Abstract
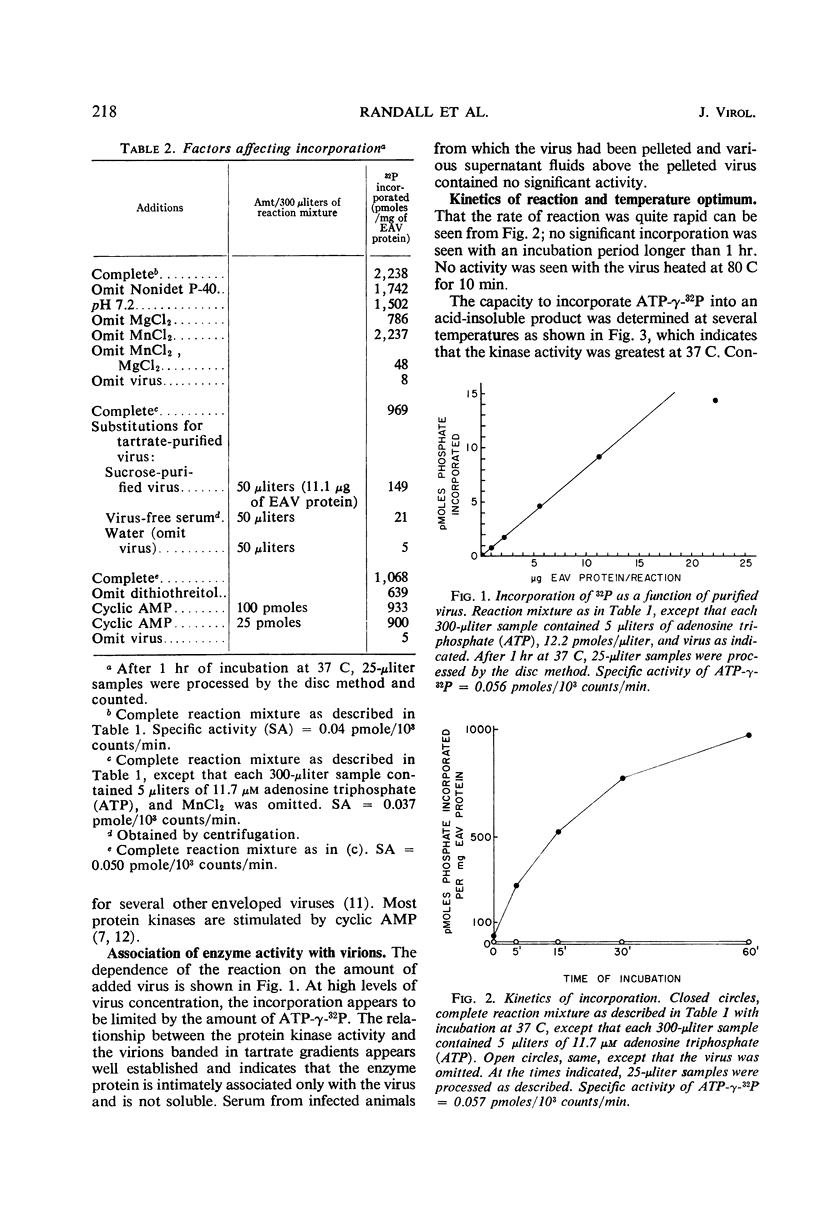
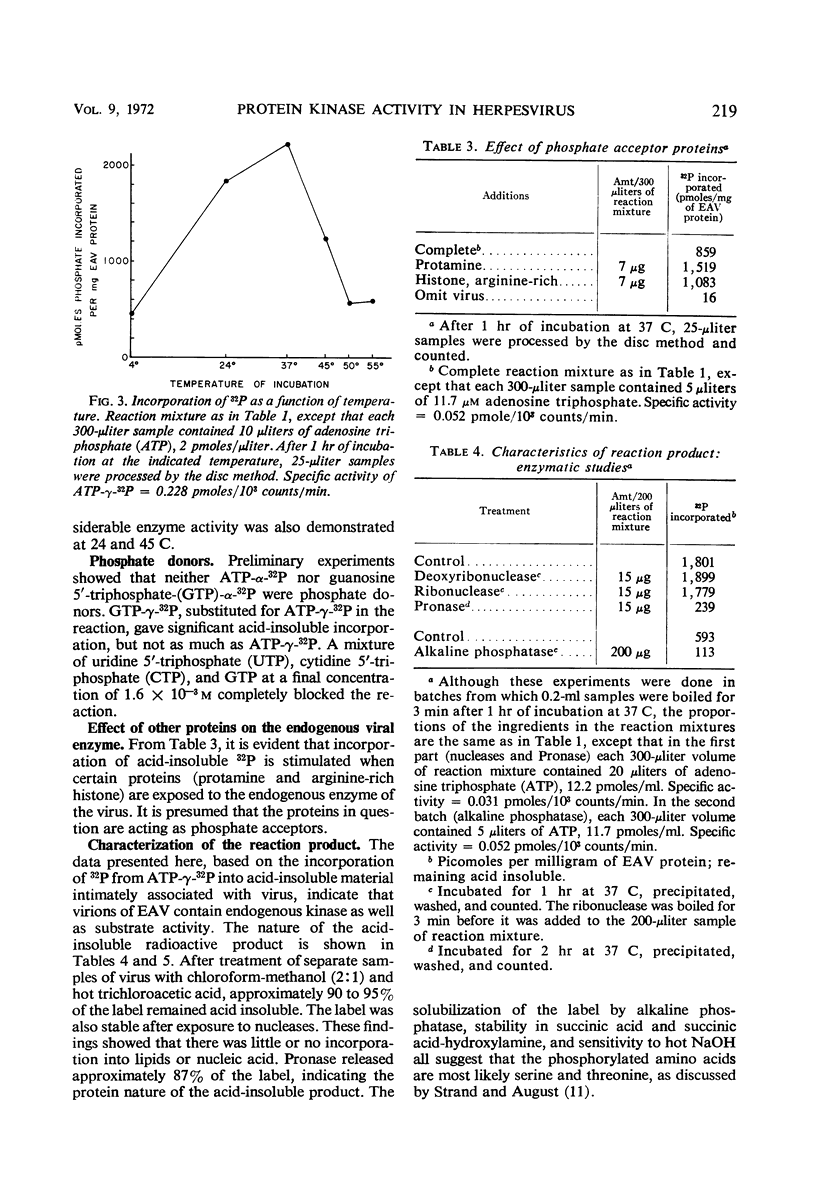
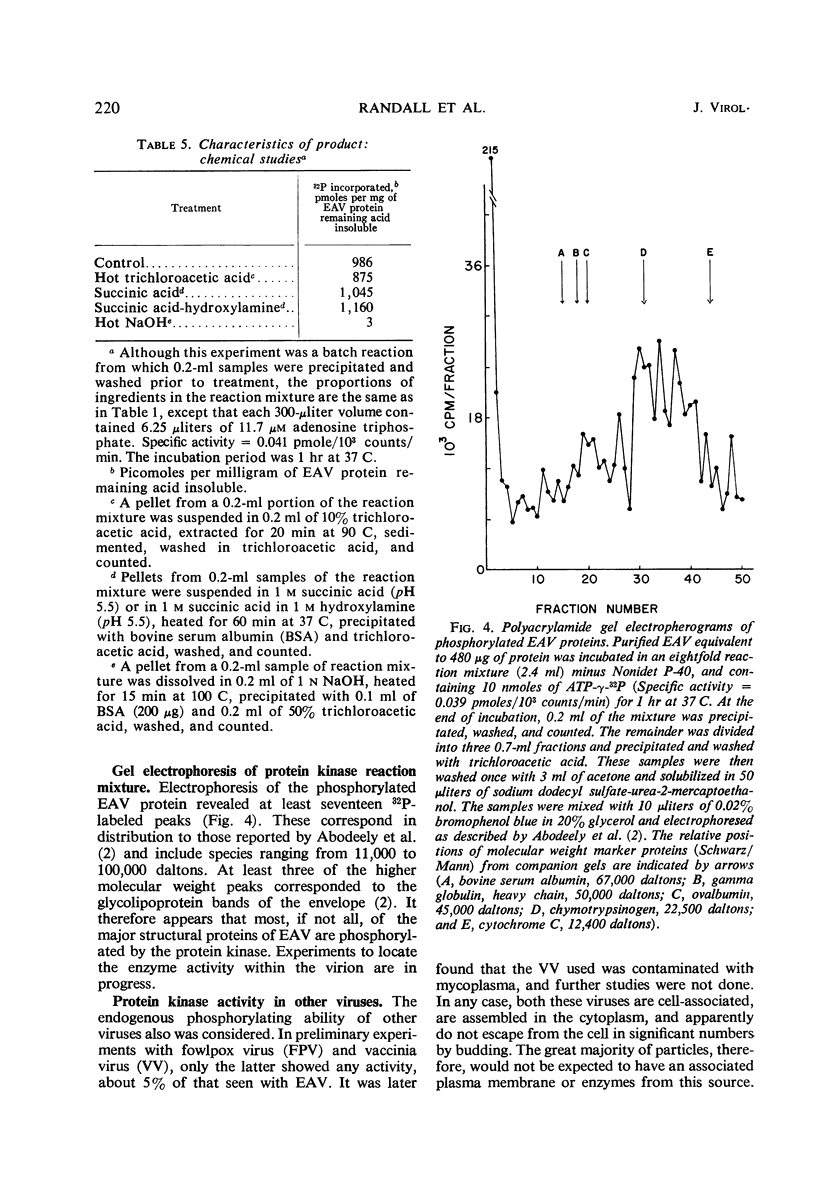
A protein kinase which is intimately associated with equine herpesvirus (equine abortion virus) was found by using adenosine triphosphate-γ-32P as a phosphate donor and virus protein as an acceptor. Consistent demonstration of the activity requires prior removal of phosphohydrolase. The kinase activity requires Mg2+, is not stimulated by cyclic adenosine monophosphate, but is enhanced by added protamine or arginine-rich histone. The labeled product is resistant to ribonuclease, deoxyribonuclease, and chloroform-methanol but is sensitive to Pronase. Other tests suggest that serine and threonine residues are the acceptor sites. In the in vitro reaction, the incorporation represents an average of approximately 4,500 phosphate residues per virion, and all 17 virus protein bands resolved by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis appear to be labeled.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abodeely R. A., Lawson L. A., Randall C. C. Morphology and entry of enveloped and deenveloped equine abortion (herpes) virus. J Virol. 1970 Apr;5(4):513–523. doi: 10.1128/jvi.5.4.513-523.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DARLINGTON R. W., RANDALL C. C. The nucleic acid content of equine abortion virus. Virology. 1963 Mar;19:322–327. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(63)90071-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darlington R. W., Moss L. H., 3rd The envelope of Herpesvirus. Prog Med Virol. 1969;11:16–45. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamiyama M., Dastugue B. Rat liver non-histone proteins: correlation between protein kinase activity and activation of RNA synthesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Jul 2;44(1):29–36. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(71)80154-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pastan I., Perlman R. L. Cyclic AMP in metabolism. Nat New Biol. 1971 Jan 6;229(1):5–7. doi: 10.1038/newbio229005a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RANDALL C. C., BRACKEN E. C. Studies on hepatitis in hamsters infected with equine abortion virus. I. Sequential development of inclusions and the growth cycle. Am J Pathol. 1957 Jul-Aug;33(4):709–727. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strand M., August J. T. Protein kinase and phosphate acceptor proteins in Rauscher murine leukaemia virus. Nat New Biol. 1971 Sep 29;233(39):137–140. doi: 10.1038/newbio233137a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeda M., Yamamura H., Oga Y. Phosphoprotein kinases associated with rat liver chromatin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Jan 8;42(1):103–110. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90368-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vilagines R., McAuslan B. R. Proteins of polyhedal cytoplasmic deoxyvirus. II. Nucleotide phosphohydrolase activity associated with frog virus 3. J Virol. 1971 May;7(5):619–624. doi: 10.1128/jvi.7.5.619-624.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



