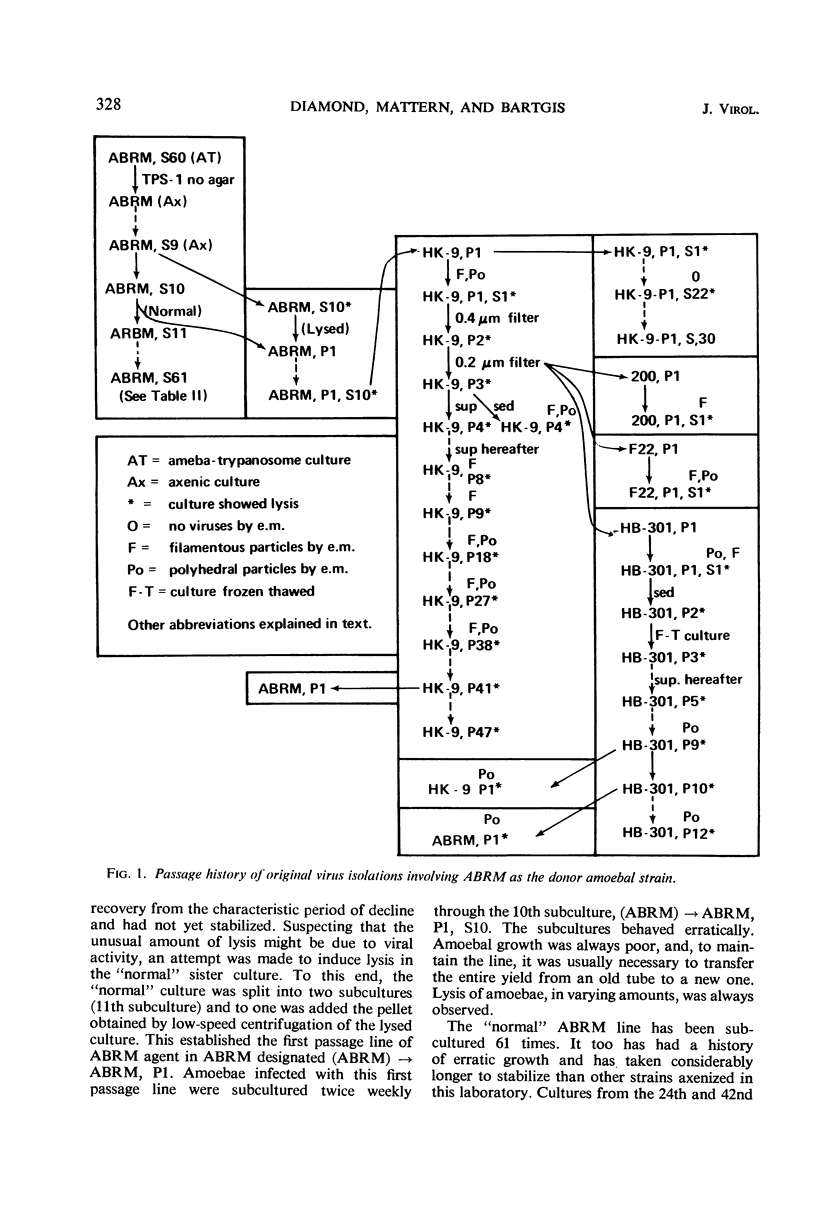
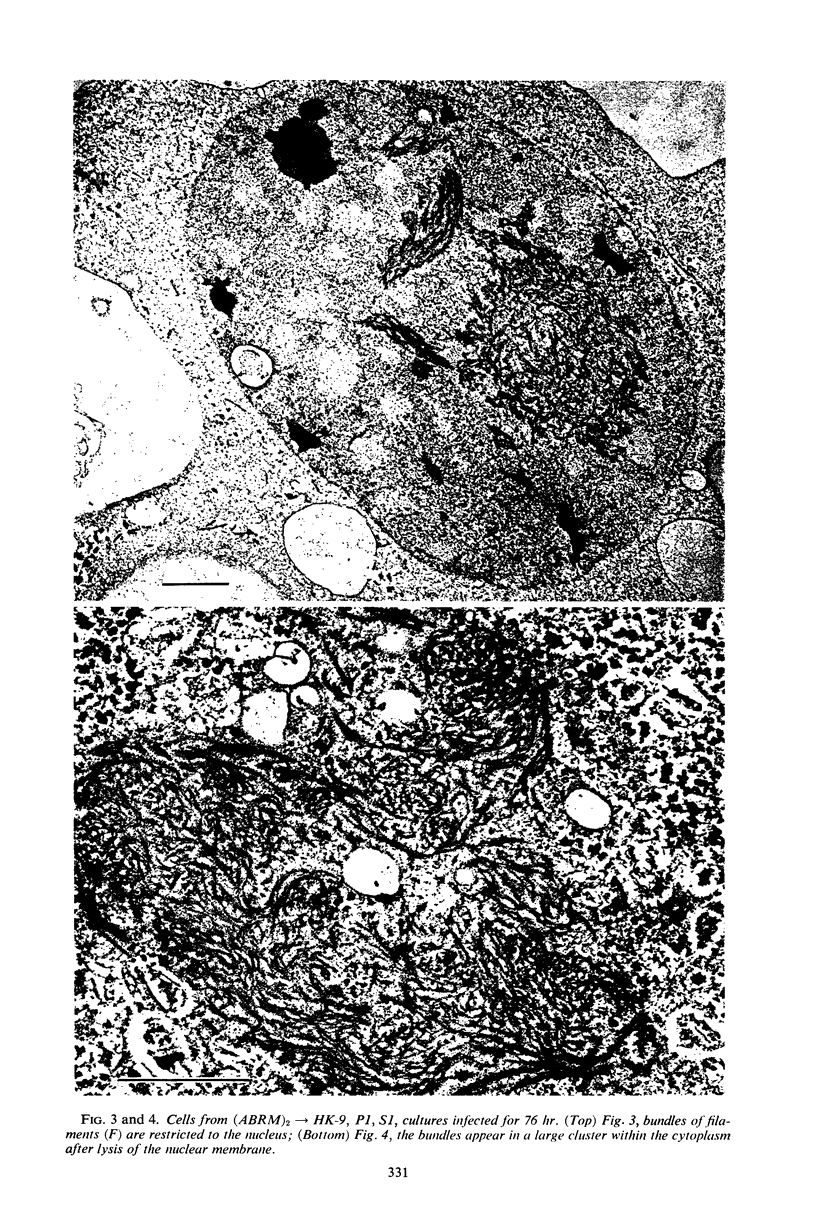
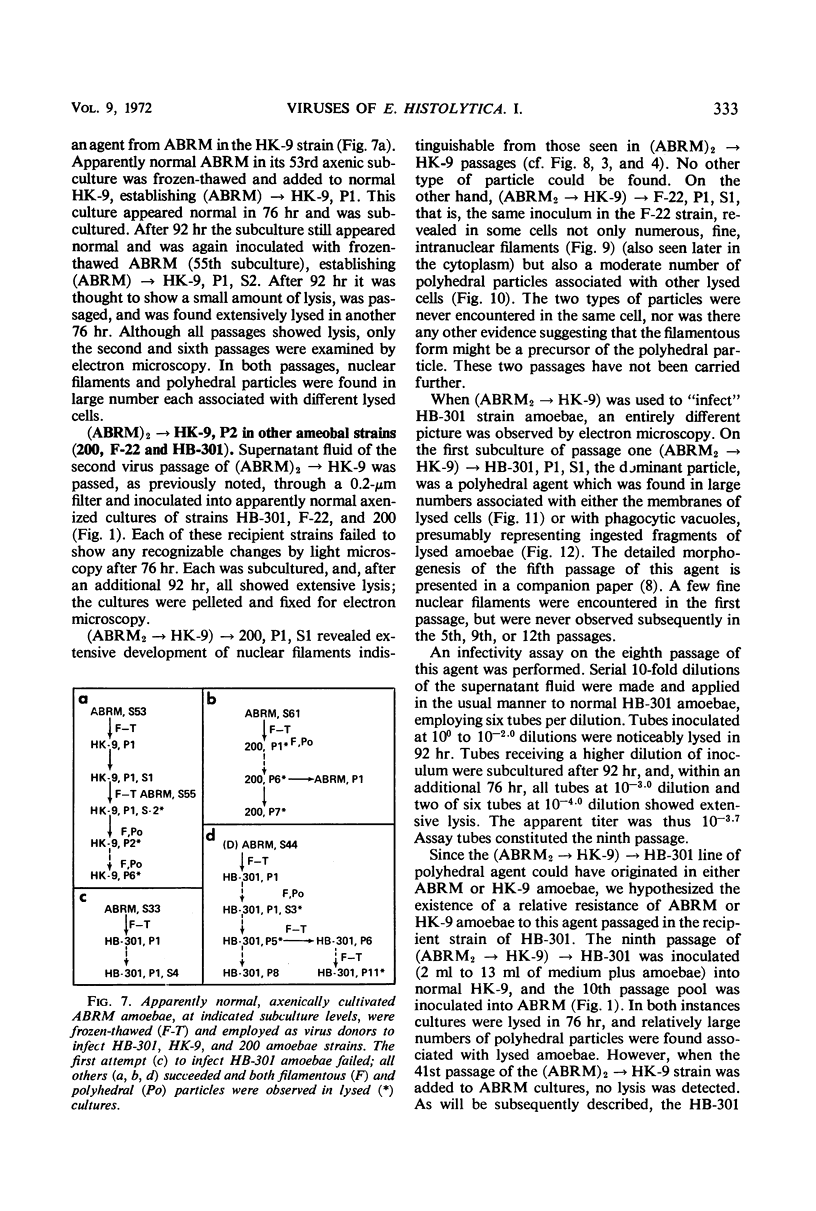
Abstract
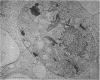
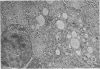
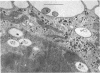
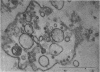
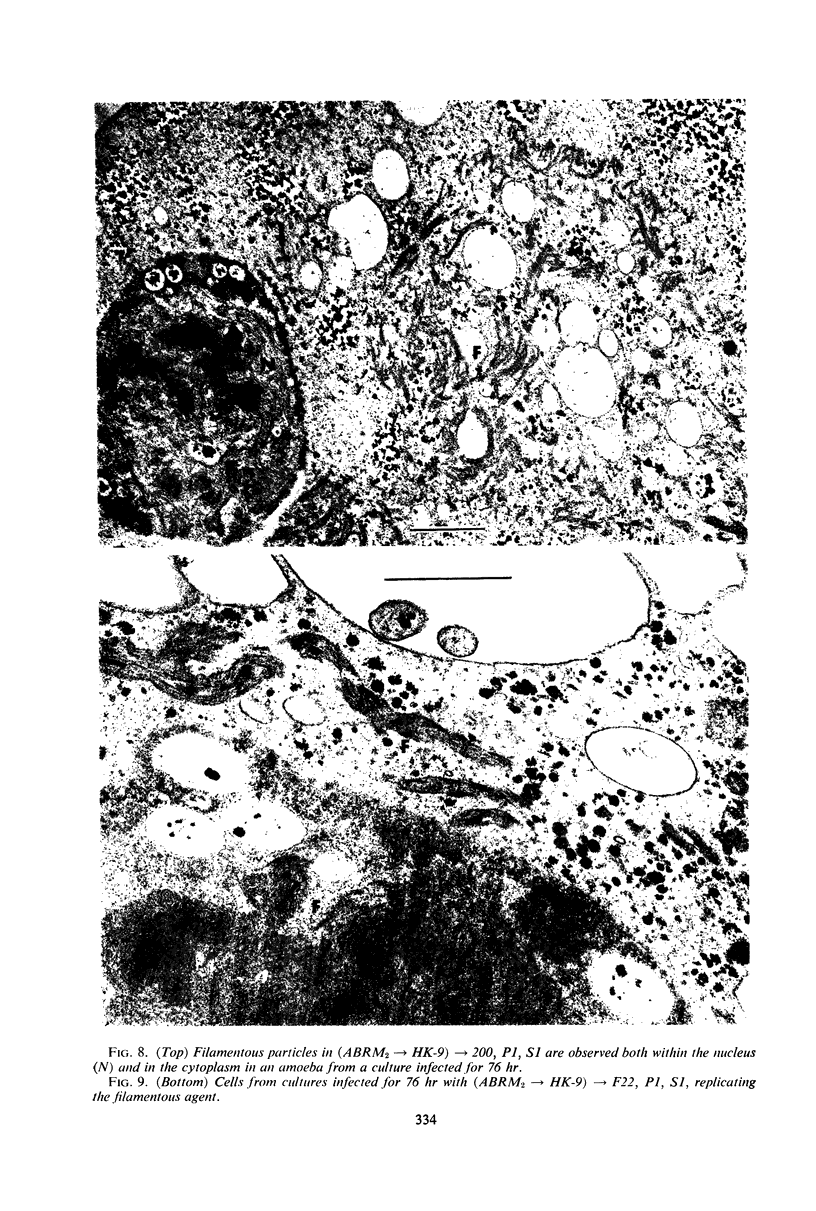
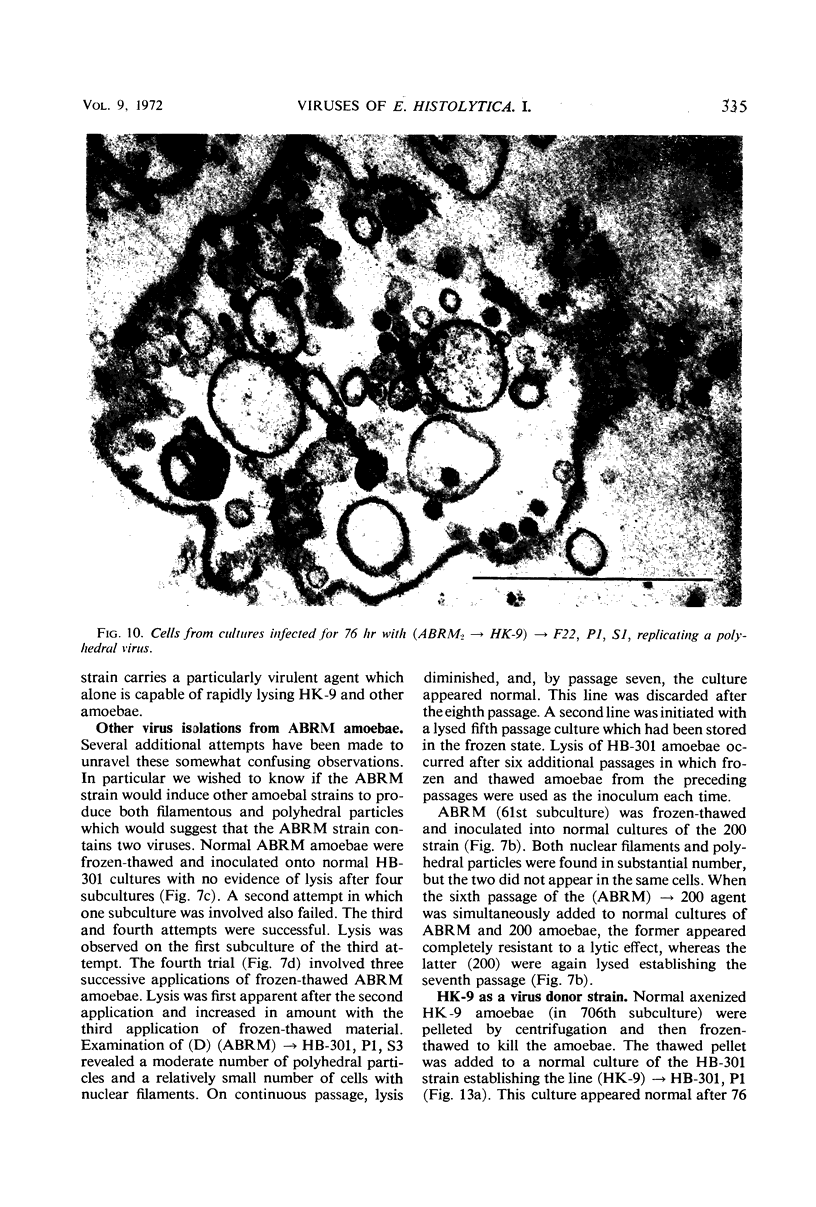
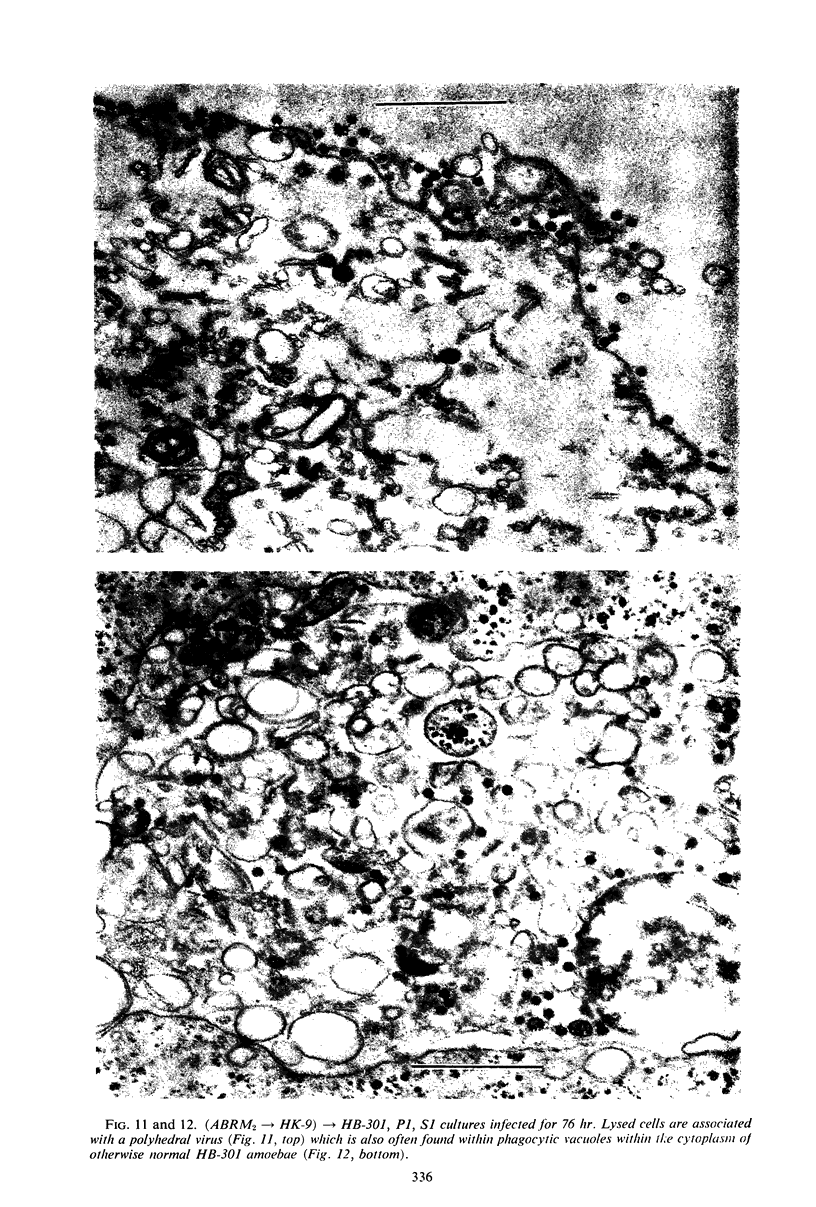
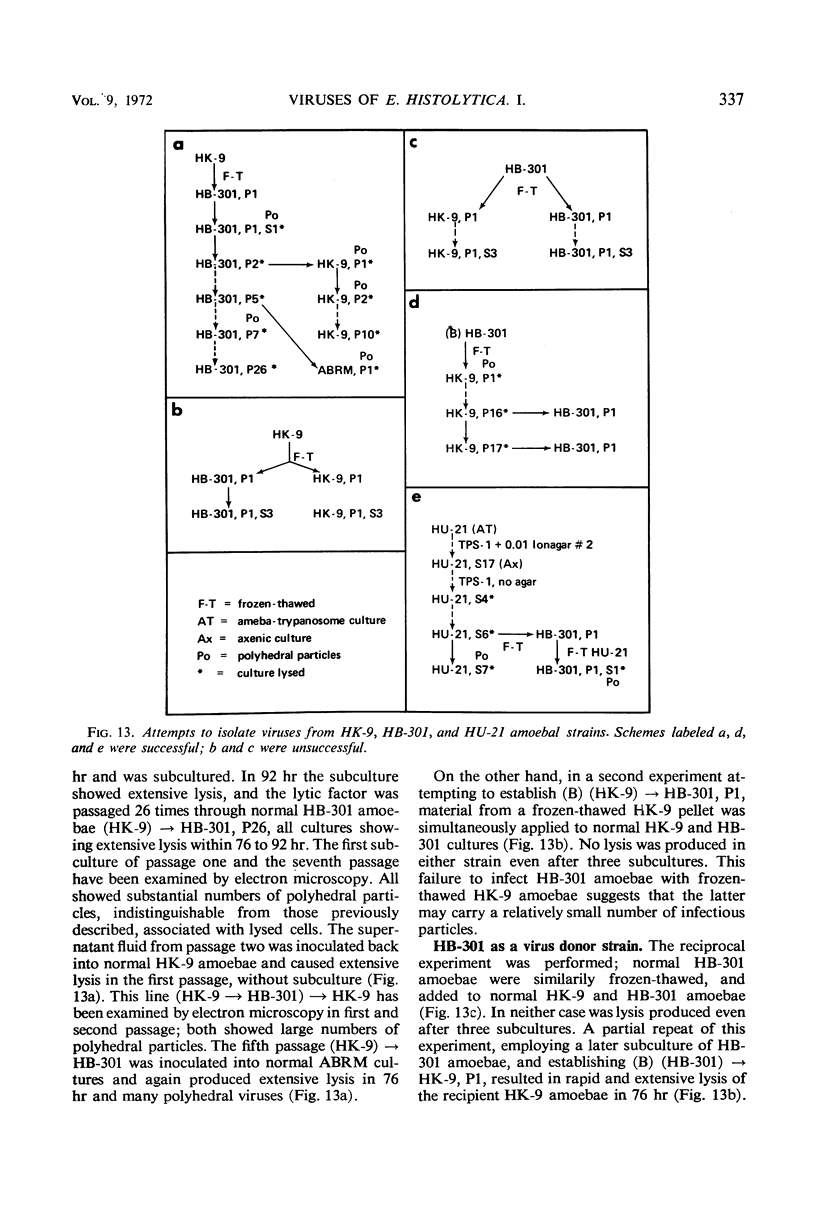
This and a companion report deal with the identification and morphogenesis of viruses in axenized cultures of Entamoeba histolytica. There are probably two different types of virus each producing a different pathological picture in different amoebal strains, or, less likely, there is one type of agent having widely different morphological and morphogenetical pictures in different strains of E. histolytica. Both types of agent produce a lytic response in axenized amoebae and have been serially passaged to an extent assuring their replicating nature. One appears to replicate in the nucleus as multiple clusters of fine filaments which ultimately lyse the nucleus, causing cell death. The second type of agent appears to be a typical polyhedral virus, seen only in the cytoplasm and also resulting in lysis of the cell. A particle morphologically indistinguishable from this second agent is also found in late passages of the agent producing the nuclear pathology.
Full text
PDF
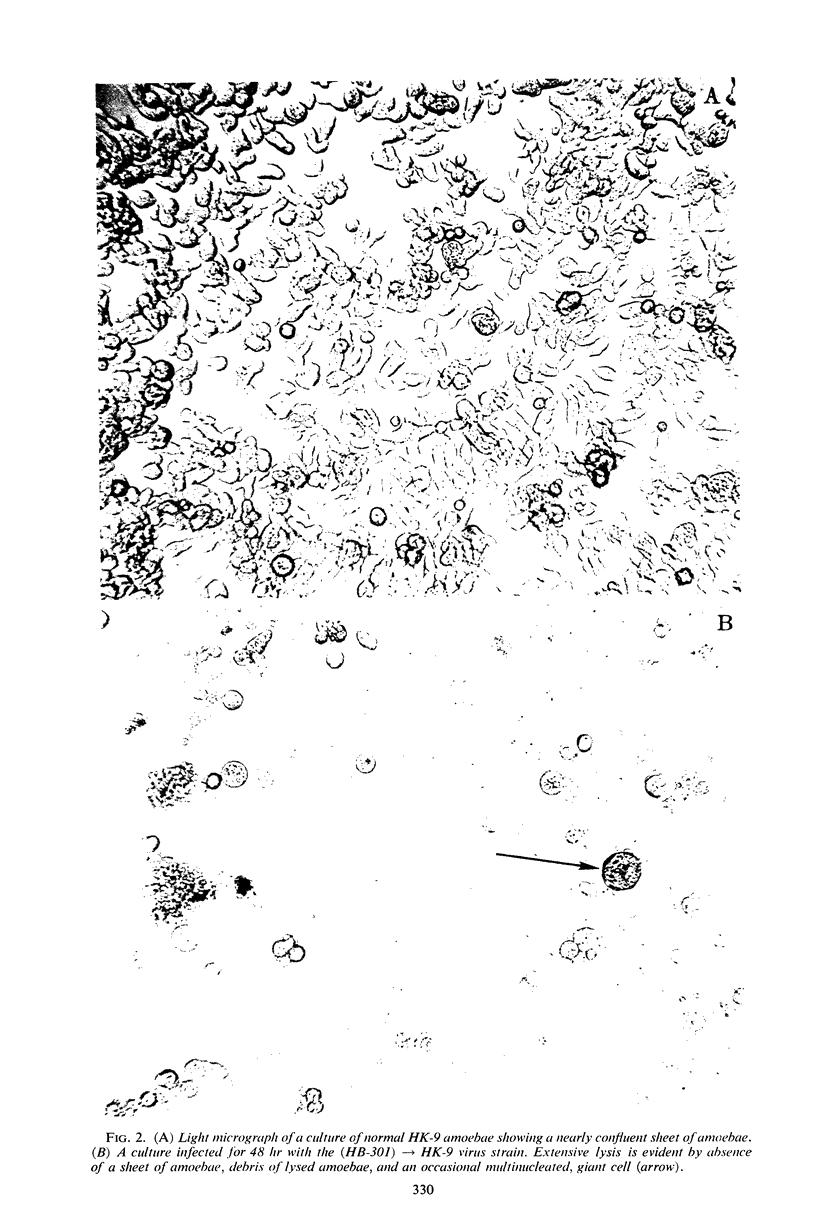
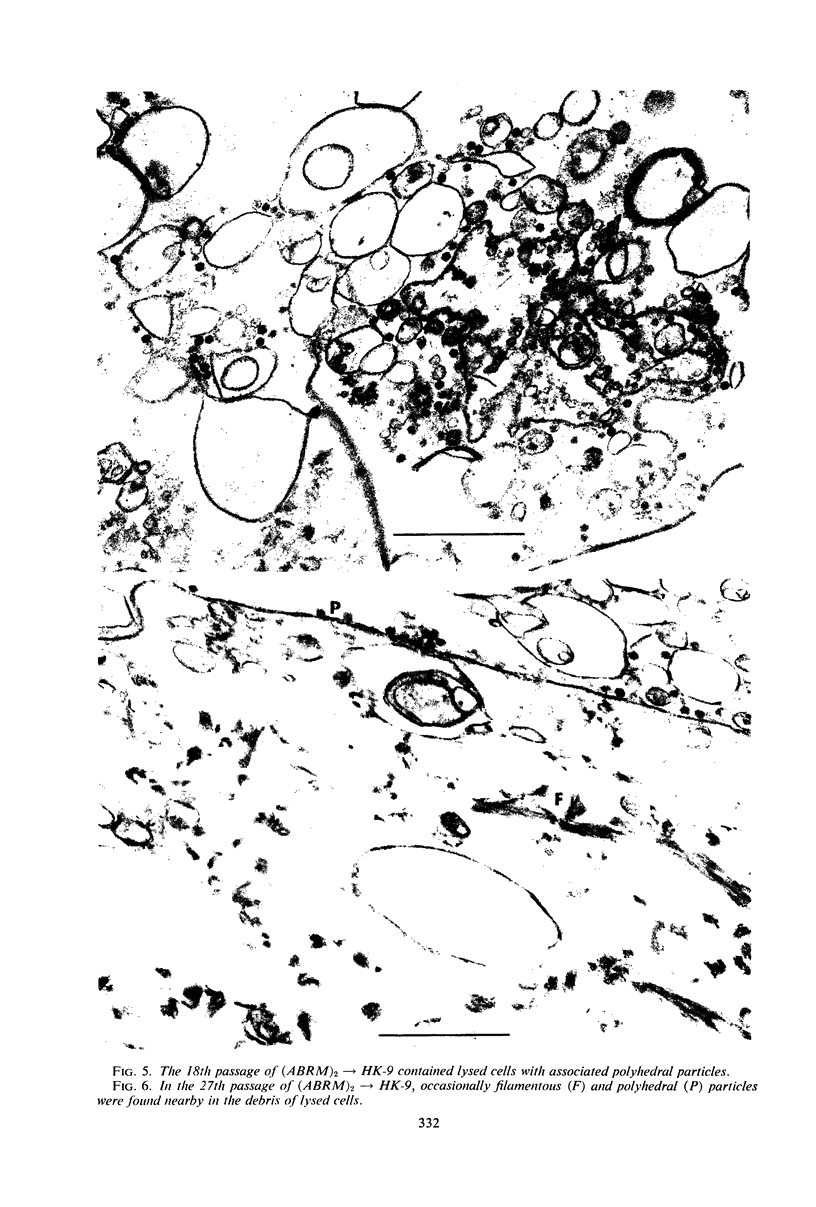








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BARILE M. F., YAGUCHI R., EVELAND W. C. A simplified medium for the cultivation of pleuropneumonia-like organisms and the L-forms of bacteria. Am J Clin Pathol. 1958 Aug;30(2):171–176. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/30.2_ts.171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beale G. N., Jurand A., Preer J. R. The classes of endosymbiont of Paramecium aurelia. J Cell Sci. 1969 Jul;5(1):65–91. doi: 10.1242/jcs.5.1.65. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies E. E., Howells R. E. A pathogen of the malaria parasite. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1971;65(1):13–14. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond L. S. Improved method for the monoxenic cultivation of Entamoeba histolytica Schaudinn, 1903 and E. histolytica-like amebae with trypanosomatids. J Parasitol. 1968 Aug;54(4):715–719. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond L. S. Techniques of axenic cultivation of Entamoeba histolytica Schaudinn, 1903 and E. histolytica-like amebae. J Parasitol. 1968 Oct;54(5):1047–1056. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunnebacke T. H., Schuster F. L. Infectious agent from a free-living soil amoeba, Naegleria gruberi. Science. 1971 Oct 29;174(4008):516–518. doi: 10.1126/science.174.4008.516. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattern C. F., Diamond L. S., Daniel W. A. Viruses of Entamoeba histolytica. II. Morphogenesis of the polyhedral particle (ABRM 2 leads to HK-9) leads to HB-301 and the filamentous agent (ABRM) 2 leads to HK-9. J Virol. 1972 Feb;9(2):342–358. doi: 10.1128/jvi.9.2.342-358.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkins F. O. Ultrastructure of vegetative stages in Labyrinthomyxa marina (Dermocystidium marinum), a commercially significant oyster pathogen. J Invertebr Pathol. 1969 Mar;13(2):199–222. doi: 10.1016/0022-2011(69)90211-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preer J. R., Jr, Jurand A. The relation between virus-like particles and R bodies of Paramecium aurelia. Genet Res. 1968 Dec;12(3):331–340. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300011915. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preer J. R., Jr, Preer L. B. Virus-like bodies in killer paramecia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Oct;58(4):1774–1781. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.4.1774. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuster F. L. Intranuclear virus-like bodies in the amoeboflagellate Naegleria gruberi. J Protozool. 1969 Nov;16(4):724–727. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1969.tb02333.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terzakis J. A. A protozoan virus. Mil Med. 1969 Sep;134(10):916–921. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]