Abstract
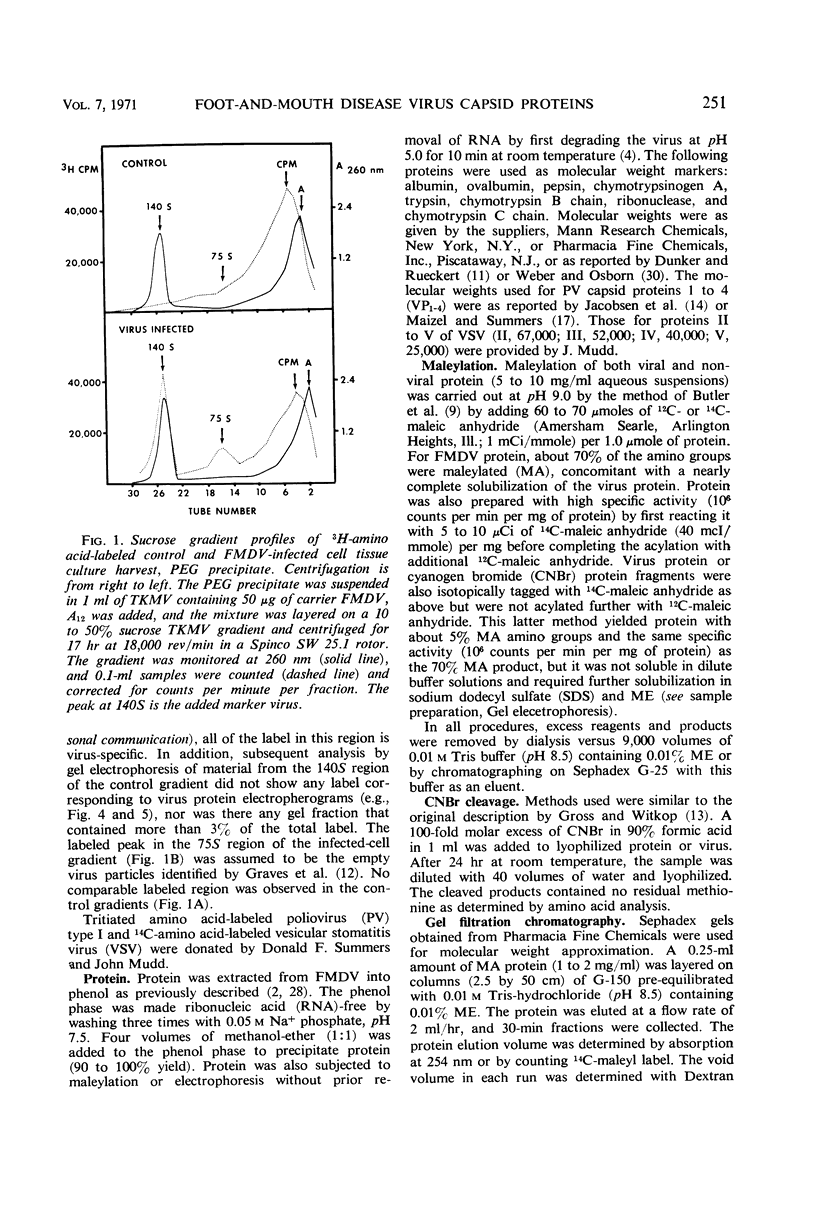
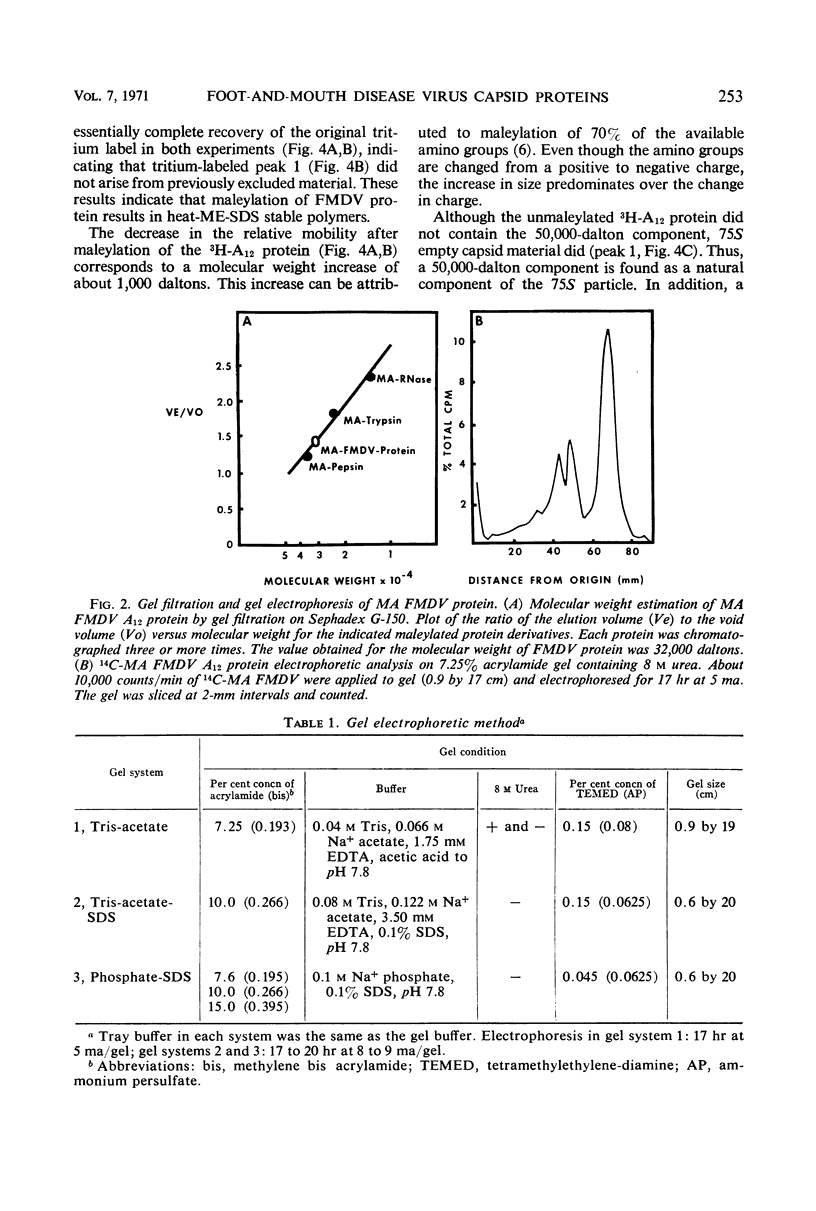
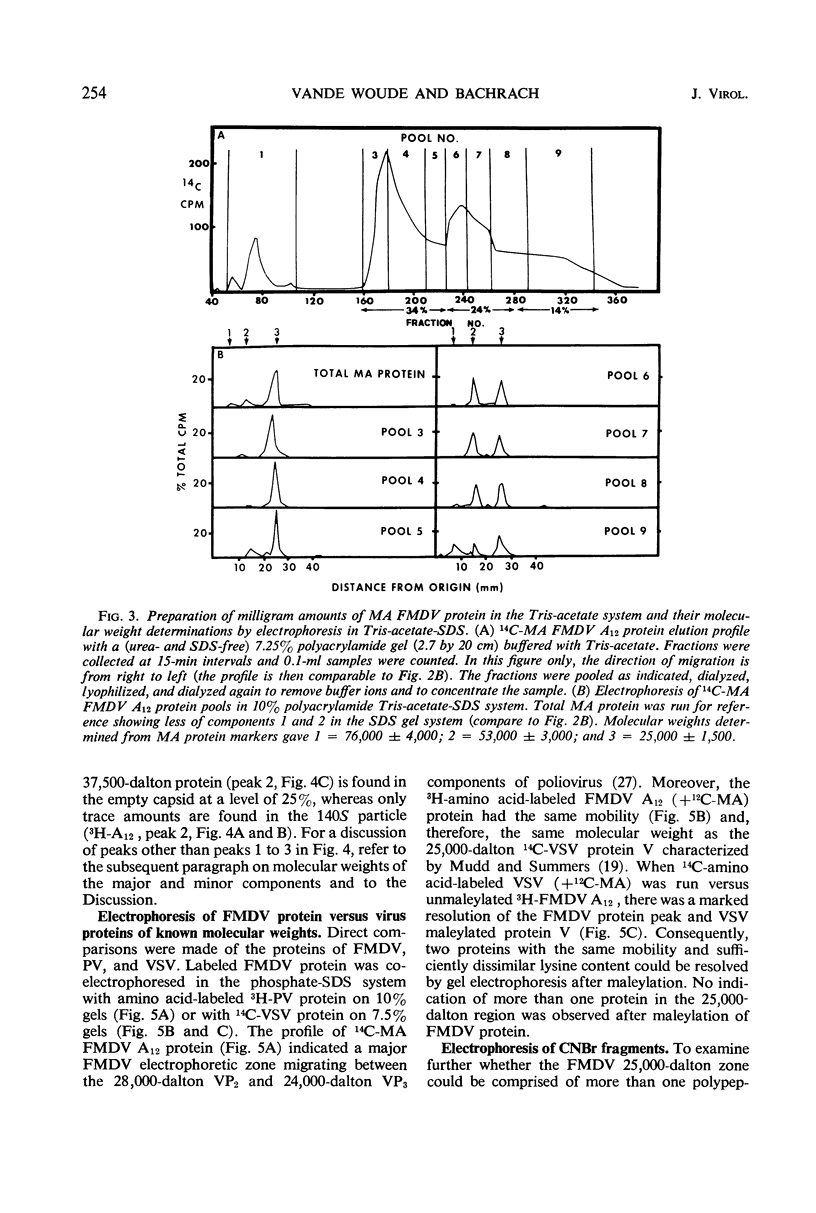
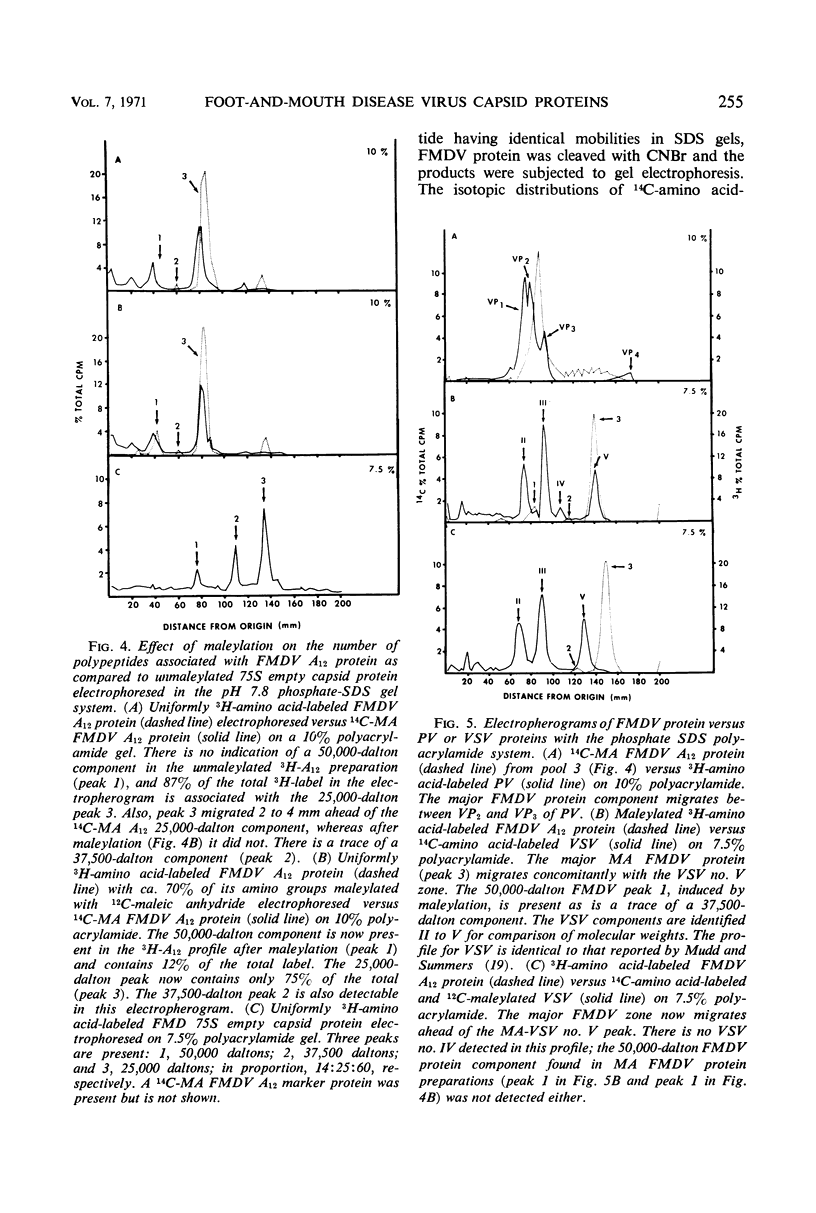
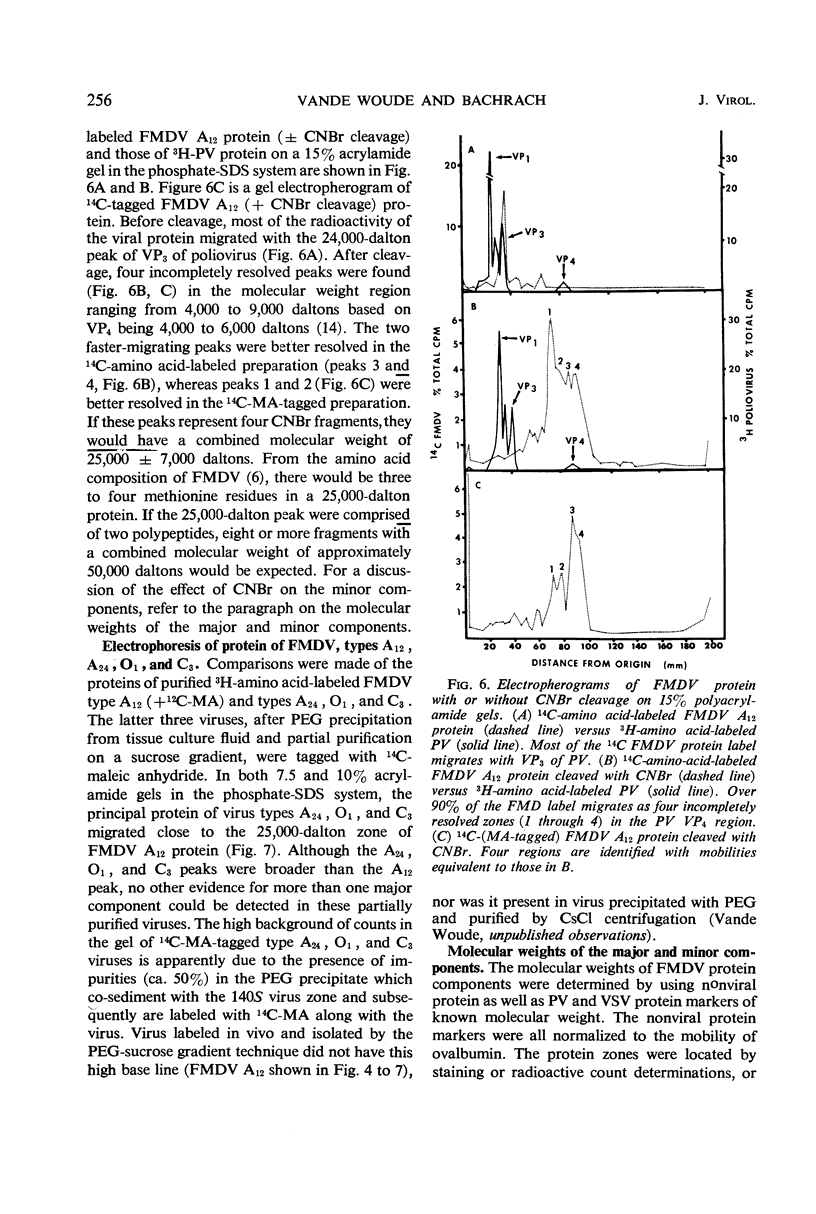
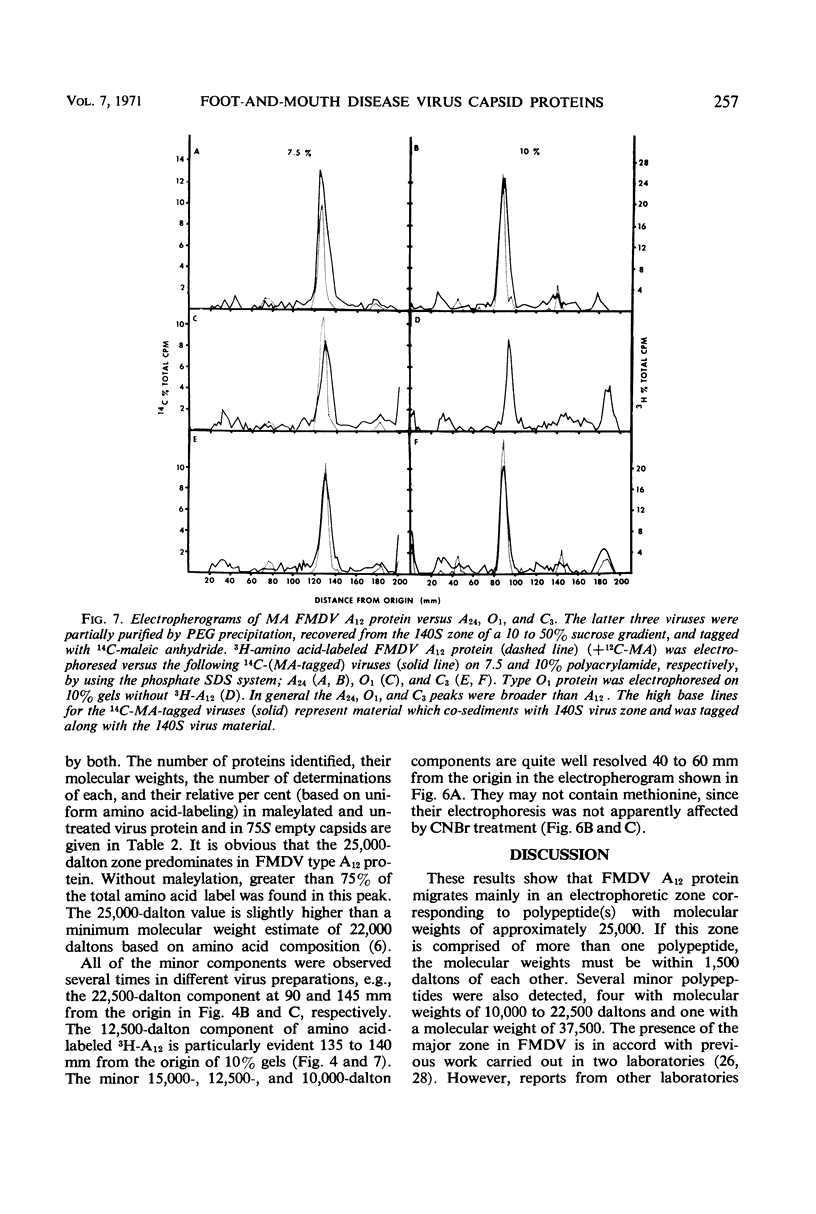
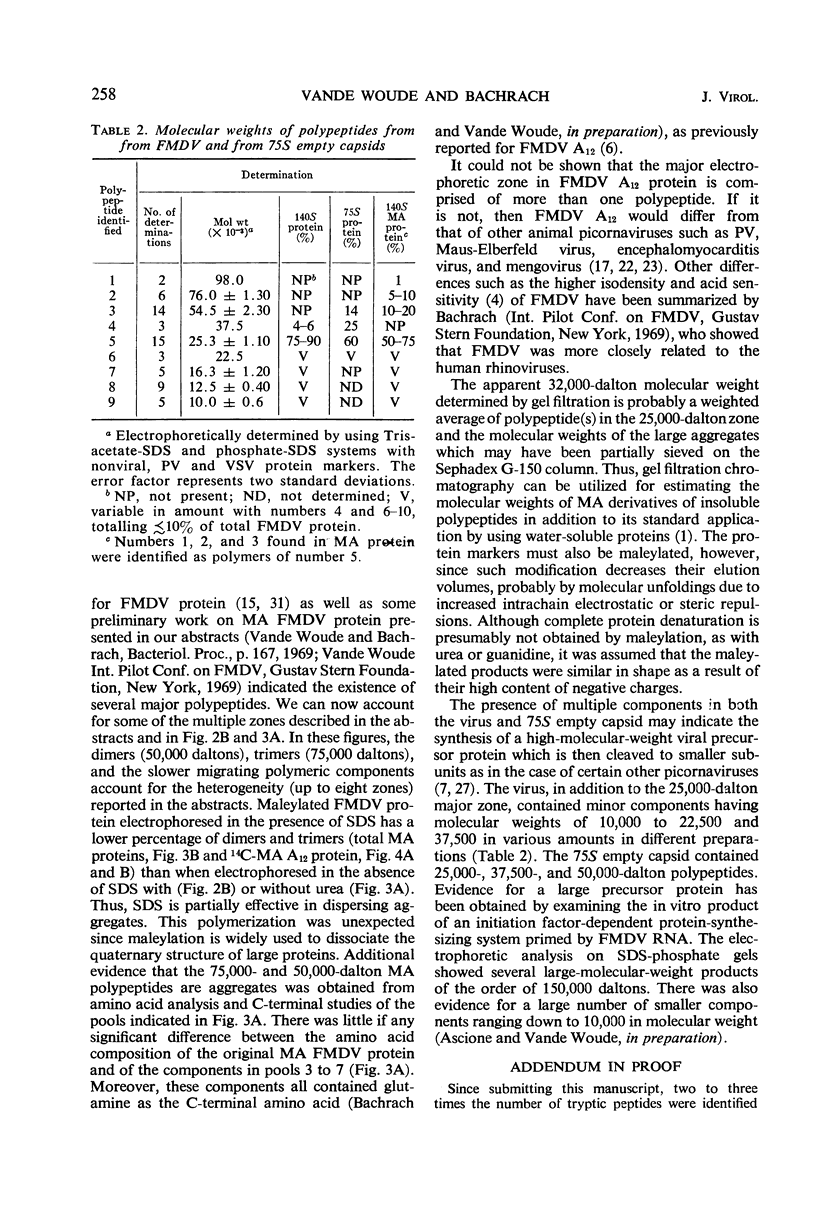
Evidence was obtained by gel electrophoresis that foot-and-mouth disease virus (FMDV) type A12 protein migrates mainly in a zone corresponding to polypeptide(s) approximately 25,000 daltons in molecular weight. Additional minor components were observed, four with molecular weights ranging from 10,000 to 22,500 daltons and one with a molecular weight of 37,500 daltons. The minor components comprised about 10% of the total protein and were present in variable amounts. The 75S empty capsids contained primarily 25,000-, 37,500- and 50,000-dalton zones. These molecular weights were estimated by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis in sodium dodecyl sulfate versus proteins of known molecular weight, including poliovirus and vesicular stomatitis virus proteins. Maleylation of the amino residues of FMDV protein solubilized it to about 5 to 10 mg/ml in aqueous, nondenaturing solvents. This permitted molecular weights to be estimated also by gel filtration. Maleylation of 70% of the available amino groups of the FMDV protein produced heat and sodium dodecyl sulfate-stable polymeric aggregates of 10 to 20% of the 25,000-dalton zone. It also resulted in an increase in the molecular weight of this zone by an amount equivalent (ca. 1,000) to that expected from the added maleyl residues.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews P. The gel-filtration behaviour of proteins related to their molecular weights over a wide range. Biochem J. 1965 Sep;96(3):595–606. doi: 10.1042/bj0960595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ascione R., Vande Woude G. F. Inhibition of host cell ribosomal ribonucleic acid methylation by foot-and-mouth disease virus. J Virol. 1969 Nov;4(5):727–737. doi: 10.1128/jvi.4.5.727-737.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BACHRACH H. L., BREESE S. S., Jr, CALLIS J. J., HESS W. R., PATTY R. E. Inactivation of foot-and-mouth disease virus by pH and temperature changes and by formaldehyde. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1957 May;95(1):147–152. doi: 10.3181/00379727-95-23148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BACHRACH H. L., TRAUTMAN R., BREESE S. S., Jr CHEMICAL PHYSICAL PROPERTIES OF VIRTUALLY PURE FOOT-AND-MOUTH DISEASE VIRUS. Am J Vet Res. 1964 Mar;25:333–342. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachrach H. L. Foot-and-mouth disease. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1968;22:201–244. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.22.100168.001221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachrach H. L., Vande Woude G. F. Amino acid composition and C-terminal sequence of foot-and-mouth disease virus protein. Virology. 1968 Feb;34(2):282–289. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(68)90238-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breese S. S., Jr, Trautman R., Bachrach H. L. Rotational Symmetry in Foot-and-Mouth Disease Virus and Models. Science. 1965 Dec 3;150(3701):1303–1305. doi: 10.1126/science.150.3701.1303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruton C. J., Hartley B. S. Sub-unit structure and specificity of methionyl-transfer-ribonucleic acid synthetase from Escherichia coli. Biochem J. 1968 Jun;108(2):281–288. doi: 10.1042/bj1080281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler P. J., Harris J. I., Hartley B. S., Leberman R. Reversible blocking of peptide amino groups by maleic anhydride. Biochem J. 1967 Jun;103(3):78P–79P. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowan K. M. Immunochemical studies of foot-and-mouth disease. V. Antigenic variants of virus demonstrated by immunodiffusion analyses with 19S but not 7S antibodies. J Exp Med. 1969 Feb 1;129(2):333–350. doi: 10.1084/jem.129.2.333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunker A. K., Rueckert R. R. Observations on molecular weight determinations on polyacrylamide gel. J Biol Chem. 1969 Sep 25;244(18):5074–5080. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GROSS E., WITKOP B. Nonenzymatic cleavage of peptide bonds: the methionine residues in bovine pancreatic ribonuclease. J Biol Chem. 1962 Jun;237:1856–1860. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graves J. H., Cowan K. M., Trautman R. Immunochemical studies of foot-and-mouth disease. II. Characterization of RNA-free viruslike particles. Virology. 1968 Feb;34(2):269–274. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(68)90236-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson M. F., Asso J., Baltimore D. Further evidence on the formation of poliovirus proteins. J Mol Biol. 1970 May 14;49(3):657–669. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90289-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maizel J. V., Jr Acrylamide-gel electrophorograms by mechanical fractionation: radioactive adenovirus proteins. Science. 1966 Feb 25;151(3713):988–990. doi: 10.1126/science.151.3713.988. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maizel J. V., Jr, Summers D. F. Evidence for differences in size and composition of the poliovirus-specific polypeptides in infected HeLa cells. Virology. 1968 Sep;36(1):48–54. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(68)90115-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinsen J. S. The effect of diethylaminoethyl dextran and agar overlay pH on plaque formation by two plaque-size variants of foot-and-mouth disease virus. Can J Comp Med. 1970 Jan;34(1):13–19. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mudd J. A., Summers D. F. Protein synthesis in vesicular stomatitis virus-infected HeLa cells. Virology. 1970 Oct;42(2):328–340. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90277-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POLATNICK J., BACHRACH H. L. PRODUCTION AND PURIFICATION OF MILLIGRAM AMOUNTS OF FOOT-AND-MOUTH DISEASE VIRUS FROM BABY HAMSTER KIDNEY CELL CULTURES. Appl Microbiol. 1964 Jul;12:368–373. doi: 10.1128/am.12.4.368-373.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RUECKERT R. R. STUDIES ON THE STRUCTURE OF VIRUSES OF THE COLUMBIA SK GROUP. II. THE PROTEIN SUBUNITS OF ME-VIRUS AND OTHER MEMBERS OF THE COLUMBIA SK GROUP. Virology. 1965 Jun;26:345–358. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(65)90282-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapoport G., Davis L., Horecker B. L. The subunit structure of the fructose diphosphate aldolase from spinach leaf. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1969 Jun;132(1):286–293. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(69)90364-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rueckert R. R., Duesberg P. H. Non-identical peptide chains in mouse encephalitis virus. J Mol Biol. 1966 Jun;17(2):490–502. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80159-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro A. L., Viñuela E., Maizel J. V., Jr Molecular weight estimation of polypeptide chains by electrophoresis in SDS-polyacrylamide gels. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1967 Sep 7;28(5):815–820. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(67)90391-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sia C. L., Traniello S., Pontremoli S., Horecker B. L. Studies on the subunit structure of rabbit liver fructose diphosphatase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1969 Jun;132(1):325–330. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(69)90369-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strohmaier K., Schwöbel W. Zur Proteinstruktur des Virus der Maul- und Klauenseuche. Z Naturforsch B. 1967 Dec;22(12):1362–1364. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers D. F., Maizel J. V., Jr Evidence for large precursor proteins in poliovirus synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Mar;59(3):966–971. doi: 10.1073/pnas.59.3.966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vande Woude G. F., Bachrach H. L. Evidence for a single structural polypeptide in foot-and-mouth disease virus. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1968;23(4):353–361. doi: 10.1007/BF01242131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner G. G., Card J. L., Cowan K. M. Immunochemical studies of foot-and-mouth disease. VII. Characterization of foot-and-mouth disease virus concentrated by polyethylene glycol precipitation. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1970;30(4):343–352. doi: 10.1007/BF01258364. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wild T. F., Burroughs J. N., Brown F. Surface structure of foot-and-mouth disease virus. J Gen Virol. 1969 Apr;4(3):313–320. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-4-3-313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


