Abstract
The genes of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium LT2 encoding functions needed for the utilization of tricarballylate as a carbon and energy source were identified and their locations in the chromosome were established. Three of the tricarballylate utilization (tcu) genes, tcuABC, are organized as an operon; a fourth gene, tcuR, is located immediately 5′ to the tcuABC operon. The tcuABC operon and tcuR gene share the same direction of transcription but are independently transcribed. The tcuRABC genes are missing in the Escherichia coli K-12 chromosome. The tcuR gene is proposed to encode a regulatory protein needed for the expression of tcuABC. The tcuC gene is proposed to encode an integral membrane protein whose role is to transport tricarballylate across the cell membrane. tcuC function was sufficient to allow E. coli K-12 to grow on citrate (a tricarballylate analog) but not to allow growth of this bacterium on tricarballylate. E. coli K-12 carrying a plasmid with wild-type alleles of tcuABC grew on tricarballylate, suggesting that the functions of the TcuABC proteins were the only ones unique to S. enterica needed to catabolize tricarballylate. Analyses of the predicted amino acid sequences of the TcuAB proteins suggest that TcuA is a flavoprotein, and TcuB is likely anchored to the cell membrane and probably contains one or more Fe-S centers. The TcuB protein is proposed to work in concert with TcuA to oxidize tricarballylate to cis-aconitate, which is further catabolized via the Krebs cycle. The glyoxylate shunt is not required for growth of S. enterica on tricarballylate. A model for tricarballylate catabolism in S. enterica is proposed.
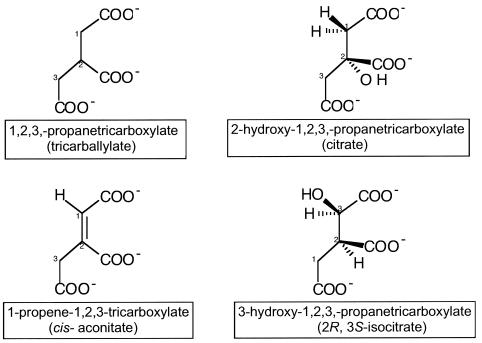
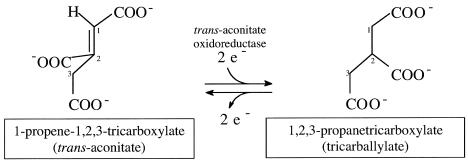
Tricarballylate (1,2,3-propanetricarboxylate) is structurally related to citric acid; hence, its catabolism is thought to proceed via the tricarboxylic acid (Krebs) cycle (Fig. 1). Tricarballylate is the causative agent of grass tetany, a disease in ruminants characterized by a pronounced magnesium ion deficiency. Reports in the literature have established a strong correlation between high levels of trans-aconitate (trans-1-propene-1,2,3-tricaboxylate) in the rumen with the incidence of the disease (6). In the rumen, trans-aconitate is rapidly converted to tricarballylate in a single reductive step (Fig. 2) (25). It is not clear how tricarballylate causes grass tetany; however, it is known that tricarballylate is a good chelator of magnesium ions and that it enhances excretion of this important divalent metal ion (33). In addition, tricarballylate is known to be a potent inhibitor of aconitase, a key enzyme of the Krebs cycle (26, 29, 33). This effect on aconitase makes tricarballylate particularly toxic to organisms that rely on the Krebs cycle for energy generation and are unable to catabolize tricarballylate into nontoxic metabolites.
FIG. 1.
Structure of tricarballylate and related analogs.
FIG. 2.
Reduction of trans-aconitate to tricarballylate. 2e−, reducing equivalent carried by an unidentified electron carrier.
In the rumen, Selenomonas ruminantium is the primary producer of tricarballylate (25). Not surprisingly, this bacterium has been the target of studies aimed at blocking the accumulation of this compound. The bacterium Acidaminococcus fermentans (another inhabitant of the rumen) is known to oxidize trans-aconitate to acetate; cocultures of S. ruminantium and A. fermentans showed a level of tricarballylate that was reduced to 50% of that measured in cultures of S. ruminantium lacking A. fermentans (10). Some prokaryotes possess the metabolic capability needed to use tricarballylate as a source of carbon and energy.
Of particular interest to us was the report by Gutnik et al. that Salmonella enterica can grow on tricarballylate as a sole source of carbon and energy (14). To date, neither the biochemistry nor the genetics of tricarballylate catabolism has been studied for this bacterium. Interestingly, E. coli (a close relative of S. enterica) cannot grow on tricarballylate or related compounds such as citrate, cis-aconitate, or isocitrate (Fig. 1) (20, 27, 35), a fact that correlates with the absence in the E. coli genome of the set of genes identified by the work reported here as the ones needed to catabolize tricarballylate (4).
The work reported here identifies a set of three open reading frames (ORFs) of previously unknown function and the gene previously known as citA, which are all required for the utilization of tricarballylate as a carbon and energy source by S. enterica. These genes are hereafter referred to as the tricarballylate utilization (tcu) genes, of which two are proposed to encode tricarballylate catabolic enzymes, namely tcuA (formerly ORF STM0691) and tcuB (formerly citB, ORF STM0690). The tcuC gene (formerly citA, STM0689) encodes a protein likely to transport tricarballylate across the inner membrane, and the tcuR gene (formerly ORF STM0692) is likely to encode a regulatory protein that modulates the expression of the tcuABC genes. As noted above, the tcuB gene was formerly known as citB and had an undetermined role in citrate catabolism, and the tcuC gene was previously identified as citA (a citrate transporter) (35, 36). On the basis of the work reported here, the names of these genes have been changed to tcuB and tcuC, respectively, to reflect their true role in S. enterica physiology and to distinguish them from other cit genes in the literature (32). The inability of E. coli to use tricarballylate was used to identify the full complement of S. enterica genes required for the catabolism of this tricarboxylic acid. A model for tricarballylate catabolism in S. enterica is proposed.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Bacterial strains, culture media, and growth conditions.
A list of strains and plasmids used and their genotypes is provided in Table 1. All chemicals were purchased from Sigma unless otherwise stated. E. coli cultures were grown in Luria-Bertani (LB) broth (Difco). Antibiotic concentrations in rich medium were (in μg/ml) ampicillin (Ap), 100; chloramphenicol (Cm), 20; kanamycin (Km), 50; and tetracycline (Tc), 20. Antibiotic concentrations in minimal medium were (in μg/ml) ampicillin, 50; kanamycin, 25; tetracycline, 10; and chloramphenicol, 4. No-Carbon E (NCE) (3) was used as a minimal medium and was supplemented with 1 mM MgSO4, 0.5 mM methionine, and trace minerals (2, 11). Solid medium contained Difco agar (1.5% wt/vol)-10 mM tricarballylate. Liquid medium contained 20 mM tricarballylate. As carbon and energy sources, citrate was used at a concentration of 20 mM, acetate was used at a concentration of 30 mM, and succinate was used at a concentration of 30 mM. For growth curves, S. enterica strains were grown overnight in LB broth. Two microliters of the overnight cultures was used to inoculate 198 μl of fresh medium in 96-well microtiter dishes. Growth was monitored with an ELx808 high-throughput spectrophotometer (Bio-Tek Instruments). Absorbance readings at 650 nm (A650) were taken every 10 min for 36 h. Cultures were shaken for 240 s between measurements. The incubation chamber was maintained at 37°C. Each culture had at least six replicates.
TABLE 1.
Strains and plasmids used in this study
| Strain | Genotype | Reference or source |
|---|---|---|
| E. coli | ||
| DH5α/F′ | F′/endA1 hsdR17(rK− mK+) supE44 thi-1 recA1 gyrA (Nalr)relA1 Δ(lacZYA-argF)U169 deoR [φ80dlacΔ(lacZ)M15] | New England Biolabs |
| ER2566 | F− λ−fhuA2 [lon] ompT lacZ::T7 gene1 gal sulA11 Δ(mcrC-mrr)114::IS10 R(mcr-73::mini-Tn10)2 R(zgb-210::Tn10)1(Tets) endA1 [dcm] | New England Biolabs |
| JE5635 | Wild-type strain K-12 | Lab collection |
| JE6161 | DH5α/pTCU3 (tcuC+kan+) | |
| JE6160 | DH5α/pTCU5 (tcuC+bla+) | |
| JE6360 | DH5α/pTCU8 (tcuA+bla+) | |
| JE6383 | DH5α/pTCU18 (tcuB+bla+) | |
| JE6794 | DH5α/pTCU19 (tcuR+bla+) | |
| JE7660 | DH5α/pTCU21 (tcuABC+bla+) | |
| S. enterica | ||
| TR6583 | metE205 ara-9 | K. Sanderson via J. Roth |
| JR501 | hsdSA29 hsdSB121 hsdL6 metA22 metE551 trpC2 ilv-452 rpsL120 xyl-404 galE719 H1-b H2-e,n,x nml (Fels2)−fla-66 | 38 |
| Derivatives of TR6583 | ||
| JE5174 | tcuC35::Tn10d(tet+)a | |
| JE5188 | ybfM106::MudJ(kan+)b | |
| JE2397 | srl-203::Tn10d(cat+) recA1 | |
| JE4271 | pBAD30 (bla+) | |
| JE6319 | ybfM106::MudJ(kan+) tcuC1 | |
| JE6329 | ybfM106::MudJ(kan+) tcuR11 | |
| JE6335 | ybfM106::MudJ(kan+) tcuB17 | |
| JE6346 | ybfM106::MudJ(kan+) tcuA28 | |
| JE7562 | ybfM106::MudJ(kan+) srl-203::Tn10d(cat+) recA1 tcuB17 | |
| JE7585 | ybfM106::MudJ(kan+) srl-203::Tn10d(cat+) recA1 tcuC1 | |
| JE7586 | ybfM106::MudJ(kan+) srl-203::Tn10d(cat+) recA1 tcuA28 | |
| JE7212 | tcuA33::MudJ(kan+) | |
| JE7213 | tcuR34::MudJ(kan+) | |
| JE7286 | tcuR34::MudJ(kan+) srl-203::Tn10d(cat+) recA1 | |
| JE7287 | tcuA33::MudJ(kan+) srl-203::Tn10d(cat+) recA1 | |
| JE4172 | aceA112::MudJ(kan+) | |
| JE4561 | icd1::Tn10d(tet+) |
Genetic crosses.
Transductions involving phage P22 HT105 int-201 were performed as described elsewhere (9, 11, 30, 31).
Isolation of tcu mutants carrying insertions of the Tn10Δ16Δ17 element.
A pool of mutant strains (ca. 100,000), each containing the transposition-defective Tn10Δ16Δ17 element (hereafter referred to as Tn10d(tet+) (40), was prepared as described elsewhere (12). Strain TR6583 was transduced to tetracycline resistance with P22 lysate grown on the pool of strains carrying Tn10d(tet+) elements. Tetracycline-resistant (Tcr) transductants were replica printed onto NCE medium supplemented with either succinate or tricarballylate as a carbon and energy source. Tcr transductants able to grow on succinate but not tricarballylate were freed of phage and analyzed further.
Isolation of a MudI1734 (MudJ) element near tcuC.
A pool of mutant strains (ca. 50,000), each containing a MudI1734 (lacZYA kan+) element (hereafter referred to as MudJ) was prepared as described (8, 18). Strain JE5174 [tcuC35::Tn10d(tet+)] was transduced to kanamycin resistance by using a P22 lysate grown on a pool of ∼50,000 strains, each carrying one MudJ element inserted in the chromosome. Kanamycin-resistant (Kmr) transductants were replica printed onto NCE medium supplemented with tricarballylate and kanamycin. Kmr transductants able to grow on tricarballylate were freed of phage and analyzed further. The physical location of the MudJ element near the tcu genes was determined by sequencing the region of DNA flanking the element by using PCR amplification protocols described elsewhere (7, 17, 23).
Isolation of MudJ elements in tcuR and tcuA.
Strain JE5174 [tcuC35::Tn10d(tet+)] was transduced to kanamycin resistance by using a phage P22 lysate grown on a pool of ∼50,000 strains, each of which carried one MudJ element in the chromosome. Kmr transductants were replica printed to LB-Tc plates to identify clones that were Kmr and Tcs, i.e., strains with a MudJ element near the tcuRABC operon. Kmr Tcs colonies were freed of phage, and their ability to grow on tricarballylate as a carbon and energy source was assessed. Kmr strains unable to grow on tricarballylate were studied further. The precise location of the insertion was determined by arbitrary PCR mapping. Strain JE7212 contains a tcuA33::MudJ insertion, and JE7213 contains a tcuR34::MudJ insertion.
Localized chemical mutagenesis of the tcuRABC genes.
Random mutagenesis of the region containing the tcuRABC genes was achieved by the method of Hong and Ames (16), as described (11). For this purpose, we first isolated a MudJ element in the ybfM (ORF STM0687) gene, which is one gene away from tcuC and was shown to be 94% cotransducible with tcuC by phage P22. A bacteriophage P22 lysate grown on strain JE5188 (ybfM106::MudJ) was mutagenized with hydroxylamine, and the mutagenized phage lysate was used as the donor to transduce strain TR6583 (tcuRABC+) to kanamycin resistance on LB medium containing kanamycin. Thirty Kmr transductants unable to grow on tricarballylate were isolated after the selection plates were replica printed onto minimal medium containing kanamycin and citrate or tricarballylate as the carbon and energy source.
Construction of recombination-deficient tcu mutants.
Phage P22 lysate grown on strain JE2397 [srl-203::Tn10d(cat+) recA1] was used to transduce strains to chloramphenicol resistance. Chloramphenicol resistant (Cmr) transductants that coinherited the recA1 allele were identified by their sensitivity to UV irradiation.
Recombinant DNA techniques.
Restriction and modification enzymes were purchased from Promega unless stated otherwise and were used according to the manufacturer's instructions. All DNA manipulations were performed in E. coli DH5α. Plasmids were transformed into cells by CaCl2 heat shock as described elsewhere (19). Plasmids transferred from E. coli into S. enterica were first introduced into the restriction-deficient, modification-proficient S. enterica strain JR501 by transformation (38). Plasmid DNA was isolated by using the Wizard Plus SV Plasmid Miniprep kit from Promega as per the manufacturer's instructions. DNA fragments were isolated from 1% (wt/vol) agarose gels and purified by using the Qiaquick Gel Extraction kit (QIAGEN). PCRs were purified by using the Qiaquick PCR purification kit from QIAGEN as suggested by the manufacturer. Nonradioactive sequencing was performed at the Biotechnology Center at the University of Wisconsin—Madison.
Plasmid constructions.
Plasmids were propagated in E. coli strain DH5α except where noted. Genomic DNA for PCR was prepared from S. enterica strain JE6583 by using the MasterPure Genomic DNA Purification kit from Epicentre Technologies. All primers used for PCR amplifications were purchased from Integrated DNA Technologies.
Plasmid pTCU5.
The tcuC gene of S. enterica was PCR amplified from TR6583 by using conditions previously described (17). For the PCR, the primers contained Gateway (GIBCO BRL) recombination sites and the sequences (without att sites) were as follows: for the 5′-tcuC primer, 5′-CCGCAACATCTTACCTATA-3′, and for the 3′-tcuC primer, 5′-GGGTAACGATCAGGCGGTCAAG-3′. The 1.4-kb PCR product was purified by using the QIAquick PCR purification kit (QIAGEN) and cloned into the pDONR201 vector by using the Gateway BP reaction according to the manufacturer's instructions. The resulting plasmid was 4-kb long, provided resistance to kanamycin, and was referred to as plasmid pTCU3. The tcuC gene was moved from plasmid pTCU3 into a Gateway-compatible pBAD30 plasmid (15) by using the Gateway LR reaction. The resulting plasmid was 6.4 kb, encoded ampicillin resistance, and was named pTCU5.
Plasmid pTCU8.
The tcuA gene was cloned into pBAD30 by using a Gateway LR reaction. The Gateway-compatible region was in the SmaI site of plasmid pBAD30. Plasmid pTCU8 was 6.4 kb and encoded ampicillin resistance.
Plasmid pTCU18.
The tcuR gene was cloned into pBAD30 by using a Gateway LR reaction. This plasmid is a minimal gene clone of tcuR. The Gateway-compatible region was in the SmaI site on pBAD30. This plasmid was 6.4 kb and encoded ampicillin resistance.
Plasmid pTCU19.
The tcuB gene of S. enterica was PCR amplified by using primers with built-in restriction sites (the restriction sites are underlined in the sequences). The 5′ primer contained a KpnI site, 5′-AATTATAGGTACCAATGTTCTGGGCAAGGGGTAT-3′, and the 3′ primer contained a XbaI site, 5′-AATTATATCTAGAGTTCAAGGAAATTGCCGCTT-3′. The 1,381-bp PCR product was cut with KpnI and XbaI restriction enzymes and cloned into pBAD30 cut with the same enzymes. Plasmid pTCU19 was 6.1 kb and encoded ampicillin resistance.
Plasmid pTCU21.
The tcuABC genes of S. enterica were PCR amplified by using primers with built-in restriction sites (the restriction sites are underlined in the sequences). The 5′ primer contained a KpnI site (5′-AATTATAGGTACCGGTACGGGAGTATAAGATGGT-3′), and the 3′ primer contained an XbaI site (5′-AATTATATCTAGATAACGATCAGGCGGTCAA-3′). The 4,022-bp PCR product was cut with KpnI and XbaI restriction enzymes and cloned into pBAD30 cut with the same enzymes. pTCU21 was 9.1 kb and encoded ampicillin resistance.
Complementation analysis.
Strains unable to grow on tricarballylate were transformed with plasmids containing wild-type alleles of tcuR (plasmid pTCU18), tcuA (plasmid pTCU8), tcuB (plasmid pTCU19), or tcuC (plasmid pTCU5). Drug-resistant transformants were patched onto LB agar supplemented with the appropriate antibiotic and replica printed to NCE medium containing tricarballylate and antibiotic. NCE medium containing glucose and antibiotic was used as the control for growth. Representative mutant alleles of each gene were sequenced to verify the location of the mutation. Growth curves were performed in liquid culture by using NCE-tricarballylate with antibiotic, with or without arabinose (250 μM or 500 μM, as noted) as the inducer of the tcu gene carried by the plasmid.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
S. enterica strains with lesions in the tcuC (ORF STM0689) gene cannot use tricarballylate as carbon and energy source.
A strain of S. enterica unable to grow on tricarballylate as the sole source of carbon and energy was isolated after transposon mutagenesis by using Tn10d(tet+) elements. To verify that the Tn10d(tet+) element in this strain was responsible for the inability of the strain to grow on tricarballylate, the insertion element was moved by phage P22-mediated transduction into the tricarballylate-proficient strain TR6583, and the phenotype of the reconstructed strain (JE5174) was assessed in liquid medium. Growth of strain JE5174 on tricarballylate was completely blocked even after extended periods of incubation but was restored to wild-type levels when a wild-type allele of tcuC was provided in trans (data not shown). Arbitrary primer PCR mapping located the Tn10d(tet+) element to the tcuC gene. These results indicated that the tcuC gene was essential for growth of S. enterica on tricarballylate. Previous studies of this bacterium showed that the tcuC gene product was a citrate transporter (35, 36). However, because tcuC is not the only citrate transport system present in S. enterica (1, 37), growth of the mutant JE5174 [tcuC35::Tn10d(tet+)] and wild-type TR6583 (tcuC+) strains on citrate was the same (doubling time, 2 h).
tcuC function is not sufficient for growth on tricarballylate.
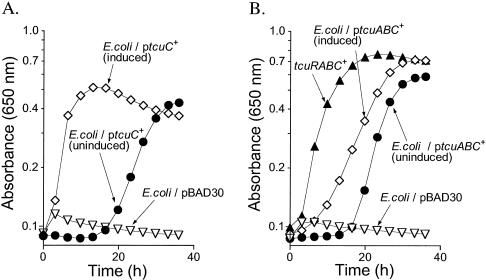
E. coli K-12, a bacterium known to be unable to grow on citrate or tricarballylate, was used to assess whether tcuC function was sufficient to allow growth on tricarballylate. For this purpose, plasmid pTCU5 (tcuC+) was introduced into E. coli K-12 and growth on citrate or tricarballylate was assessed in liquid medium. Consistent with previous studies (35), introduction of tcuC+ into E. coli allowed growth of this bacterium on citrate (Fig. 3A). This result was consistent with the hypothesis that the inability of E. coli to grow on citrate is exclusively due to the lack of transport of this compound across the cell membrane of this bacterium. However, the presence of plasmid pTCU5 (tcuC+) did not allow E. coli K-12 to grow on tricarballylate (data not shown), suggesting that additional functions present in S. enterica were needed for tricarballylate catabolism.
FIG. 3.
tcuABC functions allow growth of E. coli K-12 on citrate (A) or tricarballylate (B). In all graphs, pBAD30 is the empty cloning vector. (A) Cells were grown aerobically in NCE medium containing citrate (20 mM). Open triangles, growth response of E. coli strain K-12 on citrate medium containing 500 μM l-(+)-arabinose; closed circles, growth response of E. coli strain K-12 with tcuC+ provided in trans (plasmid pTCU5) in medium lacking l-(+)-arabinose; open diamonds, growth response of the same strain in medium containing 500 μM l-(+)-arabinose. (B) Cells were grown aerobically in NCE medium containing tricarballylate (20 mM). Solid triangles, growth response of a S. enterica strain with a wild-type tcuRABC+ set of genes (strain JE2397); open triangles, growth response of E. coli strain K-12 carrying empty cloning vector pBAD30 in medium supplemented with 500 μM l-(+)-arabinose; solid circles, growth response of E. coli strain K-12 carrying plasmid pTCU21 (tcuABC+) in medium lacking l-(+)-arabinose; open diamonds, growth response of the same strain in medium containing 250 μM l-(+)-arabinose.
The tcuC gene is part of a three-gene operon.
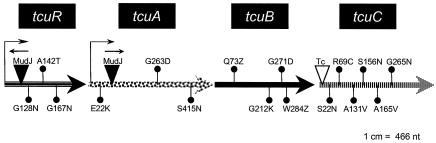
Analysis of the region of the S. enterica chromosome containing the tcuC gene (ORF STM0688) suggested that this gene was the last of a putative three-gene operon (tcuABC), with an additional gene (tcuR, ORF STM0692) encoding a putative regulatory protein needed for the expression of the operon immediately 5′ to the tcuABC operon. As shown below, tcuR and tcuABC are two independent transcriptional units (Fig. 4). The tcuABC operon was located between the fur (ORF STM0693) and ybfN (ORF STM0688) genes in the region of the chromosome between bases 752675 and 755353 (http://www.ncbi.nih.gov/genomes/altvik.cgi?gi=202&db=g&gene=fldA). The tcuABC operon was also found in S. enterica serovar Typhi and on the virulence plasmid pR27 (34) but was missing from the E. coli chromosome.
FIG. 4.
Location and nature of the mutations affecting S. enterica tcu functions. Insertion mutations are represented by solid (MudJ elements) or open [Tn10d(tet+) elements] inverted triangles, while the solid circles represent point mutations. Arrows above MudJ insertions indicate the direction of transcription of the lacZ gene in the MudJ element. Arrows at the ends of the tcuR and tcuA genes represent the promoters for each gene.
The tcuA gene (ORF STM0691; 1,404 bp).
The predicted sequence of the TcuA protein (467 amino acids [aa], 51 kDa) showed end-to-end homology to flavoproteins such as E. coli's fumarate reductase (data not shown). A significant portion of the homology was at the N terminus of the protein, where flavin cofactors are bound to fumarate reductase (5). A Kyte-Doolittle hydropathy plot of the TcuA protein primary sequence suggested that it was a cytosolic enzyme (data not shown).
The tcuB gene (ORF STM0690; 1,140 bp).
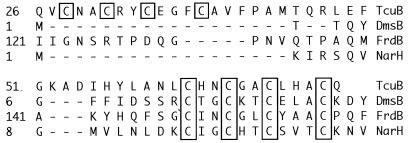
The tcuB gene was previously identified as citB during the sequencing of citA, but a function for the CitB protein was not established (35). The predicted amino acid sequence of the TcuB protein (379 aa, 42 kDa) has some interesting features. The N-terminal region of the protein displayed two distinct cysteine motifs that matched the consensus C-X2-C-X2-C-X3-C-X sequence found in proteins with iron-sulfur centers (21). These motifs are located at residues 28 to 38 and 62 to 72 in the TcuB sequence (Fig. 5). Unlike the N terminus, the C-terminal region of TcuB appears to be very hydrophobic from about residue 112 to the end of the polypeptide, suggesting that TcuB may be membrane associated (data not shown).
FIG. 5.
TcuB contains two conserved Cys-X2-Cys-X2-Cys-X3-Cys-X motifs characteristic of proteins containing 4Fe-4S centers. The conserved Cys residues are shown in boxes. DmsB, dimethyl sulfoxide reductase subunit B; FrdB, fumarate reductase Fe-S subunit; NarH, nitrate reductase Fe-S subunit.
The tcuC gene (ORF STM0689; 1,305 bp).
As pointed out above, the TcuC protein (434 aa, 47 kDa) was previously shown to allow E. coli to grow on citrate (35, 36). The S. enterica TcuC function and its homolog from Klebsiella pneumoniae (CitH) have been studied in detail (20, 36, 39). The TcuC protein belongs to a class of transporters with 12 transmembrane helices, and it transports the di-anionic form of citrate in symport with three protons. The TcuC protein is specific for citrate, and isocitrate is transported only by mutant TcuC proteins (36). Studies on this transporter did not test whether tricarballylate was a substrate for TcuC. The sequence of the tcuC gene is 97 to 99% identical to homologs identified on plasmids from natural isolates of E. coli that can grow on citrate (20, 35). A Kyte-Doolittle hydropathy plot of this protein shows a high degree of hydrophobicity throughout the protein, strongly suggestive of an integral membrane protein (data not shown). This putative membrane location would be consistent with its function as a transporter.
The tcuR gene (ORF STM0692; 927 bp).
The TcuR protein (308 aa, 33 kDa) is 31% identical and 53% similar to the nitrogen assimilation control (Nac) protein from E. coli and Klebsiella aerogenes. The Nac protein activates the transcription of the hutUH and ureDABCEFG operons, which are required for converting histidine and urea into useable nitrogen sources (13, 22). The Nac protein is a member of the LysR family of transcriptional regulators (24), which have DNA-binding domains at the N terminus of the protein and coeffector-binding sites at the C terminus (28). Consistent with other LysR family members, TcuR was homologous to other family members at the DNA-binding domain but shared little similarity at the C terminus (data not shown).
Defining tcu functions by mutation and complementation analysis.
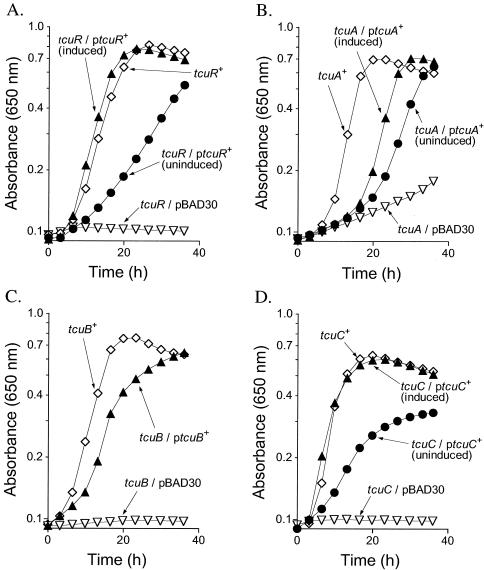
To obtain evidence that the tcuA, tcuB, and tcuR genes were involved in tricarballylate catabolism, point mutations in each one of these genes were isolated and the nature of several mutations was determined by DNA sequencing. The schematic of the tcuRABC genes shown in Fig. 4 indicates the location of lesions identified in tricarballylate-deficient strains by DNA sequencing. The growth response of recombination-deficient (recA) derivatives of representative tcu mutants carrying plasmids containing the wild-type allele of a tcu gene under the control of the arabinose-inducible ParaBAD promoter is shown in Fig. 6.
FIG. 6.
tcuRABC functions are all required for tricarballylate catabolism. In all cases, pBAD30 refers to the empty cloning vector, and recA refers to allele recA1. Cells were grown aerobically in NCE medium containing tricarballylate (20 mM) with the exception of those for panel C, where 1 mM glycerol was also added to the medium. (A) Complementation of a tcuR mutant. Open diamonds, growth response of a tcuR+ strain (JE4271); open triangles, growth response of a tcuR strain (JE6329); solid circles, growth response of a tcuR strain (JE6329) with tcuR+ provided in trans (pTCU18) in medium lacking l-(+)-arabinose; solid triangles, growth response of the same strain in medium containing 500 μM l-(+)-arabinose. (B) Complementation of a tcuA strain. Open diamonds, growth response of a tcuA+ recA strain (JE2397); open triangles, growth response of a tcuA recA strain (JE7586); solid circles, growth response of a tcuA recA strain (JE7586) with tcuA+ provided in trans (plasmid pTCU8) in medium lacking l-(+)-arabinose; solid triangles, growth response of the same strain in medium containing 500 μM l-(+)-arabinose. (C) Marker rescue of a tcuB strain. Open diamonds, growth response of a tcuB+ strain (JE4271); open triangles, growth response of a tcuB strain (JE6335); solid triangles, growth response of a tcuB strain (JE6335) with tcuB+ provided in trans (plasmid pTCU19). (D) Complementation of a tcuC strain. Open diamonds, growth response of a tcuC+ recA strain (JE2397); open triangles, growth response of a tcuC recA strain (JE7585); solid circles, growth response of a tcuC recA strain (JE7585) with tcuC+ provided in trans (plasmid pTCU5) in medium lacking l-(+)-arabinose; solid triangles, growth response of the same strain in medium containing 500 μM l-(+)-arabinose.
Unlike tcuA or tcuC strains, tcuB strains could not be complemented by a plasmid carrying only the wild-type allele of tcuB. Plasmid pTCU19 (tcuB+) rescued growth of tcuB strain JE6335, most likely by homologous recombination (Fig. 6C). Marker rescue was observed only when 1 mM glycerol was added to the medium. The effect of glycerol was likely due to an increase in the frequency of homologous recombination between the plasmid-borne allele and the chromosomal allele. Marker rescue was not observed in the tcuB mutant strain containing only the cloning vector. A recombination-deficient derivative of tcuB strain JE7562 failed to grow on tricarballylate when plasmid pTCU19 (tcuB+) was provided in trans (data not shown), supporting the conclusion that the delayed growth of the recombination-proficient tcuB strain carrying plasmid pTCU19 was due to marker rescue. In contrast to results for tcuB, complementation was observed in recombination-deficient tcuR strain JE6329, tcuA strain JE6346, and tcuC strain JE6319 when the appropriate tcu gene was provided in trans (Fig. 6A,B,D). These data indicated that tcuRABC were all required for growth of S. enterica on tricarballylate.
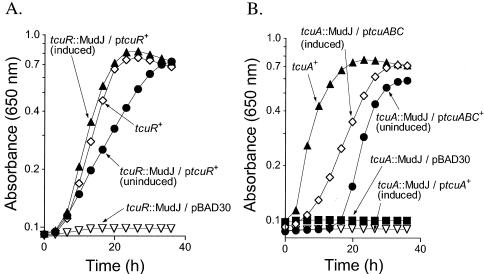
In vivo evidence that tcuR and tcuABC are two transcriptional units.
In vivo evidence in support of the conclusion that tcuR and tcuABC are two independent transcriptional units is presented in Fig. 7. The rationale of this experiment is that a MudJ (lacZYA kan+) insertion will have polar effects on cotranscribed downstream genes. To study the organization of the tcuRABC genes, recombination-deficient derivatives of strains carrying MudJ insertion mutations in the tcuR (JE7213) and tcuA (JE7212) genes were constructed and their growth on tricarballylate was assessed. When plasmid pTCU18 (tcuR+) was provided in trans in strain JE7286 (tcuR34::MudJ recA), the strain grew on tricarballylate (Fig. 7A). This result suggested that the tcuR34::MudJ mutation was not polar on tcuABC expression. In contrast, when plasmid pTCU8 (tcuA+) was provided in trans in strain JE7287 (tcuA33::MudJ recA1), complementation was not observed (Fig. 7B). Strain JE7287 did grow on tricarballylate when plasmid pTCU21 (tcuABC+) was provided in trans (Fig. 7B, open diamonds). Growth of strain JE7287 in the absence of inducer (Fig. 7B, solid circles) was explained by residual transcription of the tcuABC genes from the ParaBAD promoter. These results suggested that the tcuA::MudJ insertion had a negative effect on tcuBC expression.
FIG. 7.
Genetic evidence that tcuR and tcuABC are two distinct transcriptional units. In the graphs shown, pBAD30 refers to empty cloning vector, tcuR::MudJ refers to allele tcuR34::MudJ, tcuA::MudJ refers to allele tcuA33::MudJ, and recA refers to allele recA1. Cells were grown aerobically in NCE medium containing tricarballylate (20 mM). (A) Complementation of a tcuR strain. Open diamonds, growth response of a tcuR+ recA1 strain (JE2397); open triangles, growth response of a tcuR34::MudJ recA1 strain (JE7286); solid circles, growth response of a tcuR34::MudJ recA1 strain with tcuR+ provided in trans (plasmid pTCU18) in medium lacking l-(+)-arabinose; solid triangles, growth of the same strain in medium containing 500 μM l-(+)-arabinose. (B) Complementation of a tcuA strain. Open diamonds, growth response of a tcuRABC+ recA1 strain (JE2397); solid squares, growth response of a tcuA33::MudJ recA1 strain (JE7287); open triangles, growth of a tcuA33::MudJ recA1 strain (JE7287) with tcuA+ provided in trans (plasmid pTCU8) in medium containing 500 μM l-(+)-arabinose; solid circles, growth response of a tcuA33::MudJ recA1 strain (JE7287) with tcuABC+ provided in trans (plasmid pTCU21) in medium lacking l-(+)-arabinose; open diamonds, growth of the same strain in medium containing 250 μM l-(+)-arabinose.
tcuABC functions are necessary and sufficient for growth on tricarballylate.
E. coli K-12, which normally cannot grow on tricarballylate, was used to assess whether tcuABC functions were sufficient for growth on tricarballylate. For this purpose, plasmid pTCU21 (tcuABC+) was introduced into E. coli K-12, and growth on tricarballylate was assessed in liquid medium (Fig. 3B). Expression of the tcuABC+ functions allowed growth of this bacterium on tricarballylate, indicating that functions associated with these gene products were the only ones unique to S. enterica that were required for growth on tricarballylate.
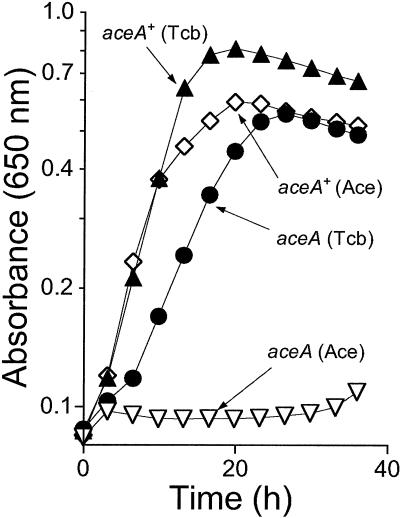
Tricarballylate catabolism does not proceed via the glyoxylate shunt.
The aceA gene encodes for isocitrate lyase, a key enzyme of the glyoxylate shunt. To investigate whether the glyoxylate shunt played a role in tricarballylate catabolism, growth of aceA mutant strain JE4172 on tricarballylate was assessed (Fig. 8). Acetate utilization was used as a negative control. In contrast, strain JE4561, lacking isocitrate dehydrogenase (icd) function, a key function of the Krebs cycle, failed to grow on tricarballylate when it was supplemented with glutamate (data not shown). Taken together, these results indicated that tricarballylate catabolism proceeded via the Krebs cycle and that the glyoxylate shunt is not required for growth of S. enterica on tricarballylate.
FIG. 8.
Tricarballylate catabolism does not proceed via the glyoxylate bypass. In the graphs described below, aceA refers to allele aceA112::MudJ. Cells were grown aerobically in NCE medium containing either tricarballylate (20 mM) or acetate (30 mM). Solid triangles, growth response of an aceA+ strain (TR6583) on tricarballylate; open diamonds, growth response of the same strain on acetate; solid circles, growth response of an aceA strain (JE4172) on tricarballylate; open triangles, growth of the same strain on acetate.
A model for tricarballylate catabolism.
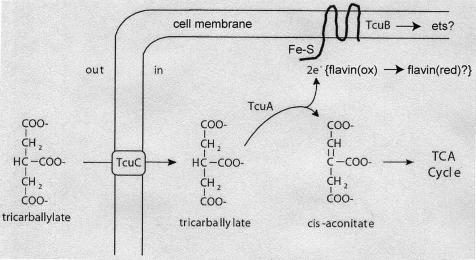
The simplest route of tricarballylate catabolism is its direct oxidation to cis-aconitate, which can be hydrated by aconitase to yield isocitrate, which can be further catabolized through the tricarboxylic acid cycle. Such a pathway would require an oxidoreductase that would require an electron carrier, e.g., flavin nucleotide or pyridine nucleotide. The TcuA protein is proposed to be the flavin nucleotide-dependent oxidoreductase enzyme responsible for the oxidation of tricarballylate to cis-aconitate. We propose that reducing equivalents from reduced TcuA are transferred to the TcuB protein via one-electron chemistry involving one or more Fe-S centers present in TcuB. The association of TcuB with the cell membrane suggests that electrons in TcuB may be transferred to other electron carriers, probably part of the electron transport system of the cell (Fig. 9). The biochemical characterization of the Tcu proteins is under way.
FIG. 9.
Model for tricarballylate catabolism in S. enterica. ets, electron transport system; TCA, tricarboxylic acid; 2e−, reducing equivalent.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by University of Wisconsin—Madison USDA Hatch grant 4659 and National Institutes of Health grants GM62203 and GM40313 to J.C.E.-S. J.A.L. was supported by National Institutes of Health Predoctoral Training grant T32 GM07215 in Molecular Biosciences, University of Wisconsin—Madison. A.R.H. was supported in part by a National Institutes of Health Biotechnology Training grant (GM08349) and a NSF predoctoral fellowship.
We thank Tenzin Paldon for technical assistance.
REFERENCES
- 1.Ashton, D. M., G. D. Sweet, J. M. Somers, and W. W. Kay. 1980. Citrate transport in Salmonella typhimurium: studies with 2-fluoro-l-erythro-citrate as a substrate. Can. J. Biochem. 58:797-803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Balch, W. E., and R. S. Wolfe. 1976. New approach to the cultivation of methanogenic bacteria: 2-mercaptoethanesulfonic acid (HS-CoM)-dependent growth of Methanobacterium ruminantium in a pressurized atmosphere. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 32:781-791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Berkowitz, D., J. M. Hushon, H. J. Whitfield, J. Roth, and B. N. Ames. 1968. Procedure for identifying nonsense mutations. J. Bacteriol. 96:215-220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Blattner, F. R., G. Plunkett III, C. A. Bloch, N. T. Perna, V. Burland, M. Riley, J. Collado-Vides, J. D. Glasner, C. K. Rode, G. F. Mayhew, J. Gregor, N. W. Davis, H. A. Kirkpatrick, M. A. Goeden, D. J. Rose, B. Mau, and Y. Shao. 1997. The complete genome sequence of Escherichia coli K-12. Science 277:1453-1474. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Blaut, M., K. Whittaker, A. Valdovinos, B. A. Ackrell, R. P. Gunsalus, and G. Cecchini. 1989. Fumarate reductase mutants of Escherichia coli that lack covalently bound flavin. J. Biol. Chem. 264:13599-13604. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Burau, R., and P. R. Stout. 1965. trans-Aconitic acid in range grasses in early spring. Science 150:766-767. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Caetano-Annoles, G. 1993. Amplifying DNA with arbitrary oligonucleotide primers. PCR Methods Appl. 3:85-92. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Castilho, B. A., P. Olfson, and M. J. Casadaban. 1984. Plasmid insertion mutagenesis and lac gene fusions with mini-Mu bacteriophage transposons. J. Bacteriol. 158:488-495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Chan, R. K., D. Botstein, T. Watanabe, and Y. Ogata. 1972. Specialized transduction of tetracycline resistance by phage P22 in Salmonella typhimurium. II. Properties of a high transducing lysate. Virology 50:883-898. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Cook, G. M., J. E. Wells, and J. B. Russell. 1994. Ability of Acidaminococcus fermentans to oxidize trans-aconitate and decrease the accumulation of tricarballylate, a toxic end product of ruminal fermentation. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 60:2533-2537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Davis, R. W., D. Botstein, and J. R. Roth. 1980. A manual for genetic engineering: advanced bacterial genetics. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, N.Y.
- 12.Elliott, T., and J. R. Roth. 1988. Characterization of Tn10d-Cam: a transposition-defective Tn10 specifying chloramphenicol resistance. Mol. Gen. Genet. 213:332-338. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Goss, T. J., and R. A. Bender. 1995. The nitrogen assimilation control protein, NAC, is a DNA binding transcription activator in Klebsiella aerogenes. J. Bacteriol. 177:3546-3555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Gutnick, D., J. M. Calvo, T. Klopotowski, and B. N. Ames. 1969. Compounds which serve as the sole source of carbon or nitrogen for Salmonella typhimurium LT-2. J. Bacteriol. 100:215-219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Guzman, L.-M., D. Belin, M. J. Carson, and J. Beckwith. 1995. Tight regulation, modulation, and high-level expression by vectors containing arabinose PBAD promoter. J. Bacteriol. 177:4121-4130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Hong, J.-S., and B. N. Ames. 1971. Localized mutagenesis of any specific small region of the bacterial chromosome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 68:3158-3162. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Horswill, A. R., A. R. Dudding, and J. C. Escalante-Semerena. 2001. Studies of propionate toxicity in Salmonella enterica identify 2-methylcitrate as a potent inhibitor of cell growth. J. Biol. Chem. 276:19094-19101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Hughes, K. T., and J. R. Roth. 1988. Transitory cis complementation: a method for providing transposition functions to defective transposons. Genetics 119:9-12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Inoue, H., H. Nojima, and H. Okayama. 1990. High efficiency transformation of Escherichia coli with plasmids. Gene 96:23-28. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Ishiguro, N., and G. Sato. 1985. Nucleotide sequence of the gene determining plasmid-mediated citrate utilization. J. Bacteriol. 164:977-982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Jung, Y. S., C. A. Bonagura, G. J. Tilley, H. S. Gao-Sheridan, F. A. Armstrong, C. D. Stout, and B. K. Burgess. 2000. Structure of C42D Azotobacter vinelandii FdI. A Cys-X-X-Asp-X-X-Cys motif ligates an air-stable [4Fe-4S]2+/+ cluster. J. Biol. Chem. 275:36974-36983. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Muse, W. B., and R. A. Bender. 1998. The nac (nitrogen assimilation control) gene from Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 180:1166-1173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.O'Toole, G. A., and R. Kolter. 1998. Initiation of biofilm formation in Pseudomonas fluorescens WCS365 proceeds via multiple, convergent signalling pathways: a genetic analysis. Mol. Microbiol. 28:449-461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Pomposiello, P. J., and R. A. Bender. 1995. Activation of the Escherichia coli lacZ promoter by the Klebsiella aerogenes nitrogen assimilation control protein (NAC), a LysR family transcription factor. J. Bacteriol. 177:4820-4824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Russell, J. B. 1985. Enrichment and isolation of rumen bacteria that reduce trans-aconitate to tricarballylic acid. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 49:120-126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Russell, J. B., and N. Forsberg. 1986. Production of tricarballylic acid by rumen microorganisms and its potential toxicity in ruminant tissue metabolism. Br. J. Nutr. 56:153-162. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Sasatsu, M., T. K. Misra, L. Chu, R. Laddaga, and S. Silver. 1985. Cloning and DNA sequence of a plasmid-determined citrate utilization system in Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 164:983-993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Schell, M. A. 1993. Molecular biology of the LysR family of transcriptional regulators. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 47:597-626. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Schloss, J. V., M. H. Emptage, and W. W. Cleland. 1984. pH profiles and isotope effects for aconitase from Saccharomycopsis lipolytica, beef heart, and beef liver. α-Methyl-cis-aconitate and threo-Ds-α-methylisocitrate as substrates. Biochemistry 23:4572-4580. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Schmieger, H. 1971. A method for detection of phage mutants with altered transduction ability. Mol. Gen. Genet. 100:378-381. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Schmieger, H., and H. Bakhaus. 1973. The origin of DNA in transducing particles of P22 mutants with increased transduction frequencies (HT-mutants). Mol. Gen. Genet. 120:181-190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Schneider, K., C. N. Kastner, M. Meyer, M. Wessel, P. Dimroth, and M. Bott. 2002. Identification of a gene cluster in Klebsiella pneumoniae which includes citX, a gene required for biosynthesis of the citrate lyase prosthetic group. J. Bacteriol. 184:2439-2946. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Schwartz, R., M. Topley, and J. B. Russell. 1988. Effect of tricarballylic acid, a nonmetabolizable rumen fermentation product of trans-aconitic acid, on Mg, Ca and Zn utilization of rats. J. Nutr. 118:183-188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Sherburne, C. K., T. D. Lawley, M. W. Gilmour, F. R. Blattner, V. Burland, E. Grotbeck, D. J. Rose, and D. E. Taylor. 2000. The complete DNA sequence and analysis of R27, a large IncHI plasmid from Salmonella typhi that is temperature sensitive for transfer. Nucleic Acids Res. 28:2177-2186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Shimamoto, T., H. Izawa, H. Daimon, N. Ishiguro, M. Shinagawa, Y. Sakano, M. Tsuda, and T. Tsuchiya. 1991. Cloning and nucleotide sequence of the gene (citA) encoding a citrate carrier from Salmonella typhimurium. J. Biochem. (Tokyo) 110:22-28. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Shimamoto, T., K. Negishi, M. Tsuda, and T. Tsuchiya. 1996. Mutational analysis of the CitA citrate transporter from Salmonella typhimurium: altered substrate specificity. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 226:481-487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Sweet, G. D., J. M. Somers, and W. W. Kay. 1979. Purification and properties of a citrate-binding transport component, the C protein of Salmonella typhimurium. Can. J. Biochem. 57:710-715. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Tsai, S. P., R. J. Hartin, and J. Ryu. 1989. Transformation in restriction-deficient Salmonella typhimurium LT2. J. Gen. Microbiol. 135:2561-2567. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Van der Rest, M. E., T. Abee, D. Molenaar, and W. N. Konings. 1991. Mechanism and energetics of a citrate-transport system of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Eur. J. Biochem. 195:71-77. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Way, J. C., M. A. Davis, D. Morisato, D. E. Roberts, and N. Kleckner. 1984. New Tn10 derivatives for transposon mutagenesis and for construction of lacZ operon fusions by transposition. Gene 32:369-379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]