Abstract
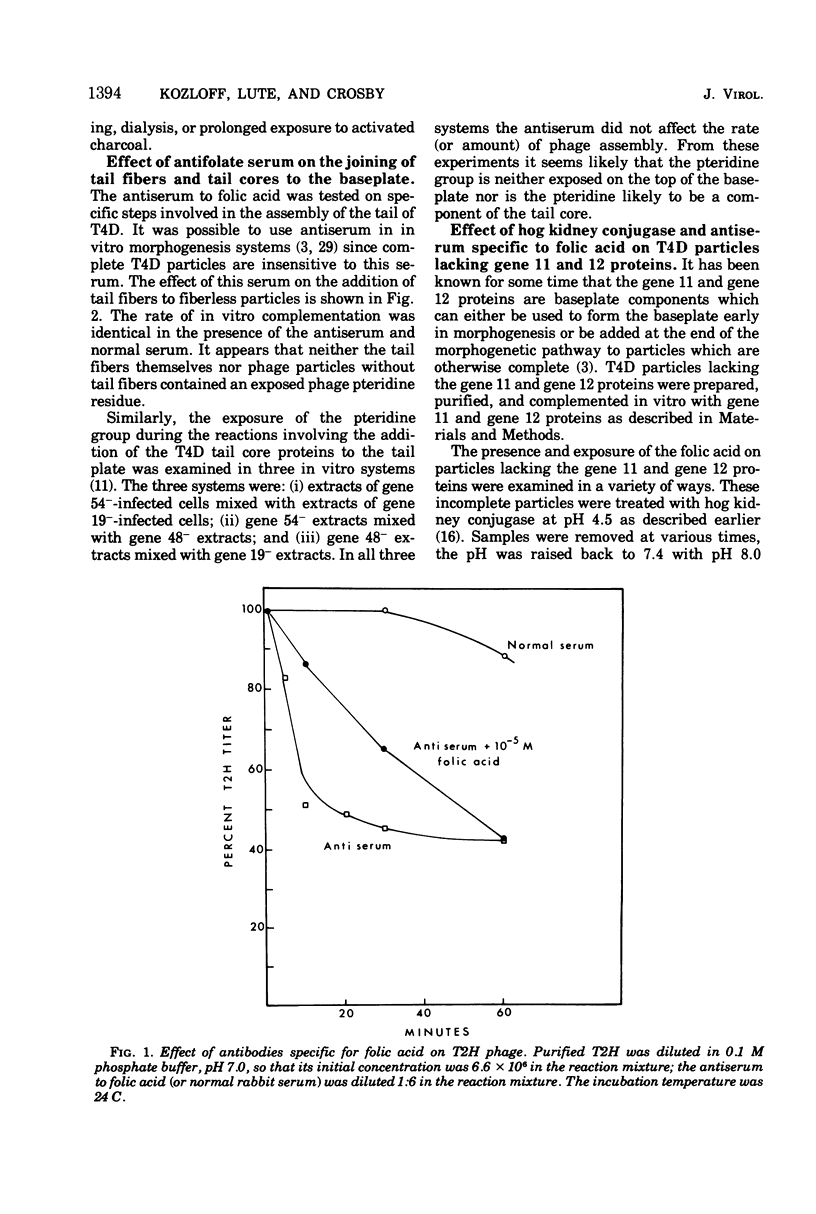
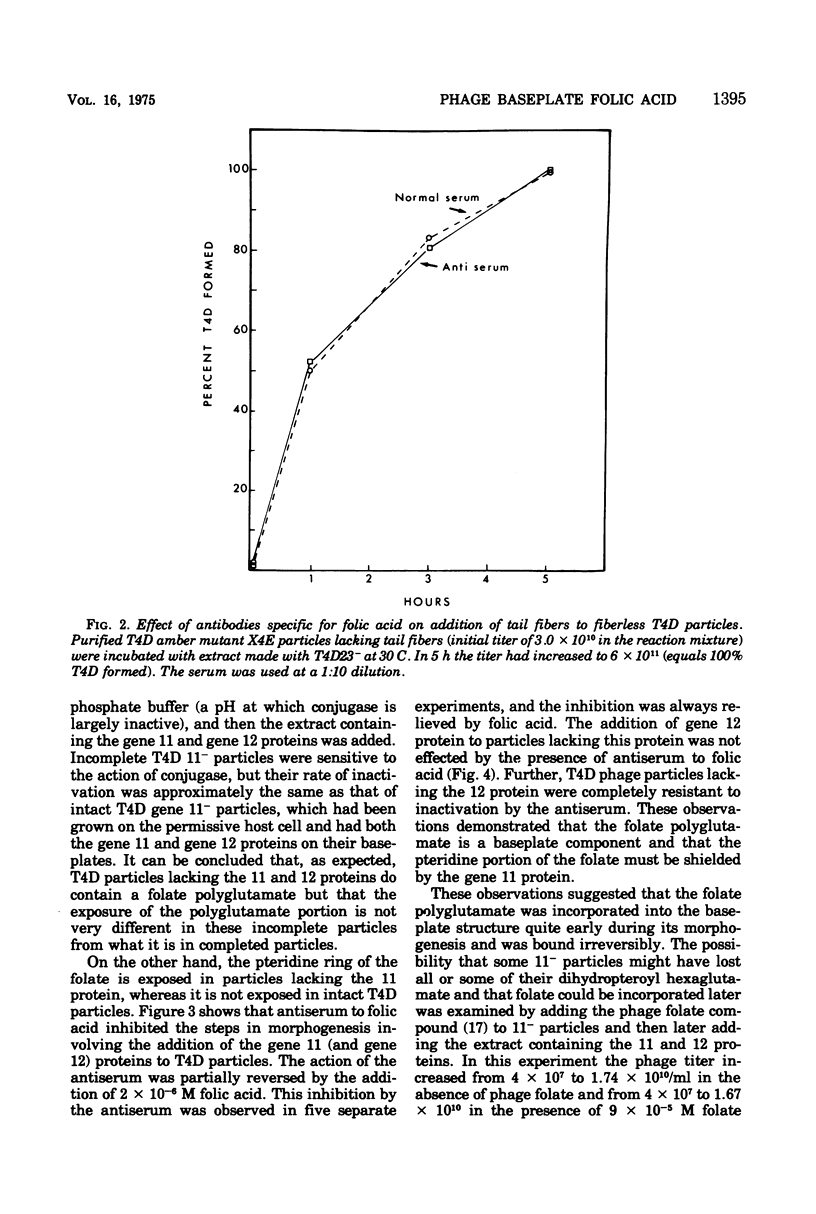
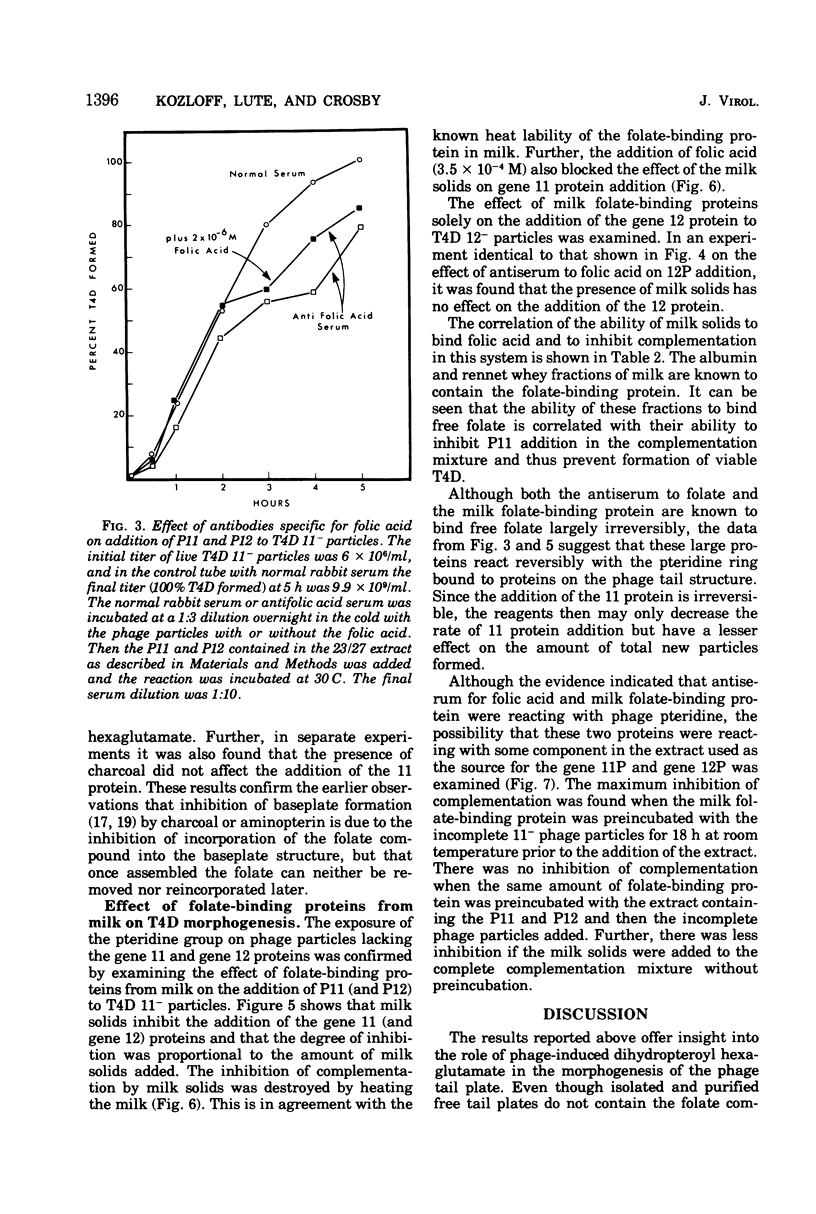
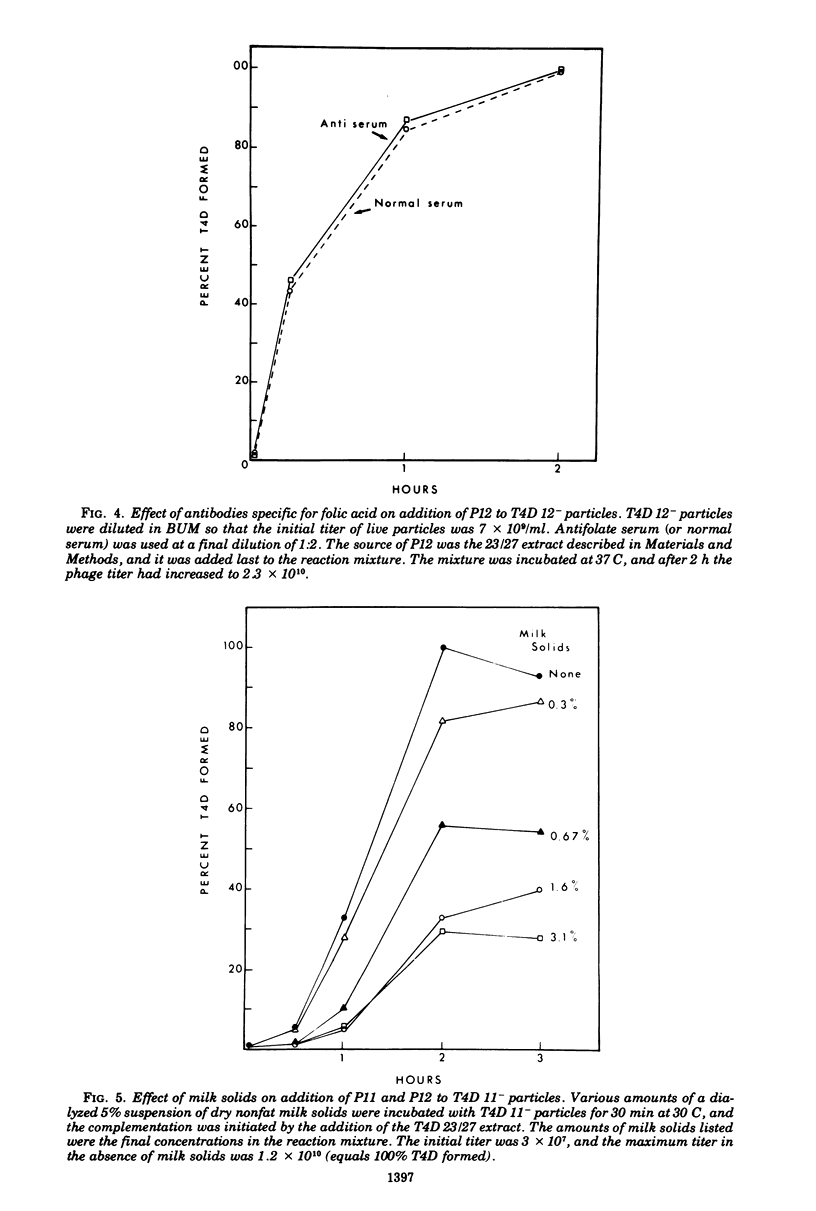
Two different proteins with high affinities for the pteridine ring of folic acid have been used to determine the location of this portion of the folate molecule in the tail plate of T4D and other T-even bacteriophage particles. The two proteins used were (i) antibody specific for folic acid and (ii) the folate-binding protein from bovine milk. Both proteins were examined for their effect on various intact and incomplete phage particles. Intact T2H was weakly inactivated by the antiserum but not by the milk protein. No other intact T-even phage, including T4D, was affected by these two proteins. When incomplete T4D particles were exposed in an in vitro morphogenesis system, it was found that neither of the two proteins affected either the addition of the long tail fibers to fiberless particles or the addition of tail cores to tail plates. On the other hand, these two proteins specifically blocked the addition of T4D gene 11 product to the bottom of T4D baseplates. After the addition of the gene 11 protein, these two reagents did not inhibit the further addition of the gene 12 protein to the baseplate. It can be concluded that the phage folic acid is a tightly bound baseplate constituent and that the pteridine portion of the folic acid is largely covered by the gene 11 protein.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Dawes J., Goldberg E. B. Functions of baseplate components in bacteriophage T4 infection. I. Dihydrofolate reductase and dihydropteroylhexaglutamate. Virology. 1973 Oct;55(2):380–390. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90178-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawes J., Goldberg E. B. Functions of baseplate components in bacteriophage T4 infection. II. Products of genes 5, 6, 7, 8, and 10. Virology. 1973 Oct;55(2):391–396. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90179-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edgar R. S., Lielausis I. Some steps in the assembly of bacteriophage T4. J Mol Biol. 1968 Mar 14;32(2):263–276. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90008-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edgar R. S., Wood W. B. Morphogenesis of bacteriophage T4 in extracts of mutant-infected cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Mar;55(3):498–505. doi: 10.1073/pnas.55.3.498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FLAKS J. G., COHEN S. S. Virus-induced acquisition of metabolic function. I. Enzymatic formation of 5-hydroxymethyldeoxycytidylate. J Biol Chem. 1959 Jun;234(6):1501–1506. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghitis J. The folate binding in milk. Am J Clin Nutr. 1967 Jan;20(1):1–4. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/20.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KANNER L. C., KOZLOFF L. M. THE REACTION OF INDOLE AND T2 BACTERIOPHAGE. Biochemistry. 1964 Feb;3:215–223. doi: 10.1021/bi00890a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kells S. S., Haselkorn R. Bacteriophage T4 short tail fibers are the product of gene 12. J Mol Biol. 1974 Mar 15;83(4):473–485. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90508-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King J. Assembly of the tail of bacteriophage T4. J Mol Biol. 1968 Mar 14;32(2):231–262. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90007-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King J., Mykolajewycz N. Bacteriophage T4 tail assembly: proteins of the sheath, core and baseplate. J Mol Biol. 1973 Apr 5;75(2):339–358. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90025-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozloff L. M., Crosby L. K., Lute M. Bacteriophage T4 baseplate components. III. Location and properties of the bacteriophage structural thymidylate synthetase. J Virol. 1975 Dec;16(6):1409–1419. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.6.1409-1419.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozloff L. M., Crosby L. K., Lute M., Hall D. H. Bacteriophage T4 baseplate components. II. Binding and location of bacteriophage-induced dihydrofolate reductase. J Virol. 1975 Dec;16(6):1401–1408. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.6.1401-1408.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozloff L. M., Lute M., Crosby L. K. Bacteriophage tail components. 3. Use of synthetic pteroyl hexaglutamate for T4D tail plate assembly. J Virol. 1970 Dec;6(6):754–759. doi: 10.1128/jvi.6.6.754-759.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozloff L. M., Lute M., Crosby L. K., Rao N., Chapman V. A., DeLong S. S. Bacteriophage tail components. I. Pteroyl polyglutamates in T-even bacteriophages. J Virol. 1970 Jun;5(6):726–739. doi: 10.1128/jvi.5.6.726-739.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozloff L. M., Lute M. Folic acid, a structural component of T4 bacteriophage. J Mol Biol. 1965 Jul;12(3):780–792. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80327-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozloff L. M., Verses C., Lute M., Crosby L. K. Bacteriophage tail components. II. Dihydrofolate reductase in T4D bacteriophage. J Virol. 1970 Jun;5(6):740–753. doi: 10.1128/jvi.5.6.740-753.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MATHEWS C. K., COHEN S. S. Virus-induced acquisition of metabolic function. VI. Dihydrofolate reductase, a new phage-induced enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1963 Feb;238:853–855. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Male C. J., Kozloff L. M. Function of T4D structural dihydrofolate reductase in bacteriophage infection. J Virol. 1973 Jun;11(6):840–847. doi: 10.1128/jvi.11.6.840-847.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason W. S., Haselkorn R. Product of T4 gene 12. J Mol Biol. 1972 May 28;66(3):445–469. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90426-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metz J., Zalusky R., Herbert V. Folic acid binding by serum and milk. Am J Clin Nutr. 1968 Apr;21(4):289–297. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/21.4.289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubenstein W. A., Little J. R. Properties of the active sites of antibodies specific for folic acid. Biochemistry. 1970 May 12;9(10):2106–2114. doi: 10.1021/bi00812a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon L. D., Anderson T. F. The infection of Escherichia coli by T2 and T4 bacteriophages as seen in the electron microscope. I. Attachment and penetration. Virology. 1967 Jun;32(2):279–297. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(67)90277-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon L. D., Anderson T. F. The infection of Escherichia coli by T2 and T4 bacteriophages as seen in the electron microscope. II. Structure and function of the baseplate. Virology. 1967 Jun;32(2):298–305. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(67)90278-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon L. D., Swan J. G., Flatgaard J. E. Functional defects in T4 bacteriophages lacking the gene 11 and gene 12 products. Virology. 1970 May;41(1):77–90. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90056-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tajuddin M., Gardyna H. A. Radioassay of serum folate, with use of a serum blank and nondialyzed milk as folate binder. Clin Chem. 1973 Jan;19(1):125–126. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terzaghi E. Purification and characterization of the protein product of gene 11 of bacteriophage T4D. J Biol Chem. 1974 Aug 25;249(16):5119–5125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waxman S., Schreiber C., Herbert V. Radioisotopic assay for measurement of serum folate levels. Blood. 1971 Aug;38(2):219–228. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood W. B., Edgar R. S., King J., Lielausis I., Henninger M. Bacteriophage assembly. Fed Proc. 1968 Sep-Oct;27(5):1160–1166. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagida M., Ahmad-Zadeh C. Determination of gene product positions in bacteriophage T4 by specific antibody association. J Mol Biol. 1970 Jul 28;51(2):411–421. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90151-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



