Abstract
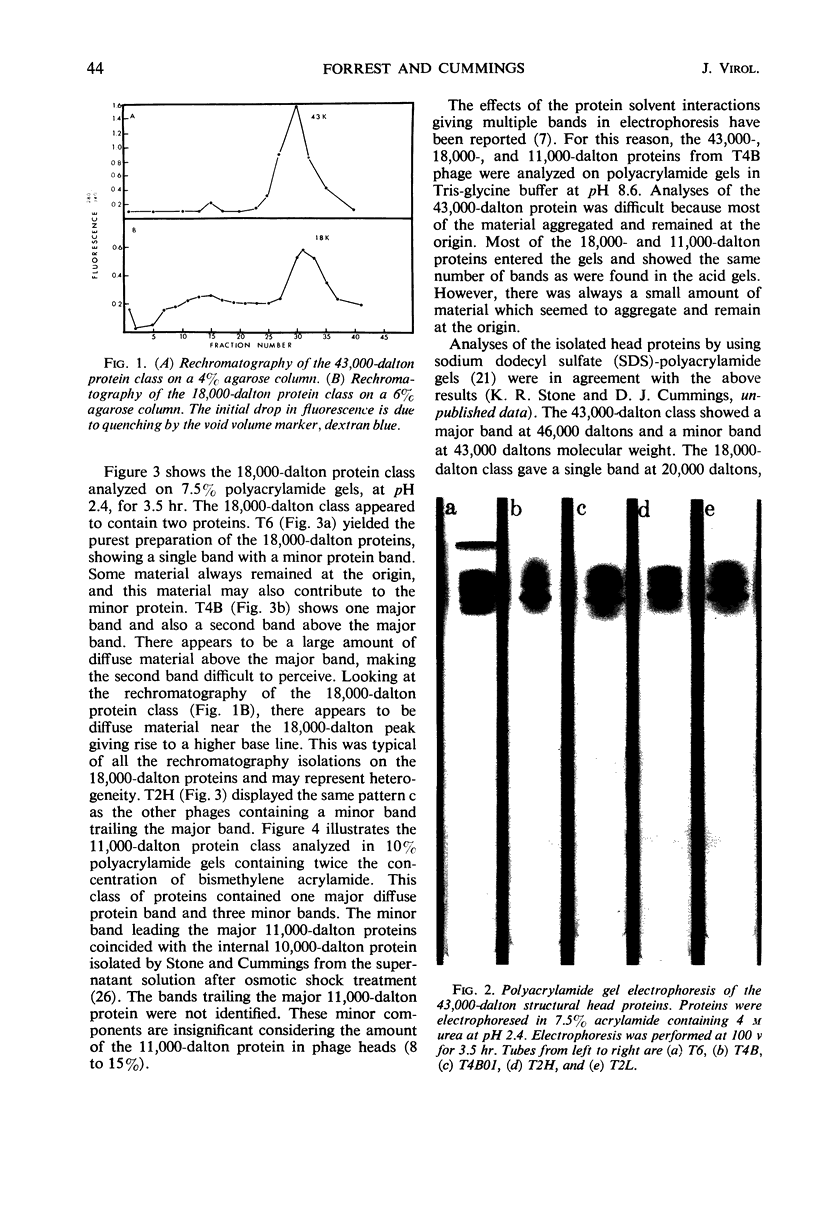
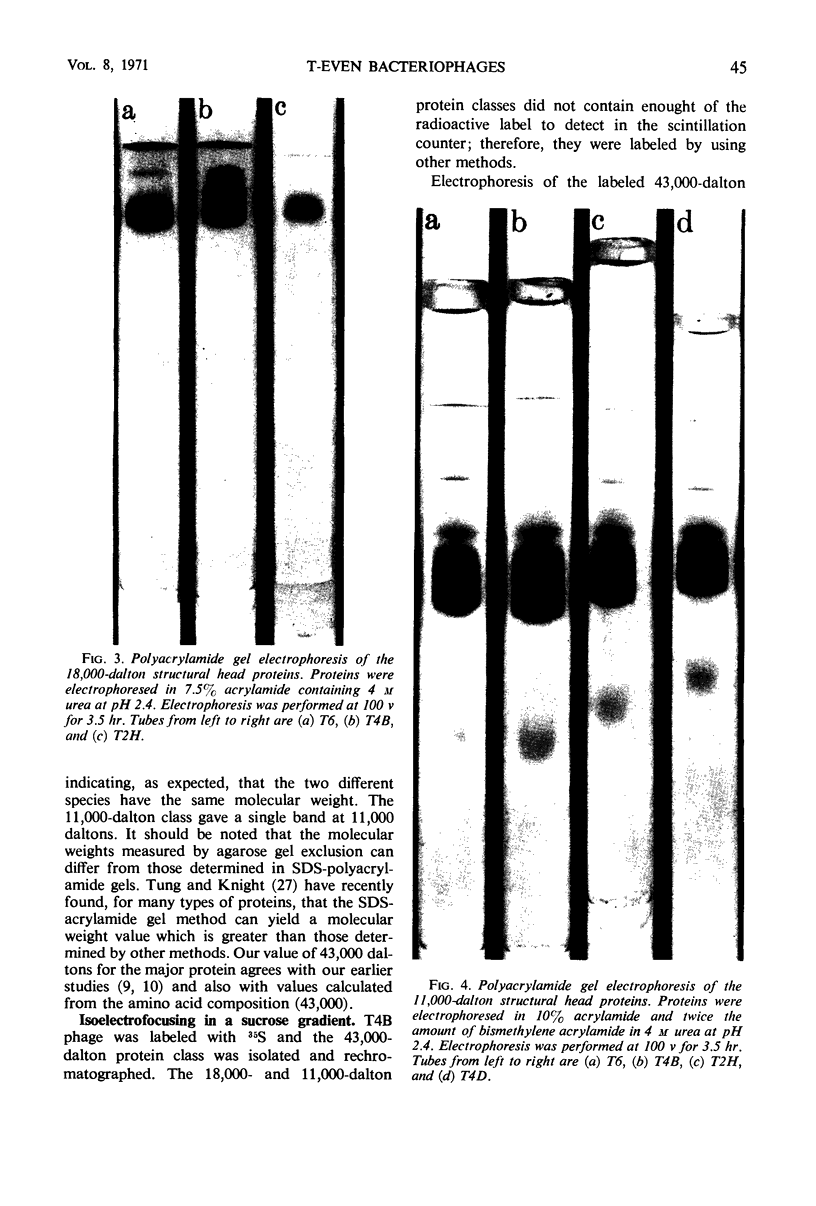
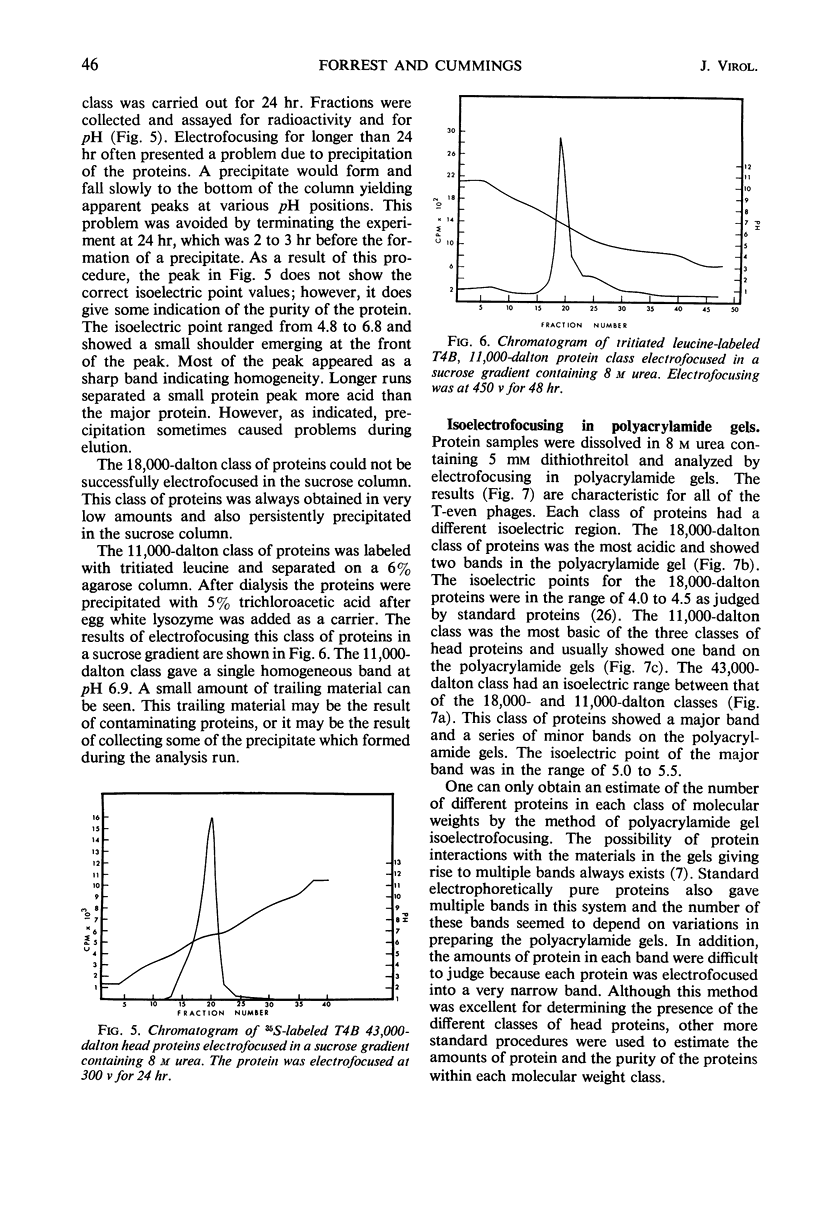
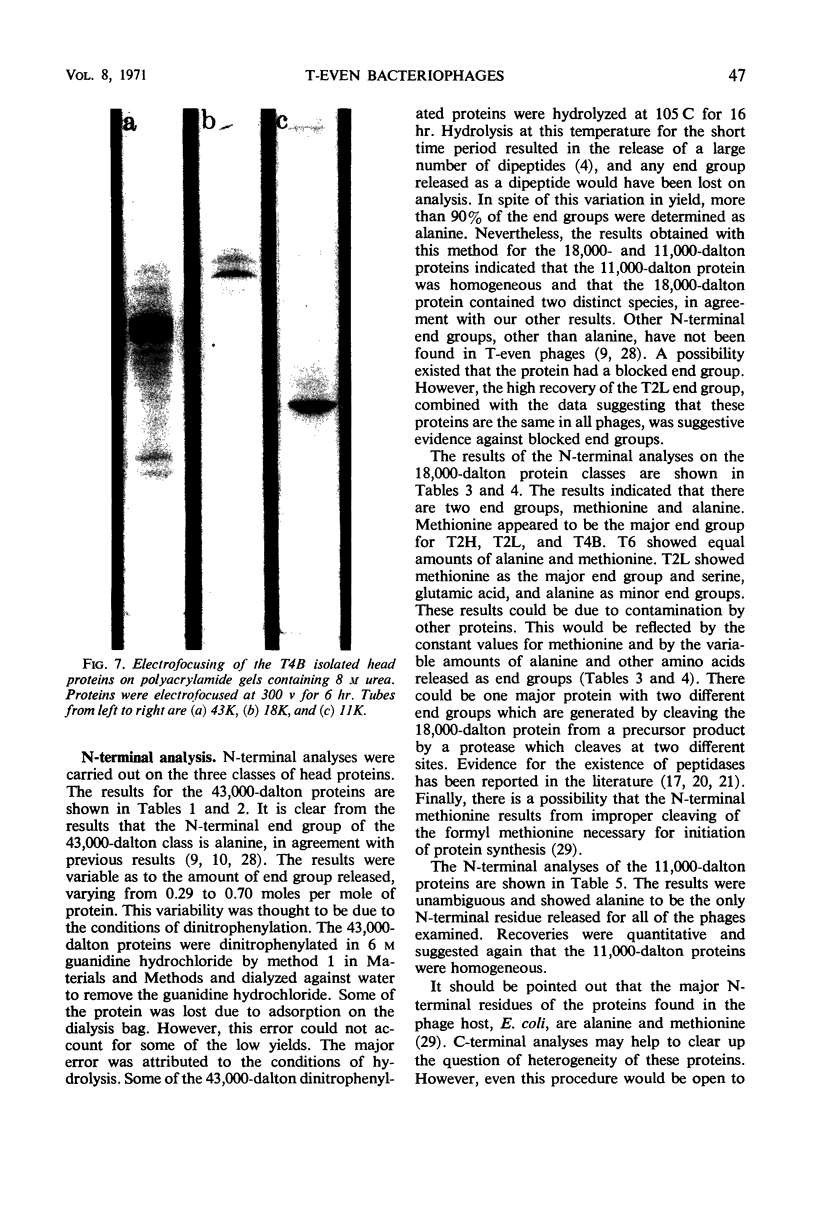
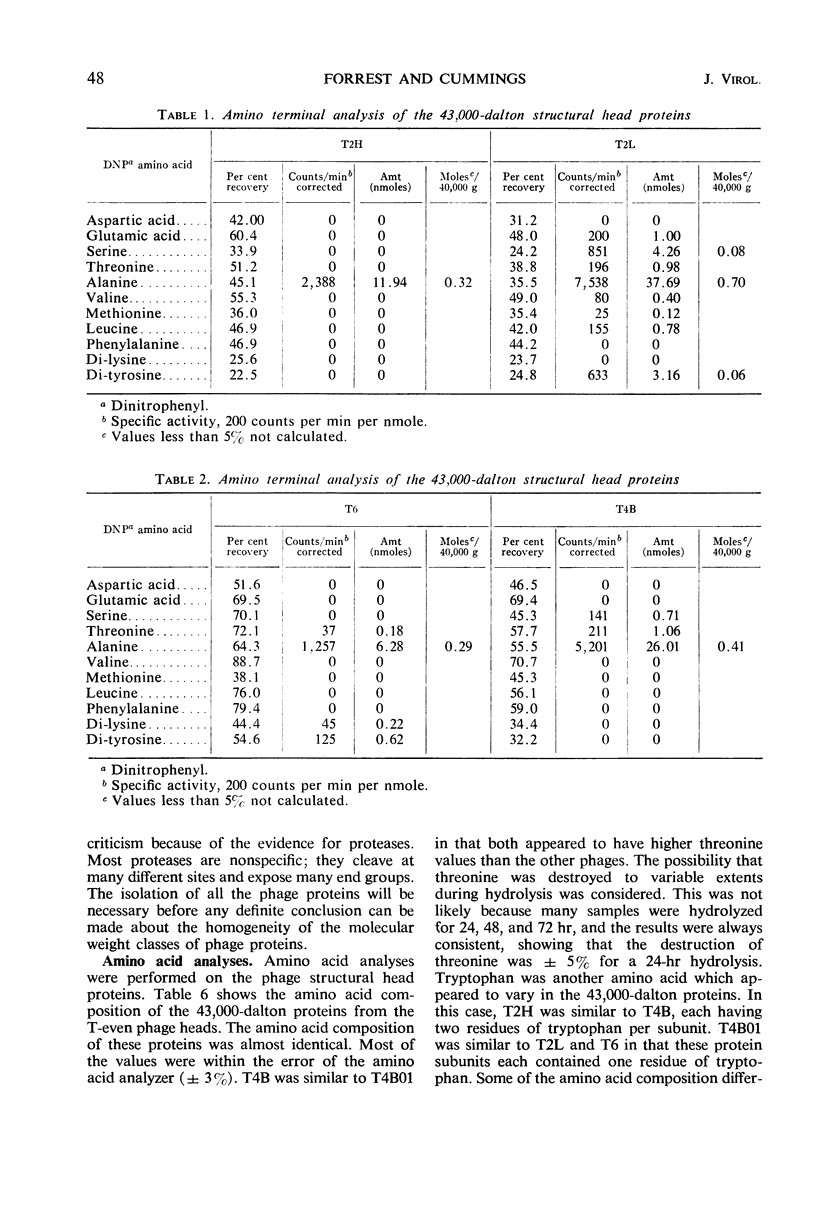
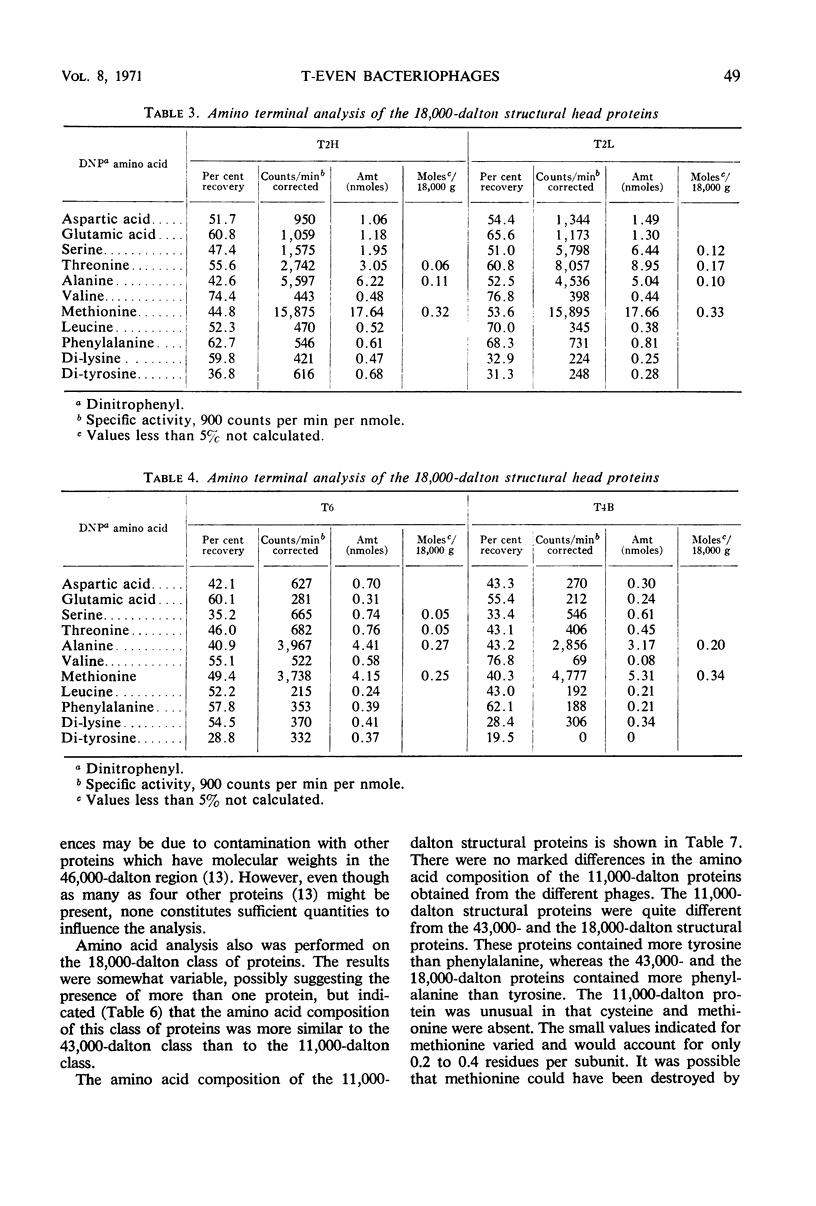
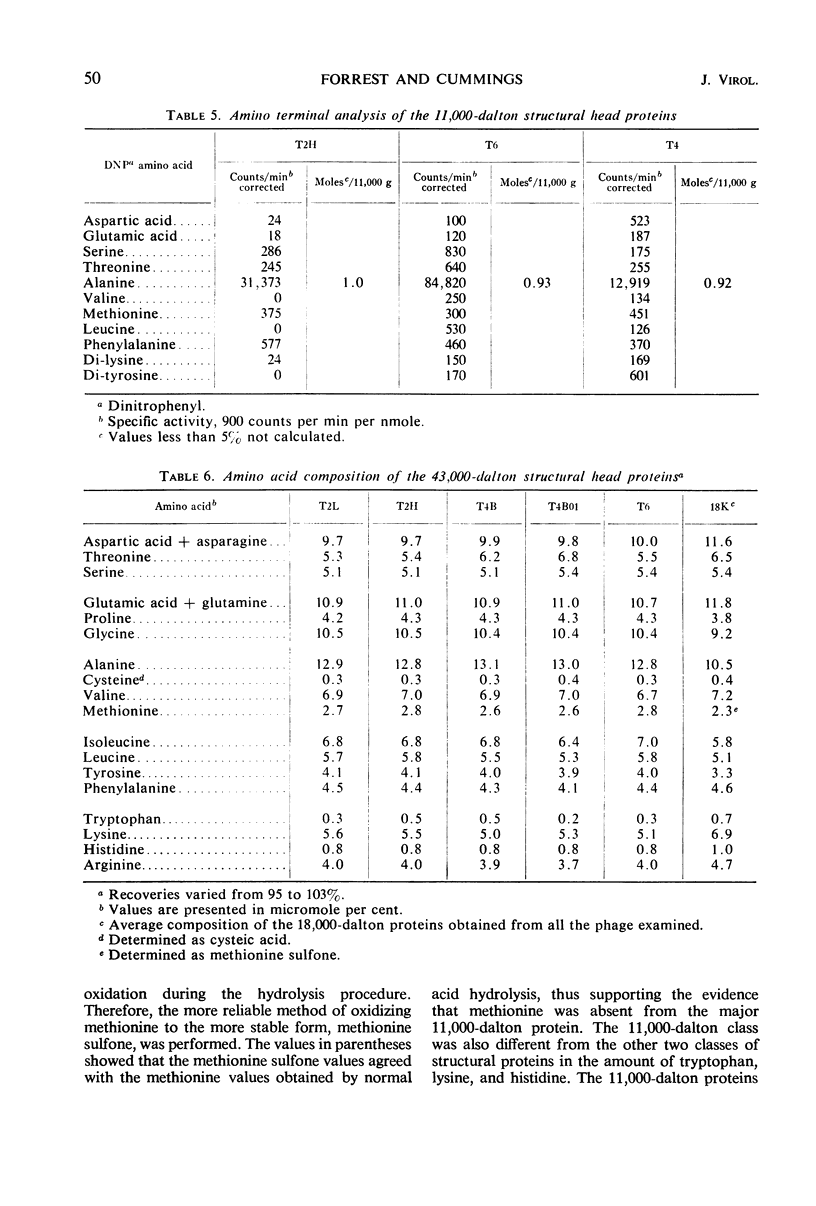
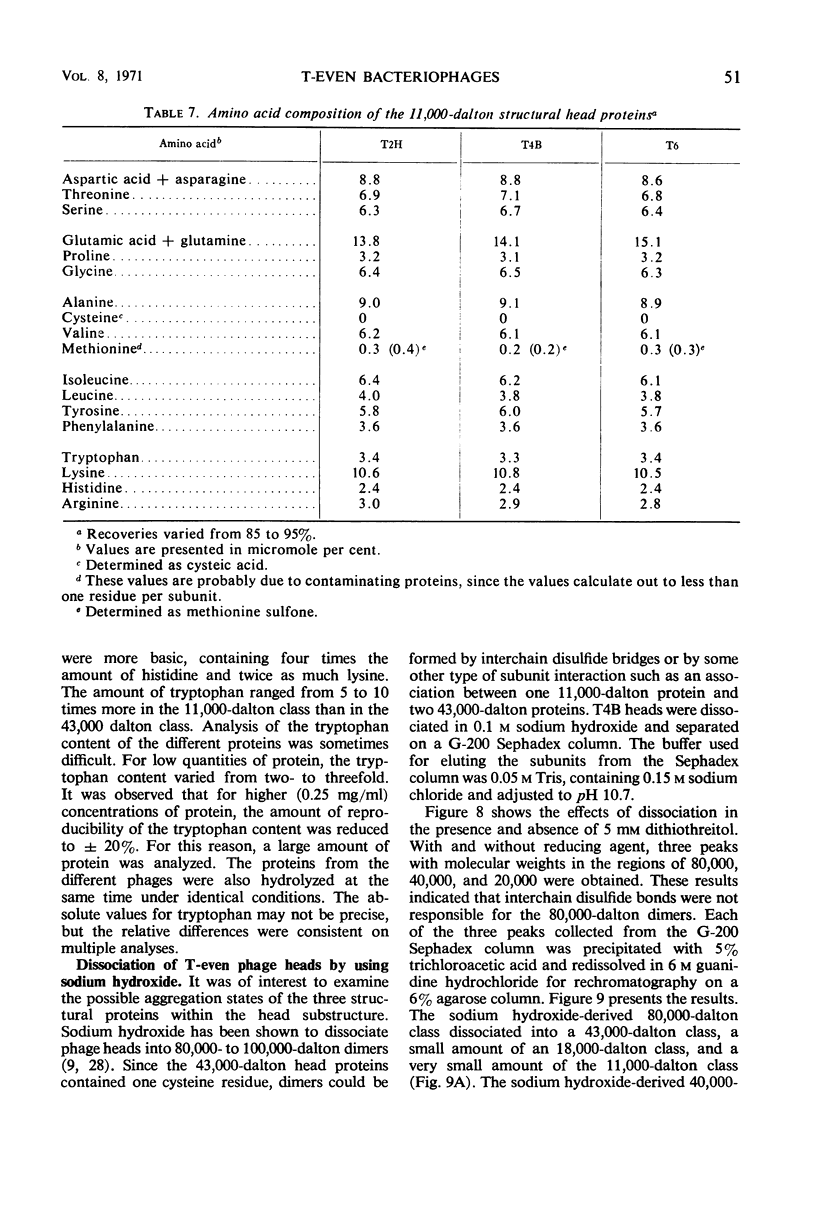
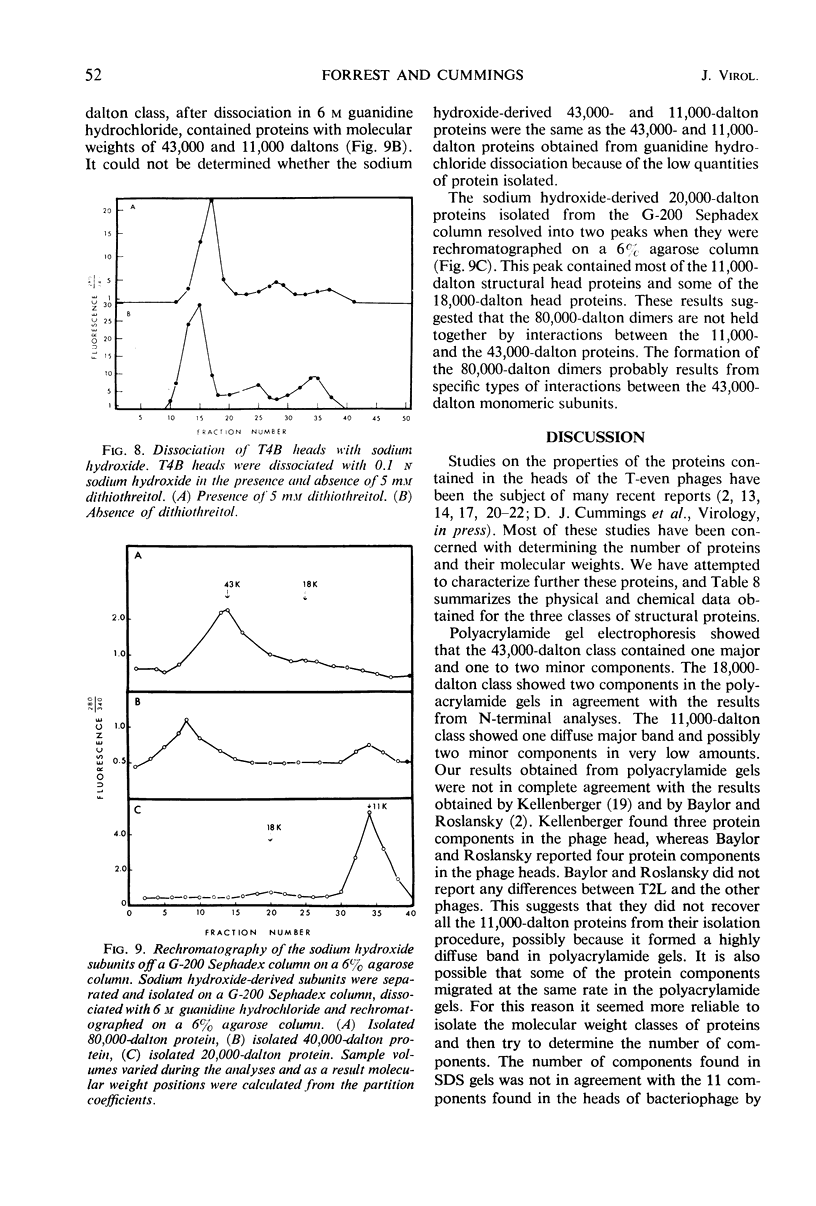
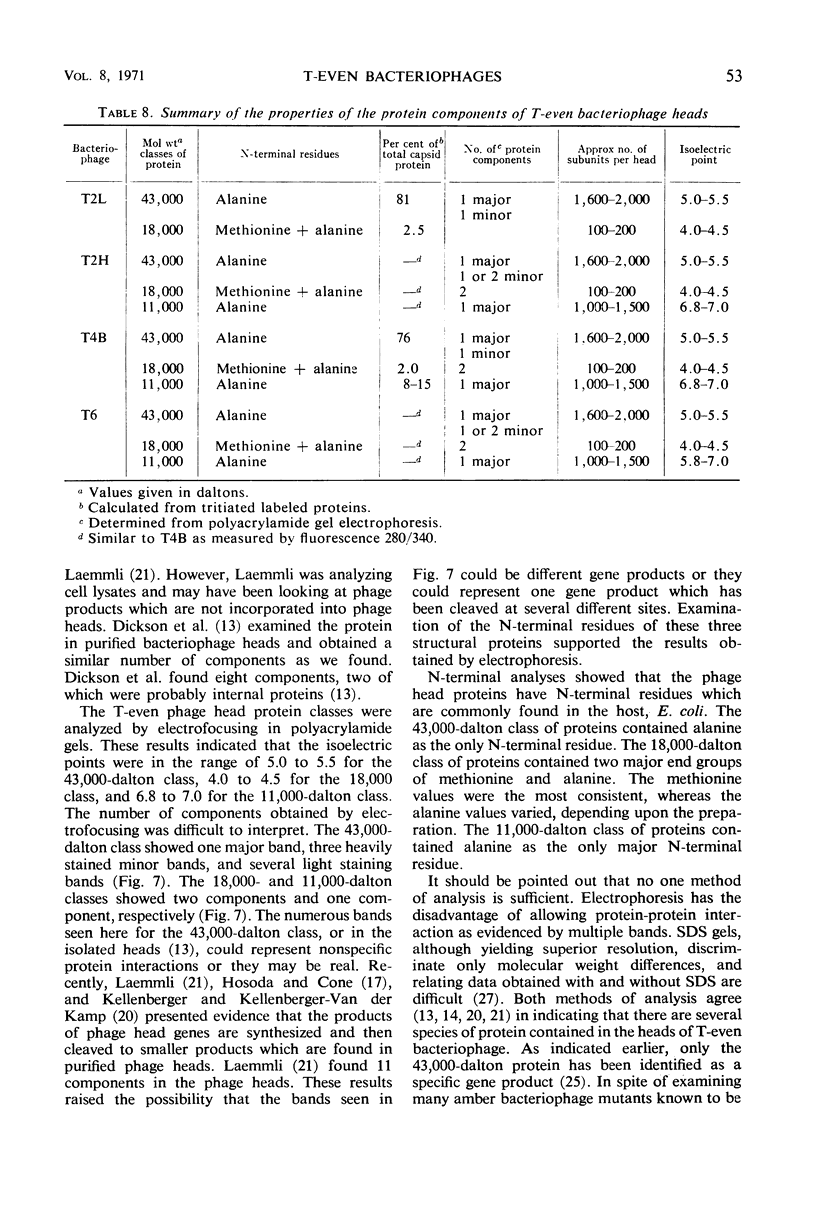
Three classes of structural head proteins, having molecular weights of 43,000, 18,000, and 11,000 daltons, were isolated from the T-even bacteriophages and were characterized. Based on electrophoretic studies, the 43,000-dalton class contained one major protein and one (or two) minor components, the 18,000-dalton class contained two protein components, and the 11,000-dalton class contained one major component. The N-terminal residues for the 43,000- and the 11,000-dalton classes were alanine, and the N-terminal residues for the 18,000-dalton class were methionine and alanine. Of the three classes of proteins, the 18,000-dalton proteins were the most acidic, whereas the 11,000-dalton proteins were the most basic. The amino acid composition of the 11,000-dalton class revealed that methionine and cysteine were absent and lysine, histidine, and tryptophan content was higher in the 11,000-dalton class than in the other two classes of proteins. Estimates of the relative number of the three classes of structural proteins were made and indicated that there were between 1,600 and 2,000 subunits of the 43,000-dalton proteins, 100 to 200 of the 18,000-dalton proteins, and 1,000 to 1,500 of the 11,000-dalton proteins. Evidence was presented that the 43,000-dalton proteins and the 11,000-dalton proteins readily formed aggregates with themselves but not with each other. The significance of these interactions to the structure of the T-even phage head was discussed.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baylor M. B., Roslansky P. F. Gel electrophoresis of the head proteins of T-even phage. Virology. 1970 Feb;40(2):251–259. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90400-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop D. H., Claybrook J. R., Spiegelman S. Electrophoretic separation of viral nucleic acids on polyacrylamide gels. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 28;26(3):373–387. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90310-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. L., Brown D. M., Zabin I. Thiogalactoside transacetylase. Physical and chemical studies of subunit structure. J Biol Chem. 1967 Sep 25;242(18):4254–4258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CANN J. R., GOAD W. B. PRECAUTIONS REQUIRED IN INTERPRETATION OF MOVING-BOUNDARY AND ZONES ELECTROPHORETIC PATTERNS. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1964 Oct;108:171–172. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(64)90369-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COLE A., LANGLEY R. Study of the radiosensitive structure of T2 bacteriophage using low energy electron beams. Biophys J. 1963 May;3:189–197. doi: 10.1016/s0006-3495(63)86815-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CUMMINGS D. J. SEDIMENTATION AND BIOLOGICAL PROPERTIES OF T-PHAGES OF ESCHERICHIA COLI. Virology. 1964 Jul;23:408–418. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(64)90264-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CUMMINGS D. J. Subunit basis of head configurational changes in T2 bacteriophage. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Mar 26;68:472–480. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)90169-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dale G., Latner A. L. Isoelectric focusing in polyacrylamide gels. Lancet. 1968 Apr 20;1(7547):847–848. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(68)90303-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison P. F. Proteins in denaturing solvents: gel exclusion studies. Science. 1968 Aug 30;161(3844):906–907. doi: 10.1126/science.161.3844.906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickson R. C., Barnes S. L., Eiserling F. A. Structural proteins of bacteriophage T4. J Mol Biol. 1970 Nov 14;53(3):461–474. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90077-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRAENKEL-CONRAT H., HARRIS J. I., LEVY A. L. Recent developments in techniques for terminal and sequence studies in peptides and proteins. Methods Biochem Anal. 1955;2:359–425. doi: 10.1002/9780470110188.ch12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forrest G. L., Cummings D. J. Head proteins from T-even bacteriophage. I. Molecular weight characterization. J Virol. 1970 Mar;5(3):398–405. doi: 10.1128/jvi.5.3.398-405.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIRS C. H. The oxidation of ribonuclease with performic acid. J Biol Chem. 1956 Apr;219(2):611–621. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hosoda J., Cone R. Analysis of T4 phage proteins. I. Conversion of precursor proteins into lower molecular weight peptides during normal capsid formation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Aug;66(4):1275–1281. doi: 10.1073/pnas.66.4.1275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hosoda J., Levinthal C. Protein synthesis by Escherichia coli infected with bacteriophage T4D. Virology. 1968 Apr;34(4):709–727. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(68)90092-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kellenberger E., Der Kamp C. K.-V. On a modification of the gene product P23 according to its use as subunit of either normal capsids of phage T4 or of polyheads. FEBS Lett. 1970 Jun 1;8(3):140–144. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(70)80247-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kellenberger E. Studies on the morphopoiesis of the head of phage T-even. V. The components of the T4 capsid and of other, capsid-related structures. Virology. 1968 Mar;34(3):549–561. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(68)90074-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larcom L. L., Bendet I. J., Mumma S. Subunits of T4 head structures. Virology. 1970 May;41(1):1–11. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90048-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell W. C., Laver W. G., Sanderson P. J. Internal components of adenovirus. Nature. 1968 Sep 14;219(5159):1127–1130. doi: 10.1038/2191127a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SARABHAI A. S., STRETTON A. O., BRENNER S., BOLLE A. CO-LINEARITY OF THE GENE WITH THE POLYPEPTIDE CHAIN. Nature. 1964 Jan 4;201:13–17. doi: 10.1038/201013a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone K. R., Cummings D. J. Isolation and characterization of two basic internal proteins from the T-even bacteriophages. J Virol. 1970 Oct;6(4):445–454. doi: 10.1128/jvi.6.4.445-454.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tung J. S., Knight C. A. Effect of charge on the determination of molecular weight of proteins by gel electrophoresis in SDS. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Mar 19;42(6):1117–1121. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90020-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VAN VUNAKIS H., BAKER W. H., BROWN R. K. Structural studies on the proteins of bacteriophages. I. Alkaline dissociation of the protein coat ghost of bacteriophage T2+. Virology. 1958 Apr;5(2):327–336. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(58)90026-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WALLER J. P. THE NH2-TERMINAL RESIDUES OF THE PROTEINS FROM CELL-FREE EXTRACTS OF E. COLI. J Mol Biol. 1963 Nov;7:483–496. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(63)80096-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]