Abstract
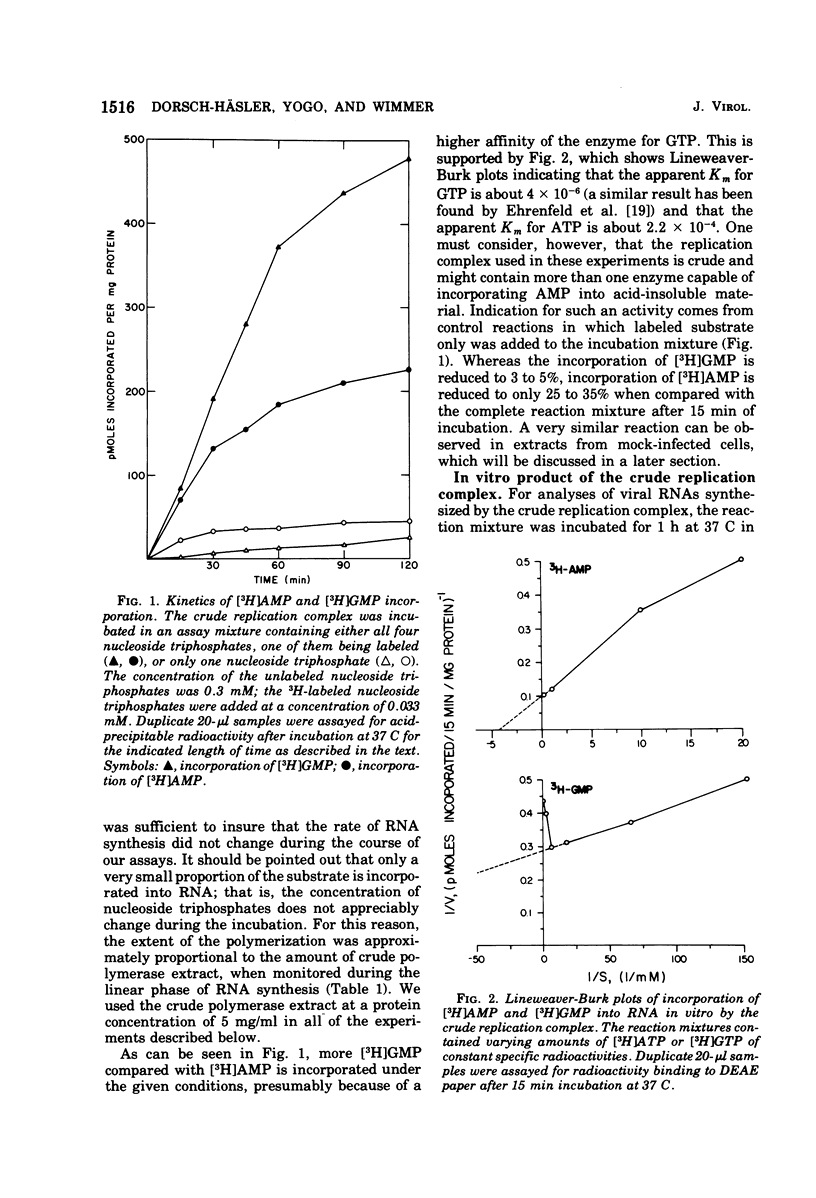
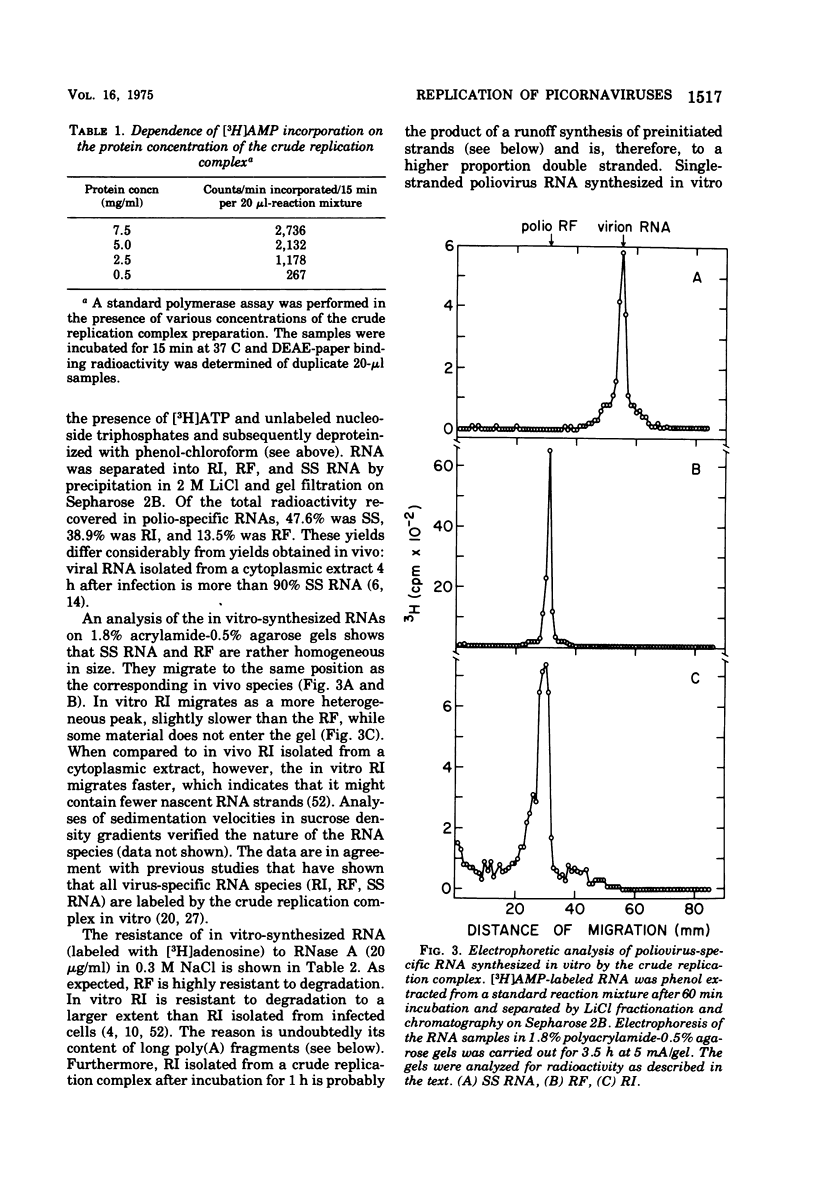
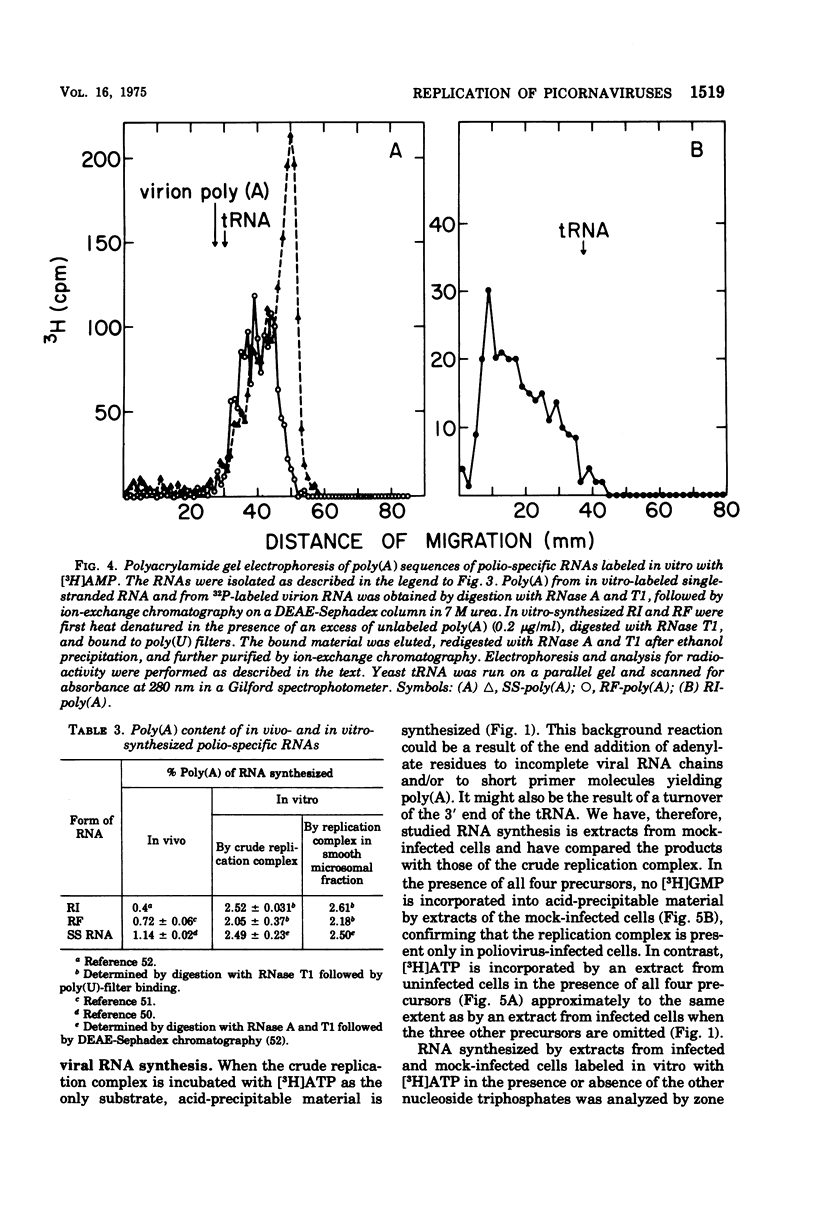
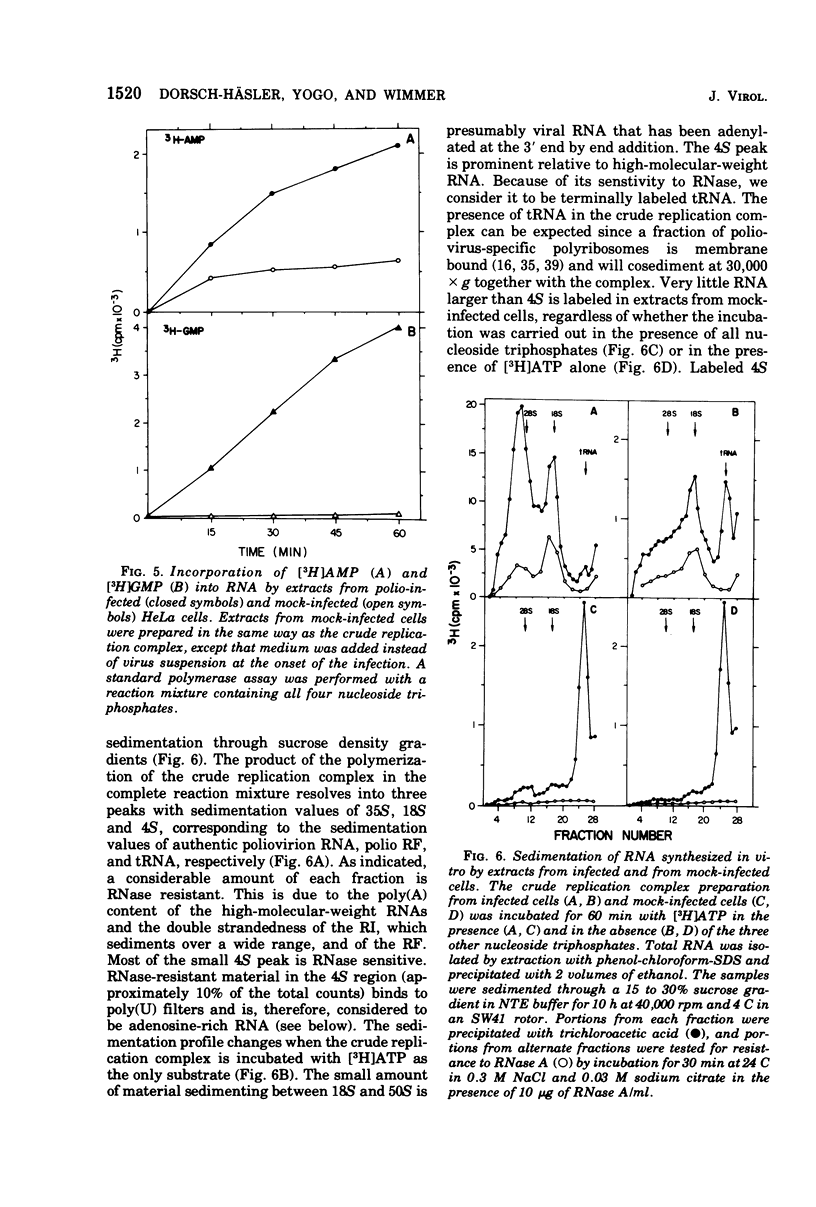
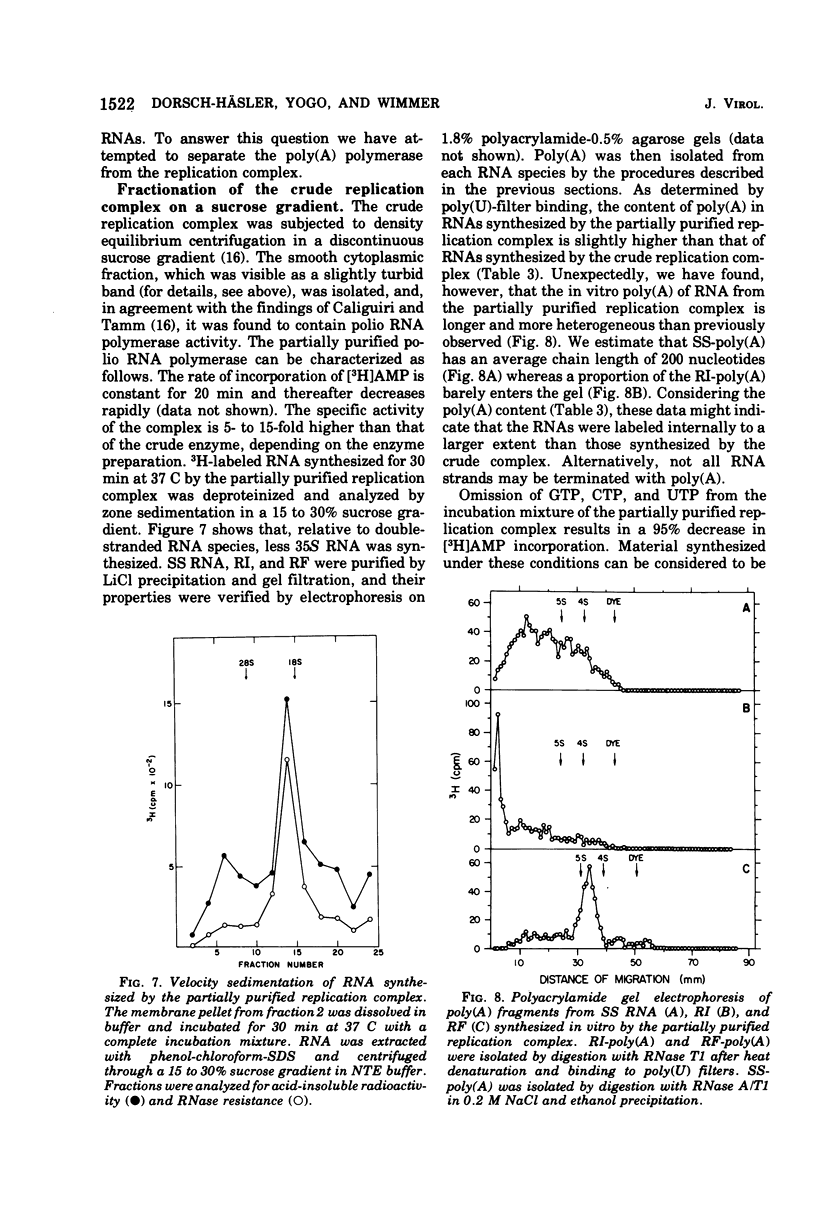
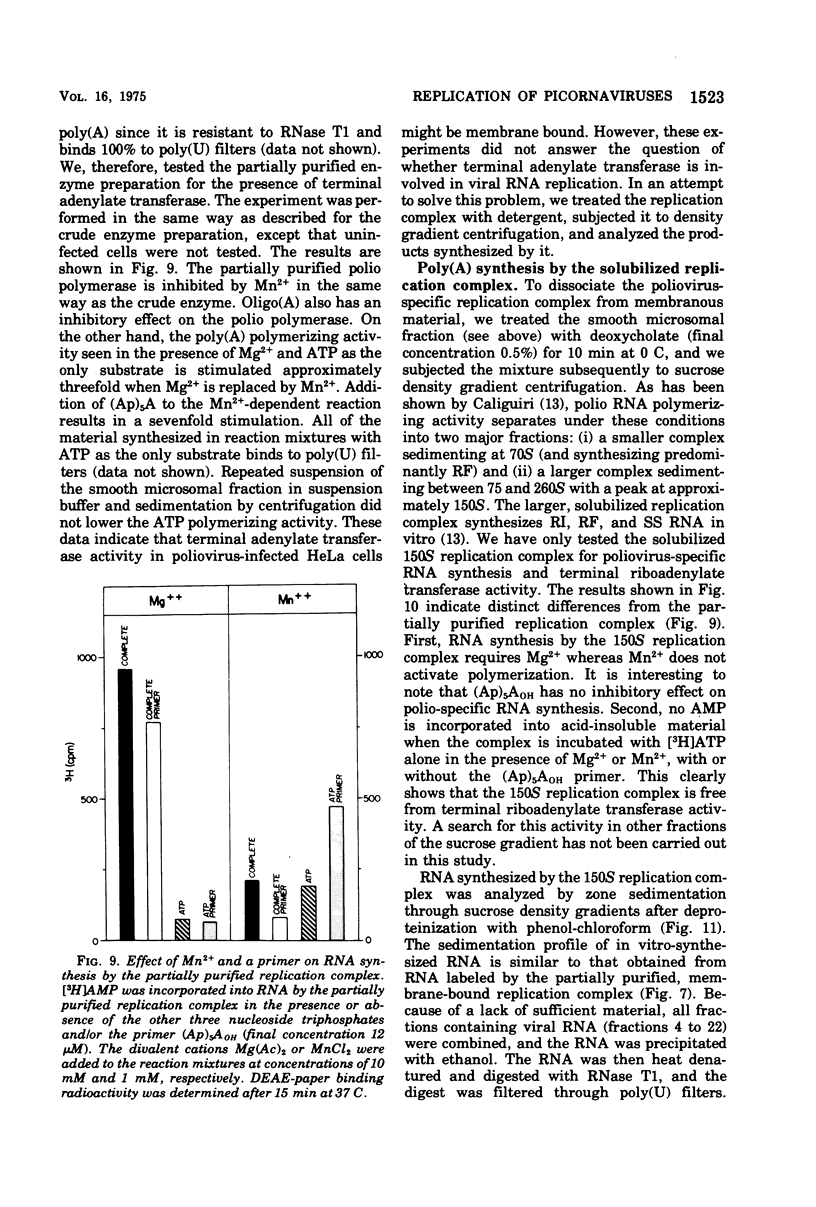
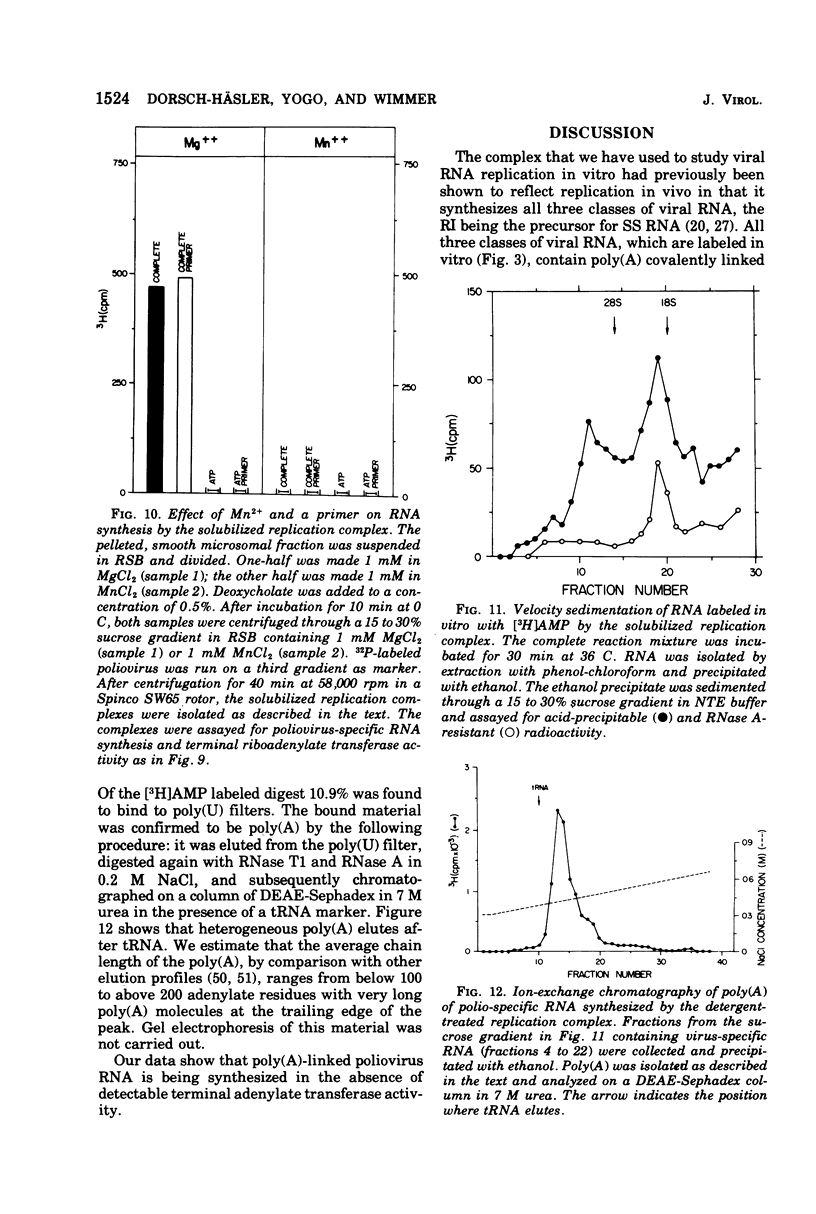
A crude replication complex has been isolated from poliovirus-infected HeLa cells and used for synthesis of poliovirus replicative intermediate (RI) RNA, replicative form (RF) RNA, and single-stranded (SS) RNA in vitro. All three classes of virus-specific RNA synthesized in vitro are shown to contain poly(A). Poly(A) of RF and of SS RNA [RF-poly(A) and SS-poly(A)] has a chain length (50 to 70 nucleotides) that is shorter than that of poly(A) of in vivo-synthesized RNAs. Poly(A) of RI [RI-poly(A),] however, is at least 200 nucleotides long and, therefore, larger than poly(A) of RI isolated from HeLa cells 4 h after infection. The crude membrane-bound replication complex contains a terminal adenylate transferase activity that is stimulated by Mn2+ and the addition of an (Ap)2AOH primer. This transferase activity is found also in extracts of mock-infected cells. Partial purificaiton of the replication complex in a stepwise sucrose gradient, in which the viral replicase is associated with the smooth cytoplasmic membrane fraction, does not remove the terminal transferase. However, when the partially purified replication complex is treated with deoxycholate and sedimented through a sucrose gradient, a soluble replication complex can be isolated that is free from terminal adenylate transferase. This soluble replication complex was found to synthesize viral RNA-linked poly(A) longer in chain length than that synthesized by the crude replication complex. Taking into account the 5'-terminal poly(U) in poliovirus minus strands, our data suggest that polyadenylation of poliovirus RNA occurs by transcription and not by end addition. When compared to other viral systems, poliovirus and, probably, all picornaviruses appear to be unique in that the poly(A) of their genome is genetically coded.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adesnik M., Darnell J. E. Biogenesis and characterization of histone messenger RNA in HeLa cells. J Mol Biol. 1972 Jun 28;67(3):397–406. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90458-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong J. A., Edmonds M., Nakazato H., Phillips B. A., Vaughn M. H. Polyadenylic acid sequences in the virion RNA of poliovirus and Eastern Equine Encephalitis virus. Science. 1972 May 5;176(4034):526–528. doi: 10.1126/science.176.4034.526. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BALTIMORE D. IN VITRO SYNTHESIS OF VIRAL RNA BY THE POLIOVIRUS RNA POLYMERASE. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Mar;51:450–456. doi: 10.1073/pnas.51.3.450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BEERS R. F., Jr Hydrolysis of polyadenylic acid by pancreatic ribonuclease. J Biol Chem. 1960 Aug;235:2393–2398. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baltimore D. Expression of animal virus genomes. Bacteriol Rev. 1971 Sep;35(3):235–241. doi: 10.1128/br.35.3.235-241.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baltimore D., Girard M. An intermediate in the synthesis of poliovirus RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Aug;56(2):741–748. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.2.741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baltimore D., Huang A. S., Stampfer M. Ribonucleic acid synthesis of vesicular stomatitis virus, II. An RNA polymerase in the virion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Jun;66(2):572–576. doi: 10.1073/pnas.66.2.572. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baltimore D. Structure of the poliovirus replicative intermediate RNA. J Mol Biol. 1968 Mar 14;32(2):359–368. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90015-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banerjee A. K., Moyer S. A., Rhodes D. P. Studies on the in vitro adenylation of RNA by vesicular stomatitis virus. Virology. 1974 Oct;61(2):547–558. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90289-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop J. M., Koch G. Infectious replicative intermediate of poliovirus: purification and characterization. Virology. 1969 Apr;37(4):521–534. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90270-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brawerman G. Eukaryotic messenger RNA. Annu Rev Biochem. 1974;43(0):621–642. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.43.070174.003201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M., Dorson J. W., Bollum F. J. Terminal riboadenylate transferase: a poly A polymerase in purified vaccinia virus. J Virol. 1973 Aug;12(2):203–208. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.2.203-208.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHAMBERLIN M., BERG P. MECHANISM OF RNA POLYMERASE ACTION: CHARACTERIZATION OF THE DNA-DEPENDENT SYNTHESIS OF POLYADENYLIC ACID. J Mol Biol. 1964 May;8:708–726. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(64)80120-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caliguiri L. A. Analysis of RNA associated with the poliovirus RNA replication complexes. Virology. 1974 Apr;58(2):526–535. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90086-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caliguiri L. A., Compans R. W. The formation of poliovirus particles in association with the RNA replication complexes. J Gen Virol. 1973 Oct;21:99–108. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-21-1-99. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caliguiri L. A., Mosser A. G. Proteins associated with the poliovirus RNA replication complex. Virology. 1971 Nov;46(2):375–386. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90039-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caliguiri L. A., Tamm I. The role of cytoplasmic membranes in poliovirus biosynthesis. Virology. 1970 Sep;42(1):100–111. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90242-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrenfeld E., Maizel J. V., Summers D. F. Soluble RNA polymerase complex from poliovirus-infected HeLa cells. Virology. 1970 Apr;40(4):840–846. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90129-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrenfeld E. Polyadenylation of vesicular stomatitis virus mRNA. J Virol. 1974 May;13(5):1055–1060. doi: 10.1128/jvi.13.5.1055-1060.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girard M. In vitro synthesis of poliovirus ribonucleic acid: role of the replicative intermediate. J Virol. 1969 Apr;3(4):376–384. doi: 10.1128/jvi.3.4.376-384.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz L., Penman S. The solvent denaturation of double-stranded RNA from poliovirus infected HeLa cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 May 25;23(4):557–560. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90765-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewin B. Units of transcription and translation: the relationship between heterogeneous nuclear RNA and messenger RNA. Cell. 1975 Jan;4(1):11–20. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90128-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall S., Gillespie D. Poly U tracts absent from viral RNA. Nat New Biol. 1972 Nov 8;240(97):43–45. doi: 10.1038/newbio240043a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonnell J. P., Levintow L. Kinetics of appearance of the products of poliovirus-induced RNA polymerase. Virology. 1970 Dec;42(4):999–1006. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90348-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milcarek C., Price R., Penman S. The metabolism of a poly(A) minus mRNA fraction in HeLa cells. Cell. 1974 Sep;3(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(74)90030-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss B., Rosenblum E. N., Paoletti E. Polyadenylate polymerase from vaccinia virions. Nat New Biol. 1973 Sep 12;245(141):59–63. doi: 10.1038/newbio245059a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nemer M., Graham M., Dubroff L. M. Co-existence of non-histone messenger RNA species lacking and containing polyadenylic acid in sea urchin embryos. J Mol Biol. 1974 Nov 5;89(3):435–454. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90474-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevins J. R., Joklik W. K. Poly (A) sequences of vaccinia virus messenger RNA: nature, mode of addition and function during translation in vitra and in vivo. Virology. 1975 Jan;63(1):1–14. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90365-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oberg B., Philipson L. Replicative structures of poliovirus RNA in vivo. J Mol Biol. 1971 Jun 28;58(3):725–737. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90036-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olivera B. M., Lehman I. R. Enzymic joining of polynucleotides. 3. The polydeoxyadenylate-polydeoxythymidylate homopolymer pair. J Mol Biol. 1968 Sep 14;36(2):261–274. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90380-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PENMAN S., BECKER Y., DARNELL J. E. A CYTOPLASMIC STRUCTURE INVOLVED IN THE SYNTHESIS AND ASSEMBLY OF POLIOVIRUS COMPONENTS. J Mol Biol. 1964 Apr;8:541–555. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(64)80010-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penman S., Rosbash M., Penman M. Messenger and heterogeneous nuclear RNA in HeLa cells: differential inhibition by cordycepin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Dec;67(4):1878–1885. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.4.1878. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roeder R. G. Multiple forms of deoxyribonucleic acid-dependent ribonucleic acid polymerase in Xenopus laevis. Isolation and partial characterization. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jan 10;249(1):241–248. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roeder R. G., Rutter W. J. Multiple forms of DNA-dependent RNA polymerase in eukaryotic organisms. Nature. 1969 Oct 18;224(5216):234–237. doi: 10.1038/224234a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roumiantzeff M., Maizel J. V., Jr, Summers D. F. Comparison of polysomal structures of uninfected and poliovirus infected HeLa cells. Virology. 1971 May;44(2):239–248. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90256-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shatkin A. J. Animal RNA viruses: genome structure and function. Annu Rev Biochem. 1974;43(0):643–665. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.43.070174.003235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheldon R., Jurale C., Kates J. Detection of polyadenylic acid sequences in viral and eukaryotic RNA(polu(U)-cellulose columns-poly(U) filters-fiberglass-HeLa cells-bacteriophage T4). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Feb;69(2):417–421. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.2.417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheldon R., Kates J. Mechanism of poly(A) synthesis by vaccinia virus. J Virol. 1974 Aug;14(2):214–224. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.2.214-224.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soria M., Little S. P., Huang A. S. Characterization of vesicular stomatitis virus nucleocapsids. I. Complementary 40 S RNA molecules in nucleocapsids. Virology. 1974 Sep;61(1):270–280. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90261-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector D. H., Baltimore D. Polyadenylic acid on poliovirus RNA. III. In vitro addition of polyadenylic acid to poliovirus RNAs. J Virol. 1975 Jun;15(6):1432–1439. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.6.1432-1439.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector D. H., Baltimore D. Requirement of 3'-terminal poly(adenylic acid) for the infectivity of poliovirus RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Aug;71(8):2983–2987. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.8.2983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoltzfus C. M., Shatkin A. J., Banerjee A. K. Absence of polyadenylic acid from reovirus messenger ribonucleic acid. J Biol Chem. 1973 Dec 10;248(23):7993–7998. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsiapalis C. M., Dorson J. W., De Sante D. M., Bollum F. J. Terminal riboadenylate transferase: a polyadenylate polymerase from calf thymus gland. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Feb 5;50(3):737–743. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)91306-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villarreal L. P., Holland J. J. Synthesis of poly(A) in vitro by purified virions of vesicular stomatitis virus. Nat New Biol. 1973 Nov 7;246(149):17–19. doi: 10.1038/newbio246017a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yogo Y., Teng M. H., Wimmer E. Poly(U) in poliovirus minus RNA is 5'-terminal. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Dec 23;61(4):1101–1109. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(74)80397-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yogo Y., Wimmer E. Poly (A) and poly (U) in poliovirus double stranded RNA. Nat New Biol. 1973 Apr 11;242(119):171–174. doi: 10.1038/newbio242171a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yogo Y., Wimmer E. Polyadenylic acid at the 3'-terminus of poliovirus RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jul;69(7):1877–1882. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.7.1877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yogo Y., Wimmer E. Sequence studies of poliovirus RNA. III. Polyuridylic acid and polyadenylic acid as components of the purified poliovirus replicative intermediate. J Mol Biol. 1975 Mar 5;92(3):467–477. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90292-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


