Abstract
Objective
Intracellular cholesterol distribution impacts cell function, however processes influencing endogenous cholesterol trafficking remain largely unknown. Atherosclerosis is associated with vascular inflammation and these studies address the role of inflammatory mediators on smooth muscle cell cholesterol trafficking.
Methods and Results
Interestingly, in the absence of an exogenous cholesterol source, serum amyloid A increased [14C] oleic acid incorporation into cholesteryl ester in rat smooth muscle cells, suggesting endogenous cholesterol trafficking to the endoplasmic reticulum. [3H] cholesteryl ester accumulated in cells prelabeled with [3H] cholesterol, confirming that serum amyloid A mediated the movement of endogenous cholesterol. Cholesterol movement was dependent upon functional endolysosomes. The cholesterol oxidase sensitive pool of cholesterol decreased in serum amyloid A-treated cells. Furthermore, the mechanism whereby serum amyloid A induced cholesterol trafficking was determined to be via activation of expression of secretory phospholipase A2, group IIA (sPLA2) and sPLA2-dependent activation of sphingomyelinase. Interestingly, although neither tumor necrosis factor α nor interferon γ induced cholesterol trafficking, interleukin-1ß induced [14C] cholesteryl ester accumulation that was also dependent upon sPLA2 and sphingomyelinase activities. Serum amyloid A activates smooth muscle cell interleukin-1ß expression and although the interleukin-1 receptor antagonist inhibited the interleukin-1ß-induced cholesterol trafficking, it had no effect on the movement of cholesterol mediated by serum amyloid A.
Conclusions
These data support a role for inflammation in endogenous smooth muscle cell cholesterol trafficking from the plasma membrane to the endoplasmic reticulum.
Keywords: Cholesterol trafficking, smooth muscle cells, serum amyloid A, interleukin-1ß
INTRODUCTION
The distribution of cholesterol varies widely among different cellular compartments such that the highest percentage (estimated to be greater than 60%) of the total cell cholesterol is found in the plasma membrane of cultured cells and a relatively low percentage (estimated to be approximately 5%) is found in the endoplasmic reticulum (1, 2). Cholesterol moves between cellular compartments and both vesicular and non-vesicular-mediated trafficking of cholesterol between organelles have been described. In addition to cholesterol movement within intracellular compartments, uptake from exogenous sources and efflux to cholesterol acceptors contribute to cholesterol homeostasis (1). Importantly, the distribution of cell cholesterol in various compartments is known to have functional implications ranging from signaling initiated at plasma membrane “lipid rafts” and caveolae to regulation of gene transcription by cholesterol in the endoplasmic reticulum (3-5).
It is believed that the differential equilibrium of cholesterol in various membranes is maintained by differences in lipid composition (6). Thus, it has been noted that the sphingomyelin content of the membrane is critical to maintaining levels of cholesterol and treatment with exogenous sphingomyelinase results in the liberation of plasma membrane cholesterol that moves to the endoplasmic reticulum (7, 8).
Little is known about what influences endogenous trafficking of cholesterol and in particular, whether inflammatory processes associated with atherosclerosis affect intracellular cholesterol movement. Acute phase serum amyloid A (SAA) and interleukin-1ß (IL-1ß) are expressed in atherosclerotic lesions (9, 10). Recently, we showed that SAA activates expression of another acute phase protein, secretory phospholipase A2, group IIA (sPLA2) in aortic smooth muscle cells (11). Likewise, IL-1ß induces smooth muscle cell sPLA2 gene expression (11-14). This report addresses the hypothesis that SAA- and IL-1ß-induced sPLA2 mediates cholesterol trafficking to the endoplasmic reticulum. The studies demonstrate that SAA and IL-1ß induce the trafficking of endogenous cholesterol to the endoplasmic reticulum in aortic smooth muscle cells and that the trafficking of cholesterol is dependent upon activation of expression of sPLA2. This work demonstrates for the first time that inflammatory processes associated with atherosclerosis are likely to have an impact on vascular smooth muscle cell function due to changes in the distribution of intracellular cholesterol pools.
METHODS
Isolation, culture and treatment of neonatal rat aortic smooth muscle cells
In accordance with practices approved by Boston University’s Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC), neonatal aortic smooth muscle cells were isolated by digestion of the aortae of three-day-old Sprague-Dawley rats (Charles River Laboratories, Inc., Wilmington, MA), as previously described (15, 16). The cells were seeded in Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s Medium supplemented with 100 units/ml penicillin, 100 μg/ml streptomycin, 0.1 mM MEM non-essential amino acids and 1 mM MEM sodium pyruvate solution (DMEM; all from Mediatech, Inc., Manassas, VA) supplemented with 20% fetal bovine serum (FBS; Atlanta Biologicals, Lawrenceville, GA) and incubated at 37°C in a humidified atmosphere of 5% CO2/95% air. Cells maintained in primary stage for approximately 1 week were then seeded into first passage at a density of 2 × 104 cells/cm2 in DMEM containing 10% FBS. Experiments were performed on cells in passages 1 - 3, plated at a density of 2 × 104 cells/cm2. Before the addition of experimental reagents, the media were removed, the cells washed twice and media containing 10% lipoprotein-deficient serum (LDS), prepared as described previously (15, 17), were added. ß-migrating very low density lipoprotein (ßVLDL) was isolated as previously described by density gradient ultracentrifugation from serum of male New Zealand White rabbits fed a diet rich in cholesterol and peanut oil (15, 17). Recombinant SAA (PeproTech, Rocky Hill, NJ) was used at concentrations of 2 - 4 μM as activity of various preparations differs somewhat. The reagents [ßVLDL, SAA, IL-1ß (eBioscience, San Diego, CA), murine tumor necrosis factor α (TNFα; Peprotech), rat interferon γ (IFNγ; eBioscience)] were then added unless inhibitors [chloroquine (MP Biomedicals, Solon, OH), bafilomycin A1 (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO), U18666A (Sigma-Aldrich), Ro 23-9358 (Sigma-Aldrich), arachidonyl trifluoromethylketone (AACOCF3; Enzo Life Sciences, Plymouth Meeting, PA), 3-O-methyl sphingomyelin (3-OMe sphingomyelin; Enzo Life Sciences), chicken egg yolk sphingomyelin (Sigma-Aldrich) and IL-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1Ra; R&D Systems, Minneapolis, MN)] were used, in which case they were added 1 hour prior to the addition of SAA or IL-1ß. To study the effect of lipid-associated SAA, high density lipoprotein (HDL; Calbiochem, La Jolla, CA)-associated SAA was prepared in DMEM-LDS by adding HDL (150 μg protein/ml) followed by SAA (2 μM) and incubating first at room temperature for 15 min while shaking, followed by 15 min at 37°C. Samples were then added to the cells and comparisons were made to similarly-treated samples containing SAA or HDL alone. Media (and reagents) were changed twice weekly and always 1 day prior to harvest.
[14C] Oleic acid and [3H] cholesterol incorporation into cholesteryl ester
[14C] oleic acid incorporation into cholesteryl ester was determined essentially as described (17). Briefly, cells were incubated with reagents in media containing 10% LDS in the presence of [14C] oleic acid (Perkin Elmer, Waltham, MA; NEC-317) complexed to albumin (0.43 μCi/ml). At the end of the indicated incubation, the lipids were extracted from the cell layer with hexane:isopropyl alcohol (3:2) and [14C] cholesteryl oleate accumulation determined by thin layer chromatography (either by liquid scintillation counting or autoradiographic imaging of cholesteryl ester spots; if the latter was used, the data were normalized to account for the difference in efficiency between the techniques). In addition, cell layer protein was solubilized with 0.2 N NaOH and total protein determined using the Pierce BCA Protein Assay Kit (ThermoFisher Scientific Inc., Rockford, IL) as per manufacturer’s instructions. The data are expressed as [14C] cholesteryl oleate (cpm)/μg protein ± SD.
A double label approach was also used to determine if endogenous cholesterol trafficked to the endoplasmic reticulum. Cells were prelabeled with [3H] cholesterol (Perkin Elmer, NET-139) by removing media, washing twice and incubating overnight with [3H] cholesterol (2-3 μCi/ml) in DMEM containing LDS. Cells were washed 4-5 times, medium containing LDS was added and cells allowed to incubate overnight to equilibrate cellular cholesterol pools. Cells were treated with (or without) SAA and [14C] oleic acid as described above. At the end of the indicated incubation, lipids were extracted with hexane/isopropyl alcohol (3:2) and [14C] cholesteryl oleate accumulation and [3H] cholesteryl ester determined by subjecting the extracts to thin layer chromatography. In addition, cell layer protein was solubilized with 0.2 N NaOH and total protein determined. The data are expressed as [14C] cholesteryl oleate or [3H] cholesteryl oleate (dpm)/μg protein ± SD.
Cell proliferation assay
Cell proliferation was determined using the MTT Cell Proliferation Assay (American Type Culture Collection, Manassas, VA) according to manufacturer’s instructions.
Cholesterol oxidase-sensitive pool of cholesterol
Cells were labeled with [3H] cholesterol as described above. After equilibration, cells were treated with SAA for 7 days, at which time the cholesterol oxidase-sensitive pool of cholesterol was determined essentially as previously described (18). Briefly, media were removed, cells were washed with 1% fatty acid free bovine serum albumin in TBS (50 mM TRIS pH 7.5, 150 mM NaCl), then with phosphate buffered saline (PBS; 21-040, Mediatech, Inc.), fixed with 1% glutaradehyde in PBS, washed with PBS, and those cells to be treated received cholesterol oxidase (Sigma-Aldrich, C8649; 2 units/ml DMEM) for 30 min at 37°C. Cells were washed with PBS, lipids were extracted with hexane:isopropyl alcohol (3:2) and subjected to thin layer chromatography using a developing solution of hexane:ethyl ether:glacial acetic acid (130:30:2). Spots corresponding to cholesterol and cholestenone were measured by liquid scintillation counting. The data are expressed as [3H] cholestenone as a percentage of the total [3H] cholesterol ± SD calculated as follows: {[3H] cholestenone (cpm)/{[3H] free cholesterol (cpm) + [3H] cholestenone (cpm)}} × 100.
Enzyme activity assays
The activity of sPLA2 in culture media harvested from cells treated in the presence or absence of SAA was determined using a commercially available kit (Cayman Chemical, Ann Arbor, MI) as previously described (11). Enzyme activity is expressed as a function of the area of the cell culture surface (nmol product/min/cm2) ± SD.
To determine neutral sphingomyelinase activity using the commercially available Amplex® Red Sphingomyelinase Assay Kit (Invitrogen, Grand Island, NY), cells treated in the presence or absence of SAA were washed twice with cold PBS on ice and then scraped in 1X reaction buffer supplied with the kit, frozen at −80°C overnight, then sonicated twice and centrifuged at 3000 × g for 10 min at 4°C. The supernatants were evaluated for enzyme activity according to the manufacturer’s instructions with fluorescence readings taken at 1 min intervals for 1 hour, with an excitation wavelength of 530 nm and emission at 590 nm. Supernatants were also evaluated for total protein (BCA) and enzyme activity is expressed as the relative fluorescence emission units (mRFU) per min during the linear range of enzyme activity, normalized to the total cell protein (mRFU/min/μg protein ± SD).
Real time polymerase chain reaction (PCR)
As previously described (11), total RNA was extracted, reverse transcribed and the resultant cDNA used to determine mRNA expression levels of rat Pla2g2a by real time PCR analysis using SYBR Green primers synthesized by Eurofins MWG Operon (Huntsville, AL) (5′GTGACTCATGACTGTTGTTAC3′ and 5′CAAAACATTCAGCGGCAGC3′). An 18S rRNA TaqMan primer set (Applied Biosystems, Grand Island, NY) was used for normalization. Calculations were carried out using the ΔΔCt method of relative quantitation (if expression levels were low such that there was no Ct value after 40 cycles, data were calculated using a Ct of 40. The data are expressed as relative mRNA levels ± SD (with expression in SAA- or IL-1ß-treated cells set to a value of 1).
Statistical analyses
The data, expressed as mean ± SD of samples from representative experiments, were analyzed by analysis of variance. Statistically significant differences of relevant comparisons were determined by Bonferroni post-hoc analysis and reported when P<0.05.
RESULTS
An acute phase protein, sPLA2 is a member of the phospholipase family that cleaves fatty acids in the sn2 position of the phospholipid backbone. Its expression is stimulated by inflammatory cytokines including IL-1β (19). Moreover, we showed that SAA activates smooth muscle cell expression of the Pla2g2a gene, resulting in an increase in sPLA2 activity (11). It has been shown that arachidonic acid stimulates the activity of sphingomyelinase (20) and that sphingomyelinase-mediated degradation of plasma membrane-associated sphingomyelin induces cholesterol movement to the endoplasmic reticulum (7). Thus, a hypothesis was formulated, that SAA-induced smooth muscle cell sPLA2 expression increases endogenous sphingomyelinase activity, thereby liberating plasma membrane-associated cholesterol that mobilizes to the endoplasmic reticulum. To test the hypothesis, rat smooth muscle cells were treated with SAA and cholesterol trafficking to the endoplasmic reticulum was monitored. Free cholesterol is esterified in the endoplasmic reticulum by acyl coenzyme A:cholesterol acyltransferase and measurements of cholesterol esterification reflect the accumulation of cholesterol in this compartment (2). Thus, to test the potential role of acute phase SAA on cholesterol movement to the endoplasmic reticulum, the incorporation of [14C] oleic acid into [14C] cholesteryl ester was measured in cultured aortic smooth muscle cells. Figure 1 shows that as expected, supplying the cells with an exogenous source of cholesterol from hyperlipoproteinemic ßVLDL (containing 0.4 or 2.0 μg protein/ml) increased cholesterol esterification. Interestingly, the data show that SAA stimulated [14C] cholesteryl ester accumulation, supporting the notion that SAA induced the movement of cholesterol to the endoplasmic reticulum. It is noteworthy that although the higher concentration of ßVLDL increased accumulation of [14C] cholesteryl ester in comparison to the lower dose, the increase did not reflect the 5-fold increase in lipoprotein concentration, suggesting that cholesterol mobilization by ßVLDL in the endoplasmic reticulum was at or near maximum and that SAA was therefore quite efficient in inducing cholesterol movement.
Figure 1.
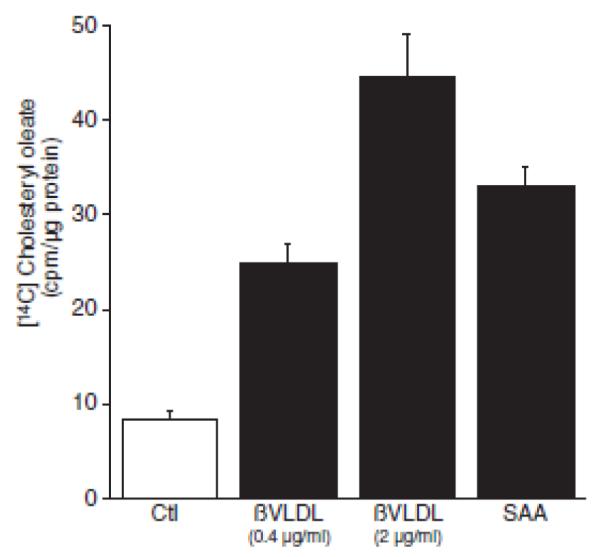
Serum amyloid A (SAA) induces cholesterol trafficking to the endoplasmic reticulum. Smooth muscle cells were treated in the absence (control [Ctl]) or presence of β-mignating very-low-density lipoprotein (βVLDL: at the indicated dose) or SAA (4 μmol/L) with [14C] oleic acid for 24 hours, at which time [14C] cholesteryl oleate accumulation was measured as described in the Materials and Methods section. The data are expressed as [14C] cholesteryl oleate(cpm)/μg protein ± SD(n=3). [14C] cholesteryl oleate accumulation in SAA-treated cells (P<0.001) and βVLDL-treated cells at both doses (P<0.001) was significantly different from that in Ctl-treated cells.
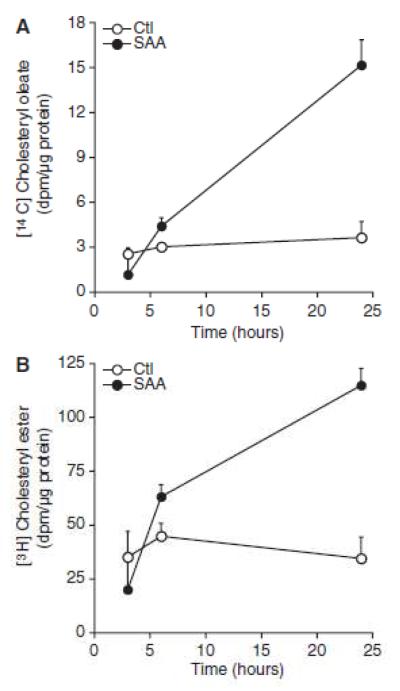
To further verify the role of endogenous cholesterol movement by SAA, a double label approach was taken. To study the movement of cell-associated cholesterol, smooth muscle cells were prelabeled with [3H] cholesterol. SAA was then added in the presence of [14C] oleic acid and at 3, 6 and 24 hours, the cells were harvested and the accumulation of both [14C] cholesteryl ester and [3H] cholesteryl ester were studied. The data in Figures 2A and 2B show that there was a time-dependent accumulation of cholesteryl ester derived either from exogenous [14C] oleic acid or cell-associated [3H] cholesterol, respectively. These data confirm that SAA mediated the movement of endogenous cholesterol to the endoplasmic reticulum. It has been shown that both vesicular and non-vesicular pathways of cholesterol trafficking exist (21). To determine whether cholesterol movement by SAA is mediated by the endolysosomal system, its trafficking was measured in the presence of inhibitors of lysosomal function. As it is known that exogenous cholesterol delivered to the endoplasmic reticulum via ßVLDL requires lysosomes(22), it was first determined whether cholesterol movement to the endoplasmic reticulum mediated by ßVLDL could be inhibited in these cultures using known inhibitors. The data (not shown) demonstrated that pretreatment with either chloroquine (10 μM), bafilomycin A1 (10 nM) or the hydrophobic amine U18666A (5 μM) (23) inhibited ßVLDL-induced cholesterol esterification, so these conditions were used to determine if lysosomal function is necessary for SAA-mediated cholesterol transport. Moreover, using the MTT assay, it was shown that inhibiting lysosomal function for 24 hours did not cause cell toxicity (data not shown). The data in Figure 3 show that the SAA-induced increase in cholesteryl ester accumulation was inhibited by treatment with chloroquine, bafilomycin A1 or U18666A.
Figure 2.
Serum amyloid A (SAA) induces endogenous cholesterol trafficking to the endoplasmic reticulum. Smooth muscle cells were prelabeled with [3H] cholesterol as described in the Materials and Methods section. After an overnight equilibration, cells were treated in the absence (control [Ctl]) or presence of SAA (2 μmol/L with [14C] oleic acid. At the indicated time points, (A) [14C] cholesteryl oleate and (B) [3H] cholesteryl ester accumulation were measured as described in the Materials and Methods section The data are expressed as (A) [14C] cholesteryl oleate (dpm)/μg protein ± SD (n=3) and (B) [3H] cholesteryl ester (dpm)/μg protein ± SD (n=3). A, [14C] cholesteryl oleate accumulation in SAA-treated cells at 6 hours and 24 hours (P<0.05) was significantly different from that in Ctl-treated cells. B, [3H] cholesteryl Oleate accumulation in SAA-treated cells at 24 hours (P<0.05) was significantly different from that in Ctl-treated cells.
Figure 3.
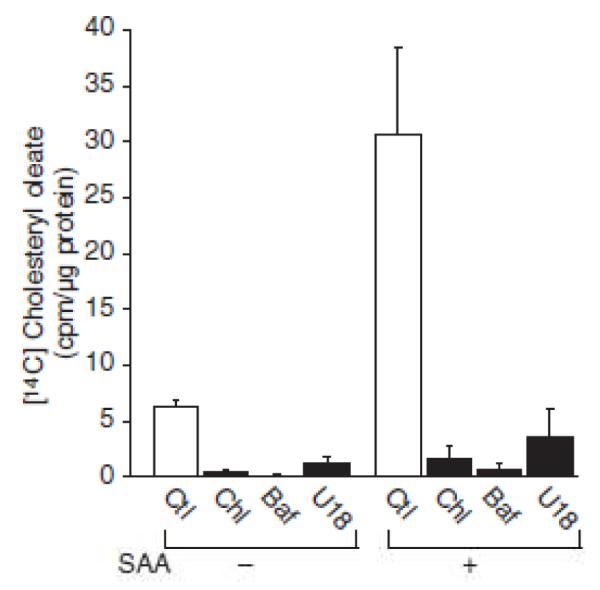
Serum amyloid A (SAA)–mediated cholesterol trafficking is lysosome–dependent. Smooth muscle cells were treated in the absence or presence of SAA (4 μmol/L) and either no inhibitor (control [Ctl]), chloroquine (Chl; 10 μmol/L), bafilomycin A1 (Baf; 10 nmol/L), or U18666A (U18; 5 μmol/L) with [14C] oleic acid for 24 hours, at which time [14C] cholesteryl oleate accumulation was measured as described in the Materials and Methods section, The data are expressed as [14C] cholesteryl oleate (cpm)/μg protein ± SD (n=3). [14C] cholesteryl oleate accumulation In Chl-treated (P<0.05). Baf-treated (P<0.05), and SAA-treated cells (P< 0.001) was significantly different from that in Ctl-treated cells. [14C] cholesteryl oleate accumulation in SAA plus Chl-treated (P<0.001), SAA plus Baf-treated (P<0.001), and SAA plus U18-treated cells (P<0.001) was significantly different from that in SAA-treated cells.
To determine if chronic SAA-mediated cholesterol trafficking resulted in a decrease in plasma membrane cholesterol, cells prelabeled with [3H] cholesterol were treated with (or without) SAA for 7 days, at which time the cholesterol oxidase-sensitive pool of cholesterol was determined. SAA-treated cells had less plasma membrane cholesterol as evidenced by a significant decrease of cholesterol oxidase-sensitive cholesterol when compared to control-treated cells (Figure 4).
Figure 4.
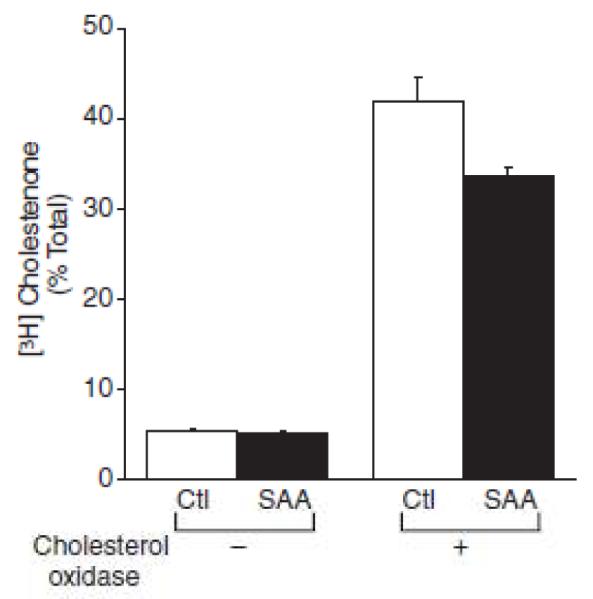
Serum amyloid A (SAA) decreases plasma membrane cholesterol. Smooth muscle cells were prelabeled with [3H] cholesterol and then treated In the absence (control [Ctl]) or presence of SAA (2 μmol/L) for 7 days, at which time the cholesterol oxidase–sensltlve pool of cholesterol was determined as described in the Materials and Methods section. The data are expressed as [3H] cholestenone as a percentage of the total [3H] cholesterol ± SD (n=3) calculated as follows: ([3H] cholestenone [cpm]/{[3H] free cholesterol [cpm]+[3H] cholestenone [cpm]})×100 ± SD (n=3). The percentage of [3H] cholestenone in SAA-treated cells (P< 0.001) was significantly different from that in control (Ctl)-treated cells In the samples treated with cholesterol oxidase.
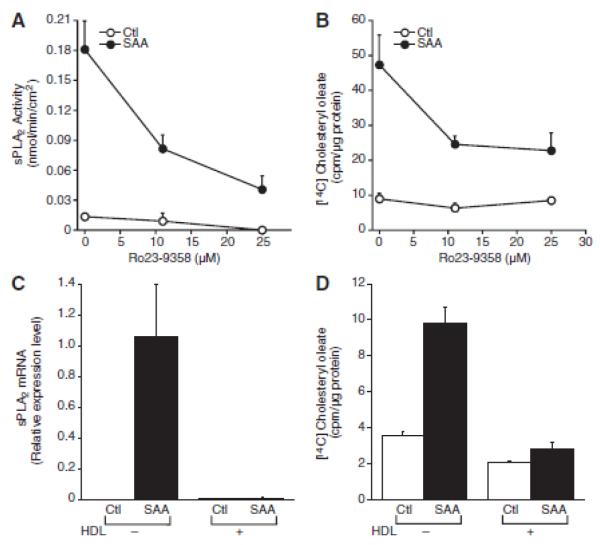
The role of sPLA2 in SAA-induced trafficking of cholesterol to the endoplasmic reticulum was explored using an inhibitor of sPLA2 activity, Ro 23-9358. Previously, we showed that Ro 23-9358 inhibits the activity of SAA-induced sPLA2 in media harvested from smooth muscle cells that were treated with SAA (11). To determine its effectiveness when incubated directly with the cells, it was added to the cultures and 24 hours later, media were collected and tested for sPLA2 activity. The data in Figure 5A indicate that Ro 23-9358 decreased the SAA-induced sPLA2 activity that accumulated during the time of incubation with SAA. Cholesterol esterification was measured in cells pretreated with Ro 23-9358 prior to the addition of SAA and Ro 23-9358 decreased the SAA-induced cholesterol trafficking, suggesting a role for sPLA2 in this process (Figure 5B). Likewise, the inhibition of SAA-mediated expression of sPLA2 in the presence of HDL as we previously reported (11) (Figure 5C) also inhibited cholesterol trafficking to the endoplasmic reticulum (Figure 5D).
Figure 5.
Serum amyloid A (SAA)-mediated cholesterol trafficking is secretory phospholipase A2, group IIA [sPLA2-dependent. A, Smooth muscle cells were treated in the absence or presence of Ro23–9358 (at the indicated dose) and either in the absence (control [Ctl] or presence of SAA (4 μmol/L) for 24 hours, at which time sPLA2 enzyme activity was measured as described in the Materials and Methods section. The data are expressed as nmol product/min/cm2 ± SD (n=3). Enzyme activity in SAA-treated cells (P<0.0001) was significantly different from that in Ctl-treated cells. Enzyme activity in SAA plus Ro23-9358-treated cells at both doses (P<0.0001) was significantly different from that in SAA-treated cells. B, Smooth muscle cells were treated in the absence or presence of Ro23-9358 (at the indicated dose) and either in the absence (Ctl) or presence of SAA (4 μmol/L) with [14C] oleic acid for 24 hours, at which time [14C] cholesteryl oleate accumulation was measured as described in the Materials and Methods section. The data are expressed as [14C] cholesteryl oleate (cpm)/μg protein ± SD (n=3). [14C] cholesteryl oleate accumulation in SAA-treated cells (P<0.001) was significantly different from that in Ctl-treated cells. [14C] cholesteryl oleate accumulation in SAA plus Ro23-9358–treated cells at both doses (P<0.001) was significantly different from that in SAA-treated cells. C, Smooth muscle cells were treated in the absence or presence of high-density lipoprotein (HDL; 150 μg protein/mL) and either in the absence (Ctl) or presence of SAA (2 μmol/L) for 24 hours, at which time total RNA was extracted and analyzed by real-time polymerase chain reaction for sPLA2 mRNA as described in the Materials and Methods section. The data are expressed as relative sPLA2 mRNA levels ± SD [n=3; with SAA-treated cells set to a value of 1). The level of sPLA2 mRNA in SAA-treated cells (P<0.05) was significantly different from that in Ctl-treated cells. The level of sPLA2 mRNA in SAA plus HDL-treated cells (P<.05) was significantly different from that in SAA-treated cells. D, Smooth muscle cells were treated in the absence or presence of HDL [150 μg protein/mL) either in the absence (Ctl) or presence of SAA (2 μmol/L) with [14C] oleic acid for 24 hours, at which time [14C] cholesteryl oleate accumulation was measured as described in the Materials and Methods section. The data are expressed as [14C] cholesteryl oleate (cpm)/μg protein ± SD (n=3). [14C] cholesteryl oleate accumulation in SAA-treated cells (P<0.001) was significantly different from that in Ctl-treated cells. [14C] cholesteryl oleate accumulation in SAA plus HDL-treated cells (P<0.001) was significantly different from that in SAA-treated cells.
To determine if cytosolic PLA2, group IV (cPLA2) plays a role in SAA-induced cholesterol trafficking, [14C] cholesteryl ester accumulation was measured in cells treated with SAA in the presence of AACOCF3, an inhibitor of cPLA2 activity (24). Interestingly, AACOCF3 completely blocked SAA-induced cholesterol trafficking (Figure 6A); moreover, inhibition of cPLA2 prevented the SAA-induced expression of sPLA2 (Figure 6B).
Figure 6.
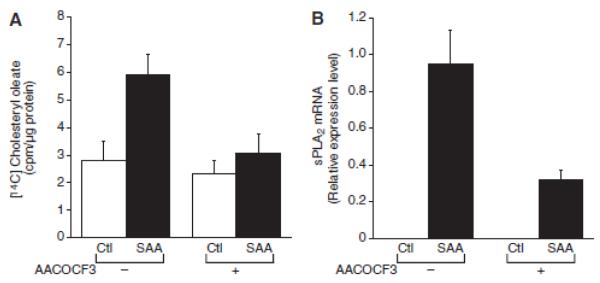
Serum amyloid A(SAA)-mediated cholesterol trafficking is cyclic phospholipase (cPL) A2–dependent. A, Smooth muscle cells were treated in the absence or presence of arachidonyl trifluoromethyl-ketone (AACOCF3; 10 μmol/L) and either in the absence (control [Ctl]) or presence of SAA (4 μmol/L) with [14C] oleic acid for 24 hours, at which time [14C] cholesteryl oleate accumulation was measured as described in the Materials and Methods section. The data are expressed as [14C] cholesteryl oleate (cpm)/μg protein ± SD (n=3). [14C] cholesteryl oleate accumulation in SAA-treated cells [P<0.001) was significantly different from that in Ctl-treated cells. [14C] cholesteryl oleate accumulation in SAA plus AACOCF3-treated cells (P<0.01) was significantly different from that in SAA-treated cells. B. Smooth muscle cells were treated in the absence or presence of AACOCF3 (10 μmol/L) and either in the absence (Ctl) or presence of SAA (2 μmol/L) for 24 hours, at which time total RNA was extracted and analyzed by real-time polymerase chain reaction for secretory phospholipase A2, group IIA (sPLA2) mRNA as described in the Materials and Methods section. The data are expressed as relative sPLA2 mRNA levels ± SD (n=3; with SAA-treated cells set to a value of 1). The level of sPLA2 mRNA in SAA-treated cells was significantly different from that in Ctl-treated cells (P<0.001). The level of sPLA2 mRNA in SAA plus AACOCF3-treated cells (P<0.0001) was significantly different from that in SAA-treated cells.
Jayadev et al., (20) showed that free arachidonic acid, a product of PLA2 activity, stimulates the activity of sphingomyelinase. Previous studies have shown that sphingomyelinase stimulates energy-independent transport of cholesterol to the endoplasmic reticulum (25). A role for sphingomyelinase in SAA-mediated cholesterol trafficking was explored; neutral sphingomyelinase activity was measured and SAA induced a chronic increase in activity (Figure 7A). To determine if the increase in sphingomyelinase activity contributed to the SAA-mediated cholesterol trafficking, cells were treated with 3-OMe sphingomyelin to inhibit sphingomyelinase activity (26) and it completely inhibited SAA-induced cholesterol trafficking (Figure 7B). Moreover, replenishing the cells with sphingomyelin prevented SAA-induced cholesterol trafficking (Figure 7C).
Figure 7.
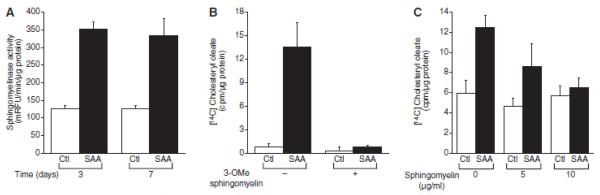
Serum amyloid A (SAA)-mediated cholesterol trafficking is sphingomyelinase-dependent. A, Smooth muscle cells is were treated in the absence (control [Ctl]) or presence of SAA (2 μmol/L) for 3 days and 7 days, at which time sphingomyelinase activity was measured as described in the Materials and Methods section. The data are expressed as relative fluorescence emission units (mRFU)/min/μg protein ± SD (n=3). Enzyme activity in SAA-treated cells was significantly different from that in Ctl-treated cells at both time points (P<0.001). B, Smooth muscle cells were treated in the absence or presence of 3-O-methyl sphingomyelin (3-OMe sphingomyelin 75 μmol/L) and either in the absence (Ctl) or presence of SAA (4 μmol/L) with [14C] oleic acid for 24 hours, at which time [14C] cholesteryl oieate accumulation was measured as described in the Materials and Methods section. The data are expressed as [14C] cholesteryl oleate (cpm)/μg protein ± SD (n=3). [14C] cholesteryl oleate accumulation in SAA-treated cells (P< 0.0001) was significantly different from that in Ctl-treated cells. [14C] cholesteryl oleate accumulation in SAA plus 3-OMe sphingomyeKn–treated cells (P< 0.0001) was significantly different from that in SAA-treated cells. C, Smooth muscle cells were treated in the absence or presence of sphingomyelin [at the indicated dose) and either in the absence (Ctl) or presence of SAA (4 μmol/L) with [14C] oleic acid for 24 hours, at which time [14C] cholesteryl oleate accumulation was measured as described in the Materials and Methods section. The data are expressed as [14C] cholesteryl oleate (cpm)/μg protein ± SD (n=3). [14C] cholesteryl oleate accumulation in SAA-treated cells (P< 0.0001) was significantly different from that in Ctl-treated cells. [14C] cholesteryl oleate accumulation in SAA plus sphingomyelin-treated cells (5 μg/mL; P<0.05) was significantly different from that in sphmgomyelin-treated cells (5 μg/mL). [14C] cholesteryl oleate accumulation in SAA plus sphingomyelin-treated cells at both doses (5 μg/mL, P<0.05: 10 μg/mL, P<0.001) was significantly different from that in SAA-treated cells.
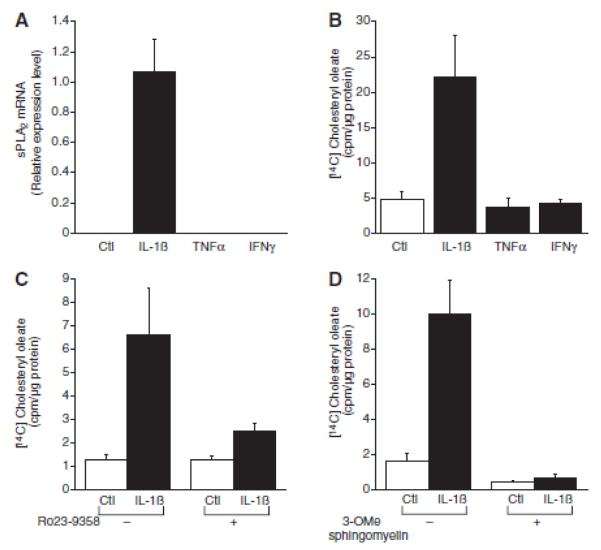
Other inflammatory mediators were evaluated for their ability to traffic cholesterol. As we and others showed previously (11-14), IL-1ß activated the expression of sPLA2 mRNA but neither TNFα nor IFNγ activated sPLA2 mRNA expression (Figure 8A). Interestingly, consistent with our hypothesis on the role of sPLA2 in cholesterol trafficking, neither TNFα nor IFNγ induced cholesterol esterification but cholesteryl ester accumulation increased in cells treated with IL-1ß (Figure 8B). Moreover, inhibiting sPLA2 activity with Ro 23-9358 blocked the IL-1ß-induced cholesterol esterification (Figure 8C). Likewise, inhibiting sphingomyelinase activity with 3-OMe sphingomyelin completely reversed the IL-1ß-mediated movement of cholesterol (Figure 8D).
Figure 8.
Interleukin (IL)-1β induces cholesterol trafficking to the endoplasmic reticulum. A, Smooth muscle cells were treated in the absence (control [Ctl]) or presence of IL-1β (100ng/mL), tumor necrosis factor-α (TNFα; 100ng/mL) or interferon (IFNγ; 50U/mL) for 24 hours, at which time total RNA was extracted and analyzed by real-time polymerase chain reaction for secretory phospholipase A2, group IIA (sPLA2) mRNA as described in the Materials and Methods section. The data are expressed as relative sPLA2, mRNA levels ± SD (n=3; with IL-1β–treated cells set to a value of 1). The levels of sPLA2 mRNA in IL-1β–treated cells (P<0.01) were significantly different from that in Ctl-treated cells. B, Smooth muscle cells were treated in the absence (Ctl) or presence of IL-1β (100ng/mL), TNFα (10 ng/mL) or IFNγ (50 U/mL) with [14C] oleic acid for 24 hours, at which time [14C] cholesteryl oleate accumulation was measured as described in the Materials and Methods section. The data are expressed as [14C] cholesteryl oleate (cpm)/μg protein ± SD (n=3). [14C]cholesteryl oleate accumulation in IL-lβ–treated cells (P<0.0001) was significantly different from that in Ctl-treated cells. C, Smooth muscle cells were treated in the absence or presence of Ro23-9358 (25 μmol/L) and either in the absence (Ctl) or presence of IL-1β (100ng/mL) with [14C] oleic acid for 24 hours, at which time [14C] cholesteryl oleate accumulation was measured as described in the Materials and Methods section. The data are expressed as [14C] cholesteryl oleate (cpm)/μg protein ± SD (n=3). [14C] cholesteryl oleate accumulation in IL-1β–treated cells (P<0.0001) was significantly different from that in Ctl-treated cells. [14C] cholesteryl oleate accumulation in IL-1β plus Ro23-9358-treated cells (P<0.0001) was significantly different from that in IL-1β–treated oells. D. Smooth muscle cells were treated in the absence or presence of 3-OMe sphingomyelin (3-O-methyl sphingomyelin; 75 μmol/L) and either in the absence (Ctl) or presence of IL-1β (100ng/mL) with [14C] oleic acid for 24 hours, at which time [14C] cholesteryl oleate accumulation was measured as described in the Materials and Methods section. The data are expressed as [14C] cholesteryl oleate (cpm)/μg protein ± SD (n=3). [14C] cholesteryl oleate accumulation in IL-1β–treated cells (P<0.0001) was significantly different from that in Ctl-treated cells. [14C] cholesteryl oleate accumulation in IL-1β plus 3-OMe sphingomyelin–treated cells (P<0.0001) was significantly different from that in IL-1β–treated cells.
We previously showed that SAA activates smooth muscle cell IL-1ß gene expression (11), so the possibility that the effect of SAA on cholesterol trafficking was mediated by IL-1ß signaling was explored. IL-1Ra inhibited the IL-1β-induced cholesterol esterification but SAA-induced trafficking was unaffected by IL-1Ra (Figure 9).
Figure 9.
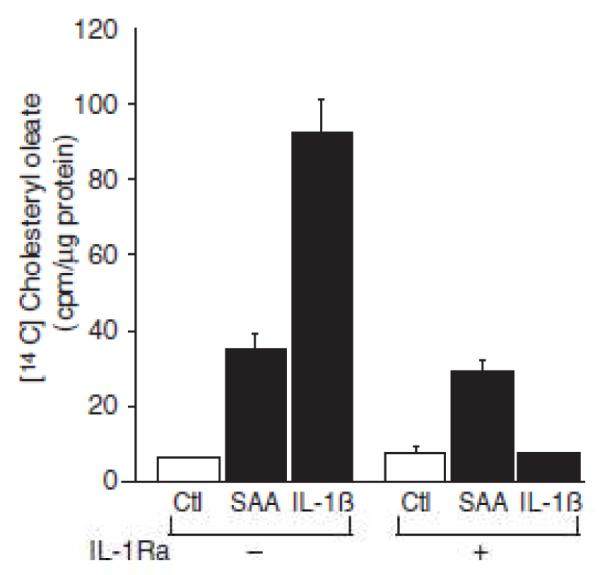
Serum amyloid A (SAA)-induced cholesterol trafficking is interleukin (IL)-1 receptor independent. Smooth muscle cells were treated in the absence or presence of IL-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1Ra; 1 μg/mL) and either in the absence (Ctl) or presence of SAA(4 μmol/L) or IL-1β (100 ng/mL) with [14C] oleic acid for 24 hours, at which time [14C] cholesteryl oleate accumulation was measured as described in the Materials and Methods section. The data are expressed as [14C] cholesteryl oleate (cpm)/μg protein ± SD (n=3). [14C] cholesteryl oleate accumulation in SAA-treated (P<0.0001) and IL-1β–treated cells (P<0.0001) was significantly different from that in Ctl-treated cells. [14C] cholesteryl oleate accumulation in IL-1β plus IL-lβ–treated cells (P<0.0001) was significantly different from that in IL-1β–treated cells.
DISCUSSION
It is well known that cholesterol entering the cell from extracellular sources i.e. from plasma-derived lipoprotein, traffics to the endoplasmic reticulum, thereby contributing to stringent regulation of cellular lipid metabolism (5). However, the influences of endogenous cholesterol trafficking remain largely unexplored. Moreover, although it is known that the distribution of cholesterol influences cell function, the role of inflammation on cholesterol repositioning has not been addressed. Smooth muscle cells are critical to proper vascular function; however, functional changes induce a phenotype that contributes to lesion formation in atherosclerosis (27). Therefore, the mechanisms inducing cholesterol movement in this cell type are of considerable interest. Recently, we reported that SAA activates smooth muscle cell expression of the sPLA2 gene (11) and it has been shown that IL-1ß activates smooth muscle cell sPLA2 gene expression (11-13). This report examines the hypothesis that SAA induces the trafficking of endogenous plasma membrane cholesterol to the endoplasmic reticulum in aortic smooth muscle cells and that the trafficking is dependent upon sPLA2 and sphingomyelinase activities. Moreover, the hypothesis that sPLA2 induced by IL-1ß also mobilizes cholesterol to the endoplasmic reticulum was studied. The data show that smooth muscle cell cholesterol esterification was stimulated by SAA as well as by IL-1ß and that the accumulation of cholesterol in the endoplasmic reticulum was cPLA2-, sPLA2- and sphingomyelinase-dependent. The data support the hypothesis that the activation of expression of sPLA2 results in the liberation of free fatty acids that activate endogenous sphingomyelinase which degrades plasma membrane sphingomyelin, resulting in the release of plasma membrane cholesterol and its trafficking to the endoplasmic reticulum.
Evidence that supports a role for sPLA2 in SAA-induced cholesterol trafficking to the endoplasmic reticulum includes the finding that the pharmacologic inhibitor of sPLA2 activity, Ro 23-9358, decreased the SAA-induced cholesterol trafficking. Ro 23-9358 didn’t fully inhibit the SAA-mediated trafficking of cholesterol but it was noted that the inhibition of SAA-induced sPLA2 activity was not complete under these experimental conditions. In our previous report (11), the inhibitor was added directly to media after it was harvested from SAA-treated cultures and even in lower doses than reported here, it was more effective in reducing enzyme activity than what is shown in Figure 5A. This discrepancy between the efficacy of Ro 23-9358 added to the cell cultures prior to the incubation of SAA vs. its efficacy when added to the enzyme-containing media samples just before assaying activity is presumably due to a loss of activity of the inhibitor during the 24 hour incubation. It is likely that the lack of an even more robust reduction in SAA-induced cholesterol trafficking by Ro 23-9358 was due to this loss of activity with time in culture i.e. the role of sPLA2 in this process is likely more profound than the pharmacologic inhibitor studies indicated.
Slotte and Bierman (7) first demonstrated that neutral sphingomyelinase treatment of skin fibroblasts results in the movement of cholesterol to the acyl coenzyme A:cholesterol acyltransferase-sensitive pool as measured by cholesterol esterification. Moreover, arachadonic acid, a product of PLA2 enzymes was shown to stimulate the activity of sphingomyelinase (20). These studies show that SAA activated neutral sphingomyelinase activity, and that inhibition of neutral sphingomyelinase or exogenous addition of sphingomyelin prevented the SAA-mediated trafficking of cholesterol. Chatterjee (28) showed that TNFα activates neutral sphingomyelinase and induces cholesteryl ester accumulation in human skin fibroblasts and it is interesting to speculate that this too was an sPLA2-mediated effect, particularly in light of the finding that arachadonic acid mediates TNFα-induced sphingomyelin hydrolysis in HL-60 cells (20). PLA2 isolated from Naja Naja caused, if anything, a small decrease in cholesterol ester accumulation in isolated renal tubules (29) and this could represent the difference in the source of PLA2 such that the endogenous enzyme might be effective due to parameters including proper localization of the reaction products, making them available to activate the endogenous sphingomyelinase. It has been shown by others that TNFα and IFNγ activate the expression of sPLA2. TNFα-mediated expression of sPLA2 was shown in endothelial cells (30), HepG2 cells (31), rat mesangial cells (32), astrocytes (33, 34) and fetal rat calvarial bone-forming cells (35). Lindbom et al. showed that IFNγ induced sPLA2 expression in human airway epithelial cells, whereas TNFα did not (36). Of particular interest is the study using human smooth muscle cells in which IFNγ induced sPLA2 expression whereas TNFα only caused a transient increase in expression and in fact, it antagonized the IFNγ-mediated response (37). In another study, TNF increased sPLA2 expression in rat smooth muscle cells (38). In the current report however, neither IFNγ nor TNFα induced cholesterol trafficking tothe endoplasmic reticulum (Figure 8B), consistent with the lack of induction of sPLA2 expression (Figure 8A).
It has been suggested that sphingomyelin and cholesterol form complexes of higher affinity than those formed between phosphatidyl choline and cholesterol. Recently however, the nature of the physical interaction between sphingomyelin and cholesterol has been questioned and an alternative explanation for sphingomyelinase-induced cholesterol trafficking has been suggested, which is that ceramide generated by sphingomyelinase might displace cholesterol from the membrane (1). In any case, degradation of sphingomyelin in the plasma membrane leads to a liberation of cholesterol from that pool and in the studies reported here, the SAA- or IL-1ß-induced increase in the activity of sphingomyelinase mediated the release of cholesterol, enabling its trafficking.
Resynthesis of sphingomyelin restored cholesterol to the plasma membrane within hours after treatment of BHK-21 cells with sphingomyelinase (39). In this study, cells were treated with SAA for 24 hours or more and accumulation of cholesteryl ester measured during that time. Moreover, sphingomyelinase activity increased and the cholesterol oxidase-sensitive pool of cholesterol i.e. the plasma membrane cholesterol, decreased in cells chronically treated with SAA for up to 7 days. These data suggest that the effects of chronic exposure during atherogenesis can potentially overcome physiologic mechanisms that maintain cholesterol pools when not challenged. There is evidence that the so-called acute phase isoforms of SAA are expressed constitutively in low levels (40, 41) in normal tissues, suggesting that SAA may affect normal tissue function and/or host defense. It is interesting to consider the possibility that the ability of SAA to mobilize endogenous cholesterol stores might play a role in this regard.
Previous work has suggested crosstalk between sPLA2 and cPLA2 enzymes in that cPLA2 activity impacts on IL-1ß/TNFα-induced sPLA2 expression in rat fibroblastic 3Y1 cells (42, 43) and IL-1β/TNFα-induced expression of cPLA2 increases by introducing sPLA2 either by exogenous addition or by transfection in the sPLA2-deficient mouse MC3T3-E1 cell line (44). Likewise, sPLA2 activates rat glomerular mesangial cell cPLA2 (45). Moreover, studies in P388D1 macrophages and overexpression of sPLA2 and cPLA2 in HEK293 cells indicate functional crosstalk such that the activity of sPLA2 is dependent upon the action of cPLA2 (43, 46, 47). The data shown here support a role for cPLA2 in the sPLA2-mediated cholesterol trafficking induced by SAA due to a cPLA2-stimulated increase in expression of sPLA2.
The functions of the SAA family, the members of which are the products of 4 genes, remain uncertain (9, 41). In inflammatory conditions, circulating plasma levels of the acute phase isoforms can be quite high, exceeding 1 mg/ml (48). Elevated plasma SAA has been shown to be an indicator of an increased risk for heart disease (49-51). SAA is expressed in human and mouse atherosclerotic lesions (52-55), suggesting that it may play a role in atherosclerosis, although whether SAA is pro-atherogenic or anti-atherogenic is controversial (9). Our previous work demonstrated that IL-1α induces synthesis of SAA in cultured aortic smooth muscle cells (56) and that SAA down-regulates endogenous lipid biosynthesis (57). It is intriguing to speculate that due to an inflammatory process in the developing plaque, available IL-1α induces local synthesis of SAA by smooth muscle cells and that the SAA then acts in an autocrine fashion to induce intracellular movement of smooth muscle cell plasma membrane cholesterol to the endoplasmic reticulum. Likewise, IL-1ß, which accumulates in atherosclerotic lesions and is known to activate smooth muscle cell sPLA2 expression, may contribute to functional changes due to the redistribution of intracellular cholesterol pools.
In summary, this study demonstrates that SAA and IL-1ß induce aortic smooth muscle cell trafficking of endogenous cholesterol via cPLA2-dependent induction of expression of sPLA2, the products of which in turn activate sphingomyelinase, which then cleaves plasma membrane sphingomyelin leading to the liberation of cholesterol that then traffics to the endoplasmic reticulum (Figure 10). To our knowledge, this is the first demonstration of regulation of intracellular trafficking of endogenous smooth muscle cell cholesterol by the inflammatory mediators SAA and IL-1ß. This represents a novel mechanism for regulation of smooth muscle cell cholesterol trafficking with potential for a role in inflammation-induced changes in cell function during atherosclerosis.
Figure 10.
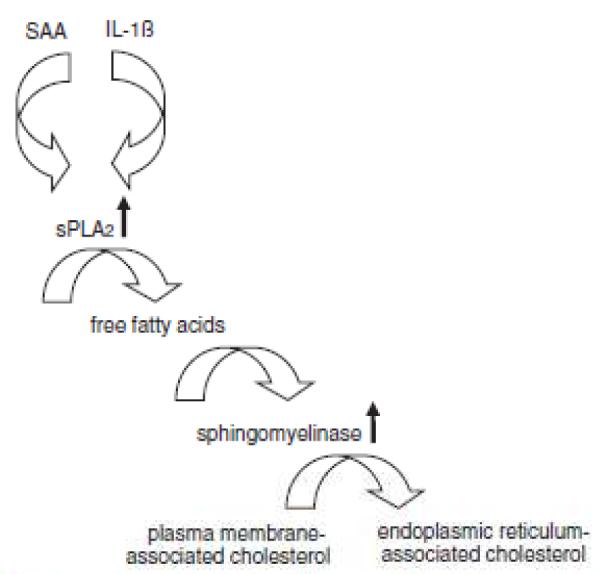
Schema depicting serum amyloid A (SAA)– and interleukin (IL)-lβ–mediated smooth muscle cell cholesterol trafficking to the endoplasmic reticulum. SAA and IL-1β induce expression of secretory phospholipase A2, group IIA (sPLA2). the activity of which liberates free fatty acids from phospholipids. The fatty acids increase the activity of sphingomyelinase, which liberates cholesterol associated with sphingomyelin in the plasma membrane and the cholesterol traffics to the endoplasmic reticulum. Note that small vertical arrows indicate an increased enzyme activity and larger arrows point to a critical product of the pathway described but they are not meant to imply a specific enzyme reaction.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Sources of Funding - This work was supported by National Institutes of Health Grant HL079201 and the American Heart Association Grants 0256215T and 0455846T.
Footnotes
Disclosures - None
This is a PDF file of an unedited manuscript that has been accepted for publication. As a service to our customers we are providing this early version of the manuscript. The manuscript will undergo copyediting, typesetting, and review of the resulting proof before it is published in its final citable form. Please note that during the production process errors may be discovered which could affect the content, and all legal disclaimers that apply to the journal pertain.
REFERENCES
- 1.Mesmin B, Maxfield FR. Intracellular sterol dynamics. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009;1791:636–645. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2009.03.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Liscum L, Munn NJ. Intracellular cholesterol transport. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1999;1438:19–37. doi: 10.1016/s1388-1981(99)00043-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Fielding CJ, Fielding PE. Cholesterol and caveolae: structural and functional relationships. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2000;1529:210–222. doi: 10.1016/s1388-1981(00)00150-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Chang TY, Chang CC, Ohgami N, Yamauchi Y. Cholesterol sensing, trafficking, and esterification. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2006;22:129–157. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cellbio.22.010305.104656. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Brown MS, Goldstein JL. Cholesterol feedback: from Schoenheimer’s bottle to Scap’s MELADL. J Lipid Res. 2009;50(Suppl):S15–27. doi: 10.1194/jlr.R800054-JLR200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Maxfield FR, Menon AK. Intracellular sterol transport and distribution. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2006;18:379–385. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2006.06.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Slotte JP, Bierman EL. Depletion of plasma-membrane sphingomyelin rapidly alters the distribution of cholesterol between plasma membranes and intracellular cholesterol pools in cultured fibroblasts. Biochem J. 1988;250:653–658. doi: 10.1042/bj2500653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Okwu AK, Xu XX, Shiratori Y, Tabas I. Regulation of the threshold for lipoprotein-induced acyl-CoA:cholesterol O-acyltransferase stimulation in macrophages by cellular sphingomyelin content. J Lipid Res. 1994;35:644–655. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Schreiber BM. Serum amyloid A; in search of function. Amyloid. 2002;9:276–278. doi: 10.3109/13506120209114107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Bujak M, Frangogiannis NG. The role of IL-1 in the pathogenesis of heart disease. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz) 2009;57:165–176. doi: 10.1007/s00005-009-0024-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Sullivan CP, Seidl SE, Rich CB, Raymondjean M, Schreiber BM. Secretory phospholipase A2, group IIA is a novel serum amyloid A target gene: activation of smooth muscle cell expression by an interleukin-1 receptor-independent mechanism. J Biol Chem. 2010;285:565–575. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.070565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Nakano T, Ohara O, Teraoka H, Arita H. Group II phospholipase A2 mRNA synthesis is stimulated by two distinct mechanisms in rat vascular smooth muscle cells. FEBS Lett. 1990;261:171–174. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80663-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Antonio V, Brouillet A, Janvier B, Monne C, Bereziat G, Andreani M, Raymondjean M. Transcriptional regulation of the rat type IIA phospholipase A2 gene by cAMP and interleukin-1beta in vascular smooth muscle cells: interplay of the CCAAT/enhancer binding protein (C/EBP), nuclear factor-kappaB and Ets transcription factors. Biochem J. 2002;368:415–424. doi: 10.1042/BJ20020658. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Jaulmes A, Thierry S, Janvier B, Raymondjean M, Marechal V. Activation of sPLA2-IIA and PGE2 production by high mobility group protein B1 in vascular smooth muscle cells sensitized by IL-1beta. FASEB J. 2006;20:1727–1729. doi: 10.1096/fj.05-5514fje. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Schreiber BM, Martin BM, Hollander W, Franzblau C. beta-VLDL-induced alterations in growth potentiating activity produced by mononuclear phagocytes. Atherosclerosis. 1988;69:69–79. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(88)90290-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Hsiao H, Stone PJ, Toselli P, Rosenbloom J, Franzblau C, Schreiber BM. The role of the carboxy terminus of tropoelastin in its assembly into the elastic fiber. Connect Tissue Res. 1999;40:83–95. doi: 10.3109/03008209909029104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Schreiber BM, Jones HV, Toselli P, Franzblau C. Long-term treatment of neonatal aortic smooth muscle cells with beta VLDL induces cholesterol accumulation. Atherosclerosis. 1992;95:201–210. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(92)90023-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Underwood KW, Andemariam B, McWilliams GL, Liscum L. Quantitative analysis of hydrophobic amine inhibition of intracellular cholesterol transport. Journal Lipid Res. 1996;37:1556–1568. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Divchev D, Schieffer B. The secretory phospholipase A2 group IIA: a missing link between inflammation, activated renin-angiotensin system, and atherogenesis? Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2008;4:597–604. doi: 10.2147/vhrm.s2008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Jayadev S, Linardic CM, Hannun YA. Identification of arachidonic acid as a mediator of sphingomyelin hydrolysis in response to tumor necrosis factor alpha. J Biol Chem. 1994;269:5757–5763. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Liscum L. Niemann-Pick type C mutations cause lipid traffic jam. Traffic. 2000;1:218–225. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-0854.2000.010304.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Goldstein JL, Ho YK, Brown MS, Innerarity TL, Mahley RW. Cholesteryl ester accumulation in macrophages resulting from receptor-mediated uptake and degradation of hypercholesterolemic canine beta-very low density lipoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1980;255:1839–1848. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Liscum L, Underwood KW. Intracellular cholesterol transport and compartmentation. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:15443–15446. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.26.15443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Street IP, Lin HK, Laliberte F, Ghomashchi F, Wang Z, Perrier H, Tremblay NM, Huang Z, Weech PK, Gelb MH. Slow- and tight-binding inhibitors of the 85-kDa human phospholipase A2. Biochemistry. 1993;32:5935–5940. doi: 10.1021/bi00074a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Skiba PJ, Zha X, Maxfield FR, Schissel SL, Tabas I. The distal pathway of lipoprotein-induced cholesterol esterification, but not sphingomyelinase-induced cholesterol esterification, is energy-dependent. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:13392–13400. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.23.13392. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Lister MD, Ruan ZS, Bittman R. Interaction of sphingomyelinase with sphingomyelin analogs modified at the C-1 and C-3 positions of the sphingosine backbone. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1995;1256:25–30. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(94)00249-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Orr AW, Hastings NE, Blackman BR, Wamhoff BR. Complex regulation and function of the inflammatory smooth muscle cell phenotype in atherosclerosis. J Vasc Res. 2010;47:168–180. doi: 10.1159/000250095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Chatterjee S. Neutral sphingomyelinase action stimulates signal transduction of tumor necrosis factor-alpha in the synthesis of cholesteryl esters in human fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1994;269:879–882. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Zager RA, Johnson A, Anderson K, Wright S. Cholesterol ester accumulation: an immediate consequence of acute in vivo ischemic renal injury. Kidney Int. 2001;59:1750–1761. doi: 10.1046/j.1523-1755.2001.0590051750.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Bae JS, Rezaie AR. Thrombin and activated protein C inhibit the expression of secretory group IIA phospholipase A(2) in the TNF-alpha-activated endothelial cells by EPCR and PAR-1 dependent mechanisms. Thromb Res. 2010;125:e9–e15. doi: 10.1016/j.thromres.2009.07.015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Ross R. The pathogenesis of atherosclerosis--an update. N Engl J Med. 1986;314:488–500. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198602203140806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Beck S, Lambeau G, Scholz-Pedretti K, Gelb MH, Janssen MJ, Edwards SH, Wilton DC, Pfeilschifter J, Kaszkin M. Potentiation of tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced secreted phospholipase A2 (sPLA2)-IIA expression in mesangial cells by an autocrine loop involving sPLA2 and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha activation. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:29799–29812. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M211763200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Thomas G, Bertrand F, Saunier B. The differential regulation of group II(A) and group V low molecular weight phospholipases A(2) in cultured rat astrocytes. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:10876–10886. doi: 10.1074/jbc.275.15.10876. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Oka S, Arita H. Inflammatory factors stimulate expression of group II phospholipase A2 in rat cultured astrocytes. Two distinct pathways of the gene expression. J Biol Chem. 1991;266:9956–9960. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Vadas P, Pruzanski W, Stefanski E, Ellies LG, Aubin JE, Sos A, Melcher A. Extracellular phospholipase A2 secretion is a common effector pathway of interleukin-1 and tumour necrosis factor action. Immunol Lett. 1991;28:187–193. doi: 10.1016/0165-2478(91)90002-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Lindbom J, Ljungman AG, Lindahl M, Tagesson C. Increased gene expression of novel cytosolic and secretory phospholipase A(2) types in human airway epithelial cells induced by tumor necrosis factor-alpha and IN-gamma. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2002;22:947–955. doi: 10.1089/10799900260286650. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Peilot H, Rosengren B, Bondjers G, Hurt-Camejo E. Interferon-gamma induces secretory group IIA phospholipase A2 in human arterial smooth muscle cells. Involvement of cell differentiation, STAT-3 activation, and modulation by other cytokines. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:22895–22904. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M002783200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Nakano T, Ohara O, Teraoka H, Arita H. Group II phospholipase A2 mRNA synthesis is stimulated by two distinct mechanisms in rat vascular smooth muscle cells. FEBS Lett. 1990;261:171–174. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80663-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Slotte JP, Harmala AS, Jansson C, Porn MI. Rapid turn-over of plasma membrane sphingomyelin and cholesterol in baby hamster kidney cells after exposure to sphingomyelinase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990;1030:251–257. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(90)90301-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Urieli-Shoval S, Cohen P, Eisenberg S, Matzner Y. Widespread expression of serum amyloid A in histologically normal human tissues. Predominant localization to the epithelium. J Histochem Cytochem. 1998;46:1377–1384. doi: 10.1177/002215549804601206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Cunnane G. Amyloid precursors and amyloidosis in inflammatory arthritis. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2001;13:67–73. doi: 10.1097/00002281-200101000-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Kuwata H, Nakatani Y, Murakami M, Kudo I. Cytosolic phospholipase A2 is required for cytokine-induced expression of type IIA secretory phospholipase A2 that mediates optimal cyclooxygenase-2-dependent delayed prostaglandin E2 generation in rat 3Y1 fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:1733–1740. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.3.1733. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Kuwata H, Yamamoto S, Miyazaki Y, Shimbara S, Nakatani Y, Suzuki H, Ueda N, Murakami M, Kudo I. Studies on a mechanism by which cytosolic phospholipase A2 regulates the expression and function of type IIA secretory phospholipase A2. J Immunol. 2000;165:4024–4031. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.165.7.4024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Murakami M, Kuwata H, Amakasu Y, Shimbara S, Nakatani Y, Atsumi G, Kudo I. Prostaglandin E2 amplifies cytosolic phospholipase A2- and cyclooxygenase-2-dependent delayed prostaglandin E2 generation in mouse osteoblastic cells. Enhancement by secretory phospholipase A2. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:19891–19897. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.32.19891. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Huwiler A, Staudt G, Kramer RM, Pfeilschifter J. Cross-talk between secretory phospholipase A2 and cytosolic phospholipase A2 in rat renal mesangial cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1997;1348:257–272. doi: 10.1016/s0005-2760(97)00073-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Balsinde J, Balboa MA, Dennis EA. Functional coupling between secretory phospholipase A2 and cyclooxygenase-2 and its regulation by cytosolic group IV phospholipase A2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998;95:7951–7956. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.14.7951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Murakami M, Shimbara S, Kambe T, Kuwata H, Winstead MV, Tischfield JA, Kudo I. The functions of five distinct mammalian phospholipase A2S in regulating arachidonic acid release. Type IIa and type V secretory phospholipase A2S are functionally redundant and act in concert with cytosolic phospholipase A2. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:14411–14423. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.23.14411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Uhlar CM, Whitehead AS. Serum amyloid A, the major vertebrate acute-phase reactant. Eur J Biochem. 1999;265:501–523. doi: 10.1046/j.1432-1327.1999.00657.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Ridker PM. Inflammation, atherosclerosis, and cardiovascular risk: an epidemiologic view. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 1999;10(Suppl 1):S9–12. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Johnson BD, KiP KE, Marroquin OC, Ridker PM, Kelsey SF, Shaw LJ, Pepine CJ, Sharaf B, Bairey Merz CN, Sopko G, Olson MB, Reis SE. Serum amyloid A as a predictor of coronary artery disease and cardiovascular outcome in women: the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute-Sponsored Women’s Ischemia Syndrome Evaluation (WISE) Circulation. 2004;109:726–732. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.0000115516.54550.B1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Ridker PM, Hennekens CH, Buring JE, Rifai N. C-reactive protein and other markers of inflammation in the prediction of cardiovascular disease in women. N Engl J Med. 2000;342:836–843. doi: 10.1056/NEJM200003233421202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Meek RL, Urieli-Shoval S, Benditt EP. Expression of apolipoprotein serum amyloid A mRNA in human atherosclerotic lesions and cultured vascular cells: implications for serum amyloid A function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994;91:3186–3190. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.8.3186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Yamada T, Kakihara T, Kamishima T, Fukuda T, Kawai T. Both acute phase and constitutive serum amyloid A are present in atherosclerotic lesions. Pathol Int. 1996;46:797–800. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1827.1996.tb03552.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Malle E, De Beer FC. Human serum amyloid A (SAA) protein: a prominent acute-phase reactant for clinical practice. Eur J Clin Invest. 1996;26:427–435. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2362.1996.159291.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Qiao JH, Xie PZ, Fishbein MC, Kreuzer J, Drake TA, Demer LL, Lusis AJ. Pathology of atheromatous lesions in inbred and genetically engineered mice. Genetic determination of arterial calcification. Arterioscler Thromb. 1994;14:1480–1497. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.14.9.1480. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Kumon Y, Sipe JD, Brinckerhoff CE, Schreiber BM. Regulation of extrahepatic apolipoprotein serum amyloid A (ApoSAA) gene expression by interleukin-1 alpha alone: synthesis and secretion of ApoSAA by cultured aortic smooth muscle cells. Scand J Immunol. 1997;46:284–291. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-3083.1997.d01-128.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Schreiber BM, Veverbrants M, Fine RE, Blusztajn JK, Salmona M, Patel A, Sipe JD. Apolipoprotein serum amyloid A down-regulates smooth-muscle cell lipid biosynthesis. Biochem J. 1999;344(Pt 1):7–13. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]