Abstract
Background
The Li-Fraumeni syndrome (LFS), an inherited rare cancer predisposition syndrome characterized by a variety of early-onset tumors, is caused by different highly penetrant germline mutations in the TP53 gene; each separate mutation has dissimilar functional and phenotypic effects, which partially clarifies the reported heterogeneity between LFS families. Increases in copy number variation (CNV) have been reported in TP53 mutated individuals, and are also postulated to contribute to LFS phenotypic variability. The Brazilian p.R337H TP53 mutation has particular functional and regulatory properties that differ from most other common LFS TP53 mutations, by conferring a strikingly milder phenotype.
Methods
We compared the CNV profiles of controls, and LFS individuals carrying either p.R337H or DNA binding domain (DBD) TP53 mutations by high resolution array-CGH.
Results
Although we did not find any significant difference in the frequency of CNVs between LFS patients and controls, our data indicated an increased proportion of rare CNVs per genome in patients carrying DBD mutations compared to both controls (p=0.0002***) and p.R337H (0.0156*) mutants.
Conclusions
The larger accumulation of rare CNVs in DBD mutants may contribute to the reported anticipation and severity of the syndrome; likewise the fact that p.R337H individuals do not present the same magnitude of rare CNV accumulation may also explain the maintenance of this mutation at relatively high frequency in some populations.
Keywords: TP53, R337H, Li-Fraumeni syndrome, CNV, Penetrance
Background
Li-Fraumeni syndrome (LFS; OMIM #151623) is an autosomal dominant highly penetrant cancer predisposition syndrome characterized by a variety of early onset tumors [1,2]. LFS arises from germline mutations in the TP53 gene, which codes for a transcription factor implicated in cell proliferation, apoptosis, and genomic stability [3,4]. Although decreases in the age of cancer onset and increases in cancer incidence over successive generations have been documented in LFS [5,6], the molecular basis of this anticipation is still a matter of debate.
Most mutations in the TP53 gene affect the DNA binding domain (DBD) and result in missense substitutions giving rise to altered proteins [7] that have a considerable longer half-life than the wild-type protein, resulting in accumulation of the mutant protein, at least in transfected or neoplastic cells [8].
It is known that different mutant p53 proteins may have diverse functional and biological effects, which could partially explain the heterogeneity reported between Li-Fraumeni families [9]. Not only the type of TP53 mutation determines the tumor spectrum and severity of phenotype, but other germline genetic factors such as polymorphisms for TP53 and MDM2[10] and telomere length [11,12] are assumed to modulate the cancer phenotype. It has been more recently observed that individuals carrying TP53 mutations show a ~3-fold increase in DNA copy number variation (CNV) compared to controls, suggesting that CNVs make an additive contribution to cancer risk [13].
In Brazil, the Li-Fraumeni syndrome also occurs as a frequent cancer predisposition alteration due to a germline mutation at codon 337 (c.1010G4A, p.R337H) that has been identified in families matching LFS definitions [14,15]. The frequency of p.R337H in the population of Southern Brazil is about 1:280 individuals, about 300 times higher than any other single germline TP53 mutation [16]. Analysis of 28 polymorphic markers showed p.R337H to have arisen from a founder mutation that has been spreading in the Brazilian population since the XVIII century [17,18]. This mildly pathogenic mutation shows a penetrance for cancer of less than 20% by age 30, compared to about 50% in classic LFS [18]: this provides more opportunity for transmitting the mutation to the next generations, which explains, at least in part, the maintenance in the Brazilian population.
Structural and functional studies have demonstrated that the p.R337H protein displays a pH-dependence, rendering the protein inactive only under conditions of increased intracellular pH, and the majority of the time behaves normally, which could explain its lower overall malignant potential [19].
It is accepted that differences in severity and age of onset of cancer manifestation linked to various germline TP53 mutations not only result from the TP53 mutations themselves, but also from their interaction with other genetic variants, of which CNVs are now becoming recognized as a significant contributant (reviewed in [20]). Based on the foregoing considerations we hypothesize that different types of TP53 mutations exhibit different CNV profiles reflecting the genotype- phenotype correlation and also possibly playing a role in the anticipation observed in LFS families.
Methods
Patients
The patients were seen in the Department of Oncogenetics in the A. C. Camargo Hospital, São Paulo, Brazil. Research protocol approval was provided by the ethics committee of the institution, and informed consent obtained from all subjects and their families. The cohort comprised 21 probands with TP53 germline mutations [14]. The characteristics of the mutations, cancer type, age at onset and clinical classification of the patients are described in Table 1.
Table 1.
Clinical data of the patients and characteristics of the detected mutations
| ID | Classification | Gender | TP53 mutation | Effect | p53 protein domain function | Tumor type (age) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Y1T0 |
Chompret |
F |
R213Q CGA>CAA |
Missense |
DNA binding |
Hydathiform mole (23), Ampulla of Vater (41) |
| Y33T0 |
LFL Birch |
F |
V173M GTG>ATG |
Missense |
DNA binding |
Soft tissue sarcoma (23), Breast (43) |
| Y53T0 |
Eeles1 |
F |
G245S GGC>AGC |
Missense |
DNA binding |
Bilateral breast (36), Gall bladder (?) |
| Y57T0 |
Eeles1 |
F |
G244D GGC>GAC |
Missense |
DNA binding |
Breast (40), Colorectal (?) |
| Y65T0 |
Chompret |
F |
V197M GTG >ATG |
Missense |
DNA binding |
Colorectal (45), Lung (51), Soft tissue sarcoma (51) |
| Y79T0 |
Chompret |
F |
T125T ACG>ACA |
Splice |
DNA binding |
Adrenal carcinoma (1) |
| Y87T0 |
LFL/Chompret |
M |
S241Y TCC>TAC |
Missense |
DNA binding |
Rhabdomyosarcoma (2), Choroid plexus tumor (7), Liposarcoma (10) |
| Y97T1 |
LFS |
F |
IVS8+1G>A |
Splice |
DNA binding |
Breast (27) |
| Y103T2 |
LFL/Chompret |
F |
H214Q |
Missense |
DNA binding |
Breast (62) |
| Y12T1 |
LFS |
F |
R337H CGC>CAC |
Missense |
Tetramerisation |
Soft tissue sarcoma (58), Breast (59), Thyroid (61), Soft tissue sarcoma (62) |
| Y15T0 |
Chompret |
F |
R337H CGC>CAC |
Missense |
Tetramerisation |
Adrenal carcinoma (6), Kidney (7) |
| Y27T0 |
LFL Birch |
F |
R337H CGC>CAC |
Missense |
Tetramerisation |
Breast (36) |
| Y49T1 |
Eeles 1 |
M |
R337H CGC>CAC |
Missense |
Tetramerisation |
Kidney (64) |
| Y99T0 |
Chompret |
F |
R337H CGC>CAC |
Missense |
Tetramerisation |
Breast (32) |
| Y100T0 |
LFS |
F |
R337H CGC>CAC |
Missense |
Tetramerisation |
Breast (46) |
| Y106T0 |
Chompret |
F |
R337H CGC>CAC |
Missense |
Tetramerisation |
Breast (43) |
| Y107T0 |
LFS |
M |
R337H CGC>CAC |
Missense |
Tetramerisation |
Adrenal carcinoma (2) |
| Y127T0 |
Chompret |
M |
R337H CGC>CAC |
Missense |
Tetramerisation |
Adrenal carcinoma (3) |
| Y131T0 |
LFS |
F |
R337H CGC>CAC |
Missense |
Tetramerisation |
Leg synovial sarcoma (32) |
| Y144T0 |
Chompret |
F |
R337H CGC>CAC |
Missense |
Tetramerisation |
Breast (29) |
| Y154T0 | Chompret | F | R337H CGC>CAC | Missense | Tetramerisation | Breast (48) |
Controls
The CNV control data used in this study was obtained from a previously reported group of 100 random individuals from the urban area of São Paulo, Brazil [21].
Array-CGH
We performed oligonucleotide microarray-based CGH (array-CGH) using a 4 × 180 K whole-genome platform (design 22060, Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, USA), which has an average spacing of 18 Kb between probes. Briefly, samples were labeled with Cy3- and Cy5-dCTPs by random priming; purification, hybridization, and washing were carried out as recommended by the manufacturer. Scanned images of the arrays were processed and analyzed using Feature Extraction software and Genomic Workbench software (both from Agilent Technologies), with the statistical algorithm ADM-2, and a sensitivity threshold of 6.7. We applied a′loop design′ in our hybridizations as previously described [22], resulting in two reverse labeling hybridizations per sample. We considered a gain or loss in copy number when the log2 ratio of the Cy3/Cy5 intensities of a given genomic segment was >0.5 or <−0.8, respectively. Alterations had to encompass at least three consecutive probes to be called by the software, and those not detected in both dye-swap experiments of the same sample were excluded from the analysis.
Analysis
The detected copy number variations were compared to CNVs reported in the Database of Genomic Variants (DGV; http://projects.tcag.ca/variation/; freeze December, 2011). We classified the CNVs into ″rare″ and ″common″, considering as ″rare″ those CNVs where the imbalances encompassed coding sequences which were never or only once reported in DGV. Mann–Whitney and Fisher-exact tests were used to evaluate CNVs regarding proportions of total and rare CNVs, frequency of deletions and duplications and size of the variation.
The frequencies were then calculated for each rare variant in the total population described in the DGV studies. For estimating the total population in DGV, BAC array publications have been excluded because they are known to overestimate the CNV boundaries; the remaining 22 studies comprised a total of 8058 individuals investigated. The frequencies of these rare variants were than cross-checked with a study comprising 8148 controls [23], which is not documented in DGV but is registered in dbVar (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/dbvar).
Results
The CNV data of this study are summarized in Table 2; a full description of the CNVs identified in the patients can be found in Additional file 1. The overall frequency of CNVs per genome did not differ either between patients and controls or between p.R33H and DBD mutants (Mann–Whitney test). No significant differences were detected between the groups regarding CNV size or frequency of deletions and duplications.
Table 2.
Copy number variation data in controls and LFS/LFL patients classified according to TP53 mutation type
| Controls | p.R337H carriers | DBD mutation carriers | |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Number of individuals |
100 |
12 |
9 |
|
Number of CNVs |
702 |
92 |
66 |
| Common |
679 |
89 |
56 |
| Rare |
23 |
3 |
10 |
|
Average number of all CNVs per diploid genome |
7.0±3.1 |
7.7±2.2 |
7.3±2.5 |
|
Average number of rare CNVs per diploid genome |
0.2±0.4 |
0.2±0.6 |
1.1±1.3a |
| Proportion of rare/common CNVs | 0.034 | 0.034b | 0.179c |
a. difference between controls and DBD mutation carriers (p=0.0026**).
b. difference between p.R337H and DBD mutation carriers (p=0.0156*).
c. difference between controls and DBD mutation carriers (p=0.0002***).
However, with regards to rarity, we found 13 rare CNVs among all LFS patients, including 9 deletions and 4 duplications. Additional file 2 describes the rare CNVs, the studies in which they have been observed and their corresponding frequencies in the combined individuals of DGV and dbVar. The calculated frequencies of these rare variants in normal populations as estimated based both on DGV and dbVar were < 0.1%, a value much inferior to the 1% threshold often associated with polimorphisms.
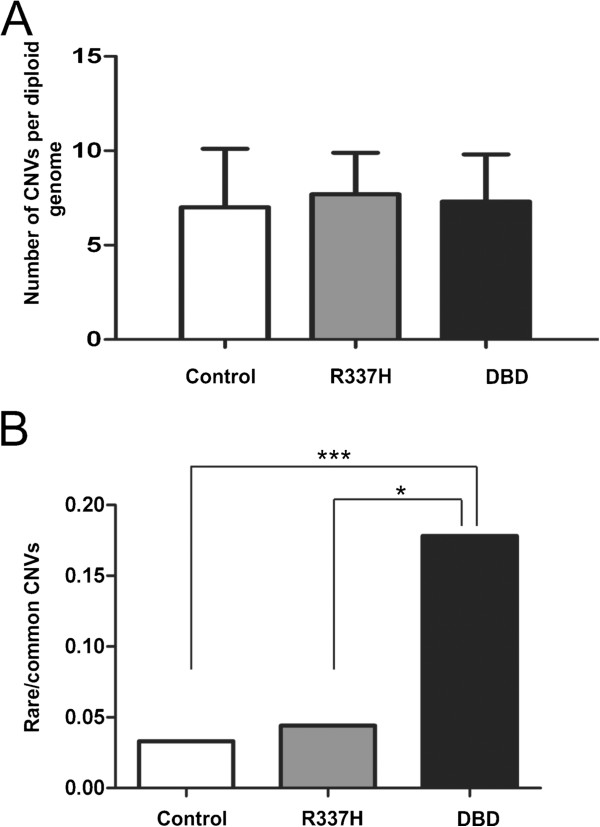
In comparison to our control group, TP53 mutated individuals (p.R337H and DBD) did not exhibit differences in the total number of CNVs/genome (Figure 1A). However, we did find a highly significant increase in the rare/common CNV ratio in the LFS patients carrying mutations in the TP53 DBD when compared to both controls (p=0.0002) and to patients carrying the p.R337H mutation (p=0.0156; Fisher-exact test) (Figure 1B). Interestingly, no significant difference was found between controls and p.R337H patients.
Figure 1.
Distribution of CNVs according to TP53 mutation status. The graphs show no differences in the frequency of total CNVs but an increased frequency of rare CNVs in DBD mutation carriers. (A) Frequency of total CNVs in LFS patients and controls; (B) Rare/common CNV ratio in LFS patients and controls. White bar represents the control individuals, grey bar represents p.R337H mutated carriers and dark black bar the TP53 DBD mutated carriers. Fisher-exact test; *p=0.0156 and ***p=0.0002.
Discussion
The vast majority of TP53 mutations lies within the DNA binding domain and target critical sites that either make contact with DNA or are required to maintain appropriate p53 protein conformation. Such alterations lead to a significant loss of TP53 transcription and tumor suppressive activity, with great impact on genomic stability and apoptosis [24-26]. In contrast, the p.R337H mutation, which affects a residue of the oligomerization domain of the p53 protein, has a markedly less severe impact on tumor predisposition, which correlates with its remaining p53 activity [19,27].
Shlien et al. [13] reported a ~3-fold increase in the frequency of CNVs in TP53 germline mutation carriers compared to normal individuals, and proposed that this increase might result from enhanced genome instability in the presence of TP53 mutations. In our study, we found no difference between the total number of germline CNVs present in LFS patients and controls; however, we noted a highly significant increase (>5 fold) in the rare CNVs in TP53 DBD mutation carriers as compared both to controls and to p.R337H carriers. A difference between Shlien et al. [13] data and ours refers to the controls samples: in their work data previously assembled in other studies were used to establish a baseline CNV control frequency, whereas our control and patient samples have been investigated in parallel in the same laboratory. We should also point out that the studies were carried out using different microarray technologies, namely array-CGH and SNP platforms. In fact, a large study comparing different platforms found that different analytic tools typically yield CNV calls with <50% concordance, overall regarding smaller CNVs [28].
An increase of only rare germline CNVs in the DBD TP53 carriers, rather than an overall increase in CNVs, suggests that a selective mechanism would be involved in this event. Under the assumption that pathogenic variants would only remain in the population at low frequency, the selection against new pathogenic CNVs (in the context of studies on schizophrenia and autism, respectively) is extremely high [29,30]. The finding of an increased proportion of rare CNVs, potentially pathogenic, among TP53 DBD mutants may be the result of an inefficient selection against new CNVs (deficient apoptosis). This hypothesis could be tested by determining the pattern of inheritance of the CNVs [13], but unfortunately parents were not available for investigation.
Anticipation, characterized by an increase of penetrance and earlier age of onset over subsequent generations, has been well documented for LFS [5,6]. An accumulation of germline CNVs impacting cancer predisposition in LFS provides a logical explanation for anticipation. How CNVs and other genetic modifiers interact and modulate TP53 tumor suppressor activities remains to be determined. Elucidating these mechanisms may hold the key to defining evidence-based strategies for diagnosis, counseling, follow-up and therapeutic care based on a detailed understanding of the nature of combined risk between TP53 and other variants, including CNVs.
Conclusions
In this work we show a highly significant increase of rare CNVs in patients with mutations in the TP53 DNA binding domain site (DBD) relative both to controls and to carriers of the mild TP53 Brazilian variant. An accumulation of rare CNVs over generations in the presence of penetrant TP53 mutation provides a plausible explanation for anticipation in LFS: in contrast, lack of this increase in rare CNVs combined with a longer lifespan and likelihood of reproduction probably contributes to the frequency of the p.R337H mutation being ~300 xs larger than reported for any other TP53 mutation.
Availability of supporting data
The data set supporting the results of this article is included within the article and its additional files.
Abbreviations
LFS: Li-Fraumeni syndrome; LFL: Li-Fraumeni like syndrome; CNV: Copy Number Variation; DBD: DNA binding domain.
Misc
Amanda G. Silva and Maria Isabel W Achatz are the first 2 authors that should be regarded as joint First Authors.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Authors' contributions
AGS carried out the molecular genetic studies. AGS and PLP wrote the manuscript. ACVK and CR participated in the design and coordination of the study and helped writing the manuscript. MIWA recruited and selected the patients. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Supplementary Material
Results of Array-CGH. Full CNV data of LFS/LFL patients, chromosome coordinates given according to Hg18 (NCBI Build 36.1/hg18; http://genome.ucsc.edu).
Frequency of the rare CNVs detected in theTP53mutated individuals.
Contributor Information
Amanda G Silva, Email: amandagonc@yahoo.com.
Isabel Maria W Achatz, Email: miachatz@gmail.com.
Ana CV Krepischi, Email: ana.krepischi@gmail.com.
Peter L Pearson, Email: peterlpearson@uol.com.br.
Carla Rosenberg, Email: carlarosenberg@uol.com.br.
Acknowledgments
We thank all patients for their participation to this study. We also thank the Brazilian National Institute of Science and Technology in Oncogenomics and FAPESP for financial support.
References
- Li FP, Fraumeni JF, Mulvihill JJ, Blattner WA, Dreyfus MG, Tucker MA, Miller RW. A cancer family syndrome in twenty-four kindreds. Cancer Res. 1988;48(18):5358–5362. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birch JM, Alston RD, McNally RJ, Evans DG, Kelsey AM, Harris M, Eden OB, Varley JM. Relative frequency and morphology of cancers in carriers of germline TP53 mutations. Oncogene. 2001;20(34):4621–4628. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1204621. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malkin D, Li FP, Strong LC, Fraumeni JF, Nelson CE, Kim DH, Kassel J, Gryka MA, Bischoff FZ, Tainsky MA. Germ line p53 mutations in a familial syndrome of breast cancer, sarcomas, and other neoplasms. Science. 1990;250(4985):1233–1238. doi: 10.1126/science.1978757. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eeles RA. Germline mutations in the TP53 gene. Cancer Surv. 1995;25:101–124. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trkova M, Hladikova M, Kasal P, Goetz P, Sedlacek Z. Is there anticipation in the age at onset of cancer in families with Li-Fraumeni syndrome? J Hum Genet. 2002;47(8):381–386. doi: 10.1007/s100380200055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown BW, Costello TJ, Hwang SJ, Strong LC. Generation or birth cohort effect on cancer risk in Li-Fraumeni syndrome. Hum Genet. 2005;118(3–4):489–498. doi: 10.1007/s00439-005-0016-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine AJ, Momand J, Finlay CA. The p53 tumour suppressor gene. Nature. 1991;351(6326):453–456. doi: 10.1038/351453a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersen TI, Holm R, Nesland JM, Heimdal KR, Ottestad L, Børresen AL. Prognostic significance of TP53 alterations in breast carcinoma. Br J Cancer. 1993;68(3):540–548. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1993.383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petitjean A, Achatz MI, Borresen-Dale AL, Hainaut P, Olivier M. TP53 mutations in human cancers: functional selection and impact on cancer prognosis and outcomes. Oncogene. 2007;26(15):2157–2165. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1210302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcel V, Palmero EI, Falagan-Lotsch P, Martel-Planche G, Ashton-Prolla P, Olivier M, Brentani RR, Hainaut P, Achatz MI. TP53 PIN3 and MDM2 SNP309 polymorphisms as genetic modifiers in the Li-Fraumeni syndrome: impact on age at first diagnosis. J Med Genet. 2009;46(11):766–772. doi: 10.1136/jmg.2009.066704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabori U, Nanda S, Druker H, Lees J, Malkin D. Younger age of cancer initiation is associated with shorter telomere length in Li-Fraumeni syndrome. Cancer Res. 2007;67(4):1415–1418. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-3682. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trkova M, Prochazkova K, Krutilkova V, Sumerauer D, Sedlacek Z. Telomere length in peripheral blood cells of germline TP53 mutation carriers is shorter than that of normal individuals of corresponding age. Cancer. 2007;110(3):694–702. doi: 10.1002/cncr.22834. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shlien A, Tabori U, Marshall CR, Pienkowska M, Feuk L, Novokmet A, Nanda S, Druker H, Scherer SW, Malkin D. Excessive genomic DNA copy number variation in the Li-Fraumeni cancer predisposition syndrome. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2008;105(32):11264–11269. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0802970105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Achatz MI, Olivier M, Le Calvez F, Martel-Planche G, Lopes A, Rossi BM, Ashton-Prolla P, Giugliani R, Palmero EI, Vargas FR. et al. The TP53 mutation, R337H, is associated with Li-Fraumeni and Li-Fraumeni-like syndromes in Brazilian families. Cancer Lett. 2007;245(1–2):96–102. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2005.12.039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmero EI, Schüler-Faccini L, Caleffi M, Achatz MI, Olivier M, Martel-Planche G, Marcel V, Aguiar E, Giacomazzi J, Ewald IP. et al. Detection of R337H, a germline TP53 mutation predisposing to multiple cancers, in asymptomatic women participating in a breast cancer screening program in Southern Brazil. Cancer Lett. 2008;261(1):21–25. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2007.10.044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Achatz MI, Hainaut P, Ashton-Prolla P. Highly prevalent TP53 mutation predisposing to many cancers in the Brazilian population: a case for newborn screening? Lancet Oncol. 2009;10(9):920–925. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(09)70089-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinto EM, Billerbeck AE, Villares MC, Domenice S, Mendonça BB, Latronico AC. Founder effect for the highly prevalent R337H mutation of tumor suppressor p53 in Brazilian patients with adrenocortical tumors. Arq Bras Endocrinol Metabol. 2004;48(5):647–650. doi: 10.1590/s0004-27302004000500009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garritano S, Gemignani F, Palmero EI, Olivier M, Martel-Planche G, Le Calvez-Kelm F, Brugiéres L, Vargas FR, Brentani RR, Ashton-Prolla P. et al. Detailed haplotype analysis at the TP53 locus in p.R337H mutation carriers in the population of Southern Brazil: evidence for a founder effect. Hum Mutat. 2010;31(2):143–150. doi: 10.1002/humu.21151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiGiammarino EL, Lee AS, Cadwell C, Zhang W, Bothner B, Ribeiro RC, Zambetti G, Kriwacki RW. A novel mechanism of tumorigenesis involving pH-dependent destabilization of a mutant p53 tetramer. Nat Struct Biol. 2002;9(1):12–16. doi: 10.1038/nsb730. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuiper RP, Ligtenberg MJ, Hoogerbrugge N, Geurts Van Kessel A. Germline copy number variation and cancer risk. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2010;20(3):282–289. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2010.03.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krepischi AC, Achatz MI, Santos EM, Costa SS, Lisboa BC, Brentani H, Santos TM, Goncalves A, Nobrega AF, Pearson PL. et al. Germline DNA copy number variation in familial and early-onset breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2012;14(1):R24. doi: 10.1186/bcr3109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allemeersch J, Van Vooren S, Hannes F, De Moor B, Vermeesch JR, Moreau Y. An experimental loop design for the detection of constitutional chromosomal aberrations by array CGH. BMC Bioinformatics. 2009;10:380. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-10-380. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu H, Poh WT, Sim X, Ong RT, Suo C, Tay WT, Khor CC, Seielstad M, Liu J, Aung T. et al. SgD-CNV, a database for common and rare copy number variants in three Asian populations. Hum Mutat. 2011;32(12):1341–1349. doi: 10.1002/humu.21601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camplejohn RS, Perry P, Hodgson SV, Turner G, Williams A, Upton C, MacGeoch C, Mohammed S, Barnes DM. A possible screening test for inherited p53-related defects based on the apoptotic response of peripheral blood lymphocytes to DNA damage. Br J Cancer. 1995;72(3):654–662. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1995.390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goi K, Takagi M, Iwata S, Delia D, Asada M, Donghi R, Tsunematsu Y, Nakazawa S, Yamamoto H, Yokota J. et al. DNA damage-associated dysregulation of the cell cycle and apoptosis control in cells with germ-line p53 mutation. Cancer Res. 1997;57(10):1895–1902. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malkin D. Li-fraumeni syndrome. Genes Cancer. 2011;2(4):475–484. doi: 10.1177/1947601911413466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zambetti GP. The p53 mutation ″gradient effect″ and its clinical implications. J Cell Physiol. 2007;213(2):370–373. doi: 10.1002/jcp.21217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinto D, Darvishi K, Shi X, Rajan D, Rigler D, Fitzgerald T, Lionel AC, Thiruvahindrapuram B, Macdonald JR, Mills R. et al. Comprehensive assessment of array-based platforms and calling algorithms for detection of copy number variants. Nat Biotechnol. 2011;29(6):512–520. doi: 10.1038/nbt.1852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rees E, Moskvina V, Owen MJ, O′Donovan MC, Kirov G. De novo rates and selection of schizophrenia-associated copy number variants. Biol Psychiatry. 2011;70(12):1109–1114. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2011.07.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itsara A, Wu H, Smith JD, Nickerson DA, Romieu I, London SJ, Eichler EE. De novo rates and selection of large copy number variation. Genome Res. 2010;20(11):1469–1481. doi: 10.1101/gr.107680.110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Results of Array-CGH. Full CNV data of LFS/LFL patients, chromosome coordinates given according to Hg18 (NCBI Build 36.1/hg18; http://genome.ucsc.edu).
Frequency of the rare CNVs detected in theTP53mutated individuals.