Abstract
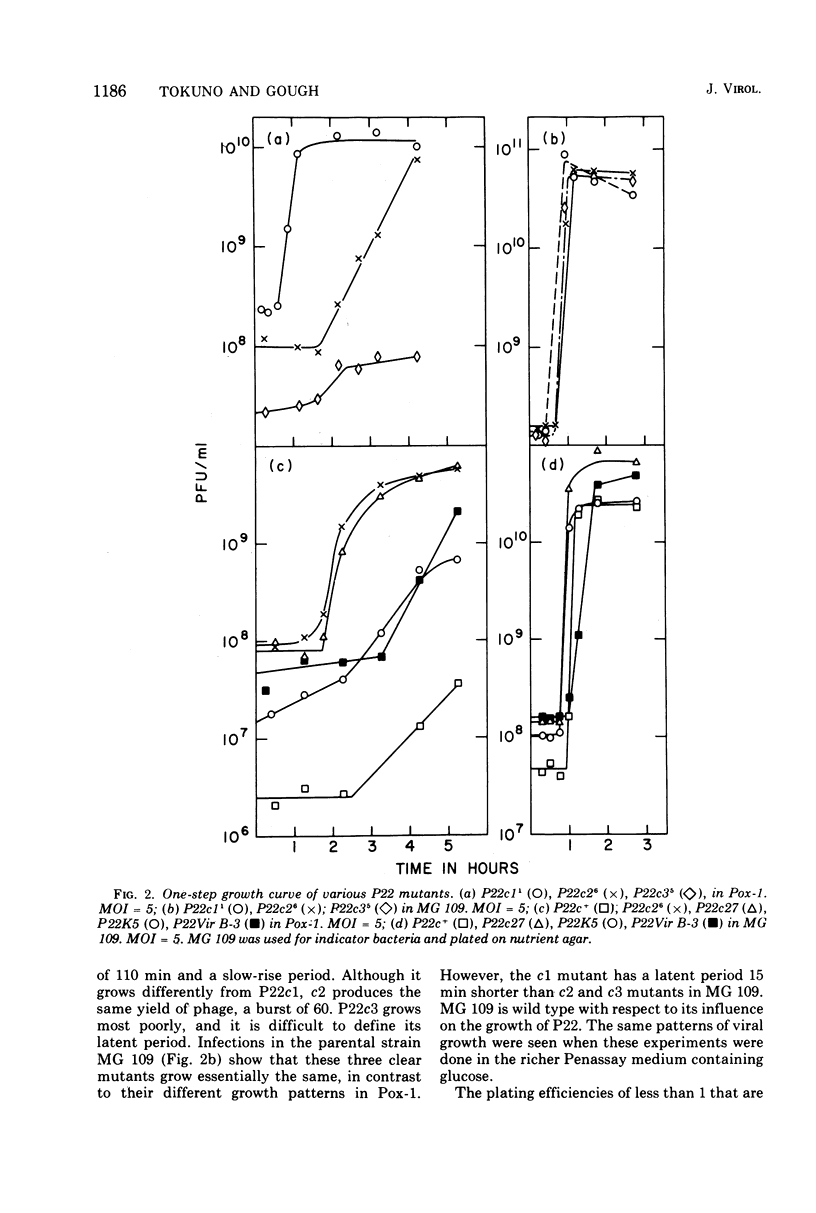
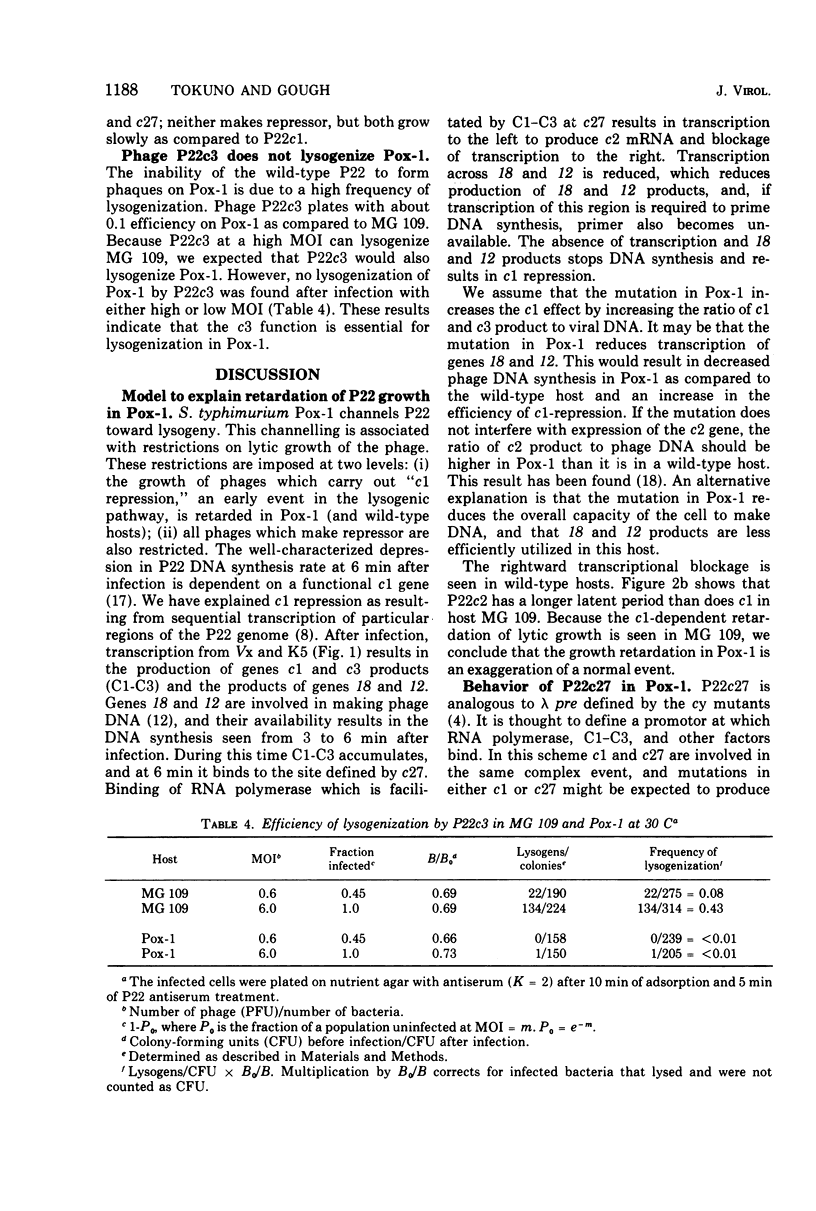
A Polymyxin B-sensitive mutant of Salmonella typhimurium (Pox-1) channels all infecting wild-type P22 toward lysogenization. The efficiency of this channeling is sufficiently high that P22c+ (wild type) cannot form plaques on Pox-1; phage mutants defective in repressor synthesis (P22c1, c2, c3) or refractory toward repressor (P22vir B) can form plaques. The lytic growth of all phages which have a functional c1 gene is retarded in Pox-1; this retardation is seen even in phages which cannot make repressor. We present experiments which are consistent with the explanation that the retardation is an exaggeration of a normal regulatory event. In a wild-type host, P22 genes c1 and c3 products, host RNA polymerase, and other host factors (?) interact at a promotor site (c27) IN THE PHAGE DNA. This interaction promotes repressor synthesis and represses transcription of lytic genes. In the mutant Pox-1, a host product involved in viral DNA synthesis and transcription is altered. The altered host product results in stronger retardation of lytic gene transcription. The importance of this interaction in the decision between lysis and lysogeny is discussed. The mutant Pox-1 alters the expression or activity of another phage gene. Gene c3 product is absolutely required for lysogenization in this host, although it is not so required in wild-type S. typhimurium.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bronson M. J., Levine M. Virulent mutants of bacteriophage p22.I. Isolation and genetic analysis. J Virol. 1971 May;7(5):559–568. doi: 10.1128/jvi.7.5.559-568.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Court D., Green L., Echols H. Positive and negative regulation by the cII and cIII gene products of bacteriophage lambda. Virology. 1975 Feb;63(2):484–491. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90321-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dopatka H. D., Prell H. H. Amber mutants of Salmonella-phage P22 in genes engaged in the establishment of lysogeny. Mol Gen Genet. 1973 Jan 24;120(2):157–170. doi: 10.1007/BF00267244. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Echols H. Developmental pathways for the temperate phage: lysis vs lysogeny,. Annu Rev Genet. 1972;6(0):157–190. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.06.120172.001105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Echols H., Green L. Establishment and maintenance of repression by bacteriophage lambda: the role of the cI, cII, and c3 proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Sep;68(9):2190–2194. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.9.2190. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gough M., Tokuno S. Further structural and functional analogies between the repressor regions of phages P22 and lambda. Mol Gen Genet. 1975;138(1):71–79. doi: 10.1007/BF00268829. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hong J. S., Smith G. R., Ames B. N. Adenosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate concentration in the bacterial host regulates the viral decision between lysogeny and lysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Sep;68(9):2258–2262. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.9.2258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAISER A. D. Mutations in a temperate bacteriophage affecting its ability to lysogenize Escherichia coli. Virology. 1957 Feb;3(1):42–61. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(57)90022-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVINE M. Mutations in the temperate phage P22 and lysogeny in Salmonella. Virology. 1957 Feb;3(1):22–41. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(57)90021-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. Replication and lysogeny with phage P22 in Salmonella typhimurium. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1972;58:135–156. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-65357-5_4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M., Truesdell S., Ramakrishnan T., Bronson M. J. Dual control of lysogeny by bacteriophage P22: an antirepressor locus and its controlling elements. J Mol Biol. 1975 Feb 5;91(4):421–438. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90270-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reichardt L., Kaiser A. D. Control of lambda repressor synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Sep;68(9):2185–2189. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.9.2185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rolfe B., Schell J., Becker A., Heip J., Onodera K., Schell-Frederick E. A colicin-tolerant mutant of Escherichia coli with reduced levels of cyclic AMP and a strong bias towards lambda lysogeny. Mol Gen Genet. 1973 Jan 18;120(1):1–16. doi: 10.1007/BF00332980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH H. O., LEVINE M. TWO SEQUENTIAL REPRESSIONS OF DNA SYNTHESIS IN THE ESTABLISHMENT OF LYSOGENY BY PHAGE P22 AND ITS MUTANTS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Aug;52:356–363. doi: 10.1073/pnas.52.2.356. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. O. Defective phage formation by lysogens of integration deficient phage P22 mutants. Virology. 1968 Feb;34(2):203–223. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(68)90231-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg B., Gough M. Altered DNA synthesis in a mutant of Salmonella typhimurium that channels bacteriophage P22 toward lysogeny. J Virol. 1975 Nov;16(5):1154–1160. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.5.1154-1160.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokuno S. I., Goldschmidt E. P., Gough M. Mutant of Salmonella typhimurium that channels infecting bacteriophage P22 toward lysogenization. J Bacteriol. 1974 Aug;119(2):508–513. doi: 10.1128/jb.119.2.508-513.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZINDER N. D. Lysogenization and superinfection immunity in Salmonella. Virology. 1958 Apr;5(2):291–326. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(58)90025-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


