Abstract
Sequences of amino acids at the N-termini of virus proteins VP1, VP2, and VP3 were determined for foot-and-mouth disease virus types A12 strain 119, O1Brugge and C3Resende. In the polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis system used to purify the proteins, VP3 migrated faster than VP1 or VP2; and in the virion, VP3 could be cleaved by trypsin into VP3a and VP3b. The N-terminal amino acids for each of the virus types were glycine in VP1, aspartic acid in VP2, and threonine in VP3. No divergences in sequence across the virus types were indicated until at least the fourth position in VP1, and the third in VP3. For virus types A12, O1 and C3, the sequences were, respectively: for VP1 (Gly-ile-phe,pro,val---), (Gly,ile,phe---) and Gly-ile-phe,ala---); for VP2 (Asp,X,met---), (Asp---) and Asp-leu---); and for VP3 (Thr-thr-ala-thr---), (Thr-thr-ser---) and (Thr-thr---). Unresolved mixtures of VP3a and VP3b, from either A12 or O1 viruses, appeared to have the N-terminal amino acids threonine, which is presumed to be the same threonine as in uncleaved VP3 and serine, which is generated by the tryptic cleavage.
Full text
PDF
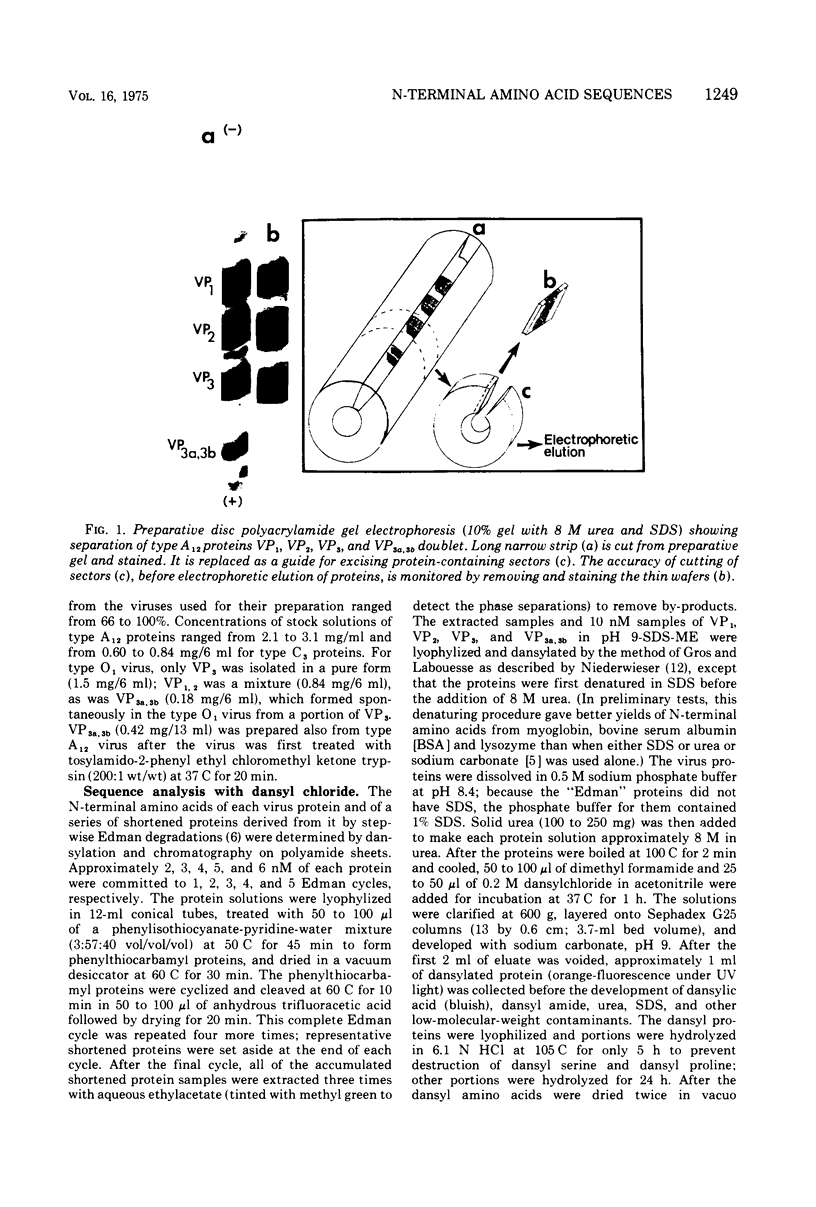
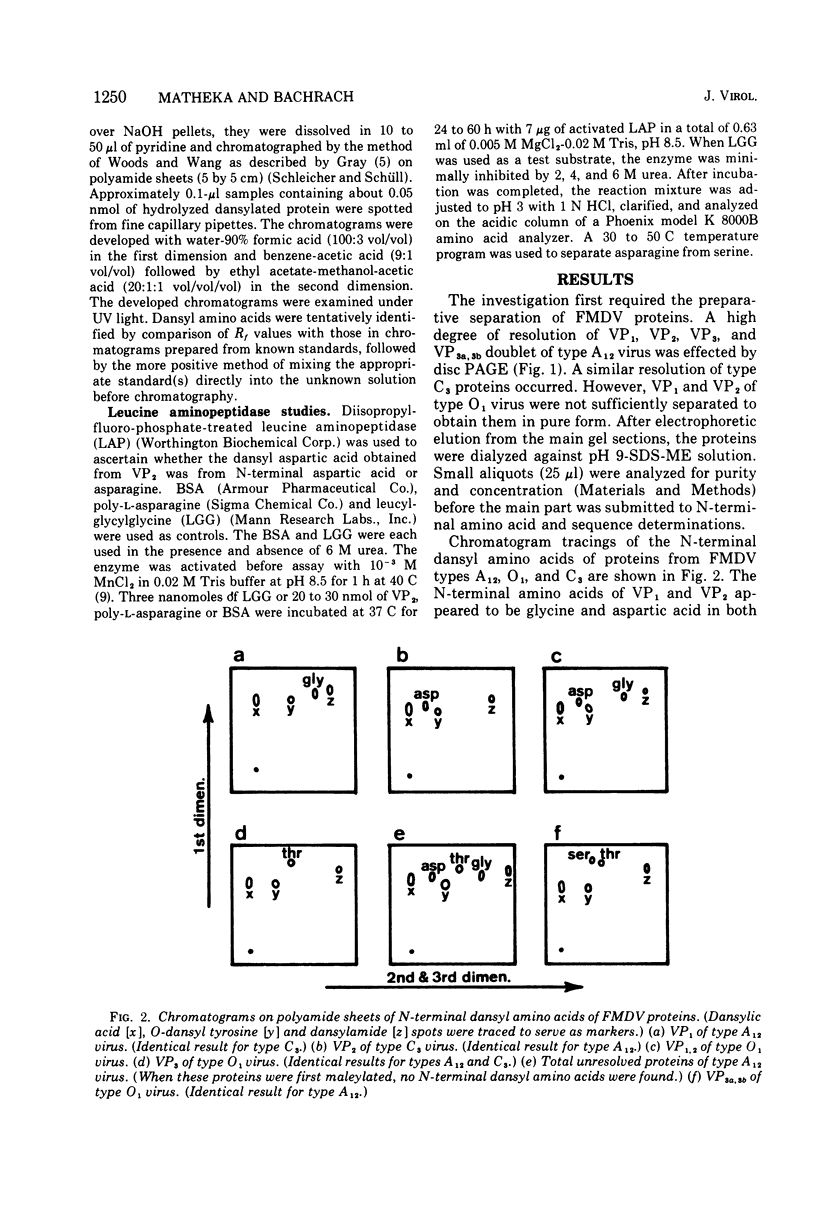



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adam K. H., Strohmaier K. Isolation of the coat proteins of foot-and-mouth disease virus and analysis of the composition and N-terminal endgroups. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Nov 6;61(1):185–192. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90551-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BACHRACH H. L., TRAUTMAN R., BREESE S. S., Jr CHEMICAL PHYSICAL PROPERTIES OF VIRTUALLY PURE FOOT-AND-MOUTH DISEASE VIRUS. Am J Vet Res. 1964 Mar;25:333–342. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachrach H. L., Swaney J. B., Vande Woude G. F. Isolation of the structural polypeptides of foot-and-mouth disease virus and analysis of their C-terminal sequences. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):520–528. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90347-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burrell C. J., Cooper P. D. N-terminal aspartate, glycine and serine in poliovirus capsid protein. J Gen Virol. 1973 Dec;21(3):443–451. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-21-3-443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King T. P., Spencer E. M. Amino acid sequences of the amino and the carboxyl terminal cyanogen bromide peptides of bovine plasma albumin. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1972 Dec;153(2):627–640. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(72)90382-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laporte J. The structure of foot-and-mouth disease virus protein. J Gen Virol. 1969 Jun;4(4):631–634. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-4-4-631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oroszlan S., Copeland T., Summers M. R., Gilden R. V. Feline leukemia and RD-114 virus group-specific proteins: comparison of amino terminal sequence. Science. 1973 Aug 3;181(4098):454–456. doi: 10.1126/science.181.4098.454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oroszlan S., Summers M. R., Foreman C., Gilden R. V. Murine type-C virus group-specific antigens: interstrain immunochemical, biophysical, and amino acid sequence differences. J Virol. 1974 Dec;14(6):1559–1574. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.6.1559-1574.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POLATNICK J., BACHRACH H. L. PRODUCTION AND PURIFICATION OF MILLIGRAM AMOUNTS OF FOOT-AND-MOUTH DISEASE VIRUS FROM BABY HAMSTER KIDNEY CELL CULTURES. Appl Microbiol. 1964 Jul;12:368–373. doi: 10.1128/am.12.4.368-373.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner G. G., Card J. L., Cowan K. M. Immunochemical studies of foot-and-mouth disease. VII. Characterization of foot-and-mouth disease virus concentrated by polyethylene glycol precipitation. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1970;30(4):343–352. doi: 10.1007/BF01258364. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Kuter D. J. Reversible denaturation of enzymes by sodium dodecyl sulfate. J Biol Chem. 1971 Jul 25;246(14):4504–4509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]