Abstract
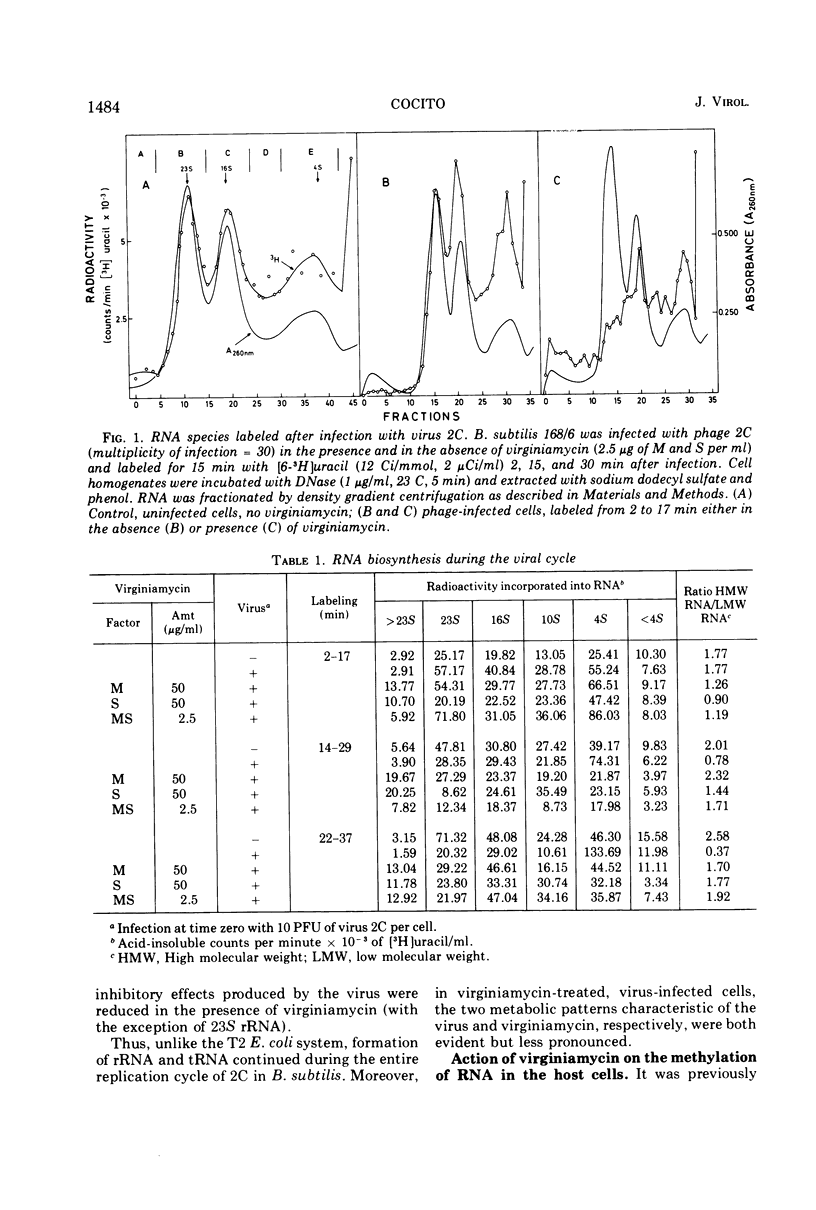
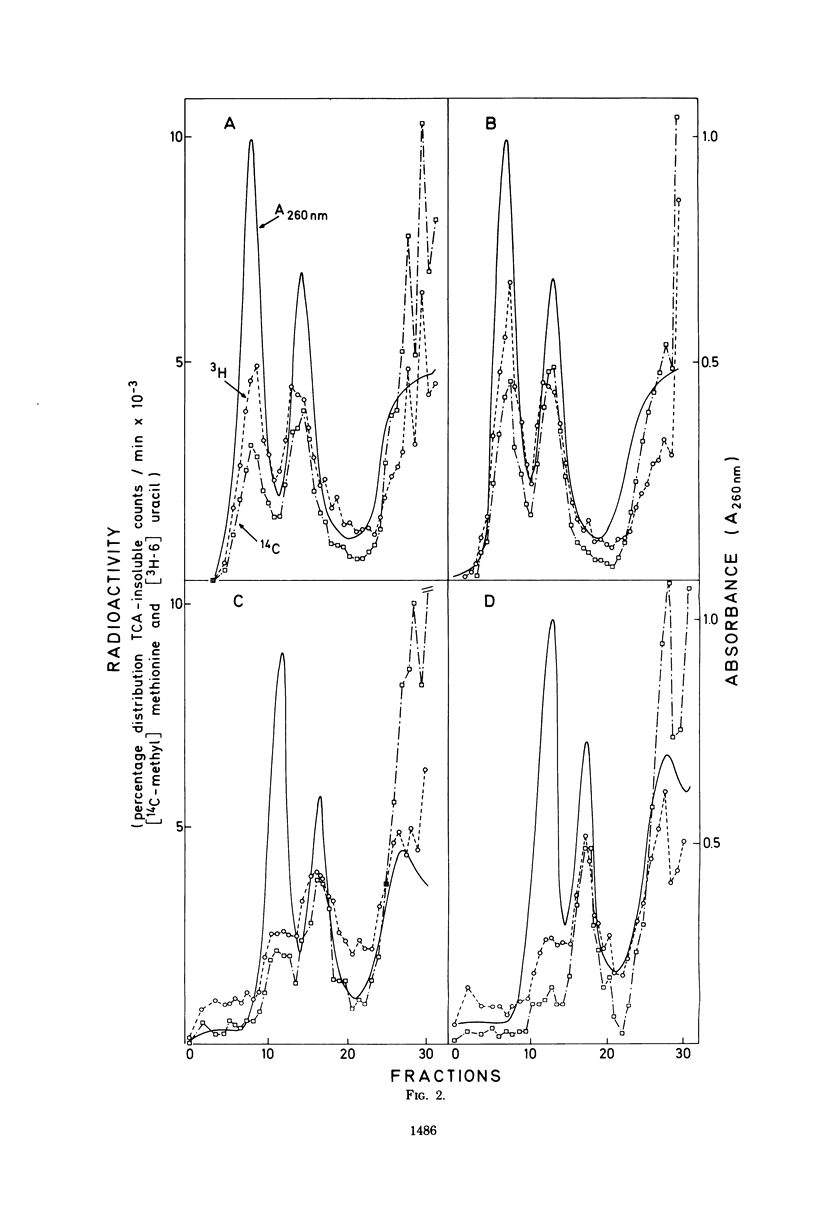
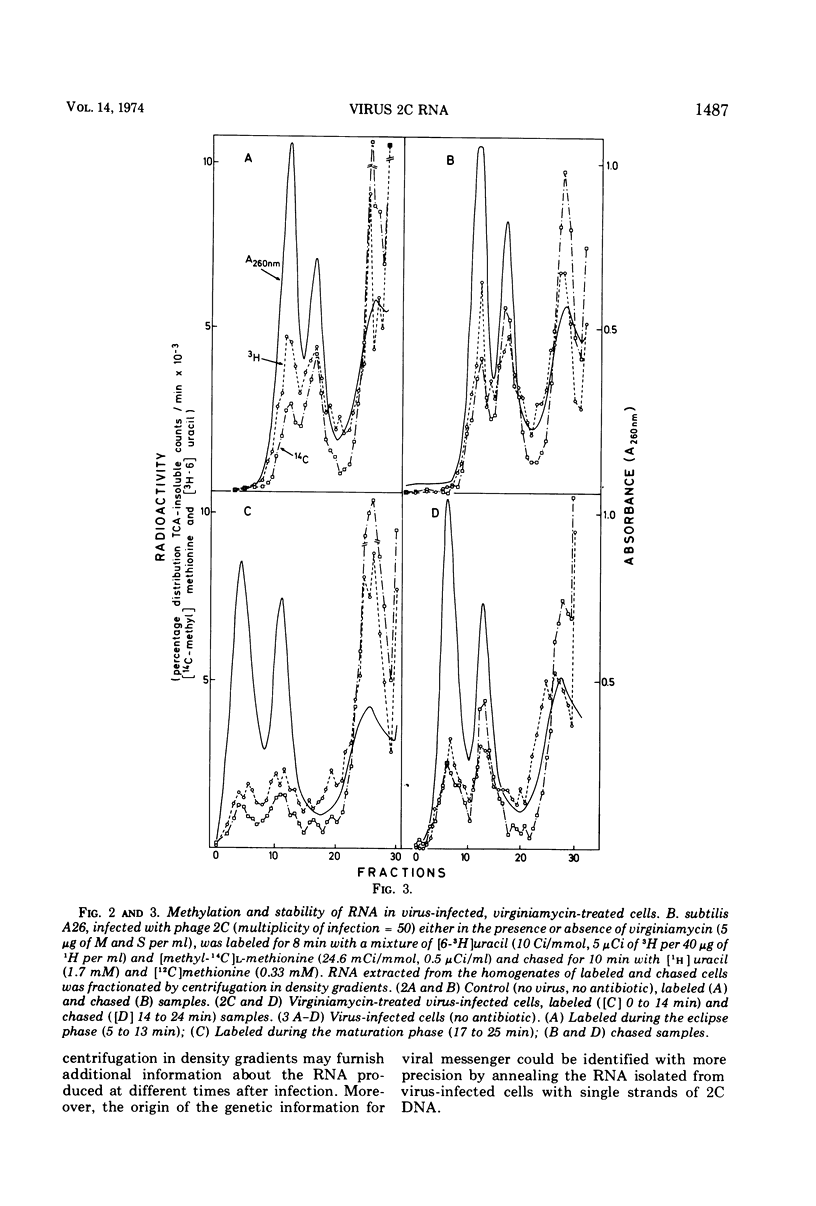
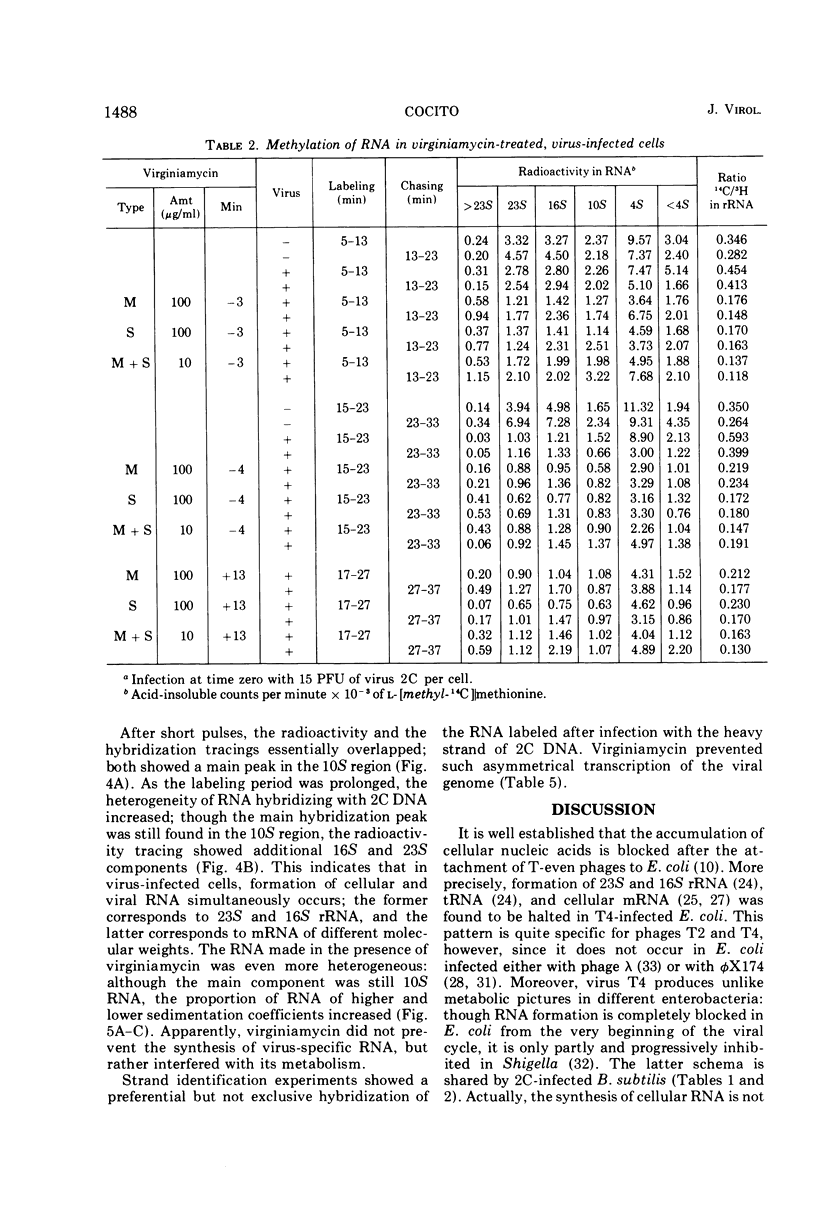
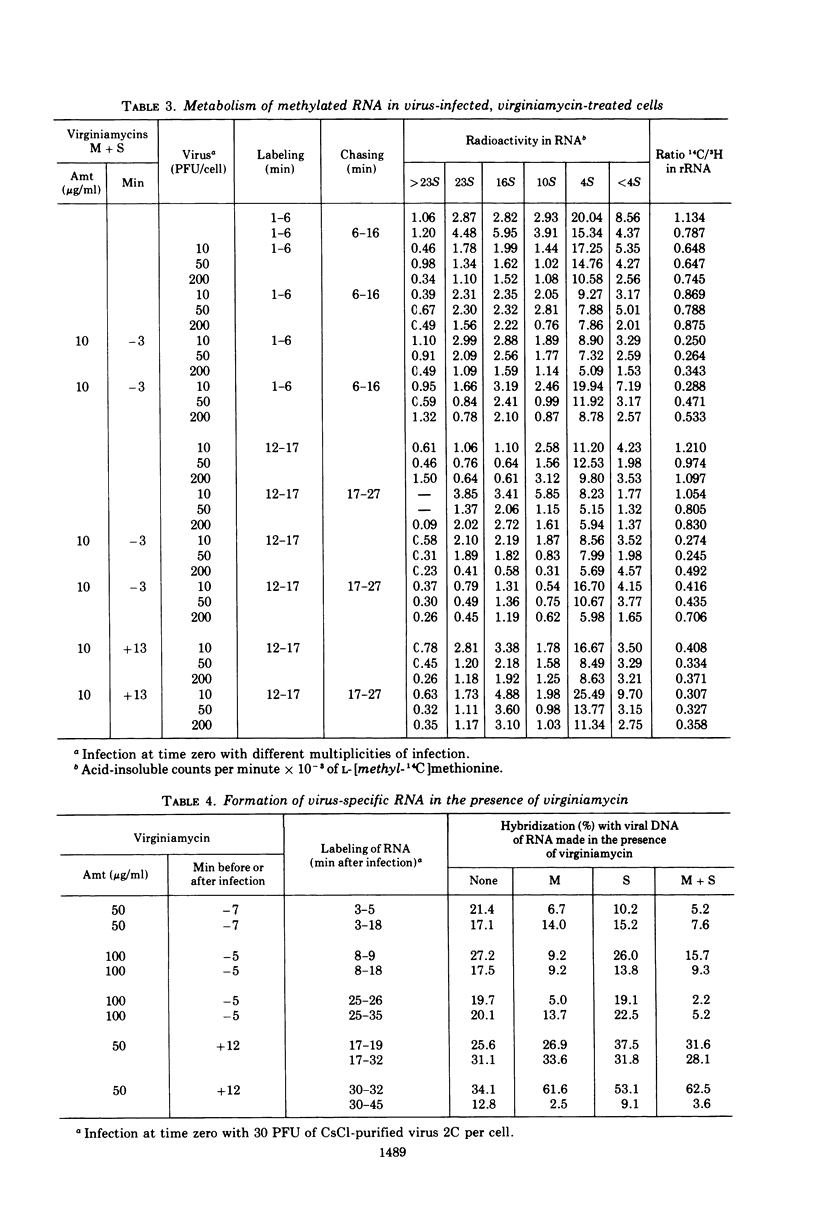
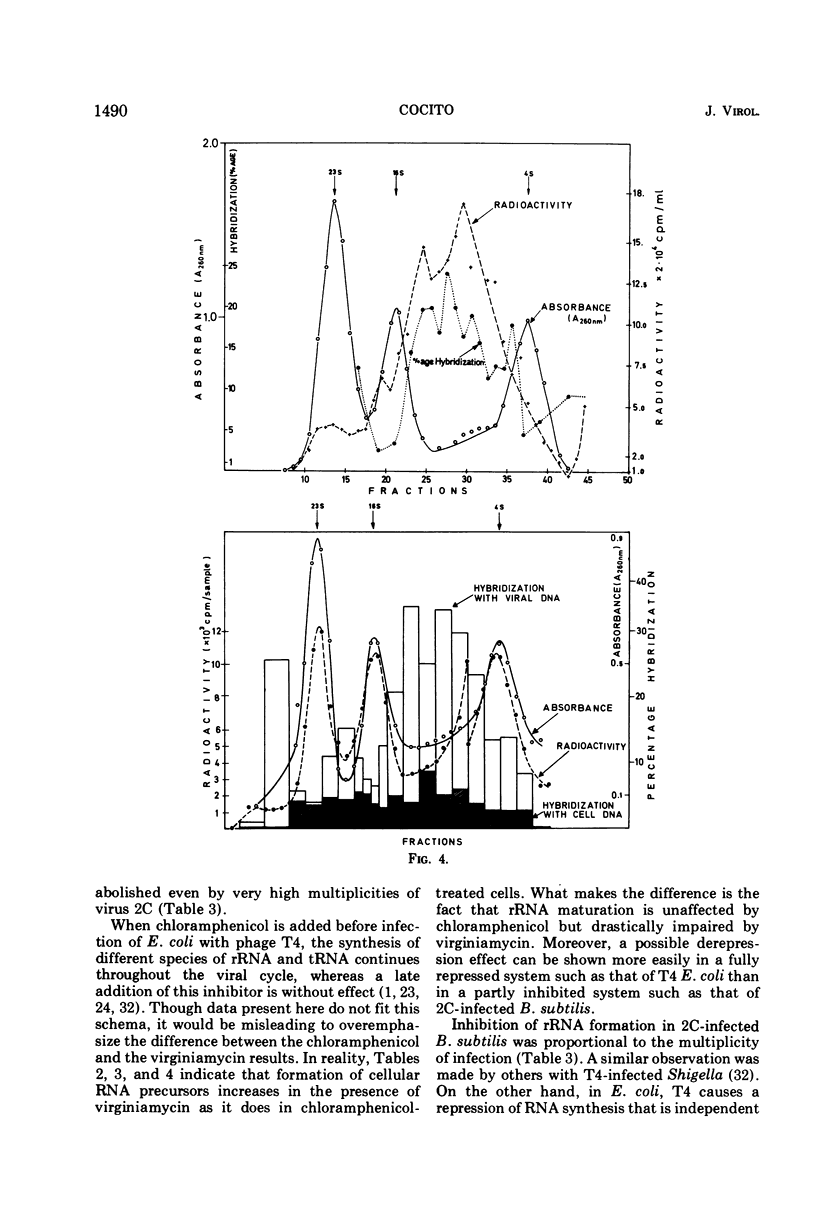
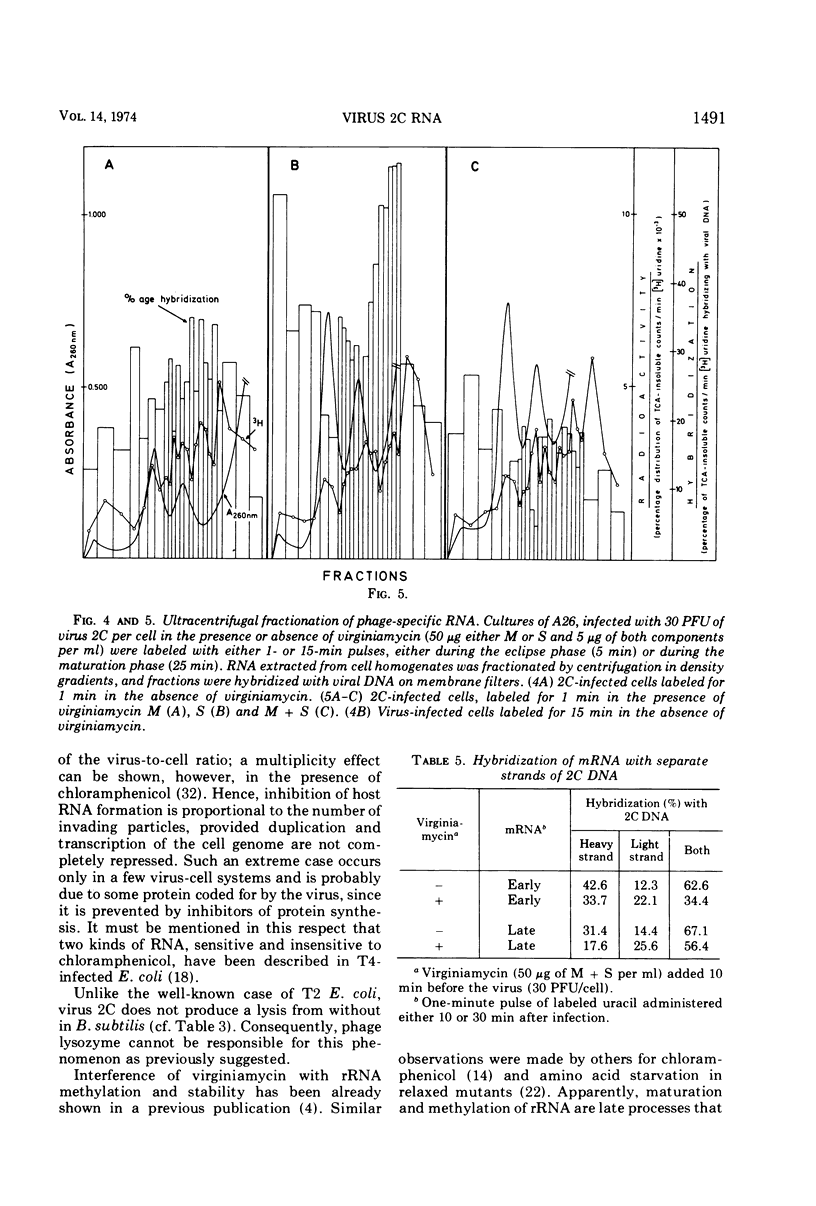
When short pulses of [3H]uracil were administered to Bacillus subtilis infected with phage 2C, the main species of labeled RNA was a 10S component that hybridized chiefly, but not exclusively, with the heavy strand of 2C DNA. After long pulses, most of the radioactivity was found in the 23S, 16S, and 5S rRNA's, which are coded for by the cell genome. Formation of such RNA species was reduced but not suppressed upon infection, the extent of inhibition being proportional to the virus-to-cell ratio. When bacteria were incubated with virginiamycin, an inhibitor of protein synthesis, and then infected with phage 2C, formation of virus-specific RNA decreased. This antibiotic also reduced the preferential transcription of the heavy strand of 2C DNA. The methylation pattern of rRNA remained unchanged upon infection with phage 2C. Virginiamycin reduced both the methylation and stability of rRNA in uninfected cells; this effect, however, was clearly reduced during the viral cycle. It can be concluded that in 2C-infected B. subtilis, cellular and viral RNA species are simultaneously synthesized and a preferential transcription of viral message depends not only on the number of available copies of viral template, but also on their translation. Moreover, virus-dictated proteins are responsible for the inhibition of cellular RNA formation as well as for the asymmetrical transcription of phage genome. Finally, virginiamycin and phage 2C have antagonistic, nonoverlapping effects on the metabolism and function of the RNA of the host cell.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adesnik M., Levinthal C. RNA metabolism in T4-infected Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1970 Mar 14;48(2):187–208. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90156-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COCITO C. NUCLEIC ACID METABOLISM IN MONOLAYERS OF HELA CELLS INFECTED WITH A DNA- AND A RNA-VIRUS. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1964;14:201–214. doi: 10.1007/BF01555092. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHEN S. S. Virus-induced acquisition of metabolic function. Fed Proc. 1961 Jul;20:641–649. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cocito C. G., Bronchart R., Van Pel B. Phenotypic and genotypic changes induced in eucaryotic cells by protein inhibitors. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Feb 25;46(4):1688–1694. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90804-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cocito C., Fraselle G. The properties of virginiamycin-resistant mutants of Bacillus subtilis. J Gen Microbiol. 1973 May;76(1):115–125. doi: 10.1099/00221287-76-1-115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cocito C., Kaji A. Virginiamycin M, a specific inhibitor of the acceptor site of ribosomes. Biochimie. 1971;53(6):763–770. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(71)80117-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cocito C. Metabolism of macromolecules in bacteria treated with virginiamycin. J Gen Microbiol. 1969 Aug;57(2):179–194. doi: 10.1099/00221287-57-2-179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cocito C. The action of virginiamycin on nucleic acid and protein synthesis in Bacillus subtilis infected with bacteriophage 2C. J Gen Microbiol. 1969 Aug;57(2):195–206. doi: 10.1099/00221287-57-2-195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cocito C., Voorma H. O., Bosch L. Interference of virginiamycin M with the initiation and the elongation of peptide chains in cell-free systems. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Mar 27;340(3):285–298. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(74)90274-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GEIDUSCHEK E. P., TOCCHINI-VALENTINI G. P., SARNAT M. T. ASYMMETRIC SYNTHESIS OF RNA IN VITRO: DEPENDENCE OF DNA CONTINUITY AND CONFORMATION. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Aug;52:486–493. doi: 10.1073/pnas.52.2.486. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GORDON J., BOMAN H. G., ISAKSSON L. A. IN VIVO INHIBITION OF RNA METHYLATION IN THE PRESENCE OF CHLORAMPHENICOL. J Mol Biol. 1964 Sep;9:831–833. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(64)80190-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillespie D., Spiegelman S. A quantitative assay for DNA-RNA hybrids with DNA immobilized on a membrane. J Mol Biol. 1965 Jul;12(3):829–842. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80331-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAYASHI M., HAYASHI M. N., SPIEGELMAN S. RESTRICTION OF IN VIVO GENETIC TRANSCRIPTION TO ONE OF THE COMPLEMENTARY STRANDS OF DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Oct;50:664–672. doi: 10.1073/pnas.50.4.664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes S., Szybalski W. Control of short leftward transcripts from the immunity and ori regions in induced coliphage lambda. Mol Gen Genet. 1973 Nov 22;126(4):275–290. doi: 10.1007/BF00269438. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayward S. D., Smith M. G. The chromosome of bacteriophage T5. 3. Patterns of transcription from the single-stranded DNA fragments. J Mol Biol. 1973 Oct 25;80(2):345–359. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90177-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ISHIHAMA A., MIZUNO N., TAKAI M., OTAKA E., OSAWA S. Molecular and metabolic properties of messenger RNA from normal and T2-infected Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1962 Sep;5:251–264. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(62)80069-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MANDELL J. D., HERSHEY A. D. A fractionating column for analysis of nucleic acids. Anal Biochem. 1960 Jun;1:66–77. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(60)90020-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- May P., May E., Granboulan P., Granboulan N., Marmur J. Ultrastructure du bactériophage 2C et propriétés de son DNA. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1968 Dec;115(6):1029–1046. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NAKADA D., ANDERSON I. A., MAGASANIK B. FATE OF THE RIBOSOMAL RNA PRODUCED BY A "RELAXED" MUTANT OF ESCHERICHIA COLI. J Mol Biol. 1964 Aug;9:472–488. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(64)80220-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NOMURA M., OKAMOTO K., ASANO K. RNA metabolism in Escherichia coli infected with bacteriophage T4. Inhibition of host ribosomal and soluble RNA synthesis by phage and effect of chloromycetin. J Mol Biol. 1962 May;4:376–387. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(62)80018-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NYGAARD A. P., HALL B. D. A method for the detection of RNA-DNA complexes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1963 Jul 18;12:98–104. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(63)90242-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomura M., Witten C., Mantei N., Echols H. Inhibition of host nucleic acid synthesis by bacteriophage T4: effect of chloramphenicol at various multiplicities of infection. J Mol Biol. 1966 May;17(1):273–278. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80107-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OKAMOTO K., SUGINO Y., NOMURA M. Synthesis and turnover of phage messenger RNA in E. coli infected with bacteriophage T4 in the presence of chloromycetin. J Mol Biol. 1962 Nov;5:527–534. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(62)80126-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RUECKERT R. R., ZILLIG W. Biosynthesis of virus protein in Escherichia coli C in vivo following infection with bacteriophage phi-X-174. J Mol Biol. 1962 Jul;5:1–9. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(62)80056-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salser W., Bolle A., Epstein R. Transcription during bacteriophage T4 development: a demonstration that distinct subclasses of the "early" RNA appear at different times and that some are "turned off" at late times. J Mol Biol. 1970 Apr 28;49(2):271–295. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90246-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone A. B. General inhibition of Escherichia coli macromolecular synthesis by high multiplicites of bacteriophage phiX174. J Mol Biol. 1970 Jan 28;47(2):215–229. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90341-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TOCCHINI-VALENTINI G. P., STODOLSKY M., AURISICCHIO A., SARNAT M., GRAZIOSI F., WEISS S. B., GEIDUSCHEK E. P. ON THE ASYMMETRY OF RNA SYNTHESIS IN VIVO. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Nov;50:935–942. doi: 10.1073/pnas.50.5.935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terzi M., Levinthal C. Effects of lambda-phage infection on bacterial synthesis. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 28;26(3):525–535. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90320-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terzi M. Studies on the mechanism of bacteriophage T4 interference with host metabolism. J Mol Biol. 1967 Aug 28;28(1):37–44. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(67)80075-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Truffaut N. Isolement et propriétés des chaînes du DNA de bactériophage 2 C. Eur J Biochem. 1970 Apr;13(3):438–446. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1970.tb00947.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Pel B., Bronchart R., Kebers F., Cocito C. Structure and function of cytoplasmic organelles in transiently and permanently bleached Euglena. Exp Cell Res. 1973 Mar 30;78(1):103–110. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(73)90043-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Pel B., Cocito C. Formation of chloroplast ribosomes and ribosomal RNA in Euglena incubated with protein inhibitors. Exp Cell Res. 1973 Mar 30;78(1):111–117. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(73)90044-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



