Abstract
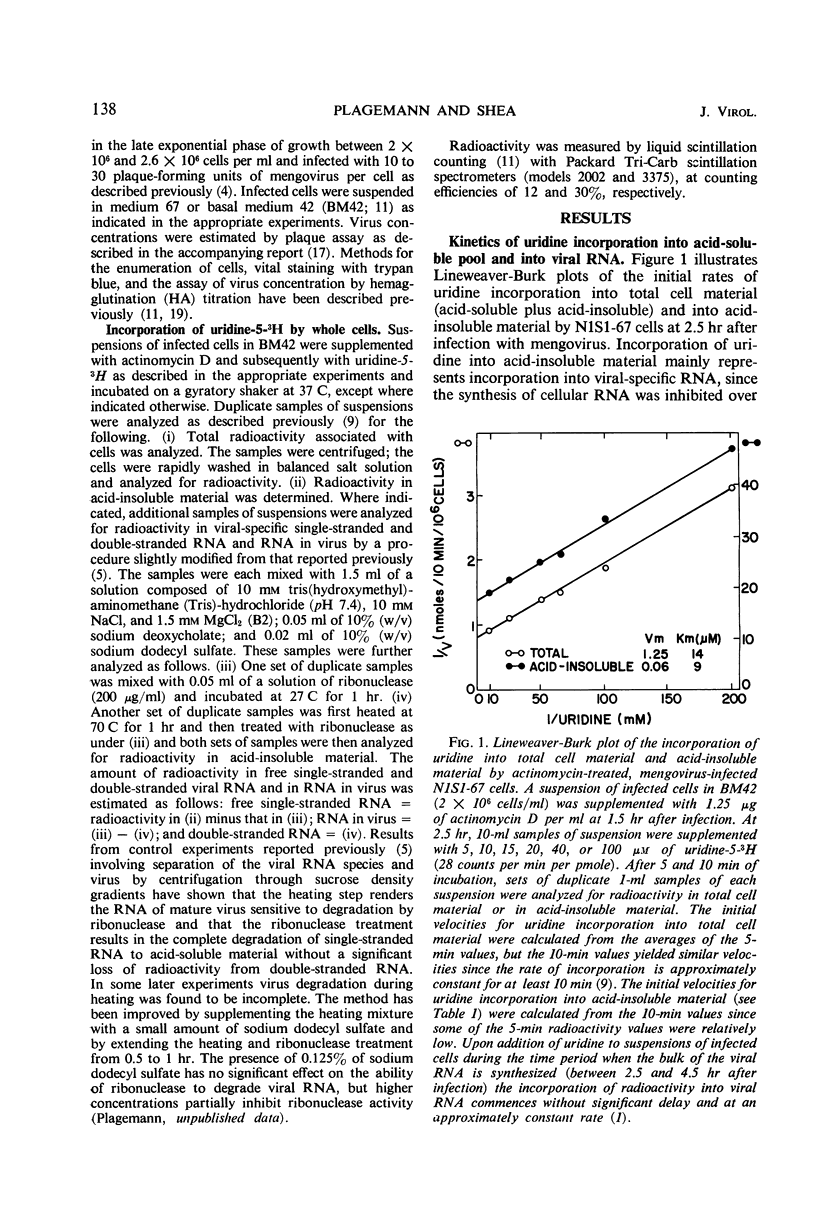
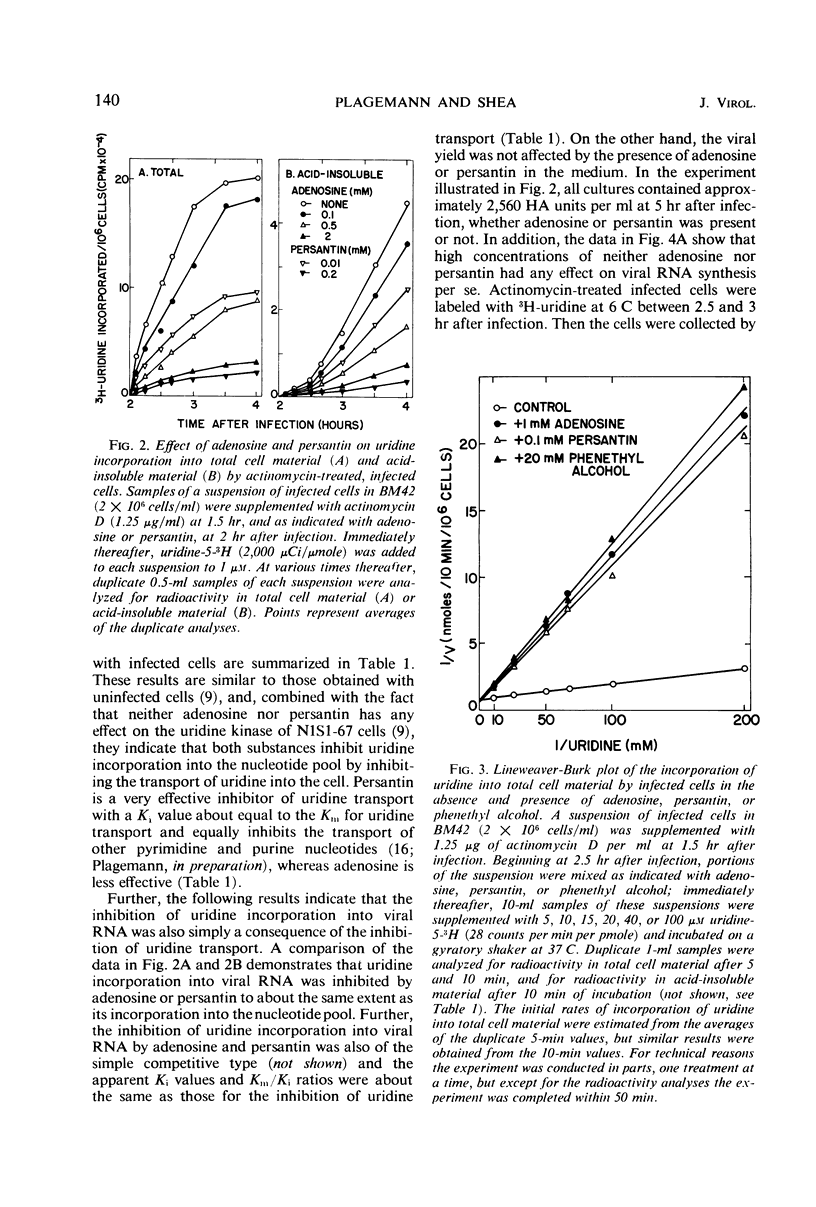
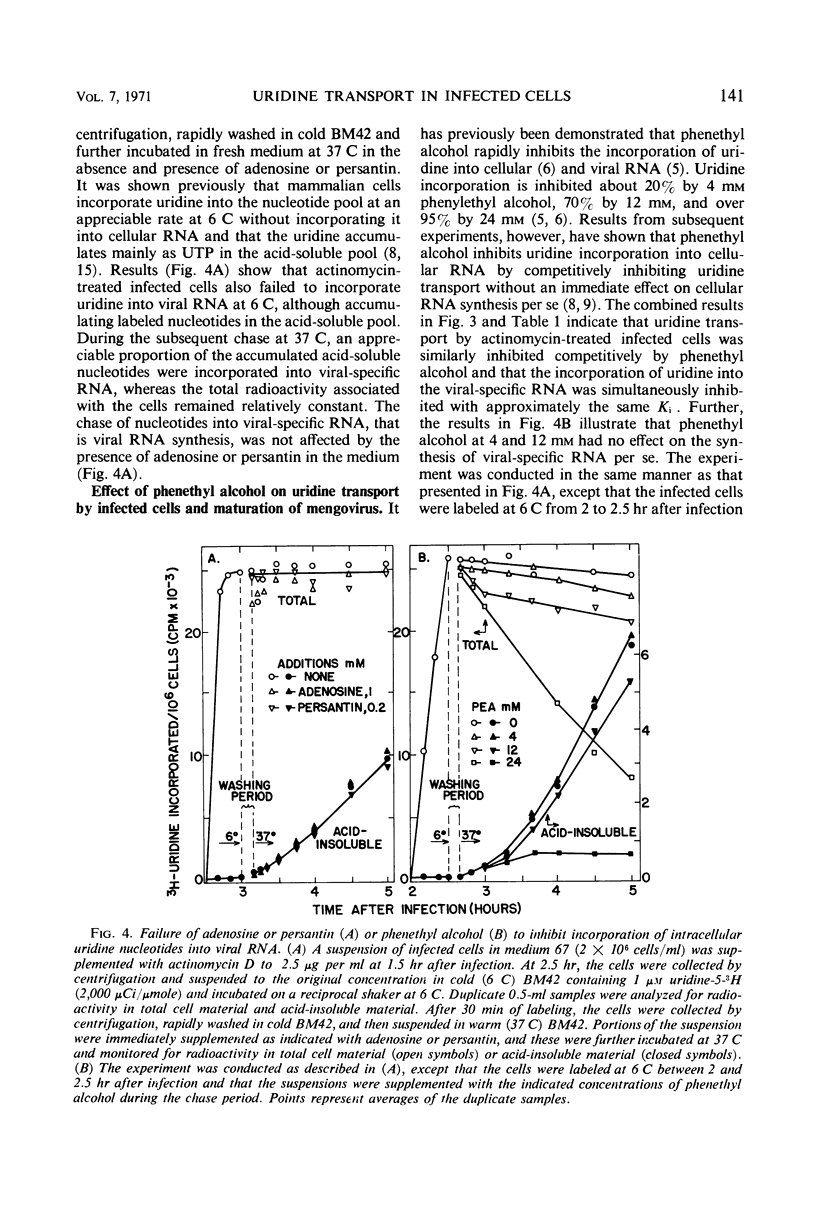
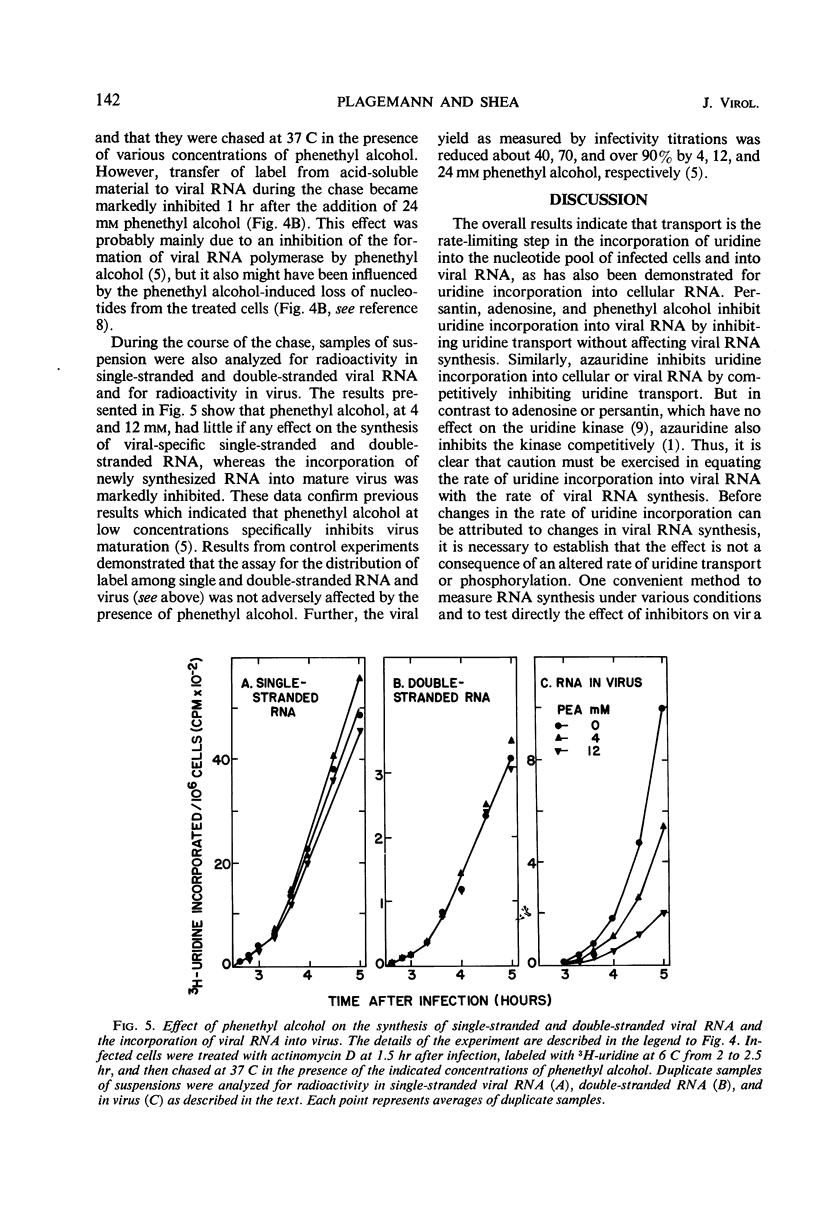
The incorporation of uridine into the nucleotide pool of actinomycin-treated, mengovirus-infected Novikoff rat hepatoma cells in culture follows simple Michaelis-Menten kinetics, and the apparent Vmax and Km values are similar to those for uridine transport by uninfected cells. Incorporation of uridine into mengovirus-specific ribonucleic acid (RNA) also follows Michaelis-Menten kinetics, and the apparent Km (about 10 μm) is approximately the same as for uridine transport. Inhibition of uridine transport by the presence of adenosine, persantin, or phenethyl alcohol inhibits simultaneously and to the same extent the incorporation of uridine into the nucleotide pool and into viral RNA, without affecting viral RNA synthesis per se. Phenethyl alcohol, however, also inhibits virus maturation. The inhibition of uridine incorporation into the nucleotide pool and into viral RNA is of the simple competitive type, indicating that transport into the cells is the rate-limiting step in the incorporation of uridine into mengovirus RNA. The results also indicate that treatment with actinomycin D or mengovirus infection does not affect uridine transport.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Korbecki M., Plagemann P. G. Competitive inhibition of uridine incorporation by 6-azauridine in uninfected and mengovirus-infected Novikoff hepatoma cells. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1969 Nov;132(2):587–595. doi: 10.3181/00379727-132-34266. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malamud D., Baserga R. Uridylate kinase activity: effect of isoproterenol. Science. 1968 Oct 18;162(3851):373–374. doi: 10.1126/science.162.3851.373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakata Y., Bader J. P. The uptake of nucleosides by cells in culture. II. Inhibition by 2-mercapto-1-(beta-4-pyridethyl)benzimidazole. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Oct 22;190(2):250–256. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(69)90076-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plagemann P. G. Effect of temperature on the transport of nucleosides into Novikoff rat hepatoma cells growing in suspension culture. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1970 Sep;140(1):223–227. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(70)90026-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plagemann P. G. Effects of phenethyl alcohol on transport reactions, nucleotide pools and macromolecular synthesis in Novikoff rat hepatoma cells growing in suspension culture. J Cell Physiol. 1970 Jun;75(3):315–327. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040750308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plagemann P. G. Mengovirus replication in Novikoff rat hepatoma and mouse L cells: effects on synthesis of host-cell macromolecules and virus-specific synthesis of ribonucleic acid. J Virol. 1968 May;2(5):461–473. doi: 10.1128/jvi.2.5.461-473.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plagemann P. G. Phenethyl alcohol: reversible inhibition of synthesis of macromolecules and disaggregation of polysomes in rat hepatoma cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Jan 29;155(1):202–218. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(68)90350-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plagemann P. G. Reversible inhibition of induction of mengovirus RNA polymerase and of virus maturation in Novikoff rat hepatoma cells by phenethyl alcohol. Virology. 1968 Feb;34(2):319–330. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(68)90242-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plagemann P. G., Roth M. F. Permeation as the rate-limiting step in the phosphorylation of uridine and choline and their incorporation into macromolecules by Novikoff hepatoma cells. Competitive inhibition by phenethyl alcohol, persantin, and adenosine. Biochemistry. 1969 Dec;8(12):4782–4789. doi: 10.1021/bi00840a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plagemann P. G., Swim H. E. Replication of mengovirus. I. Effect on synthesis of macromolecules by host cell. J Bacteriol. 1966 Jun;91(6):2317–2326. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.6.2317-2326.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plagemann P. G., Swim H. E. Symposium on replication of viral nucleic acids. 3. Replication of mengovirus ribonucleic acid. Bacteriol Rev. 1966 Jun;30(2):288–308. doi: 10.1128/br.30.2.288-308.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rau J., Scholtissek C. Inhibitoren der Nucleosidphosphorylierung in vivo. Z Naturforsch B. 1970 Mar;25(3):292–299. doi: 10.1515/znb-1970-0313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy-Burman S., Roy-Burman P., Visser D. W. Showdomycin, a new nucleoside antibiotic. Cancer Res. 1968 Aug;28(8):1605–1610. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scholtissek C. Nucleotide metabolism in tissue culture cells at low temperatures. I. Phosphorylation of nucleosides and deoxynucleosides in vivo. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Sep 26;145(2):228–237. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(67)90041-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scholtissek C. Studies on the uptake of nucleic acid precursors into cells in tissue culture. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Jun 24;158(3):435–447. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(68)90297-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shea M. A., Plagemann P. G. Effects of elevated temperatures on mengovirus ribonucleic acid synthesis and virus production in Novikoff rat hepatoma cells. J Virol. 1971 Jan;7(1):144–154. doi: 10.1128/jvi.7.1.144-154.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steck T. L., Nakata Y., Bader J. P. The uptake of nucleosides by cells in culture. I. Inhibition by heterologous nucleosides. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Oct 22;190(2):237–249. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(69)90075-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward G. A., Plagemann P. G. Fluctuations of DNA-dependent RNA polymerase and synthesis of macromolecules during the growth cycle of Novikoff rat hepatoma cells in suspension culture. J Cell Physiol. 1969 Jun;73(3):213–231. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040730307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


