutes from consultant and that each visit requires 10 minutes of nursing staff time. Estimates based upon actual salaries and number of patients seen in an epilepsy clinic session at University Teaching Hospital. | We evaluated the effect of increasing the number of annual visits at the tertiary level from annually to quarterly. Assumes patient is referred back to primary level for continuing care. |
| Diagnostic tests: primary and secondary level | Reports from Ministry of Health6,7 | Marginal costs for diagnostic tests | Not applicable |
| Diagnostic tests:tertiary level | Estimates based upon costs estimated from tertiary care clinic | Includes head CT, but not EEG | Not applicable |
| Capital expenses:primary and secondary levels | Average facility capital costs (facility maintenance, power, etc.) | Estimated proportionate usage | We assessed the impact of proportionate usage ranging from 0.1–3%. |
| Capital expenses: tertiary level | Estimated rental and utilization costs for space within tertiary facility | Assumes specialty clinic sole usage is epilepsy care | Not applicable |
| Medication purchasing | Published costs for 20078 | Assumes purchasing in bulk for best prices. | We compared the least vs. most expensive wholesale listed purchase price of first line AED at primary healthcare level |
| Medication distribution | 2010 Zambian Medical Stores Annual Budget | Proportionate costing | We estimated costs based upon proportionate usage ranging from 0.1–3% |
| Training | Program to train 10% of staff at primary care clinics in the basic treatment of epilepsy | 1 week course and training materials to be held in each province for skilled workers at the primary health care centers. | Not applicable |
| Social marketing to increase care seeking (annual campaign) | Estimates based upon costs of existing social marketing program | Includes radio, TV, posters, etc. | Not applicable |
PWE, people with epilepsy; CT, computed tomography; EEG, electroencephalogram.
Target population for care
A door-to-door survey of epilepsy prevalence was conducted in 2000–2001 in a rural region of Zambia, which identified a minimum of 12.5/1000 PWE who had experienced seizures in the past 12 months.5 Later follow-up identified a significant number of people who had initially denied the condition but who then admitted to having epilepsy after treatment services became broadly available thus increasing the prevalence to 14.2/1000.2 The recommended epidemiologic estimate of epilepsy prevalence includes all PWE who have either been on treatment or had a seizure in the past five years,9 but since PWE in Zambia who have been seizure free for more than a year off treatment are unlikely to be given antiepileptic drugs, our model only includes PWE who have had a seizure or been on treatment in the past year. Including only those PWE who are presently on treatment and/or have had a seizure in the past year, the existing epilepsy prevalence data and the most recent census data, we estimated the number of people in Zambia with epilepsy who had a seizure in the past year to be at least 170,000. The treatment gap in the prevalence study was >95%, but given greater service availability in urban regions of Zambia we estimated the baseline treatment gap to be 90%.
Available services
Services available in our model are described in Table 2 and reflect personnel supported through Ministry of Health (MoH) budget allocations, diagnostic tests available at each level often used to assess seizures,2,6,7 and AEDs included in the Zambian essential drugs list.
Table 2. Services provided at each level.
| Level of care | Care provider | Diagnostics | Medications | Follow-up and referral schedule |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Primary | Clinical officer or nurse | 1. Blood smear for malaria parasites | Phenobarbitone | Monthly for 3 months, then Q 3 monthly thereafter 30% referred to secondary level |
| Secondary* | General physician |
|
Phenobarbitone (80%) Carbamazepine (20%) | Two initial visits for assessment. Referred back to primary level for monthly reviews. Annual assessment at secondary level. 10% referred to tertiary level for care |
| Tertiary | Neurologist | 1. Head computed tomography | Phenobarbitone (50%) Carbamazepine (20%) Valproate (20%) Phenytoin (10%) | Two initial visits for assessment. Referred back to primary level for monthly reviews. Annual assessment at tertiary level. |
Includes care at District Hospitals.
Labor costs
Cost estimates for primary and secondary level personnel were obtained through internal documents from the Zambian MoH in which packages for primary and secondary level healthcare were priced. These packages defined the cost of providing curative intervention and/or disease management for 33 diseases/health conditions within existing public facilities. Medical experts then estimated the amount of staff time required for care provision. Given the volatile nature of civil servants salary in low income countries, the sensitivity analysis includes a 20% increase in labor costs.
Medical examination costs
Diagnostic tests costs were limited to those routinely available at each level of care. Note that at the time of this study, electroencephalogram (EEG) in Zambia was available only through the private sector and the private EEGs available failed to meet any of the standard recommendations for EEG recordings.10 As such, the service was considered to be of insufficient quality for inclusion in the package of care. Head computed tomography (CT) is available at the tertiary level, but associated costs are passed along to the consumer (US $520). We included the cost of head CT as a direct cost in our model with the supposition that if made available to appropriate, selected referrals, CT use would be cost effective.
Capital expenditures
To estimate the marginal additional capital expenditure cost per patient at each level of care the average annual capital expenditures at primary and secondary clinics were obtained through the Ministry of Health and the relative proportion of this to be used by PWE was estimated ranging from 0.1–3% (with an associated range as the treatment gap declines and numbers increase). This broad range was assessed due to the imprecise nature of this estimate. As capital expenditures at the tertiary level were not available and we assumed that there would be condition specific clinics at this level (i.e. an Epilepsy Clinic where 100% of the cases seen have the condition of interest), estimates were based upon rental and utility rates for space at the tertiary care centers.
Medication costs
Drug purchasing
Estimated average costs for medications were based upon international prices for 2007 and the average dose required for a 65 kg adult and a 10 kg child.8 Pediatric syrups are rarely available in Zambia. The common practice entails sectioning adult-size tablets multiple times for pediatric dosing. We assumed this mechanism of drug delivery would be part of the baseline model, but also conducted a sensitivity analysis to assess the marginal additional costs to purchase pediatric AED formulations for children less than five years.
Drug distribution
Drug distribution remains a major challenge in many low and middle income countries and Zambia, with its vast land mass and extreme population density variability (between urban and rural regions) is no exception. Medical Stores is the Division of the MoH responsible for drug distribution. Distribution costs were estimated based upon the annual budget for Zambian Medical Stores and proportionate use of services at 0.1–3%. This broad range of values was assessed since the cost of distributing medications depends largely on fuel costs which can fluctuate wildly based upon regional availability in land-locked Zambia and local currency valuation.
Educational costs
For epilepsy care services to be delivered at the primary health center level in Zambia, non-physician healthcare workers staffing primary clinics must be trained. Physicians are not generally available at the primary clinic level and travel for physician services from rural regions are on average more than 50 km.11 In this program, we included the cost of providing primary healthcare workers with a 1-week training course held within each Province. Costs include sitting fees, training materials (25 page manual), transportation, and accommodation (sitting fees are paid to participants for overload work or to their institutions to cover the cost of locums workers while the attendee is absent from work to attend the training).
Social marketing (increasing healthcare-seeking)
To increase healthcare seeking behaviors, we included the costs of a social marketing campaign. Such a campaign might include any number of media and educational programs. Given the financially elastic nature of such a potential program, we chose to extrapolate costs by using the costs of an established, successful program - the Child Health Week budget.
Results
The costs associated with decreasing the treatment gap from 90–80% are depicted in Table 3. The annual costs of treatment per person with epilepsy were $13.58, $18.81 and $61.63 at the primary, secondary and tertiary levels, respectively. Costs were higher when secondary level care was provided at District Hospitals ($31.79) rather than urban health centers ($18.81). The initial year of treatment at the tertiary care level was $165.63 due to the cost of diagnostic studies, but decreased to $61.63 in subsequent years. Fluctuations in capital expenditures and labor costs had minimal impact on overall costs, but purchasing phenobarbitone at the highest rather than lowest wholesale price increased costs from $13.58 to $74.83. The additional cost associated with training 10% of the primary healthcare workers to provide epilepsy care was marginal at $1.39 per person with epilepsy per year. Social marketing campaigns to increase clinic attendance cost $6.62 per person with epilepsy per year, though this would become substantially more cost effective as the epilepsy treatment gap is further decreased and more people are benefiting from such programs.
Table 3. Costs of an epilepsy care program aimed at decreasing the treatment gap from 90–80%.
| Program item | Baseline cost | Cost change in sensitivity analysis* |
|---|---|---|
| Number of PWE seeking/receiving care | Reduction of treatment gap to 80% for the 170,000 PWE in Zambia | None |
| Rx1 | Labor1+cap1(.1%)+dx1+drugs1 $13.58 per PWE per year | Increase cap costs to 3%= $16.73+20% labor costs= $14.90 Purchase most expensive wholesale phenobarbitone= $74.83 Add pediatric AED formulations for 10% of PWE= $14.88 |
| Rx2 | Labor2+cap2(.1%)+dx2+drugs2 $18.81 per PWE per year at Urban Health Center | +20% labor costs= $21.32 Seen at District Hospital= $31.79 |
| Rx3 | Labor3+cap3(.1%)+dx3+drugs3 $165.63 per PWE per year in diagnosis year | $61.63 per PWE per year after dx |
| Training | 10% of primary care staff $1.39 per PWE | - |
| Social marketing | Sponsoring Epilepsy Week° $6.62 per PWE | - |
PWE, people with epilepsy.
Assumes all other costs remain at baseline model.
Based upon the annual costs of Child Health Week.
Discussion
There are several limitations to this analysis. While the mhGAP guidelines are based upon evidence, there is little available evidence regarding what feasible system of epilepsy care delivery would be the most effective in a low income, high gap region. We developed the model here based upon group consensus with a group that included Zambian clinicians, health services researchers, neurologists, and healthcare economists. Certainly other potential models exist, for example mobile care delivery, and these too deserve consideration. Although the model is predicated upon epilepsy care delivery by non-physician primary healthcare workers, no formal studies have established that this cadre of worker can actually provide adequate care-though some indirect data does exist.12 Despite this lack of evidence, the mhGAP programme developed by WHO is predicated on the delivery of epilepsy care by non-physician healthcare workers making this the relevant approach for financial analysis. Finally, although we tried to include reasonable ranges of variability in our sensitivity analysis, the model presented was simplified to show single item variation and more complex models might reveal other results.
The burden of non-communicable diseases (NCDs), such as epilepsy, in low income countries is increasing and in some regions now exceeds the burden of infectious disorders.13 Unfortunately, the capacity of developing country health care systems to cope with the dual burden of infectious and NCDs is limited not only by resource availability but also by health care systems that evolved with the purpose of providing brief curative interventions for conditions such as malaria and pneumonia. These healthcare systems are often poorly staffed and structured to manage the challenges of chronic disease care. Provision of affordable care for common NCDs will require a significant proportion of this care be made available at the primary care level with only selected cases referred for higher level care. Though formal assessments are limited regarding the quality of care that can be delivered at the primary care level by non-physicians, studies in some low income regions have shown that using guidelines appropriate for such settings can result in reasonable service delivery.14 Both direct and indirect costs of care increase substantially with higher level services. If sufficient care can be offered at a local level, access is optimized and cost contained.
The WHO recognizes epilepsy as one of the most cost effective conditions to treat.15 Unfortunately, epilepsy often goes untreated altogether in low income countries.16 Effective medications are inexpensive and nonphysician primary healthcare workers can be trained to adequately treat the condition,17 but access still remains problematic.18 Furthermore, since non-physician primary healthcare workers in most low incomes regions are inadequately trained in epilepsy management, epilepsy cases presenting at the primary level often go unrecognized or are referred for higher level services where healthcare is substantially more costly. Furthermore, referrals for higher level services entail indirect costs (transportation, user fees) that are significant barriers for people with epilepsy who often already face marginal economic subsistence.11,19 Under these circumstances, patients and their families may choose to forego treatment altogether or seek care through locally available traditional healers.20,21
The cost of providing epilepsy care at the primary care level in Zambia is about $13.58–18.81 annually, which is quite comparable to the cost of epilepsy care provision at the primary care level in China based upon data from the China demonstration project which was $11.02–21.96.22 Importantly, the cost of reducing the epilepsy treatment gap in Zambia by providing epilepsy care at the primary healthcare level is quite modest compared to treatment for other common chronic conditions. For example, the annual drug cost alone for first line antiretroviral therapies in Zambia is $147.50–177.00 per patient annually.23 Estimates for other non-communicable conditions in Zambia are not available, but direct costs for diabetes care in Sudan are estimated to be $175/person/year.24 The necessary healthcare worker training programs and social marketing campaigns add only marginal additional costs and even including these expenses epilepsy care provision would be <$25.00 per person per year. Evidence suggests that these modest expenditures in epilepsy care could avert 150–650 disability-adjusted life years per 1,000,000 population.25
The potential fiscal benefits of decreasing the epilepsy treatment gap were not included in this analysis, but deserve consideration. In terms of savings to the healthcare sector, ample data indicate that people with untreated epilepsy experience high rates of seizure related injuries, especially burns.4,5,26 Although these individuals may not seek medical services for their epilepsy, they do bring their seizure-related injuries to medical attention.4 Furthermore, such burns may result in permanent disabilities.4,26 Recurrent seizures also result in lost educational opportunities,27 lost employment opportunities,19 and lost time from work for caregivers.19,28
The most cost effective means of improving epilepsy care will ultimately be to provide sufficient training to healthcare providers during their primary training as opposed to in-service training. Now that WHO-endorsed evidence-based guidelines for epilepsy care at the primary care level are available, implementation research is needed to assess the cost effectiveness and utility of epilepsy care - keeping in mind the standard of epilepsy care in most low income countries today is no care at all.
Conclusions
Evidence-based epilepsy care guidelines can be implemented in high gap, low income countries at a cost substantially less than that of other common chronic conditions, even when including the cost of healthcare worker training and social marketing campaigns.
References
- 1.WHO. [Accessed on: 27 April 2012];WHO mental health gap action programme 2011. Available from: http://www.who.int/mental_health/mhgap/en/index.html.
- 2.Baskind R, Birbeck GL. Epilepsy-associated stigma in sub-Saharan Africa: the social landscape of a disease. Epilepsy Behav. 2005;7:68–73. doi: 10.1016/j.yebeh.2005.04.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.WorldBank. [Accessed on: 9 March 2006];Zambia-Country brief. Available from: http://web.worldbank.org/WBSITE/EXTERNAL/COUNTRIES/AFRICAEXT/ZAMBIA;2005.
- 4.Birbeck GL. Seizures in rural Zambia. Epilepsia. 2000;41:277–81. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1157.2000.tb00156.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Birbeck GL, Kalichi EM. Epilepsy prevalence in rural Zambia: a door-to-door survey. Trop Med Int Health. 2004;9:92–5. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-3156.2003.01149.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Zambian Ministry of Health. Costing First Level Basic Health Care Package in Zambia; Lusaka. Presentation to the Central Board of Health; 2001November. [Google Scholar]
- 7.Zambian Ministry of Health. Final Report: Costing at the Secondary Health Care Level in Zambia; Lusaka. Presentation to the Central Board of Health; 2003 April. [Google Scholar]
- 8.Frye J. International drug price indicator guide. DFID. 2007 [Google Scholar]
- 9.Shorvon SD. The epidemiology and treatment of chronic and refractory epilepsy. Epilepsia. 1996;37(suppl 2):S1–S3. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1157.1996.tb06027.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.ACNS. Guideline 1: Minimum technical requirements for performing clinical electroencephalography. J Clin Neurophysiol. 2006;23:86–91. doi: 10.1097/00004691-200604000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Birbeck GL, Munsat T. Neurologic services in Sub-Saharan Africa: a case study among Zambian primary healthcare workers. J Neurol Sci. 2002;200:75–8. doi: 10.1016/s0022-510x(02)00132-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Rwiza HT. The Muhimbili epilepsy project, a three pronged approach. Assessment of the size of the problem, organization of an epilepsy care system and research on risk factors. Trop Geogr Med. 1994;46:S22–4. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Maher D, Sekajugo J, Harries AD, Grosskurth H. Research needs for an improved primary care response to chronic non-communicable diseases in Africa. Trop Med Int Health. 2010;15:176–81. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3156.2009.02438.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Farzadfar F, Murray CJ, Gakidou E, et al. Effectiveness of diabetes and hypertension management by rural primary healthcare workers (Behvarz workers) in Iran: a nationally representative observational study. Lancet. 20;379:47–54. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(11)61349-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.WHO. Geneva, Switzerland: WHO Press; 2006. Neurological disorders: public health challenges; pp. 218–218. [Google Scholar]
- 16.Meyer A, Dua T, Ma J, et al. Global disparities in care for epilepsy: a systematic review and analysis of variation of the epilepsy treatment gap. Bulletin of the World Health Organization. 2010;88:260–6. doi: 10.2471/BLT.09.064147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Liu L, Zhang Q, Yao Z, et al. The operational model of a network for managing patients with convulsive epilepsy in rural West China. Epilepsy and Behavior. 2010;17:75–81. doi: 10.1016/j.yebeh.2009.10.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Chomba EN, Haworth A, Mbewe E, et al. The current availability of antiepileptic drugs in Zambia: implications for the ILAE/WHO out of the shadows campaign. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2010;83:571–4. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.2010.10-0100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Birbeck G, Chomba E, Atadzhanov M, et al. The social and economic impact of epilepsy in Zambia: a cross-sectional study. Lancet Neurol. 2007;6:39–44. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(06)70629-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Birbeck G, Kalichi E. Health services in Zambia: the primary healthcare workers' perspective. Tropical Doctor. 2004;2004:84–6. doi: 10.1177/004947550403400208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Baskind R, Birbeck G. Epilepsy care in Zambia: a study of traditional healers. Epilepsia. 2005;46:1121–6. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1167.2005.03505.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Ding D, Hong Z, Chen GS, et al. Primary care treatment of epilepsy with phenobarbital in rural China: cost-outcome analysis from the WHO/ILAE/IBE global campaign against epilepsy demonstration project. Epilepsia. 2008;49:535–9. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1167.2007.01529_2.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.The Clinton Foundation. Antiretroviral (ARV) Price List. Clinton Health Access Initiative, 2010. 2010 Nov; [Google Scholar]
- 24.Elrayah-Eliadarous H, Yassin K, Eltom M, et al. Direct costs for care and glycaemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes in Sudan. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 2010;118:220–5. doi: 10.1055/s-0029-1246216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Chisholm D. Cost-effectiveness of first-line antiepileptic drug treatments in the developing world: a population-level analysis. Epilepsia. 2005;46:751–9. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1167.2005.52704.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Jilek-Aall L, Rwiza HT. Prognosis of epilepsy in a rural African community: a 30-year follow-up of 164 patients in an outpatient clinic in rural Tanzania. Epilepsia. 1992;33:645–50. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1157.1992.tb02341.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Birbeck GL, Chomba E, Atadzhanov M, et al. Zambian teachers: what do they know about epilepsy and how can we work with them to decrease stigma? Epilepsy Behav. 2006;9:275–80. doi: 10.1016/j.yebeh.2006.06.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Chomba E, Haworth A, Atadzhanov M, et al. Family environment and influence on children with epilepsy. Zambian Medical Journal. 2008;34:116–9. [Google Scholar]


