Abstract
Background and purpose
Historically, the treatment of periprosthetic femoral fractures (PFFs) has been associated with a high frequency of complications and reoperations. The preferred treatment is internal fixation, a revision of the femoral stem, or a combination of both. An improved understanding of plate use during internal fixation, and the introduction of locking-plate osteosynthesis may lead to improved outcome. We evaluated the outcome of Vancouver type B1 and C PFFs treated by locking-plate osteosynthesis, by assessing rates of fracture union and reoperations and by analyzing failure cases.
Patients and methods
From 2002 through 2011, 58 consecutive patients (60 fractures) with low-energy PFF around or below a stable femoral stem, i.e. Vancouver type B1 and C fractures, underwent osteosynthesis with a locking plate. All patients had a total hip replacement (THR). They were followed up clinically and radiographically, with 6 weeks between visits, until fracture union or until death. Fracture union was evaluated 6 months postoperatively.
Results
At a median follow-up time of 23 (0–121) months after PFF, 8 patients (8 fractures) had been reoperated due either to infection (n = 4), failure of fixation (n = 3), or loosening of the femoral stem (n = 1). All the patients who had been followed up for at least 6 months—and who did not undergo reoperation or die—went on to fracture union (n = 43).
Interpretation
Locking-plate osteosynthesis of periprosthetic Vancouver type B1 and C fractures gives good results regarding fracture union. It appears that spanning of the prosthesis to avoid stress-rising areas is important for successful treatment. Infection is the major cause of failure.
Data from the Mayo Clinic Joint Replacement Database has shown a 1% prevalence of periprosthetic femoral fractures (PFFs) after primary total hip replacement (THR) (238 of 23,980) and a prevalence of 4% after revision THR (252 of 6,349) (Berry 1999). With increasing numbers of THRs, the incidence of PFF is on the rise (Lindahl et al. 2005). Treatment of PFF can be technically demanding, with a high frequency of complications and reoperations (Lindahl et al. 2006, Giannoudis et al. 2007, Zuurmond et al. 2010). Nonoperative treatment (McElfresh and Coventry 1974, Scott et. al 1975, Mont and Maar 1994) has been abandoned due to high mortality, and the preferred treatment today is internal fixation, a revision of the femoral stem, or a combination of both. The Vancouver classification has become the universally accepted one, and it is used to guide the surgeon in the choice of treatment (Duncan and Masri 1995, Masri et al. 2004) (Table 1).
Table 1.
The Vancouver classification system
| Type | Subtype | Fracture description | Treatment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Type A | Fracture in trochanteric region | ||
| AG | Fractures of the greater trochanter | Conservative or cable wires | |
| AL | Fractures of the lesser trochanter | Conservative or cable wires | |
| Type B | Fracture around stem or just below it | ||
| B1 | Well-fixed stem | ORIF | |
| B2 | Loose stem with good proximal bone stock | Revision THR | |
| B3 | Loose stem with poor-quality bone stock | Revision THR | |
| Type C | Fracture occurring well below the tip of the stem | ORIF |
ORIF: open reduction and internal fixation; THR: total hip replacement.
Previous reports have recommend that the plate used for internal fixation must be of sufficient length to allow as much overlap of the femoral stem as possible (Ricci et al. 2006, Ehlinger et al. 2010). Spanning of most of the femur appears to be mechanically advantageous for patients with Vancouver type B1 and C fractures (Fulkerson et al. 2006). During the last decade, locking-plate osteosynthesis has been introduced in the treatment of PFF. Due to the higher strength of fixation offered with this technique, treatment outcomes could improve.
We evaluated the outcome of Vancouver type B1 and C PFF in THR patients who were treated by locking-plate osteosynthesis by assessing rates of fracture union and reoperations. Based on analysis of failures, our aim was to make recommendations for improvement of treatment algorithms.
Patients and methods
From May 2002 through October 2011, 68 consecutive patients with low-energy Vancouver type B1 and C PFF around or below a THR presented at our hospital (70 fractures). AP and lateral radiographs were classified according to the Vancouver classification. Vancouver type A involves fracture in the trochanteric region, type B in the diaphysis, including or just distal to the tip of the stem, and type C involves fracture in the diaphysis well distal to the tip of the stem (Duncan and Masri 1995, Brady et al. 1999). Type A and B were classified further as shown in Table 1.
The following parameters regarding the status of the hip at the time of PFF were assessed from the radiographs and patients files: femoral stem type (primary or revision), mode of fixation (cemented or cementless), Vancouver type, operative technique (conventional open or minimally invasive), implant used for osteosynthesis, and plate overlap as percentage of stem length (Table 2; see Supplemantary data).
Surgeons with special interest in trauma surgery performed the operations using either minimally invasive percutaneous osteosynthesis (MIPO) or open reduction and internal fixation (ORIF). The locking plates used were either locking compression plates (LCP, Synthes) or less invasive stabilization system (LISS, Synthes). MIPO was performed with the patient in the supine position on a radiolucent table. The plate was placed on the bone through a distal, lateral approach. First, fixation was achieved in the distal segment and indirect reduction techniques were used to reduce the fracture before fixation to the proximal segment.
ORIF was performed with the patient in the lateral decubitus position on a radiolucent table. A long skin incision and subvastus approach to the lateral femur was used. Care was taken to protect the periosteum and only retract it at the fracture edge, to allow reduction before sliding the plate into position. The plate was fixed to the bone with bicortical conventional screws before securing it further with locking screws. Locked unicortical screws were used against the prosthesis if bicortical screws could not be passed anterior or posterior to the stem. Cables (n = 3), locking attachment plates (n = 4) (LAP, Synthes), or both (n = 9) were used according to the surgeon’s preference. Femoral stem stability was assessed on preoperative radiographs; however, intraoperative testing was not performed. Drains were not used. Preoperative antibiotics (intravenous Cefuroxime, 1.5 g) and thromboprophylaxis were administered to all patients.
Postoperatively, the patients were mobilized either with full weight bearing or partial weight bearing: about 15 kg for the first 6 weeks on the operated extremity. With 6 weeks between visits, the patients were assessed clinically and radiographically in the outpatient clinic at least until fracture union, or until death when this preceded fracture union. Fracture union was evaluated on the radiographs taken 6 months postoperatively. In cases in which relative stability of the fracture complex was achieved, we considered fracture union when 3 out of 4 cortices had bridging callus in anteroposterior and lateral views. In cases in which absolute stability had been achieved, fracture union was considered when patients had no pain when walking and the radiographs showed no evidence of loosening of screws or fracture dislocation.
Confidence intervals (CIs) were calculated using the immediate command in the STATA software package (version 10.1).
Results
Patients treated with osteosynthesis other than locking-plate osteosynthesis were excluded (n = 10). Thus, 60 fractures remained for study: 15 fractures in 14 males and 45 fractures in 44 females. Median age at operation was 78 (49–97) years. The median follow-up after PFF surgery was 23 (0–121) months (Table 2). At follow-up, 28 patients (30 fractures) were deceased. 9 had died less than 6 months after they experienced the PFF, and thus fracture union was not evaluated. 43 fractures went on to union. 8 fractures were reoperated 1–36 months after PFF surgery (rate = 0.13, CI: 0.06–0.25) (Table 3).
Table 3.
Patients who were reoperated
| A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | C | MIPO | LISS | 42 | 9 | Loose stem | Revision arthroplasty |
| 15 | B1 | MIPO | LCP | 85 | 10 | Infection | THR removed, antibiotics, revision arthroplasty |
| 19 | C | ORIF | LISS, Cable | 45 | 36 | Failure of fixation | Revision arthroplasty |
| 20 | C | MIPO | LISS | 38 | 4 | Failure of fixation | Osteosynthesis |
| 42 | C | MIPO | LISS | 24 | 17 | Failure of fixation | Revision arthroplasty |
| 43 | B1 | ORIF | LISS | 100 | 17 | Infection | THR removed, antibiotics, revision arthroplasty |
| 59 | B1 | ORIF | LISS, Cable, LAP | 89 | 2 | Infection | THR removed, antibiotics, revision arthroplasty |
| 60 | B1 | ORIF | LISS, Cable, LAP | 100 | 1 | Infection | THR removed, antibiotics, revision arthroplasty |
MIPO: minimally invasive percutaneous osteosynthesis; ORIF: open reduction and internal fixation; LISS: less invasive stabilization system; LCP: locking compression plate; LAP: locking attachment plate.
A Patient no.
B Vancouver type
C Tehnique
D Stem
E Plate overlap of stem length, %
F Time from fracture surgery to reoperation, months
G Cause of reoperation
H Treatment
Reoperation due to infection occurred in 4 patients, all of whom had a type B1 fracture around a primary THR (2 cemented, 2 cementless). 3 of the patients had the PFF operated using ORIF and 1 patient was operated using MIPO technique. They had the THR removed and received antibiotic treatment for at least 6 weeks before a revision arthroplasty was inserted. Reoperation due to failure of fixation occurred in 3 patients following new low-energy falls. Common to these patients was that less than 50% of the stem had been spanned. 2 of them had loosening of the femoral stem and stem revision procedures were performed. The third patient had a stable femoral stem and was reoperated with ORIF, obtaining absolute stability using a locking plate with spanning of the femoral stem and the distal part of the diaphysis (Figure 1). In 1 patient, the stem was initially misinterpreted as being stable on the preoperative radiographic assessments. This patient had a loose stem, and a revision femoral stem was inserted after the fracture had healed.
Figure 1.
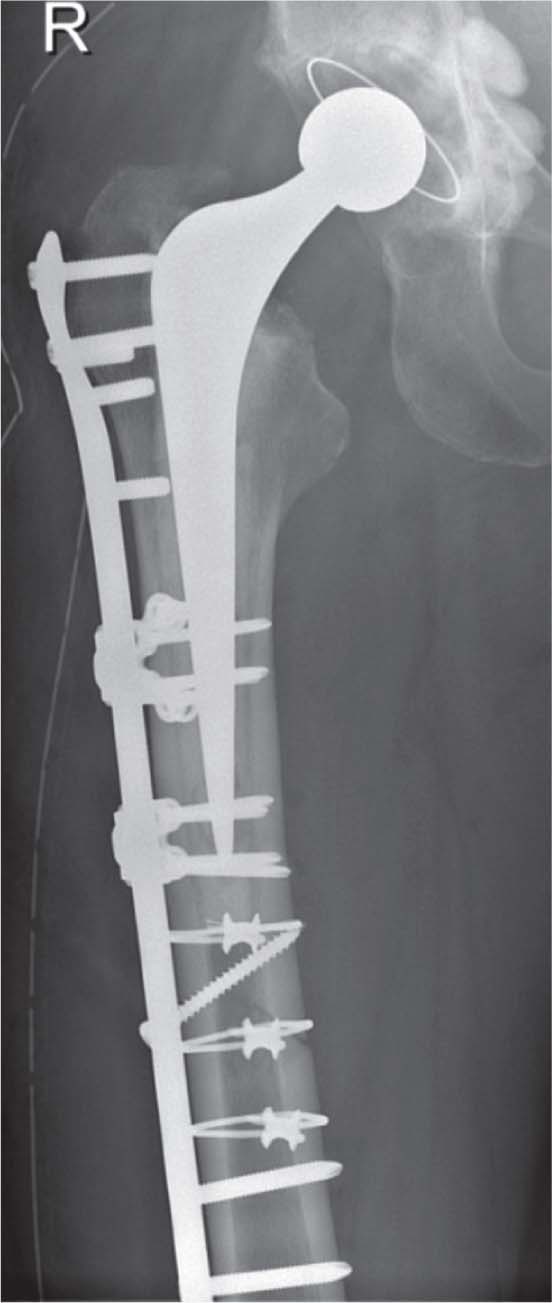
Reoperation after a new fall and loss of fixation (the stem remained stable). Open reduction and internal fixation using a locking plate, additional cable, and locking attachment devices was performed to obtain absolute stability. The locking plate spanned both the femoral stem and the distal part of the femoral diaphysis.
Discussion
The literature on the outcome of PFF treatment often describes a combination of PFF occurring intraoperatively and postoperatively (Jukkala-Pertio et al. 1998), various types and location of the PFF (Jukkala-Partio et al. 1998, Lindahl et al. 2006), fractures occurring in THR and hemiarthroplasties (Stuchin 1990), a combination of spontaneous, minor, or major trauma (Jukkala-Partio et al. 1998, Zuurmond et al. 2010), and different osteosynthesis techniques (Venu et al. 2001, Zuurmond et al. 2010). The present study has several methodological strengths. Firstly, only Vancouver types B1 and C fractures sustained during low-energy falls and treated by locking-plate osteosynthesis were included. Secondly, the Vancouver classification system we used is reproducible, reliable, and valid (Brady et al. 2000, Gohar et al. 2012). Thirdly, patients were operated by surgeons with special interest in trauma, as recommended (Lindahl et al. 2006, Young et al. 2008). Fourthly, the ratio of males to females was 1:3, and the median age at PFF surgery was 78 years, which is comparable to that reported in other studies on PFF in primary and revision THR. Thus, we have no reason to believe that there was bias regarding sex and age (van der Wal et al. 2005, Buttaro et al. 2007, Charkravarthy et al. 2007, Zuurmond et al. 2010). Lastly, Lindahl et al. (2006) described no difference in the outcome of PFF between cemented and cementless stems; thus, both types of fixation were included. The methodological limitations of the study were those inherent in retrospective data collection.
In the present study, the rate of reoperation due to deep infection was 4 of 60 fractures, all 4 of which were of type B1. In other studies, infection rates in type B1 and C fractures have varied from 2 (type B1 fractures) of 94 (Lindahl et al. 2006) to 1 (type B1 fracture) of 12 (Mukundan et al. 2010). The relatively large proportion of reoperations due to deep infections may have been caused by a disturbed blood supply due to prior surgery and tissue damage, as well as a long skin incision. 3 patients were reoperated due to failure of fixation. They had all sustained new low-energy falls, with a fracture occurring at the stress-rising area where the plate overlapped the prosthesis. Common to these patients was the fact that they initially had a type C fracture, where the plate overlapped less than half the length of the prosthesis (Figure 2). It appears likely that fractures could have been prevented if the plate had spanned the length of the femur and if bicortical fixation into the proximal femur had been achieved, as suggested in previous reports (Fulkerson et al. 2006, Ricci et al. 2006, Ehlinger et al. 2010).
Figure 2.
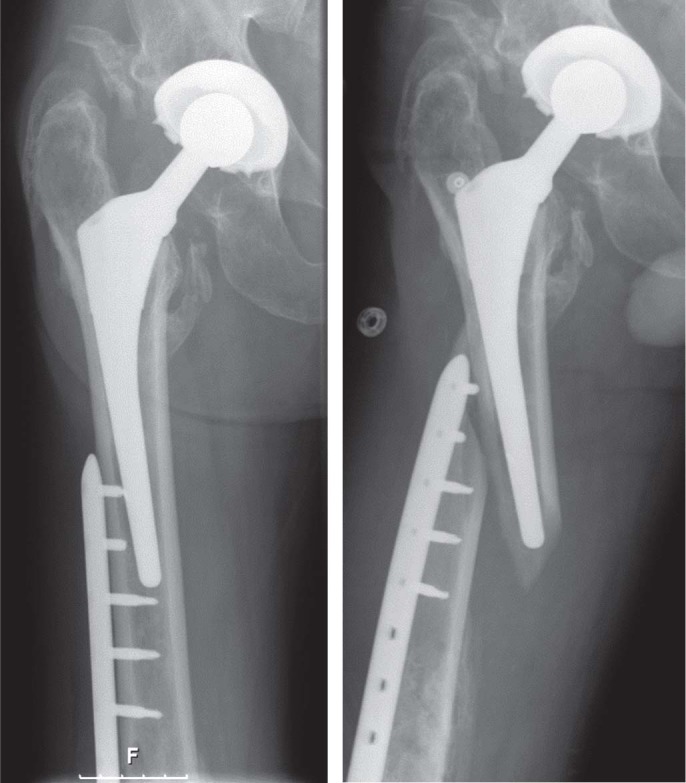
Three patients were reoperated due to failure of fixation. All 3 had experienced a new low-energy fall, with a fracture occurring at the stress-rising area where there was overlap between the plate and the prosthesis.
In 1 case, we misinterpreted the radiographs in a type C fracture occurring in a revision THR and considered the stem to be stable. In 20% of radiographically stable stems, the stem is unstable when tested intraoperatively (Corten et al. 2009). Pike et al. (2009) have suggested that when the stability of the stem is in question, it should be tested intraoperatively. This can be performed using a posterolateral approach to make an arthrotomy and posterior dislocation of the stem, or if the distal aspect of the stem is exposed by generating a shear force along the longitudinal axis. However, as there was only 1 occurrence of radiographic misinterpretation of stem stability in our study, arthrotomy, dislocation of the THR, and testing of stem stability do not seem warranted.
8 of 60 fractures with 2-year follow-up were reoperated due to infection, failure of fixation, or failure to identify a loose femoral stem. In previous studies, reoperation rates for type B1 and C fractures in primary and revision THR have varied from 1 of 12 fractures with 14 months of follow-up (Chakravarthy et al. 2007) to 28 of 97 fractures with 5 years of follow-up (Lindahl et al. 2006). No cases of nonunion were seen in survivors with at least 6 months of follow-up. This is in line with the results of Chakravarthy et al. (2007), who reported union in 10 of 11 type B1 or type C PFFs in THR treated with a locking plate, but it contrasts with the results of Buttaro et al. (2007), who reported union in 8 of 14 type B1 or type C PFFs in primary and revision THR.
In conclusion, locking-plate osteosynthesis of periprosthetic Vancouver type B1 and C fractures gives good results in terms of fracture union. It appears that spanning of the prosthesis to avoid stress-rising areas is important for successful treatment. Infection remains the major cause of failure.
Acknowledgments
LF and MB: study design, collection and analysis of data, and preparation of the manuscript. AT: preparation of the manuscript.
No competing interests declared.
Supplementary data
Table 2 is available at our website (www.actaorthop.org), identification number 5614.
References
- Berry DJ. Epidemiology: Hip and knee. Orthop Clin North Am. 1999;30:183–90. doi: 10.1016/s0030-5898(05)70073-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brady OH, Garbuz DS, Masri BA, Duncan CP. Classification of the hip. Orthop Clin North Am. 1999;30:235–47. doi: 10.1016/s0030-5898(05)70076-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brady OH, Garbuz DS, Masri BA, Duncan CP. The reliability and validity of the Vancouver classification of femoral fractures after hip replacement. J Arthroplasty. 2000;15(1):59–62. doi: 10.1016/s0883-5403(00)91181-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buttaro MA, Farfalli G, Parades Núñez P, Comba F, Piccaluga F. Locking compression plate fixation of Vancouver type B1 periprosthetic femoral fractures. J Bone Joint Surg (Am) 2007;89:1964–9. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.F.01224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakravarthy J, Bansal R, Cooper J. Locking plate osteosynthesis for Vancouver type B1 and type C periprosthetic fractures of femur. A report on 12 patients. Injury. 2007;38(6):725–33. doi: 10.1016/j.injury.2007.02.038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corten K, Vanrykel F, Bellemans J, Frederix PR, Simon JP, Broos PL. An algorithm for the surgical treatment of periprosthetic fractures of the femur around a well-fixed femoral component. J Bone Joint Surg (Br) 2009;91(11):1424–30. doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.91B11.22292. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan CP, Masri BA. Fractures of the femur after hip replacement. Instr Course Lect. 1995;44:293–304. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehlinger M, Adam P, Moser T, Delpin D, Bonnomet F. Type C periprosthetic fractures treated with locking plate fixation with a mean follow-up of 2.5 years. Orthop Trauma Surg Res. 2010;96:44–8. doi: 10.1016/j.rcot.2009.11.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fulkerson E, Koval K, Preston CF, Iesaka K, Kummer FJ, Egol KA. Fixation of periprosthetic femoral shaft fractures associated with cemented femoral stems: a biomechanical comparison of locked plating and conventional cable plates. J Orthop Trauma. 2006;20(2):89–93. doi: 10.1097/01.bot.0000199119.38359.96. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giannoudis PV, Kanakaris NK, Tsiridis E. Principles of internal fixation and selection of implants for periprosthetic femoral fractures. Injury. 2007;38:669–87. doi: 10.1016/j.injury.2007.02.050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gohar AN, Shakoor AB, Awan N. Interobserver and intraobserver reliability and validity of the Vancouver classification system of periprosthetic femoral fractures after hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2012;27(6):1047–50. doi: 10.1016/j.arth.2011.11.021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jukkala-Partio K, Partio EK, Solovieva S, Paavilainen T, Hirvensalo E, Alho A. Treatment of periprosthetic fractures in association with total hip arthroplasty – a retrospective comparison between revision stem and plate fixation. Ann Chir Gynaecol. 1998;87:229–35. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl H, Malchau H, Herberts P, Garellick G. Periprosthetic femoral fractures classification and demographics of 1049 periprosthetic femoral fractures from the Swedish National Hip Arthroplasty Register. J Arthoplasty. 2005;20:857–65. doi: 10.1016/j.arth.2005.02.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl H, Garellick G, Regner H, Herberts P, Malchau H. Three hundred and twenty-one periprosthetic femoral fractures. Jour Bone Joint Surg (Am) 2006;88(6):1215–22. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.E.00457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masri BA, Meek RM, Duncan CP. Periprosthetic fractures evaluation and treatment. Clin Orthop. 2004;(420):80–95. doi: 10.1097/00003086-200403000-00012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McElfresh EC, Coventry MB. Femoral and pelvic fractures after total hip arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg (Am) 1974;56:483–92. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mont MA, Maar DC. Fractures of the ipsilateral femur after hip arthroplasty. A statistical analysis of outcome based on 487 patients. J Arthroplasty. 1994;9:511–9. doi: 10.1016/0883-5403(94)90098-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukundan C, Rayan F, Kheir E, Macdoonald D. Management of late periprostethic femur fractures: a retrospective cohort of 72 patients. Int Orthop. 2010;34:485–9. doi: 10.1007/s00264-009-0815-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pike J, Davidson D, Garbuz D, Duncan CP, O’Brien PJ, Masri BA. Principles of treatment for periprosthetic femoral shaft fractures around well-fixed total hip arthroplasty. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2009;17(11):677–88. doi: 10.5435/00124635-200911000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ricci WM, Bolhofner BR, Loftus T, Cox C, Mitchell S, Borelli J. Jr. Indirect reduction and plate fixation, without grafting, for periprosthetic femoral shaft fractures about a stable intramedullary implant: Surgical technique. J Bone Joint Surg (Am) (Suppl 1) 2006;88:275–82. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.F.00327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott RD, Turner RH, Leitzes SM, Aufranc OE. Femoral fractures in conjunction with total hip replacement. J Bone Joint Surg (Am) 1975;57:494–501. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuchin SA. Femoral shaft fracture in porous and press-fit total hip arthroplasty. Orthop Rev. 1990;19:153–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van der Wal B CH, Vischjager M, Grimm B, Heyligers IC, Tonino AJ. Periprosthetic fractures around cementless hydroxyapatite-coated femoral stems. Int Orthop. 2005;29:235–40. doi: 10.1007/s00264-005-0657-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venu KM, Koka R, Garikpati R, Shenava Y, Madhu TS. Dall-Miles cable and plate fixation for the treatment of peri-prosthetic femoral fractures-analysis of results in 13 cases. Injury. 2001;32:395–400. doi: 10.1016/s0020-1383(01)00009-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young SW, Walker CG, Pitto RP. Functional outcome of femoral periprosthetic fracture and revision hip arthroplasty. A matched-pair study from the New Zealand Registry. Acta Orthop. 2008;79(4):483–8. doi: 10.1080/17453670710015463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuurmond RG, van Wijhe W, van Raay J J AM, Bulstra SK. High incidence of complications and poor clinical outcome in the operative treatment of periprosthetic femoral fractures: An analysis of 71 cases. Injury. Int J Care Injured. 2010;41:629–33. doi: 10.1016/j.injury.2010.01.102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.


