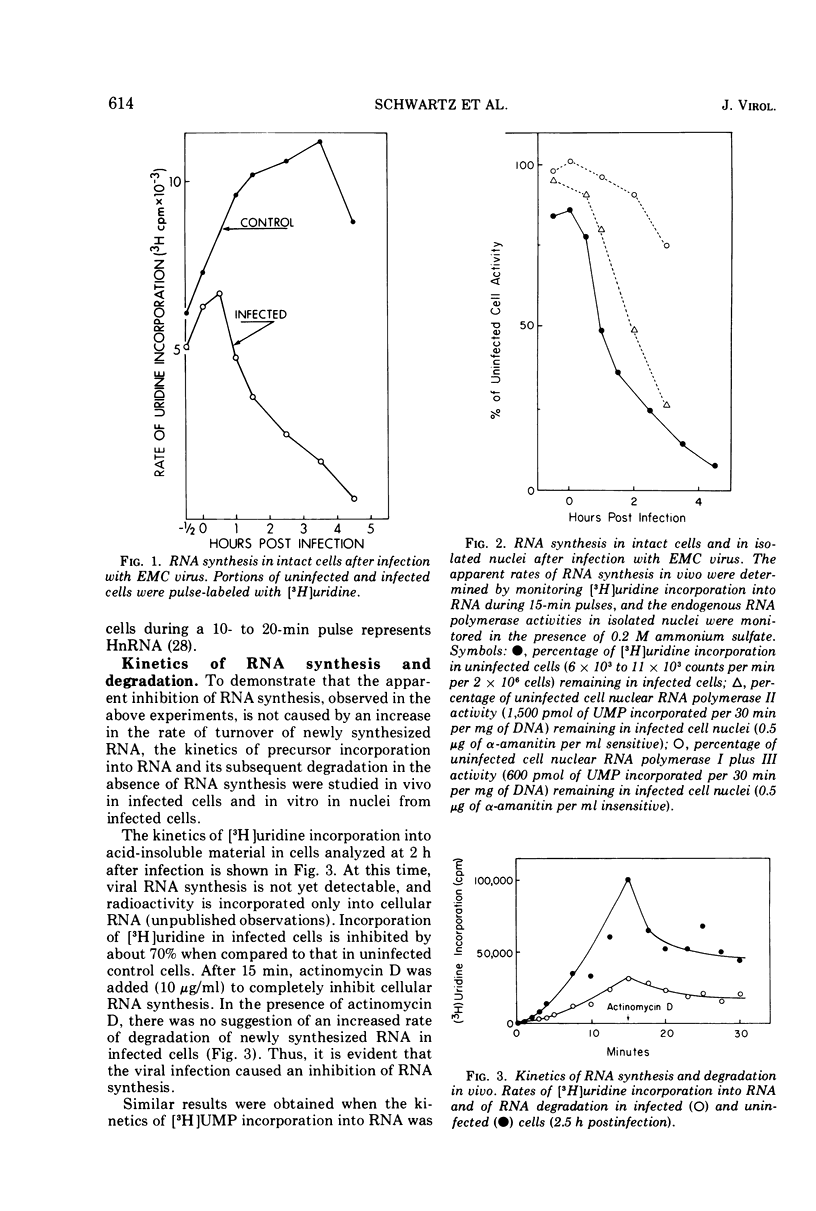
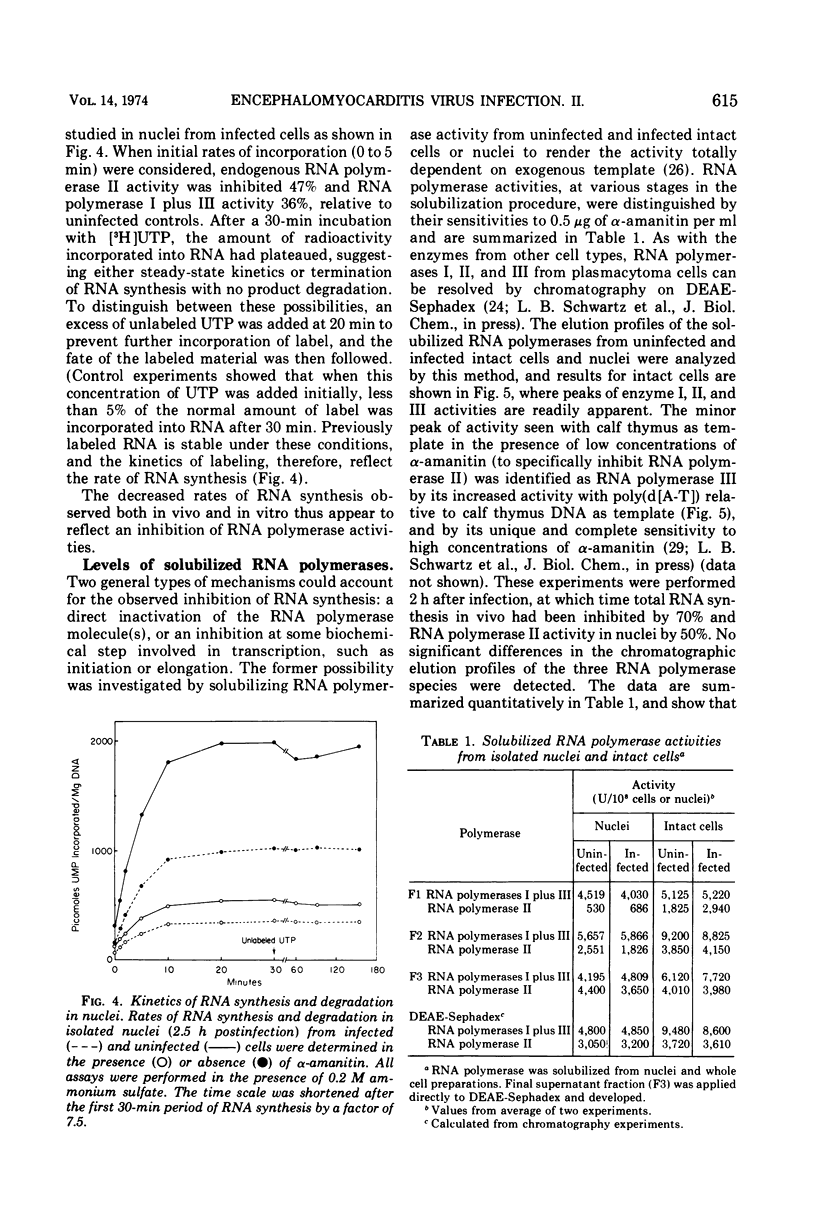
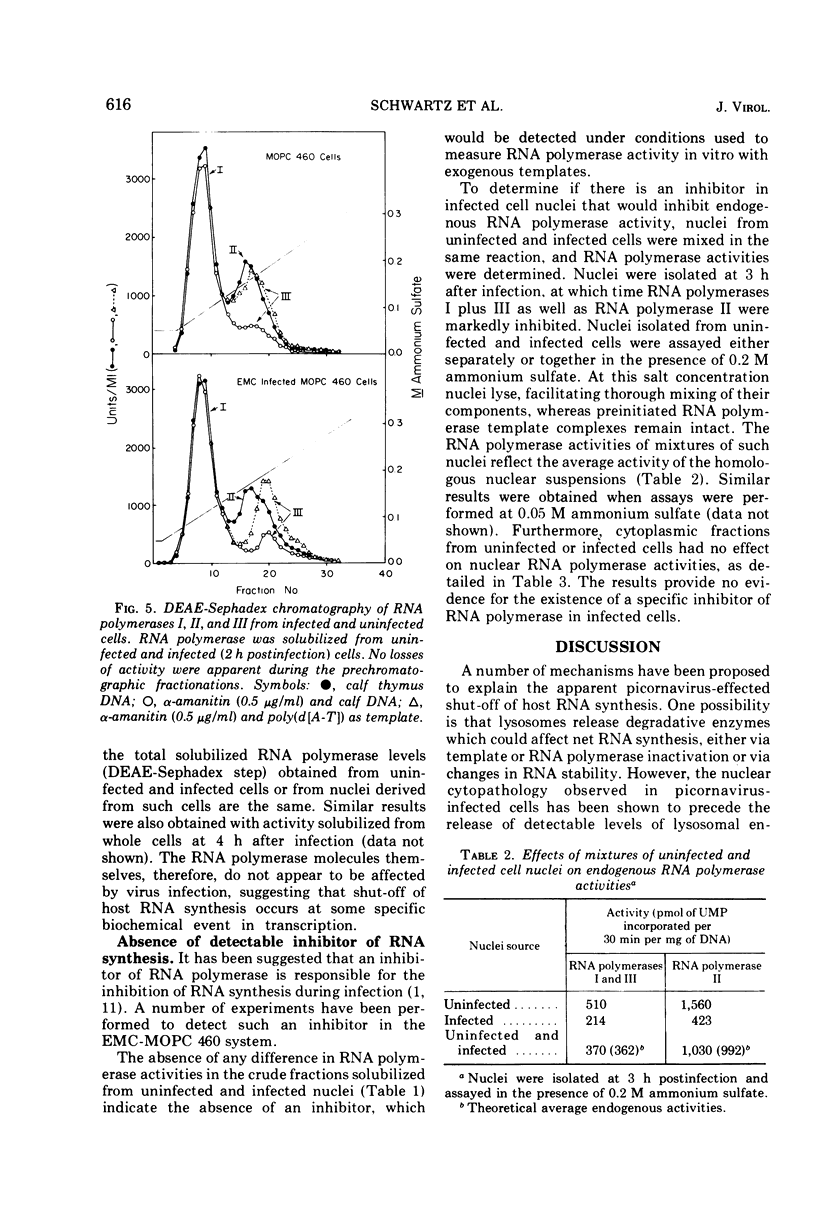
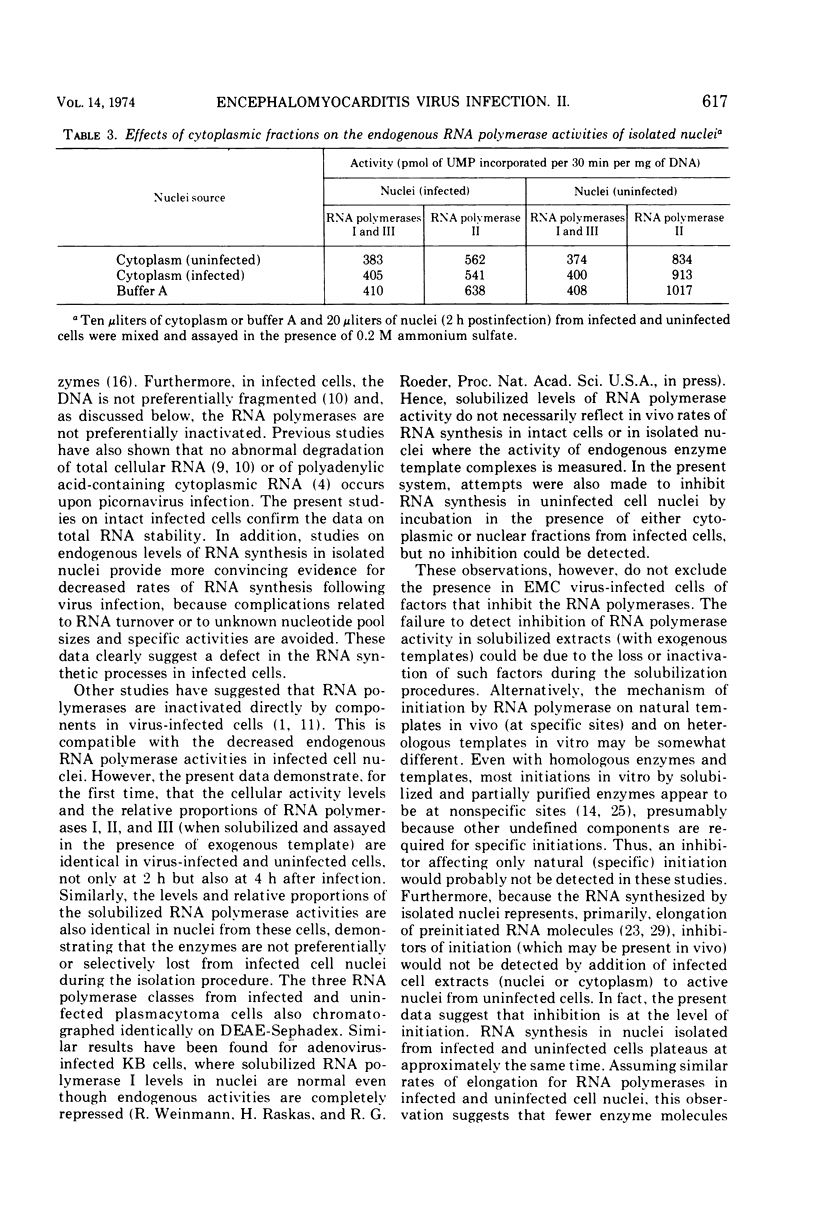
Abstract
The effect of encephalomyocarditis virus infection of MOPC 460 mouse plasmacytoma cells on host RNA synthesis and RNA polymerases was investigated. Consistent with work performed in other virus host systems, rates of RNA synthesis appeared to be inhibited in infected cells, whereas RNA degradation appeared normal. These results were further extended with isolated nuclei, in which distinct RNA polymerase activities could be studied under conditions where problems with RNA turnover and endogenous nucleotide pool sizes were insignificant. Endogenous nuclear RNA polymerase II activity was inhibited early postinfection and at 1 to 2 h prior to endogenous RNA polymerase I plus III activity. However, the solubilized enzymes were fully active with exogenous DNA as template. In fact, the levels of RNA polymerases I, II, and III, isolated from infected cells and nuclei, were indistinguishable from levels in uninfected cells and nuclei at each stage of their partial purification procedure. The chromatographic properties of the enzymes on DEAE-Sephadex were also unaltered. Furthermore, the RNA synthetic activity of these isolated enyzmes, or of nuclei isolated from uninfected cells, was resistant to extracts of nuclei or of cytoplasmic fractions from infected cells. These results are discussed in terms of a possible inhibition of RNA synthesis in vivo at the level of transcription initiation.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Balandin I. G., Franklin R. M. The effect of mengovirus infection on the activity of the DNA-dependent RNA polymerase of L-cells. II. Preliminary data on the inhibitory factor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1964 Feb 18;15(1):27–32. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(64)90097-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colby D. S., Finnerty V., Lucas-Lenard J. Fate of mRNA of L-cells infected with mengovirus. J Virol. 1974 Apr;13(4):858–869. doi: 10.1128/jvi.13.4.858-869.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins F. D., Roberts W. K. Mechanism of Mengo virus-induced cell injury in L cells: use of inhibitors of protein synthesis to dissociate virus-specific events. J Virol. 1972 Nov;10(5):969–978. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.5.969-978.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Contreras G., Summers D. F., Maizel J. V., Ehrenfeld E. HeLa cell nucleolar RNA synthesis after poliovirus infection. Virology. 1973 May;53(1):120–129. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90471-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FENWICK M. L. THE FATE OF RAPIDLY LABELLED RIBONUCLEIC ACID IN THE PRESENCE OF ACTINOMYCIN IN NORMAL AND VIRUS-INFECTED ANIMAL CELLS. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Jul 22;87:388–396. doi: 10.1016/0926-6550(64)90112-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANKLIN R. M., BALTIMORE D. Patterns of macromolecular synthesis in normal and virus-infected mammalian cells. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1962;27:175–198. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1962.027.001.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fan H., Penman S. Regulation of synthesis and processing of nucleolar components in metaphase-arrested cells. J Mol Biol. 1971 Jul 14;59(1):27–42. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90411-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLLAND J. J. Inhibition of DNA-primed RNA synthesis during poliovirus infection of human cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1962 Dec 19;9:556–562. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(62)90125-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLLAND J. J., PETERSON J. A. NUCLEIC ACID AND PROTEIN SYNTHESIS DURING POLIOVIRUS INFECTION OF HUMAN CELLS. J Mol Biol. 1964 Apr;8:556–575. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(64)80011-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho P. P., Washington A. L. Evidence for a cellular ribonucleic acid synthesis inhibitor from poliovirus-infected HeLa cells. Biochemistry. 1971 Sep 28;10(20):3646–3651. doi: 10.1021/bi00796a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honjo T., Reeder R. H. Transcription of Xenopus chromatin by homologous ribonucleic acid polymerase: aberrant synthesis of ribosomal and 5S ribonucleic acid. Biochemistry. 1974 Apr 23;13(9):1896–1899. doi: 10.1021/bi00706a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lake R. S., Ludwig E. H. Cellular changes attending mengovirus-induced cytolysis of mouse L-cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Aug 19;244(2):466–477. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(71)90251-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence C., Thach R. E. Encephalomyocarditis virus infection of mouse plasmacytoma cells. I. Inhibition of cellular protein synthesis. J Virol. 1974 Sep;14(3):598–610. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.3.598-610.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormick W., Penman S. Inhibition of RNA synthesis in HeLa and L cells by Mengovirus. Virology. 1967 Jan;31(1):135–141. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(67)90017-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller H. I., Penhoet E. E. Differential inhibition of nuclear RNA polymerases in L cells infected with mengovirus. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1972 Jun;140(2):435–438. doi: 10.3181/00379727-140-36474. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penman S., Summers D. Effects on host cell metabolism following synchronous infection with poliovirus. Virology. 1965 Dec;27(4):614–620. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(65)90187-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeder R. H., Roeder R. G. Ribosomal RNA synthesis in isolated nuclei. J Mol Biol. 1972 Jun 28;67(3):433–441. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90461-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeder R. H. Transcription of chromatin by bacterial RNA polymerase. J Mol Biol. 1973 Oct 25;80(2):229–241. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90169-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roeder R. G. Multiple forms of deoxyribonucleic acid-dependent ribonucleic acid polymerase in Xenopus laevis. Isolation and partial characterization. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jan 10;249(1):241–248. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roeder R. G., Rutter W. J. Multiple forms of DNA-dependent RNA polymerase in eukaryotic organisms. Nature. 1969 Oct 18;224(5216):234–237. doi: 10.1038/224234a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roeder R. G., Rutter W. J. Specific nucleolar and nucleoplasmic RNA polymerases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Mar;65(3):675–682. doi: 10.1073/pnas.65.3.675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soeiro R., Vaughan M. H., Warner J. R., Darnell J. E., Jr The turnover of nuclear DNA-like RNA in HeLa cells. J Cell Biol. 1968 Oct;39(1):112–118. doi: 10.1083/jcb.39.1.112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinmann R., Roeder R. G. Role of DNA-dependent RNA polymerase 3 in the transcription of the tRNA and 5S RNA genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 May;71(5):1790–1794. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.5.1790. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu F. L., Feigelson P. The rapid turnover of RNA polymerase of rat liver nucleolus, and of its messenger RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Oct;69(10):2833–2837. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.10.2833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zylber E. A., Penman S. Products of RNA polymerases in HeLa cell nuclei. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Nov;68(11):2861–2865. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.11.2861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



