Abstract
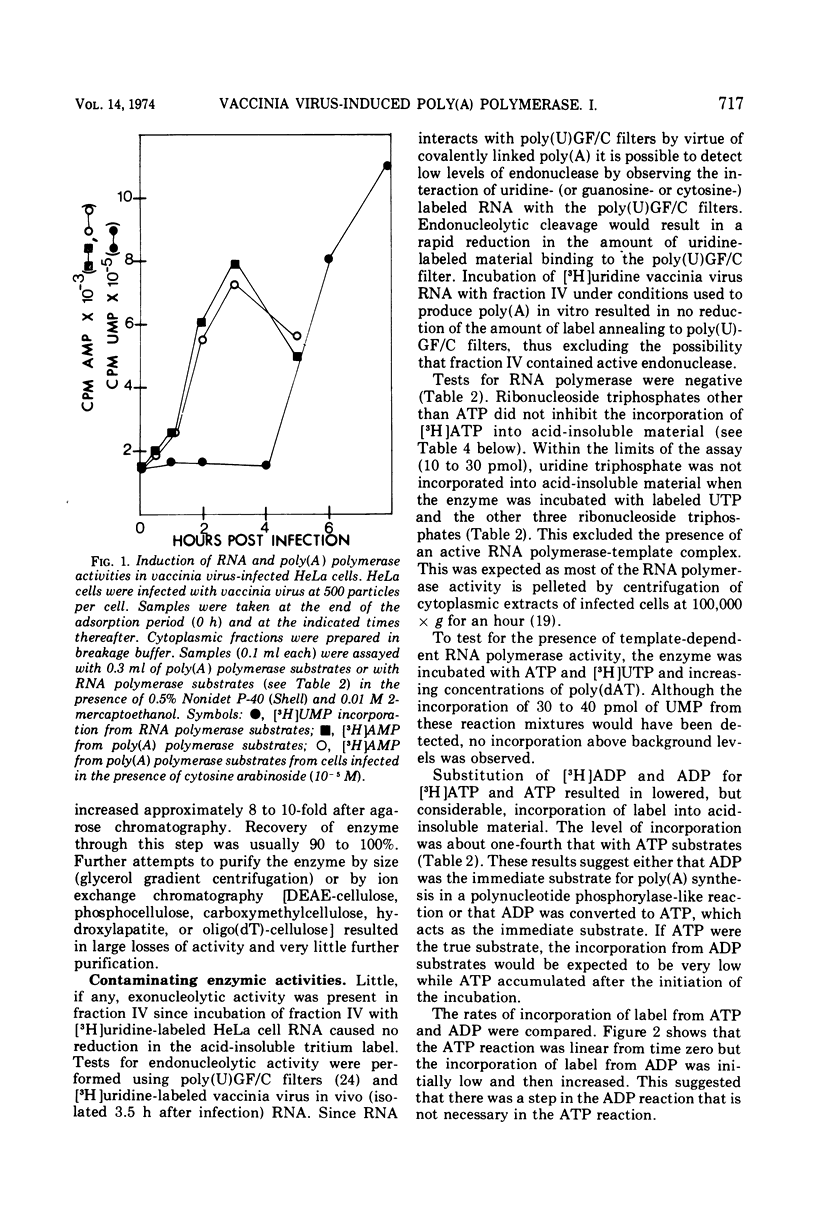
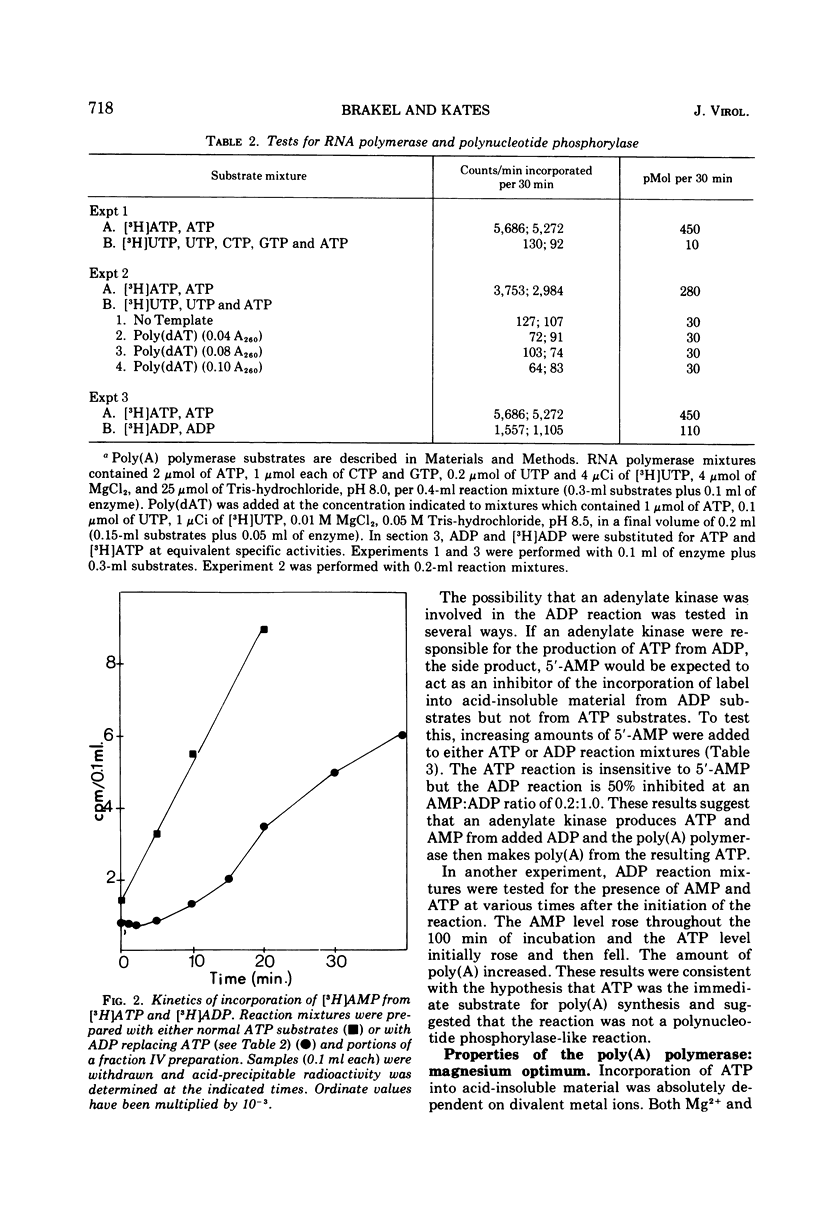
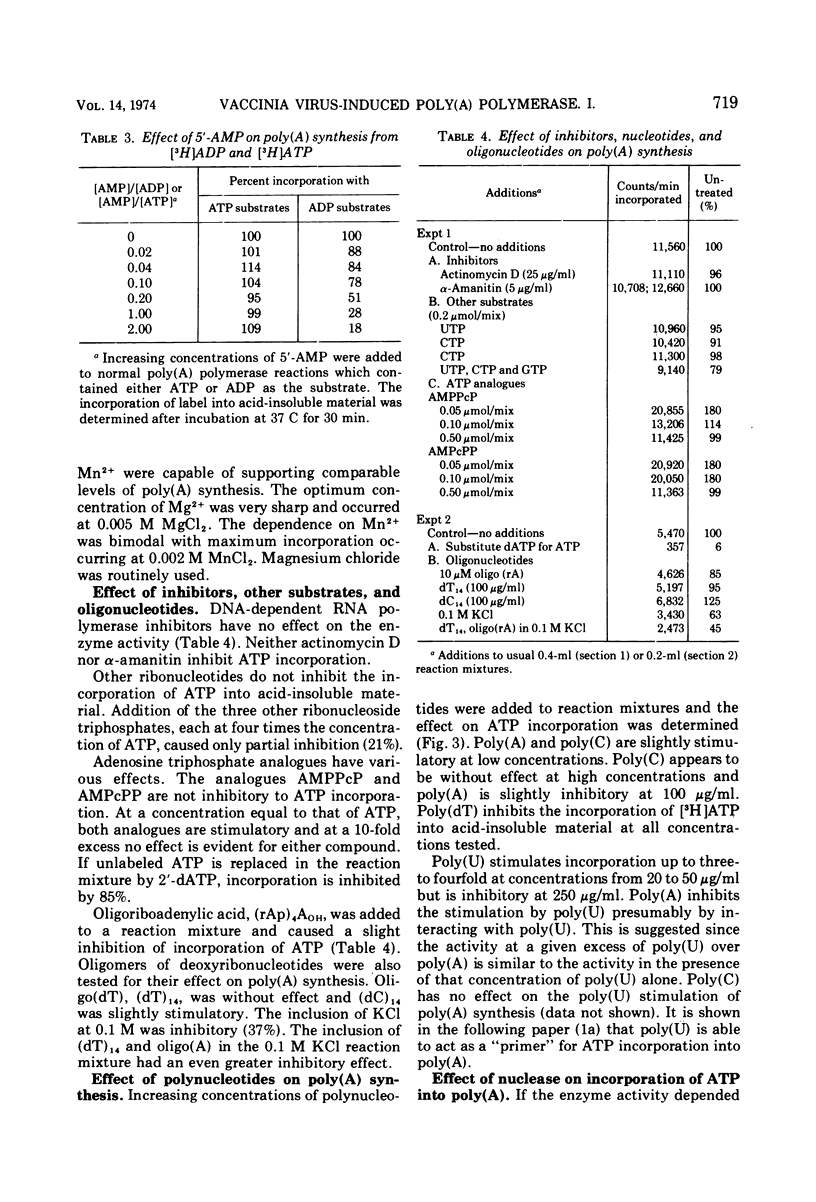
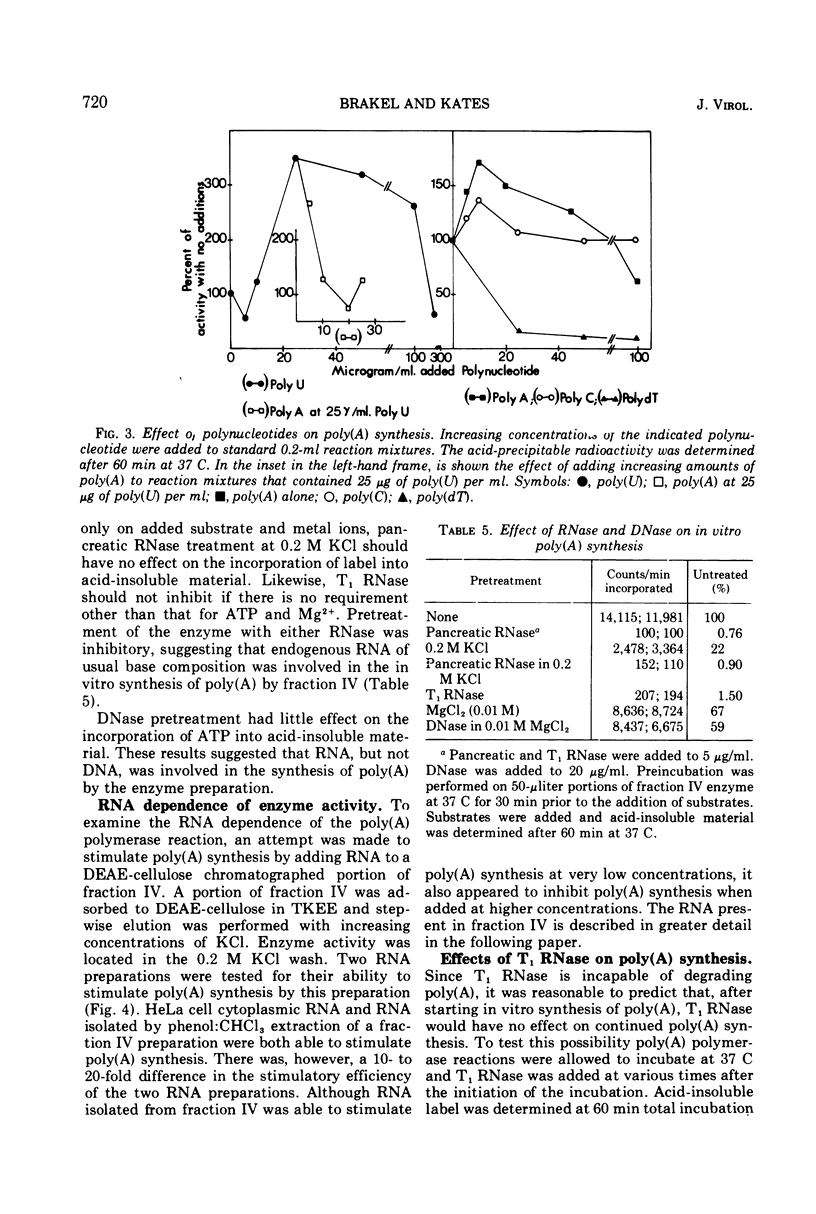
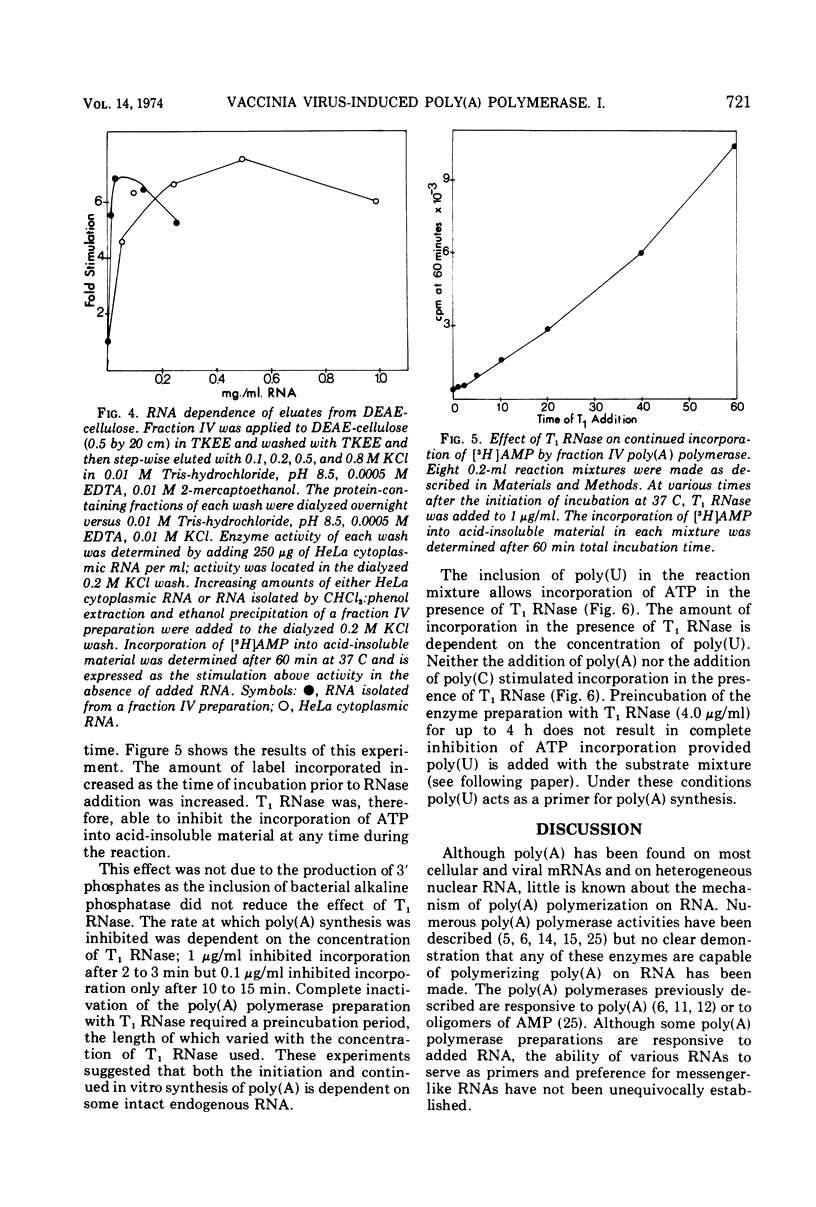
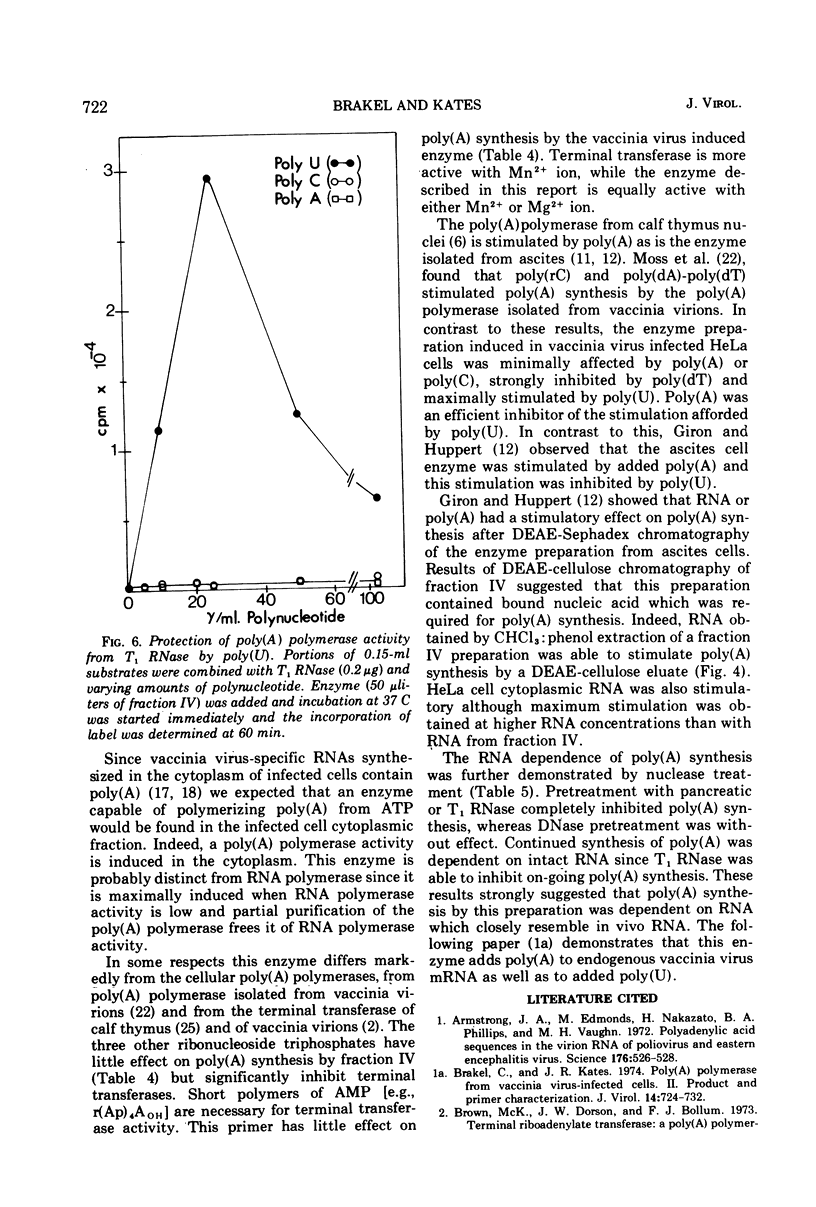
Poly(A) polymerase activity is induced during vaccinia virus infection of HeLa cells. The enzyme is maximally induced at 3.5 h postinfection. Partial purification frees the preparation of RNase activity and RNA polymerase activity. ATP is the substrate for poly(A) synthesis. A small amount of poly(A) is produced from added adenosine diphosphate due to the production of ATP by an adenylate kinase present in the preparation. The incorporation of ATP into poly(A) is dependent on divalent cations (Mg2+ or Mn2+) and is not inhibited by UTP, CTP, or GTP. Poly(U) stimulates ATP incorporation; poly(A) and poly(C) have little effect on ATP incorporation, and poly(dT) is extremely inhibitory. RNA prepared from HeLa cells and from the partially purified poly(A) polymerase (the enzyme preparation contains endogenous RNA [Brakel and Kates]) stimulates ATP incorporation by poly(A) polymerase which was subjected to DEAE-cellulose chromatography. RNase's, pancreatic and T1, inhibit the production of poly(A). DNase has little effect. Poly(U) is able to stimulate poly(A) production in the presence of T1 RNase.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armstrong J. A., Edmonds M., Nakazato H., Phillips B. A., Vaughn M. H. Polyadenylic acid sequences in the virion RNA of poliovirus and Eastern Equine Encephalitis virus. Science. 1972 May 5;176(4034):526–528. doi: 10.1126/science.176.4034.526. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brakel C., Kates J. R. Poly(A) polymerase from vaccinia virus-infected cells. II. Product and primer characterization. J Virol. 1974 Oct;14(4):724–732. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.4.724-732.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M., Dorson J. W., Bollum F. J. Terminal riboadenylate transferase: a poly A polymerase in purified vaccinia virus. J Virol. 1973 Aug;12(2):203–208. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.2.203-208.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darnell J. E., Philipson L., Wall R., Adesnik M. Polyadenylic acid sequences: role in conversion of nuclear RNA into messenger RNA. Science. 1971 Oct 29;174(4008):507–510. doi: 10.1126/science.174.4008.507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darnell J. E., Wall R., Tushinski R. J. An adenylic acid-rich sequence in messenger RNA of HeLa cells and its possible relationship to reiterated sites in DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jun;68(6):1321–1325. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.6.1321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EDMONDS M., ABRAMS R. Nature of a polynucleotide required for polyribonucleotide formation from adenosine triphosphate with an enzyme from thymus nuclei. J Biol Chem. 1962 Aug;237:2636–2642. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EDMONDS M., ABRAMS R. Polynucleotide biosynthesis: formation of a sequence of adenylate units from adenosine triphosphate by an enzyme from thymus nuclei. J Biol Chem. 1960 Apr;235:1142–1149. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edmonds M., Vaughan M. H., Jr, Nakazato H. Polyadenylic acid sequences in the heterogeneous nuclear RNA and rapidly-labeled polyribosomal RNA of HeLa cells: possible evidence for a precursor relationship. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jun;68(6):1336–1340. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.6.1336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrenfeld E., Summers D. F. Adenylate-rich sequences in vesicular stomatitis virus messenger ribonucleic acid. J Virol. 1972 Oct;10(4):683–688. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.4.683-688.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galet H., Prevec L. Polyadenylate synthesis by extracts from L cells infected with vesicular stomatitis virus. Nat New Biol. 1973 Jun 13;243(128):200–203. doi: 10.1038/newbio243200a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giron M. L., Huppert J. Polyadénylate synthétase des cellules d'ascite de souris. I. Purification et caractérisation de l'enzyme. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Dec 22;287(3):438–447. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giron M. L., Huppert J. Polyadénylate synthétase des cellules d'ascite de souris. II. Etude de la réaction enzymatique. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Dec 22;287(3):448–455. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green M., Cartas M. The genome of RNA tumor viruses contains polyadenylic acid sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Apr;69(4):791–794. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.4.791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyatt E. A. Polyriboadenylate synthesis by nuclei from developing sea urchin embryos. I. Characterization of the ATP polymerase reaction. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Jun 20;142(1):246–253. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(67)90532-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyatt E. A. Polyriboadenylate synthesis by nuclei from developing sea urchin embryos. II. Polyriboadenylic acid priming of ATP polymerase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Jun 20;142(1):254–262. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(67)90533-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOKLIK W. K. THE INTRACELLULAR UNCOATING OF POXVIRUS DNA. II. THE MOLECULAR BASIS OF THE UNCOATING PROCESS. J Mol Biol. 1964 Feb;8:277–288. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(64)80137-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kates J., Beeson J. Ribonucleic acid synthesis in vaccinia virus. II. Synthesis of polyriboadenylic acid. J Mol Biol. 1970 May 28;50(1):19–33. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90101-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kates J., Dahl R., Mielke M. Synthesis and intracellular localization of vaccinia virus deoxyribonucleic acid-dependent ribonucleic acid polymerase. J Virol. 1968 Sep;2(9):894–900. doi: 10.1128/jvi.2.9.894-900.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. Y., Mendecki J., Brawerman G. A polynucleotide segment rich in adenylic acid in the rapidly-labeled polyribosomal RNA component of mouse sarcoma 180 ascites cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jun;68(6):1331–1335. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.6.1331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss B., Rosenblum E. N., Paoletti E. Polyadenylate polymerase from vaccinia virions. Nat New Biol. 1973 Sep 12;245(141):59–63. doi: 10.1038/newbio245059a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philipson L., Wall R., Glickman G., Darnell J. E. Addition of polyadenylate sequences to virus-specific RNA during adenovirus replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Nov;68(11):2806–2809. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.11.2806. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheldon R., Jurale C., Kates J. Detection of polyadenylic acid sequences in viral and eukaryotic RNA(polu(U)-cellulose columns-poly(U) filters-fiberglass-HeLa cells-bacteriophage T4). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Feb;69(2):417–421. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.2.417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheldon R., Kates J. Mechanism of poly(A) synthesis by vaccinia virus. J Virol. 1974 Aug;14(2):214–224. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.2.214-224.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsiapalis C. M., Dorson J. W., De Sante D. M., Bollum F. J. Terminal riboadenylate transferase: a polyadenylate polymerase from calf thymus gland. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Feb 5;50(3):737–743. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)91306-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Twu J. S., Bretthauer R. K. Properties of a polyriboadenylate polymerase isolated from yeast ribosomes. Biochemistry. 1971 Apr 27;10(9):1576–1582. doi: 10.1021/bi00785a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yogo Y., Wimmer E. Polyadenylic acid at the 3'-terminus of poliovirus RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jul;69(7):1877–1882. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.7.1877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



