Abstract
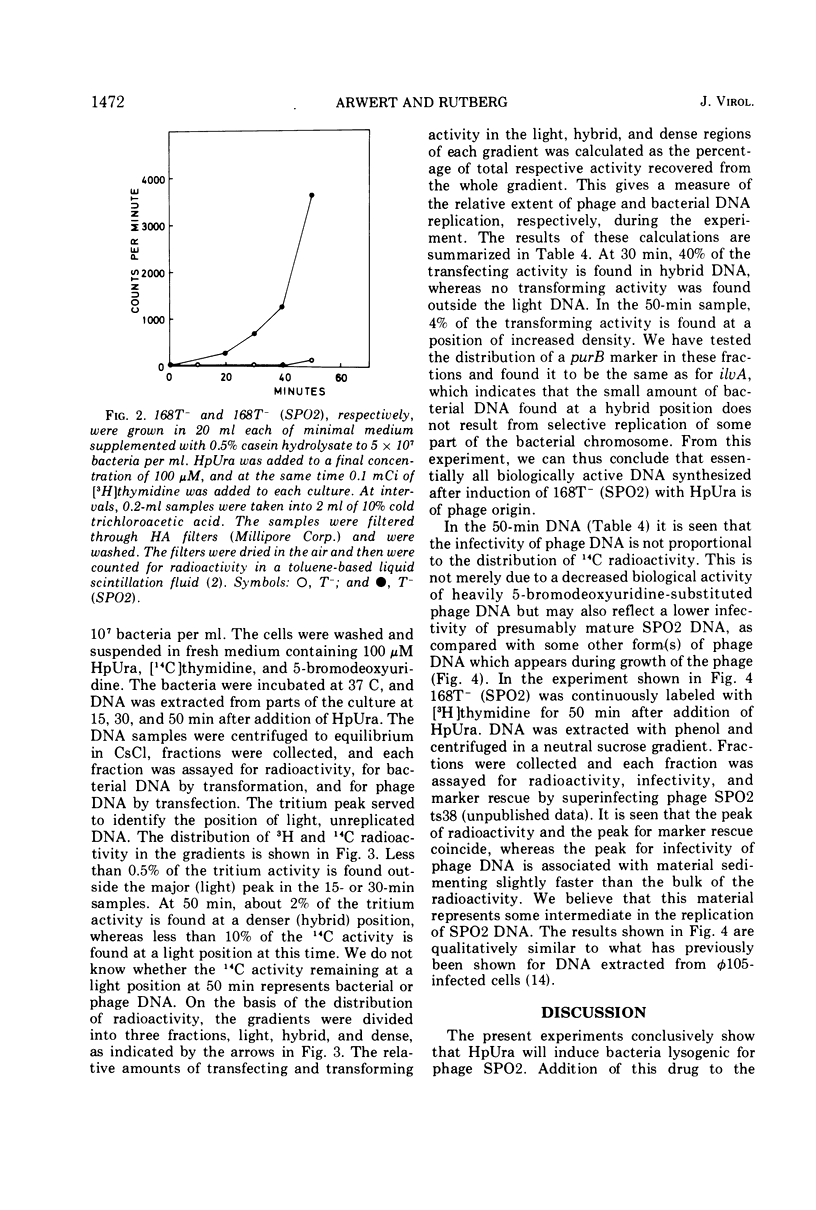
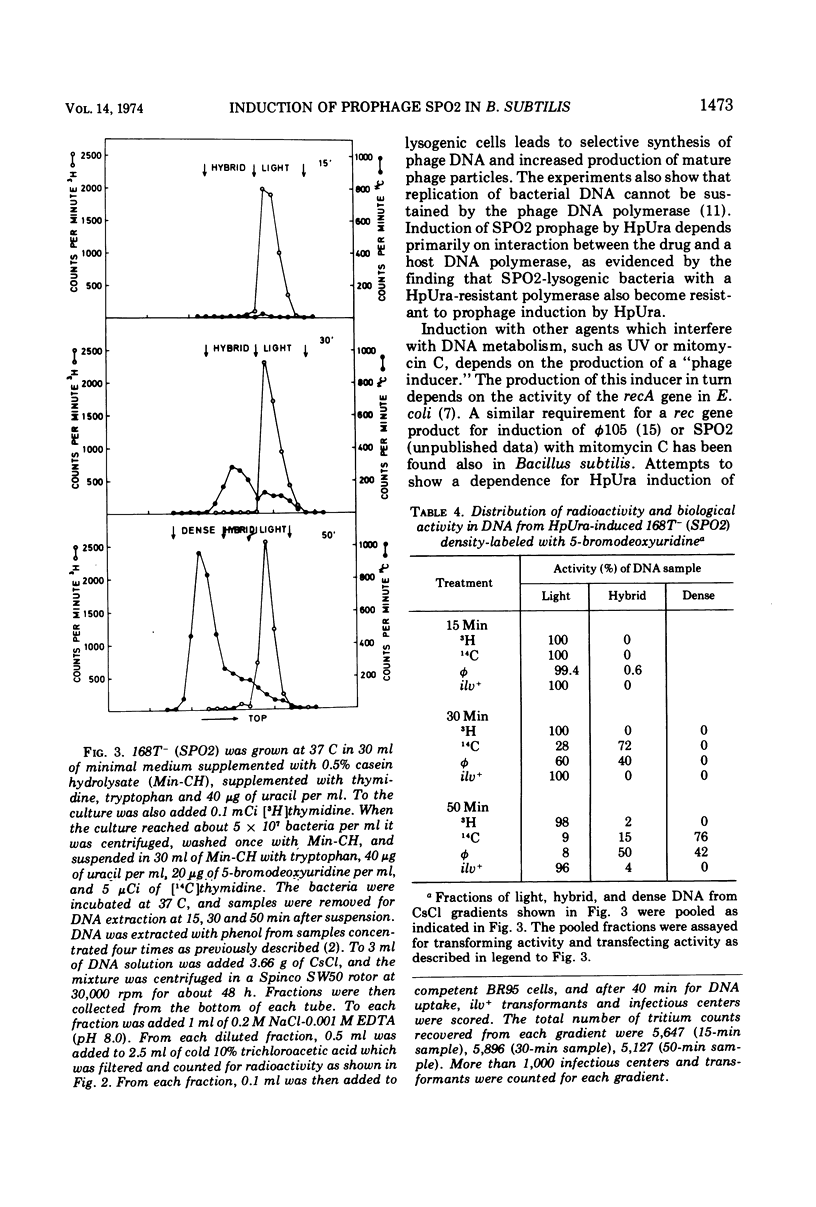
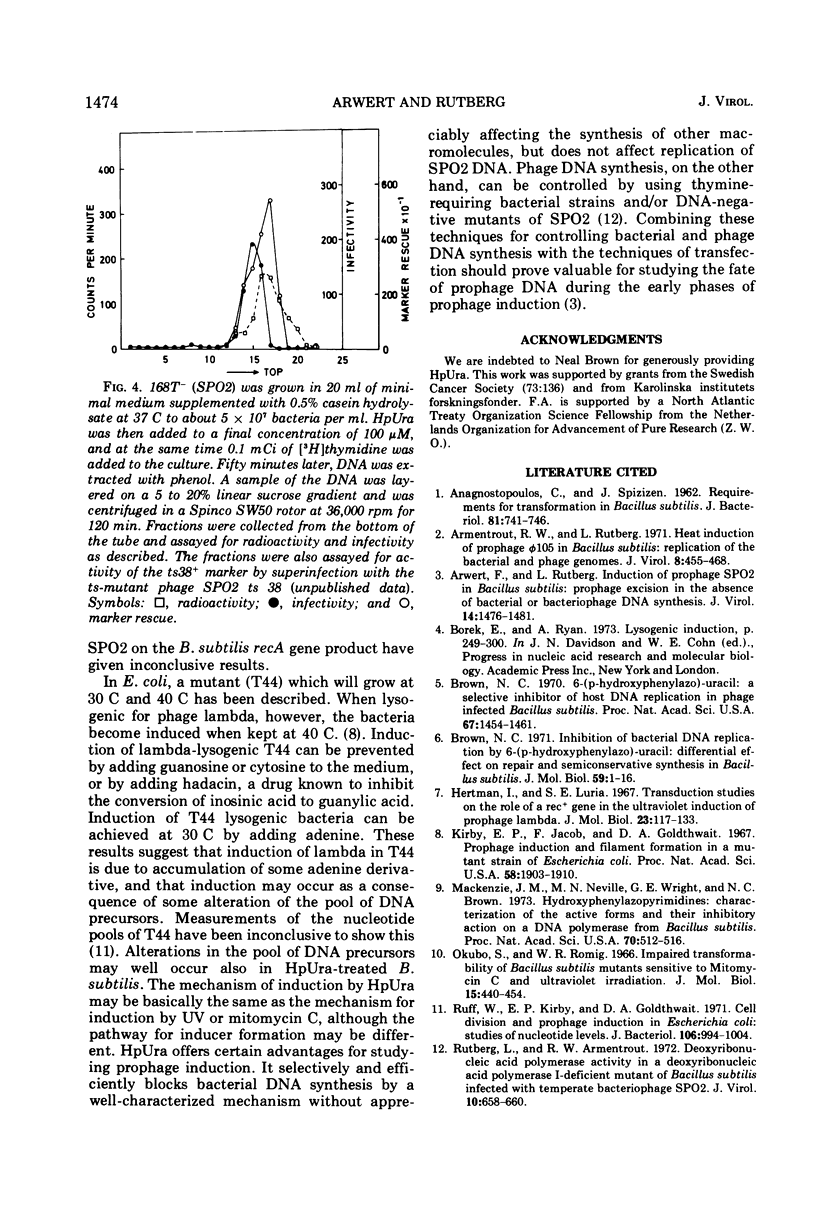
DNA replication in Bacillus subtilis is reversibly inhibited by 6-(para)-hydroxyphenylazouracil (HpUra) (1971), whereas replication of temperature phage SPO2 is not affected by the drug. Experiments are presented which show that HpUra will induce bacteria lysogenic for SPO2. Also, prophage φ105, which is sensitive to the drug, is induced by HpUra. Induction of SPO2 lysogenics in the presence of HpUra gives selective synthesis of SPO2 DNA.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anagnostopoulos C., Spizizen J. REQUIREMENTS FOR TRANSFORMATION IN BACILLUS SUBTILIS. J Bacteriol. 1961 May;81(5):741–746. doi: 10.1128/jb.81.5.741-746.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armentrout R. W., Rutberg L. Heat induction of prophage phi 105 in Bacillus subtilis: replication of the bacterial and bacteriophage genomes. J Virol. 1971 Oct;8(4):455–468. doi: 10.1128/jvi.8.4.455-468.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arwert F., Rutberg L. Induction of prophage SPO2 in Bacillus subtilis: prophage excision in the absence of bacterial or bacteriophage DNA synthesis. J Virol. 1974 Dec;14(6):1476–1481. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.6.1476-1481.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borek E., Ryan A. Lysogenic induction. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1973;13:249–300. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60105-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown N. C. 6-(p-hydroxyphenylazo)-uracil: a selective inhibitor of host DNA replication in phage-infected Bacillus subtilis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Nov;67(3):1454–1461. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.3.1454. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown N. C. Inhibition of bacterial DNA replication by 6-(p-hydroxyphenylazo)-uracil: differential effect on repair and semi-conservative synthesis in Bacillus subtilis. J Mol Biol. 1971 Jul 14;59(1):1–16. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90409-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hertman I., Luria S. E. Transduction studies on the role of a rec+ gene in the ultraviolet induction of prophage lambda. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jan 28;23(2):117–133. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(67)80021-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirby E. P., Jacob F., Goldthwait D. A. Prophage induction and filament formation in a mutant strain of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Nov;58(5):1903–1910. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.5.1903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackenzie J. M., Neville M. M., Wright G. E., Brown N. C. Hydroxyphenylazopyrimidines: characterization of the active forms and their inhibitory action on a DNA polymerase from Bacillus subtilis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Feb;70(2):512–516. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.2.512. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okubo S., Romig W. R. Impaired transformability of Bacillus subtilis mutant sensitive to mitomycin C and ultraviolet radiation. J Mol Biol. 1966 Feb;15(2):440–454. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80120-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruff W., Kirby E. P., Goldthwait D. A. Cell division and prophage induction in Escherichia coli: studies of nucleotide levels. J Bacteriol. 1971 Jun;106(3):994–1004. doi: 10.1128/jb.106.3.994-1004.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutberg B., Rutberg L. Growth of bacteriophage phi 105 and its deoxyribonucleic acid in radiation-sensitive mutants of Bacillus subtilis. J Virol. 1971 Dec;8(6):919–921. doi: 10.1128/jvi.8.6.919-921.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutberg L., Armentrout R. W. Deoxyribonucleic acid polymerase activity in a deoxyribonucleic acid polymerase I-deficient mutant of Bacillus subtilis infected with temperature bacteriophage SPO2. J Virol. 1972 Oct;10(4):658–660. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.4.658-660.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutberg L., Armentrout R. W., Jonasson J. Unrelatedness of temperate Bacillus subtilis bacteriophages SP02 and phi105. J Virol. 1972 May;9(5):732–737. doi: 10.1128/jvi.9.5.732-737.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutberg L., Rutberg B. Characterization of infectious deoxyribonucleic acid from temperature Bacillus subtilis bacteriophage phi105. J Virol. 1970 May;5(5):604–608. doi: 10.1128/jvi.5.5.604-608.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yasunaka K., Tsukamoto H., Okubo S., Horiuchi T. Isolation and properties of suppressor-sensitive mutants of Bacillus subtilis bacteriophage SP02. J Virol. 1970 Jun;5(6):819–821. doi: 10.1128/jvi.5.6.819-821.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


