Abstract
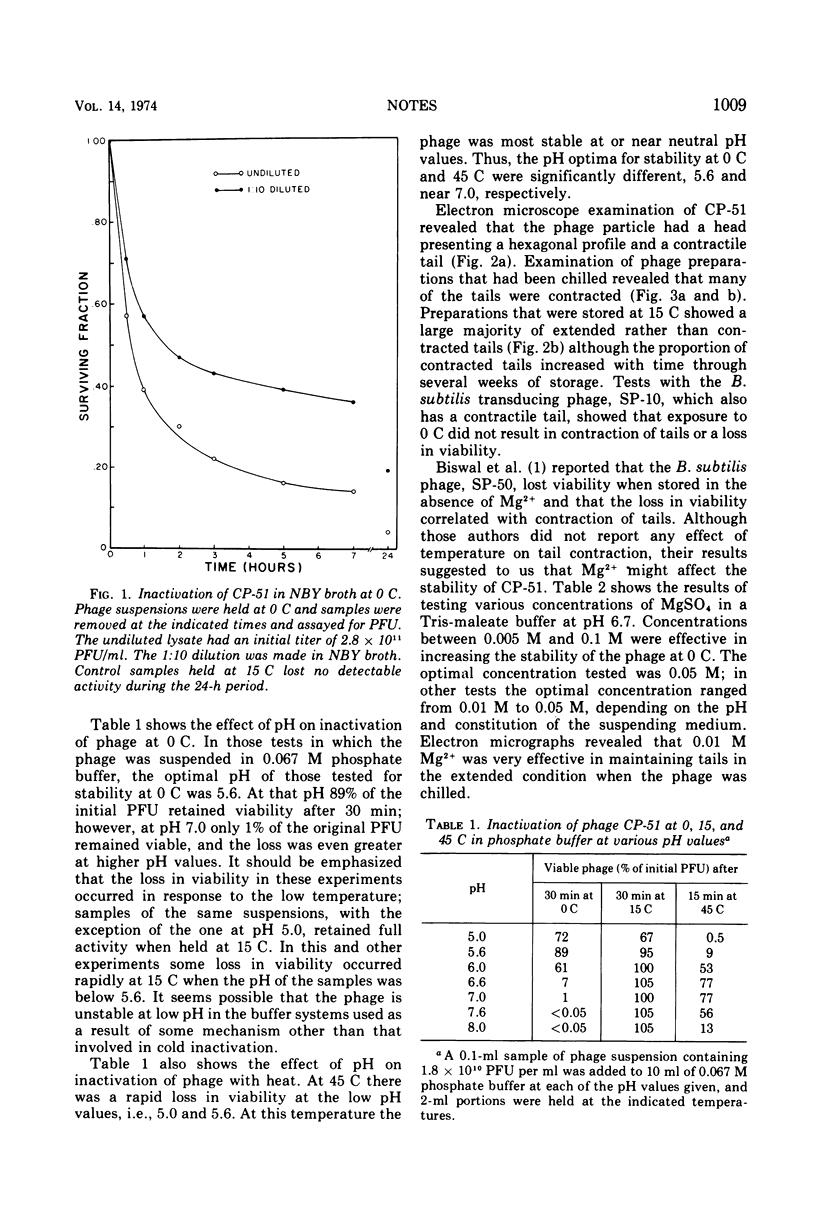
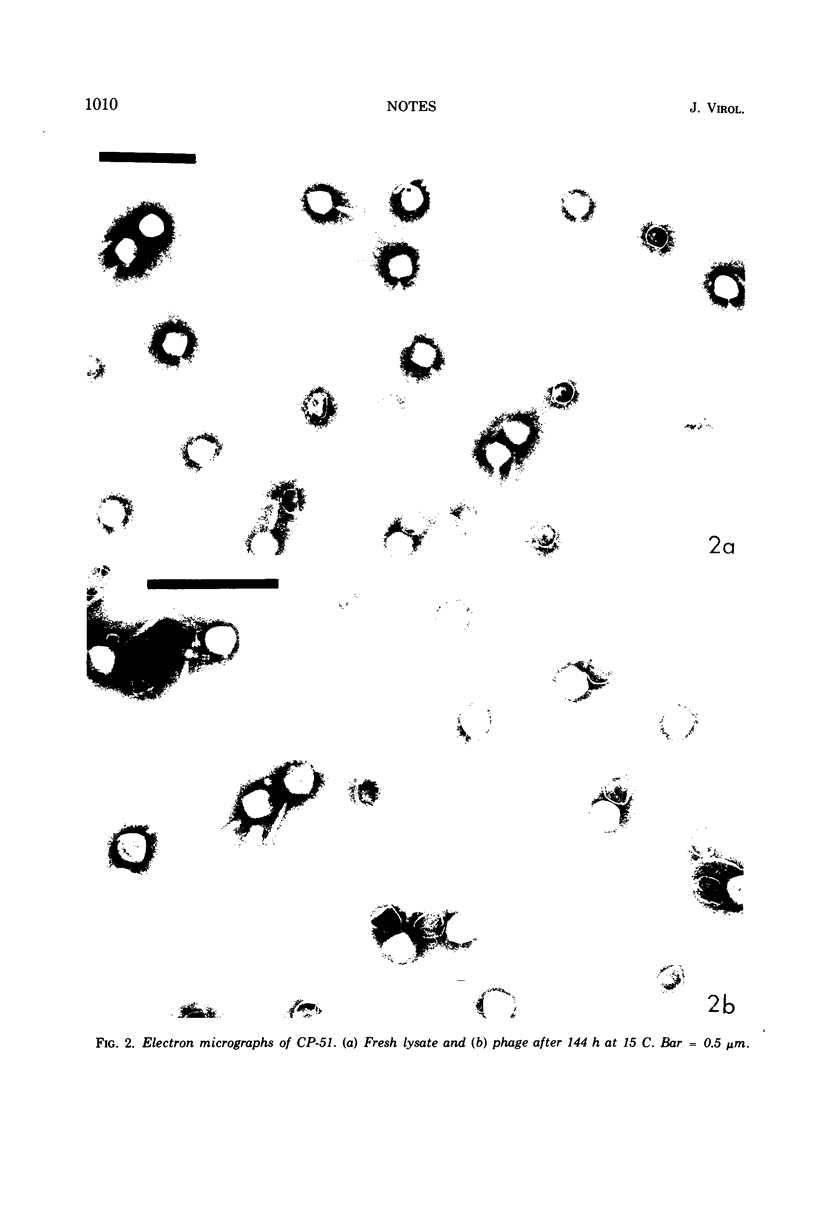
Phage CP-51 was rapidly inactivated when stored at the usual refrigerator temperatures (2 to 4 C) and even more rapidly when exposed to 0 C. The loss in viability resulting from exposure to cold appeared to correlate with the increase in number of phage particles having contracted tails. High concentrations (0.01 M) of Mg2+, Ca2+, or Mn2+ stabilized the phage considerably, but even in the presence of these divalent cations, it was much less stable at 0 C than at 15 C.
Full text
PDF
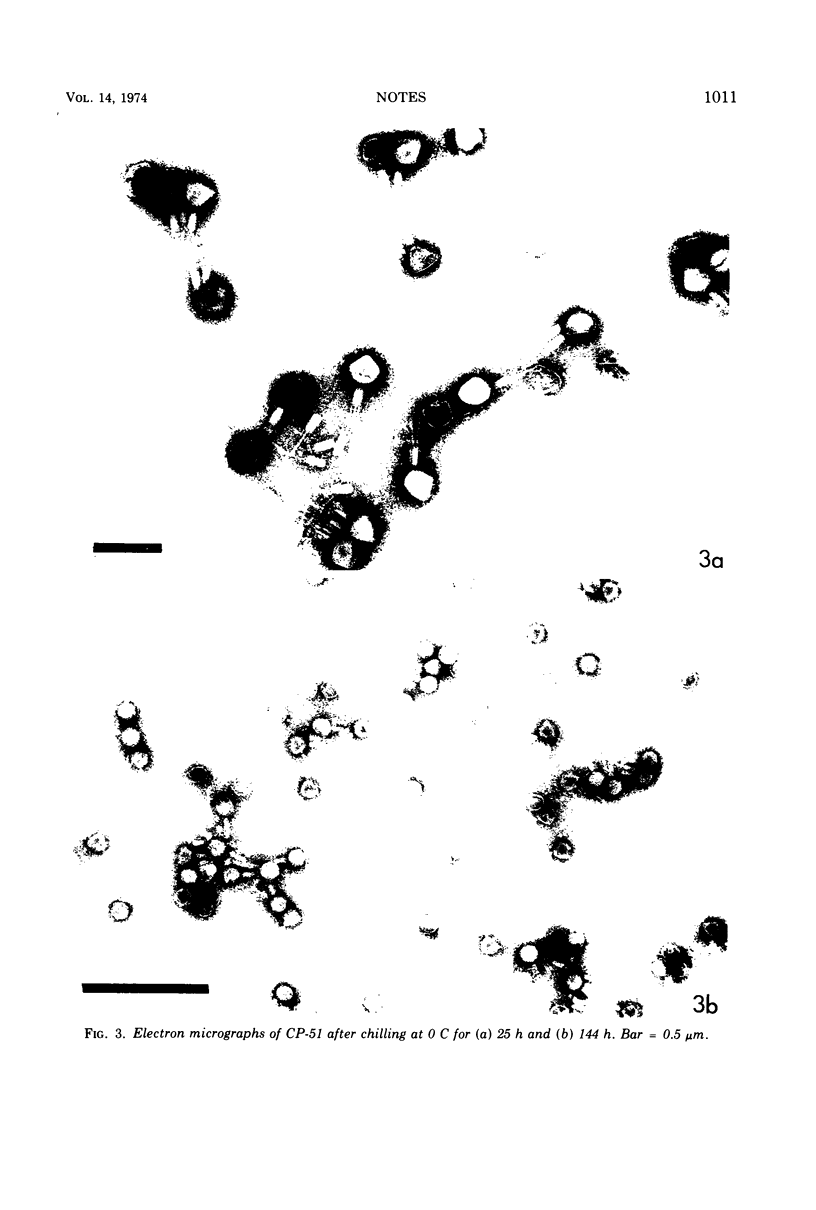

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Biswal N., Kleinschmidt A. K., Spatz H. C., Trautner T. A. Physical properties of the DNA of bacteriophage SP50. Mol Gen Genet. 1967;100(1):39–55. doi: 10.1007/BF00425774. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt S. C., Leadbetter E. R. Fine structure of Sporocytophaga myxococcoides. Arch Mikrobiol. 1967 Jun 21;57(3):199–213. doi: 10.1007/BF00405947. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorne C. B. Transducing bacteriophage for Bacillus cereus. J Virol. 1968 Jul;2(7):657–662. doi: 10.1128/jvi.2.7.657-662.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorne C. B. Transduction in Bacillus cereus and Bacillus anthracis. Bacteriol Rev. 1968 Dec;32(4 Pt 1):358–361. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yelton D. B., Thorne C. B. Transduction in Bacillus cereus by each of two bacteriophages. J Bacteriol. 1970 May;102(2):573–579. doi: 10.1128/jb.102.2.573-579.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]