Correction
After the publication of this work [1] it was brought to the authors’ attention that Figure three (Figure 1 here) contained a duplication error, where the HP1gamma staining for wild-type thymus and brain are identical. The correct figure is given below.
Figure 1.
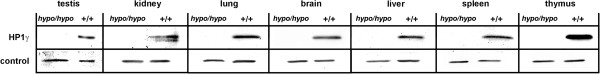
HP1γ protein expression was dramatically reduced in Cbx3hypo/hypo tissues. Protein expression was reduced to almost undetectable levels in testis, kidney, lung, brain, liver spleen and thymus tissues from the Cbx3hypo/hypomice.
Contributor Information
Jeremy P Brown, Email: jbrown@fz-borstel.de.
Jörn Bullwinkel, Email: jbullwinkel@fz-borstel.de.
Bettina Baron-Lühr, Email: bbaronl@fz-borstel.de.
Mustafa Billur, Email: mbillur@fz-borstel.de.
Philipp Schneider, Email: pschneider@fz-borstel.de.
Heinz Winking, Email: winking@molbio.mu-luebeck.de.
Prim B Singh, Email: prim.singh@charite.de.
Acknowledgement
We regret any inconvenience that this inaccuracy may have caused.
References
- Brown JP, Jorn B, Bettina B-L, Mustafa B, Phillipp S, Heinz W, Singh PB. HP1gamma function is required for male germ cell survival and spermatogenesis. Epigenetics & Chromatin. 2010;3:9. doi: 10.1186/1756-8935-3-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


