Abstract
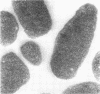
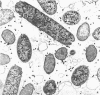
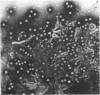
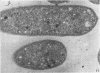
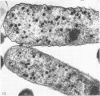
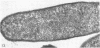
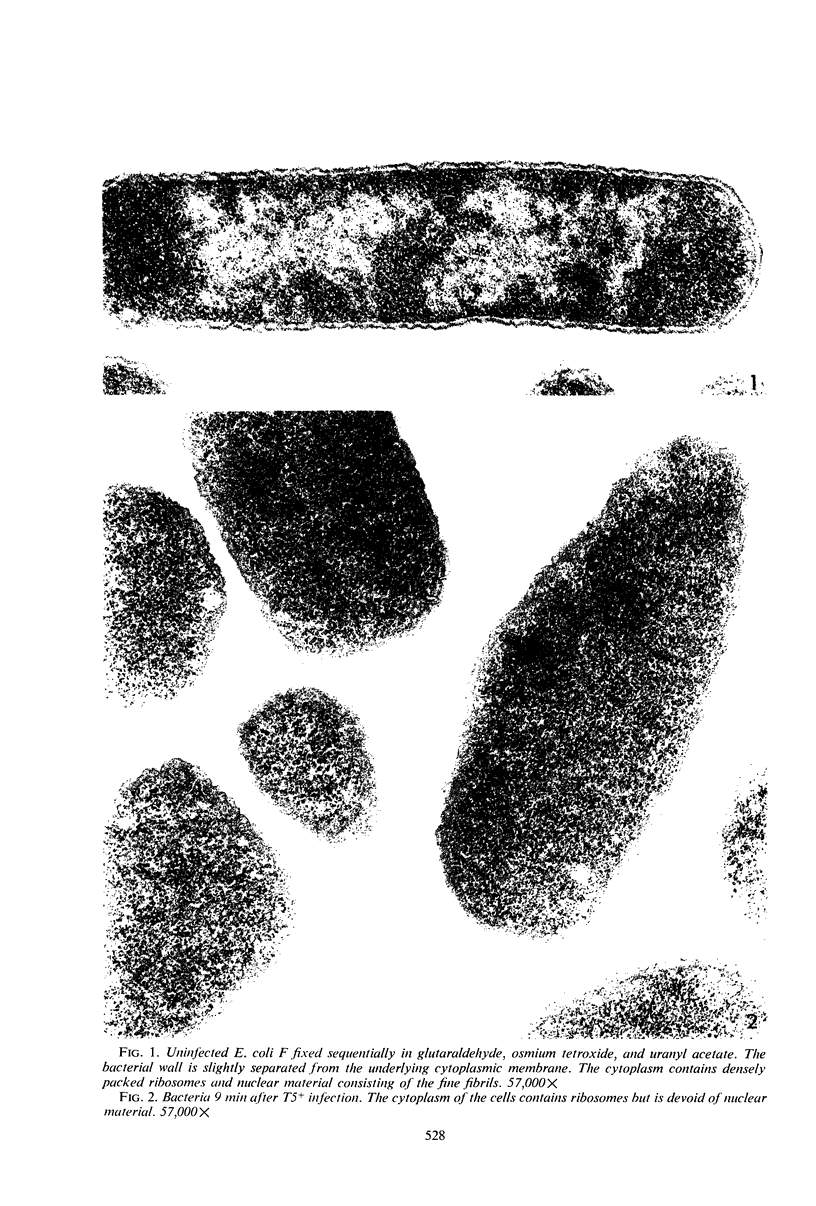
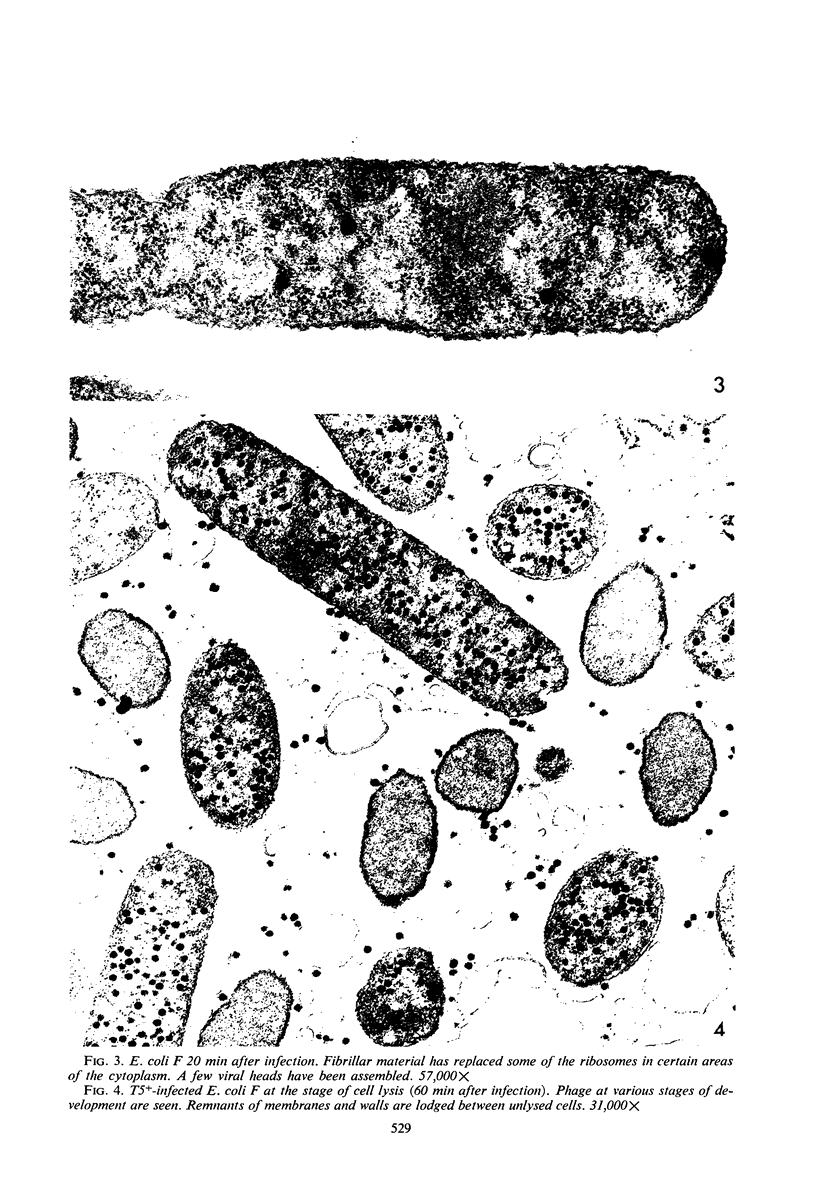
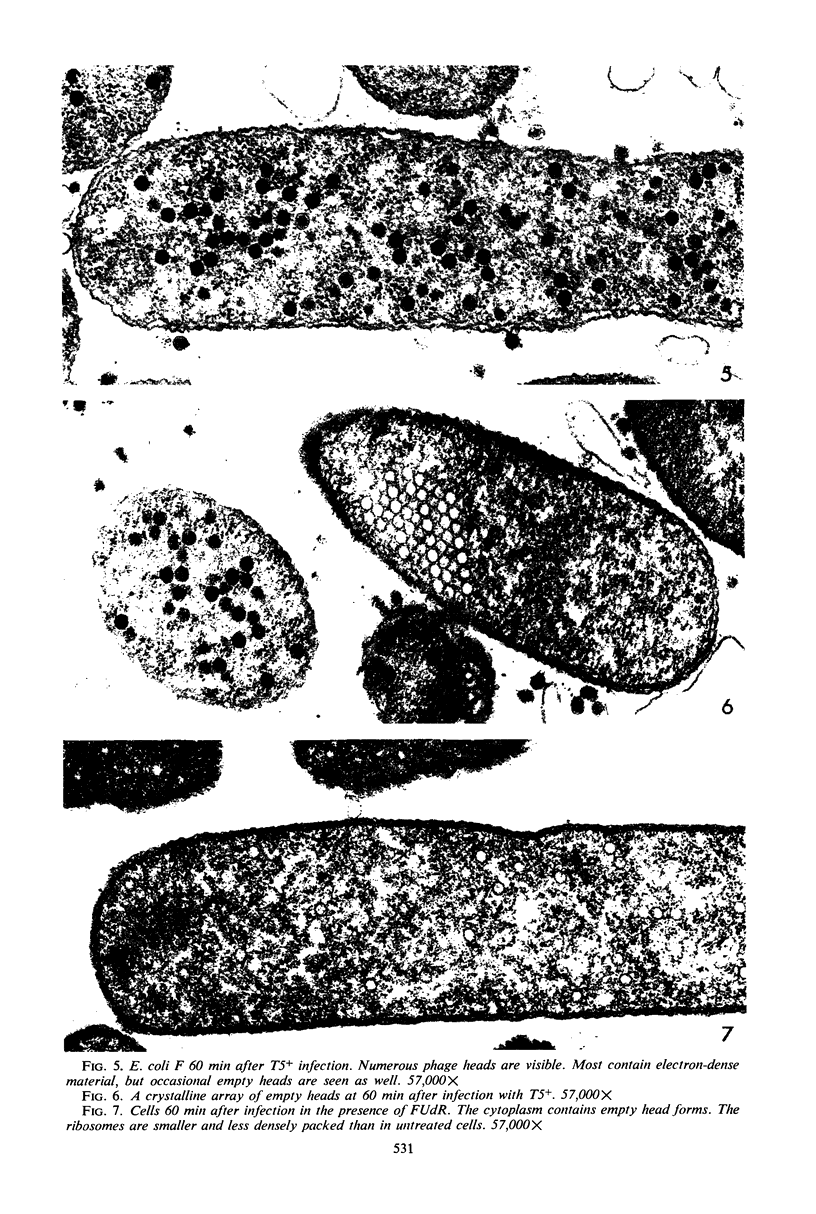
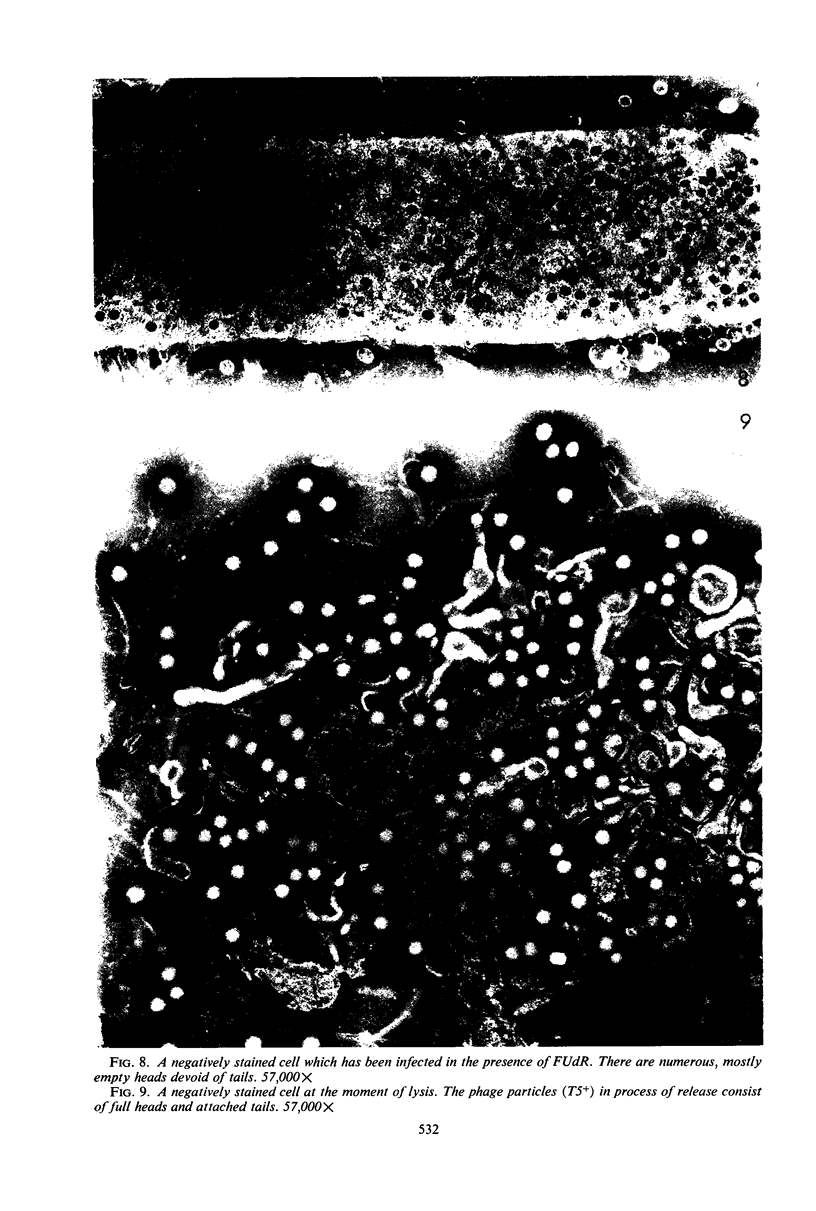
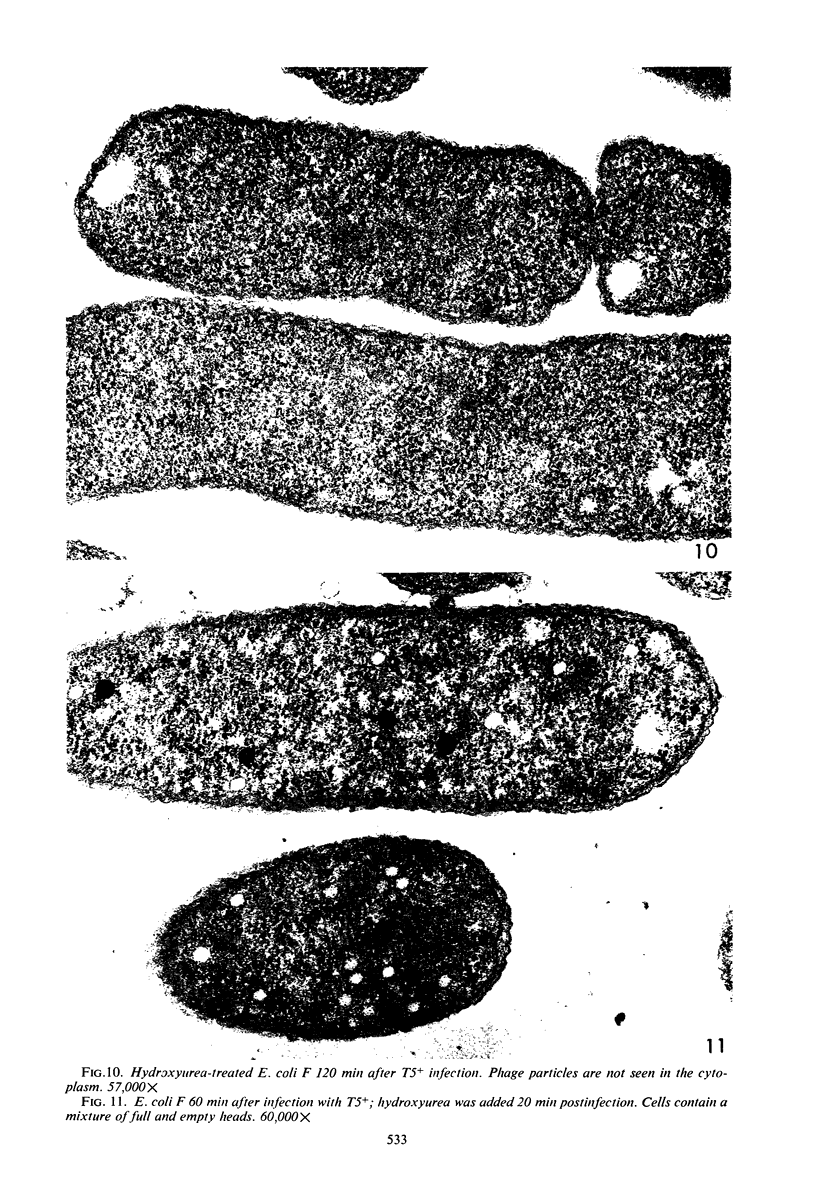
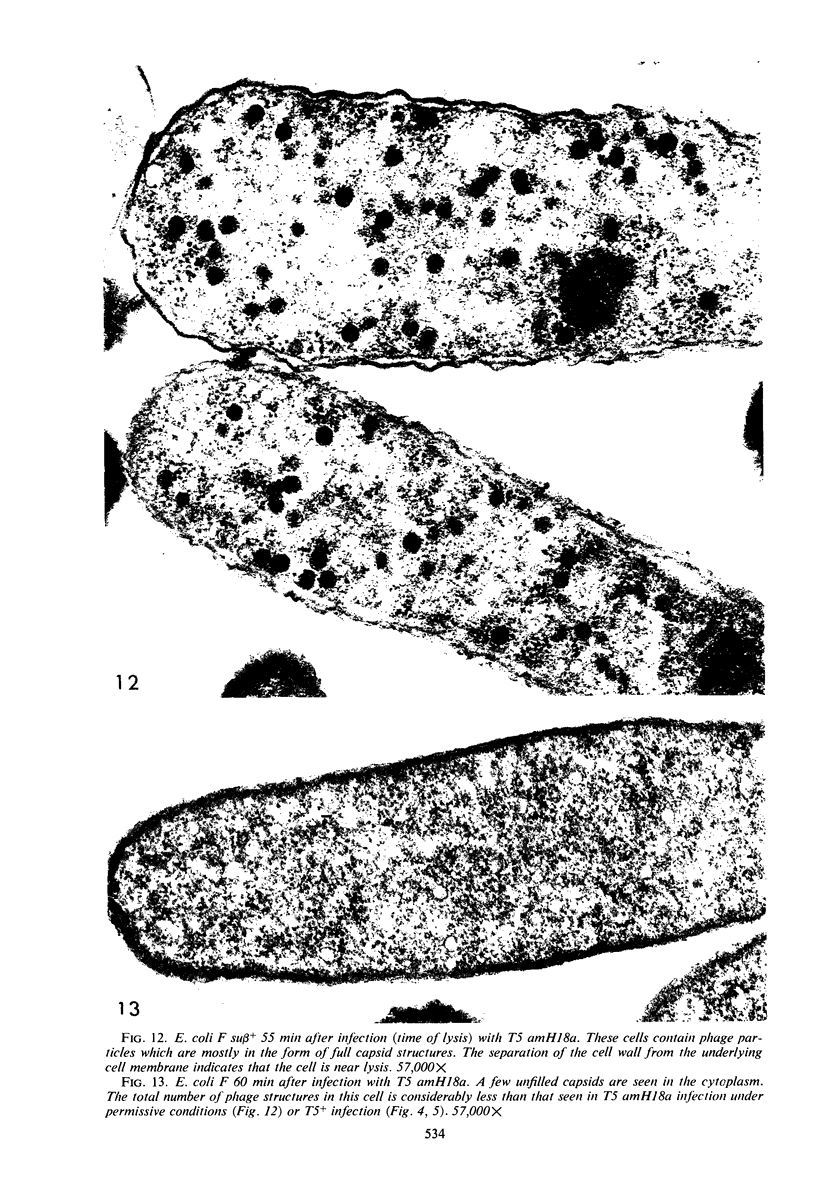
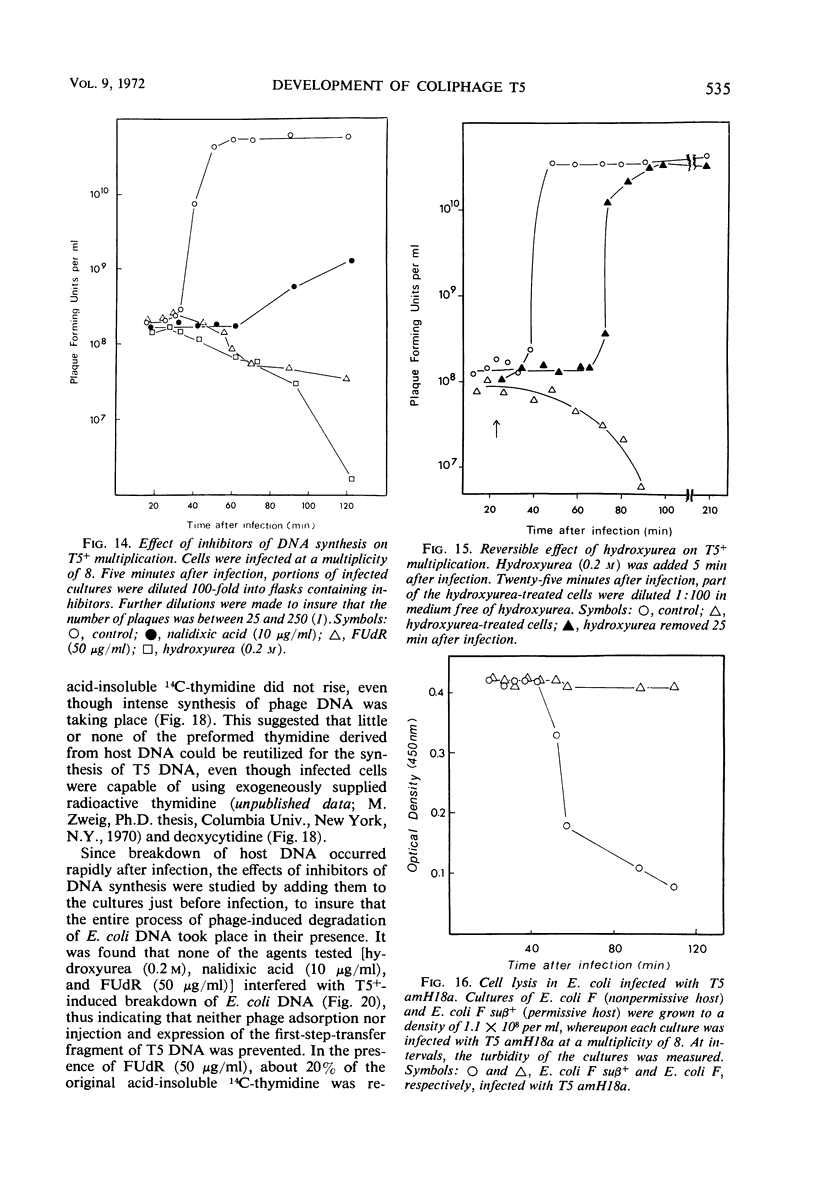
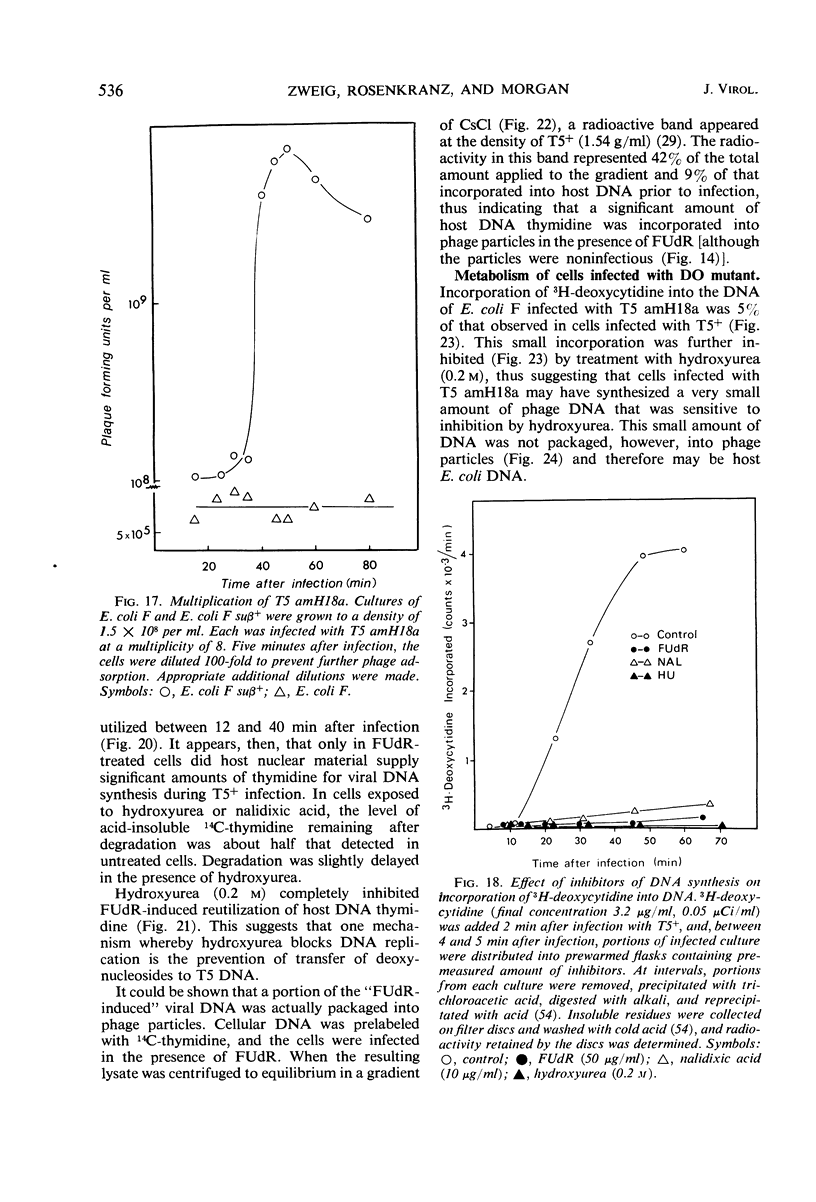
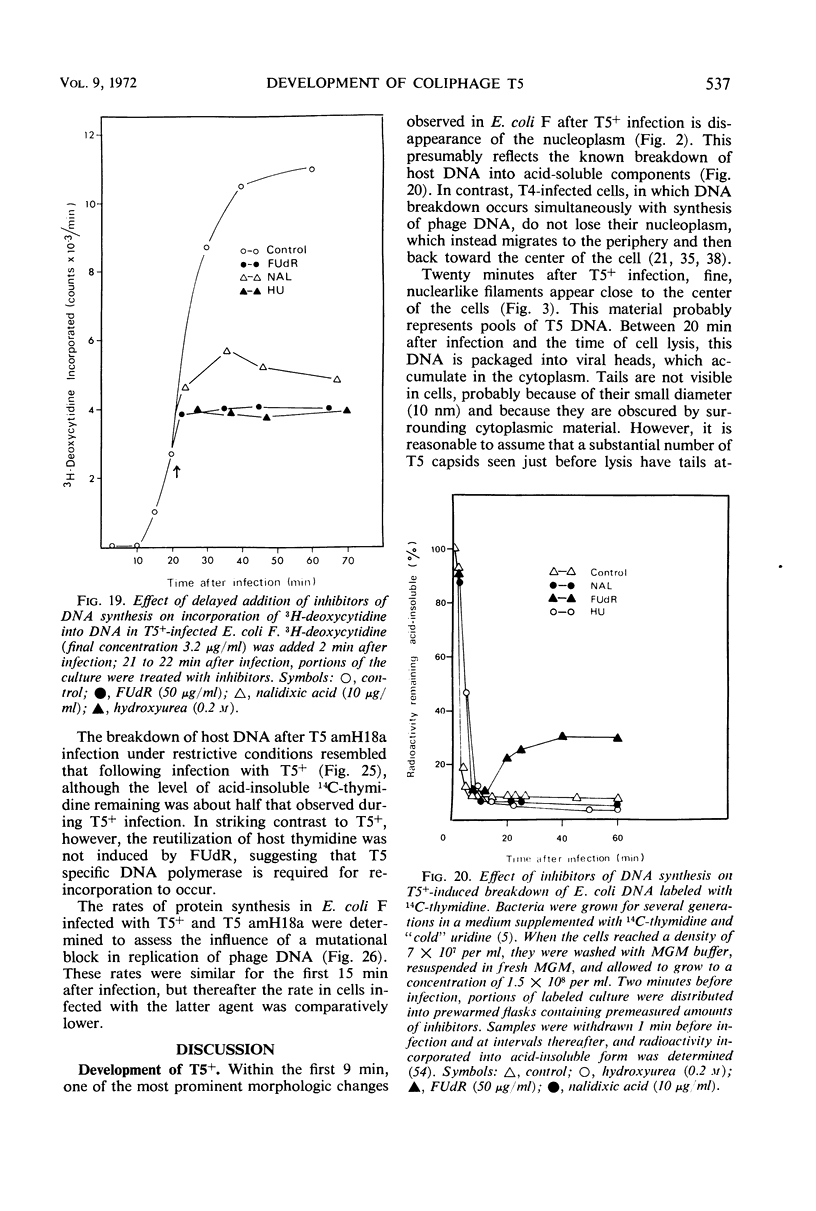
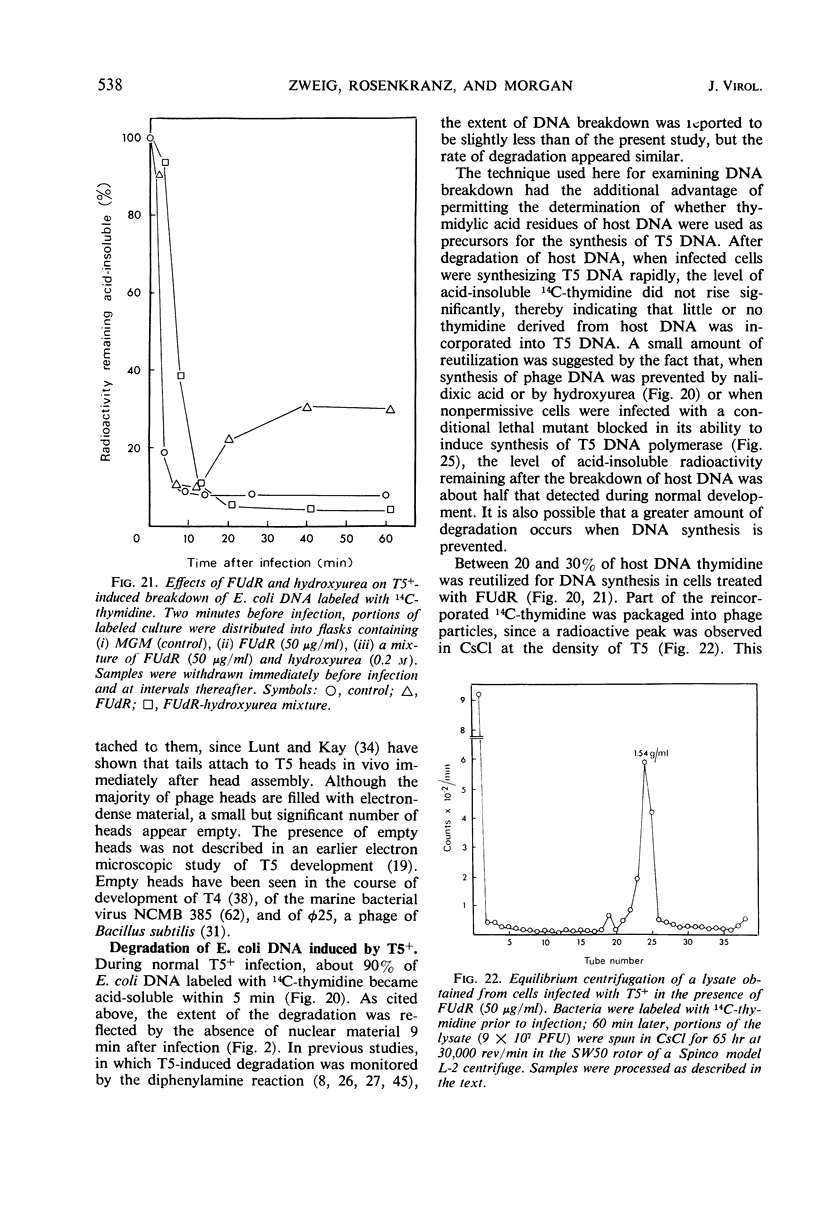
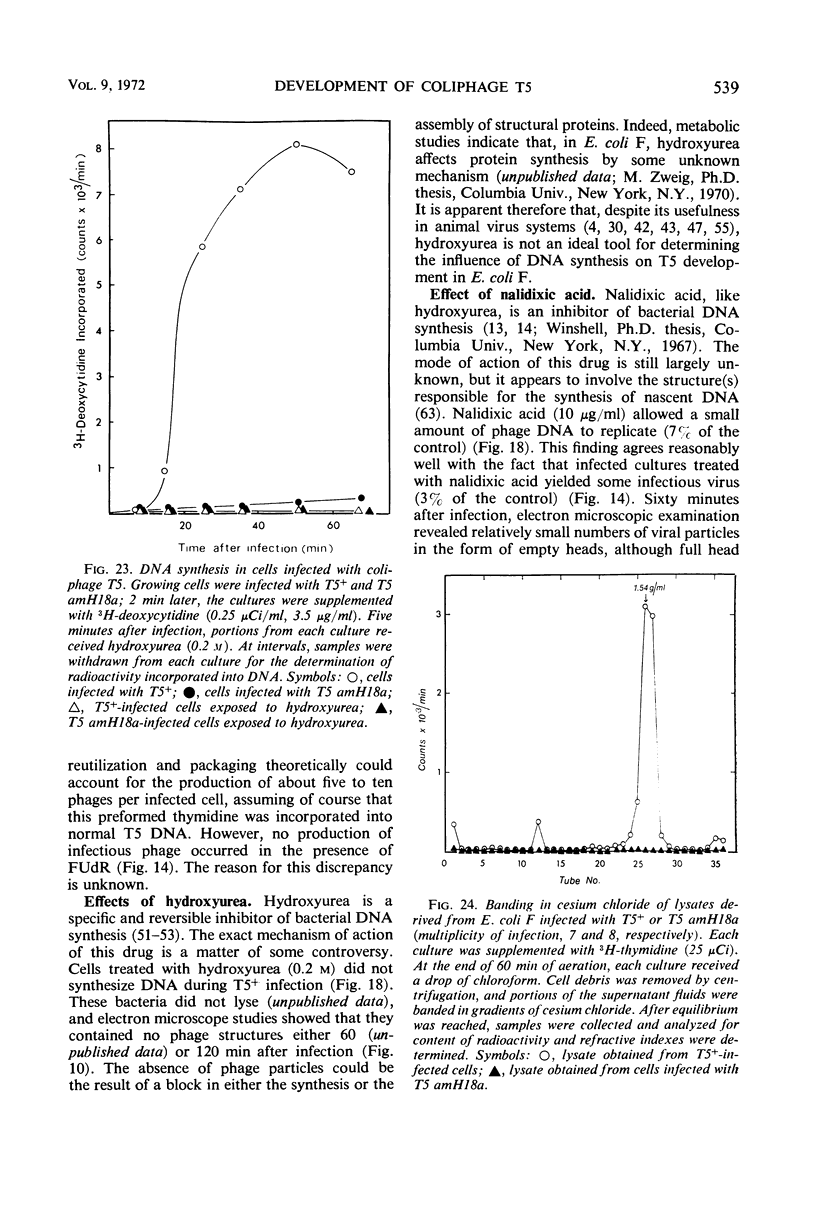
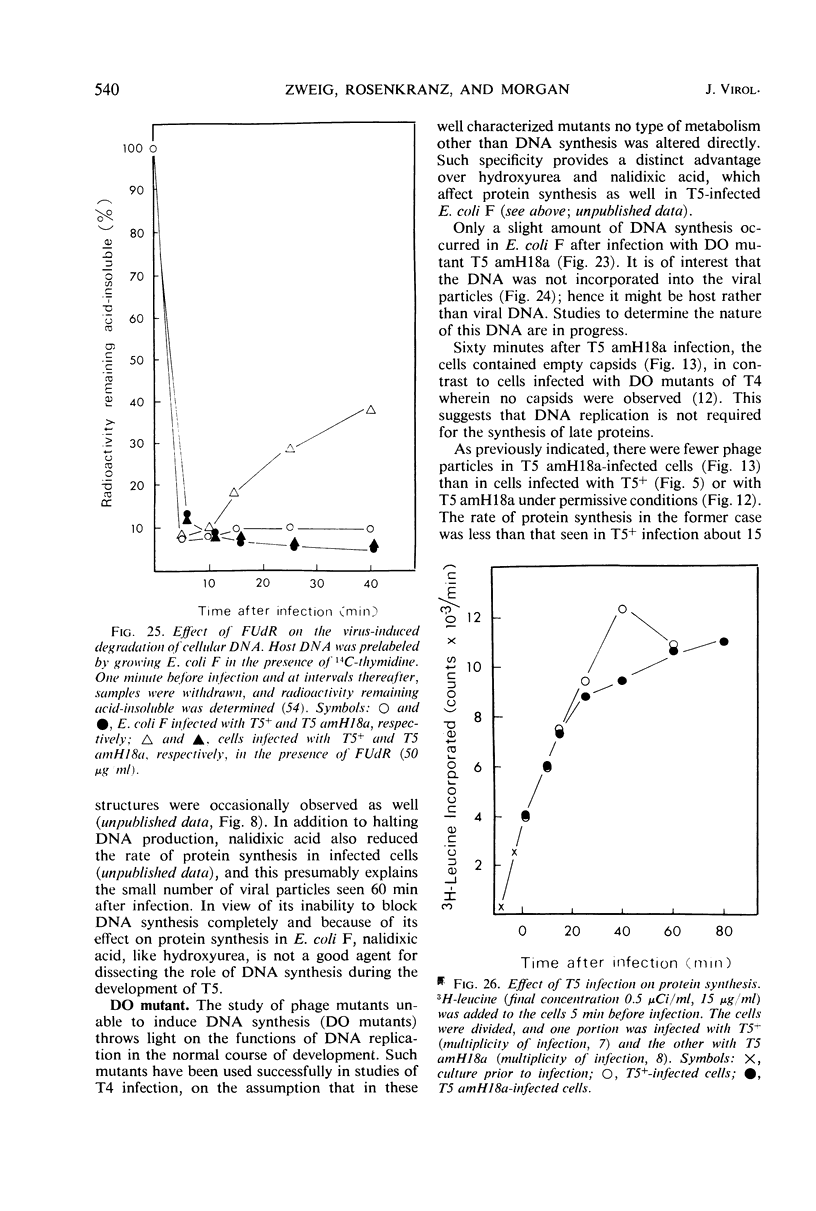
Electron microscopic studies of Escherichia coli infected with bacteriophage T5+ have revealed that host nuclear material disappeared before 9 min after infection. This disappearance seemed to correspond to the breakdown of host deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) into acid-soluble fragments. Little or no host DNA thymidine was reincorporated into phage DNA, except in the presence of 5-fluorodeoxyuridine (FUdR). Progeny virus particles were observed in the cytoplasm 20 min postinfection. Most of these particles were in the form of hexagonal-shaped heads or capsids, which were filled with electron-dense material (presumably T5 DNA). A small percentage (3 to 4%) of the phage heads appeared empty. On rare occasions, crystalline arrays of empty heads were observed. Nalidixic acid, hydroxyurea, and FUdR substantially inhibited replication of T5 DNA. However, these agents did not prevent virus-induced degradation of E. coli DNA. Most of the phage-specified structures seen in T5+-infected cells treated with FUdR or with nalidixic were in the form of empty capsids. Infected cells treated with hydroxyurea did not contain empty capsids. When E. coli F was infected with the DO mutant T5 amH18a (restrictive conditions), there was a small amount of DNA synthesis. Such cells contained only empty capsids, but their numbers were few in comparison to those in cells infected under permissive conditions or infected with T5+. The cells also failed to lyse. These results confirm other reports which suggest that DNA replication is not required for the synthesis of late proteins. The data also indicate that DNA replication influences the quantity of viral structures being produced.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BARNER H. D., COHEN S. S. Virus-induced acquisition of metabolic function. IV. Thymidylate synthetase in thymine-requiring Escherichia coli infected by T2 and T5 bacteriophages. J Biol Chem. 1959 Nov;234:2987–2991. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BESSMAN M. J., HERRIOTT S. T., ORR M. J. THE ENZYMOLOGY OF VIRUS-INFECTED BACTERIA. VI. PURIFICATION AND PROPERTIES OF THE DEOXYNUCLEOTIDE KINASE INDUCED BY BACTERIOPHAGE T5. J Biol Chem. 1965 Jan;240:439–445. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURTON K. A study of the conditions and mechanism of the diphenylamine reaction for the colorimetric estimation of deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochem J. 1956 Feb;62(2):315–323. doi: 10.1042/bj0620315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breese S. S., Jr, DeBoer C. J. Effect of hydroxyurea on the development of African swine fever virus. Am J Pathol. 1969 Apr;55(1):69–77. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Budman D. R., Pardee A. B. Thymidine and thymine incorporation into deoxyribonucleic acid: inhibition and repression by uridine of thymidine phosphorylase of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1967 Nov;94(5):1546–1550. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.5.1546-1550.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COLE R. M. CRYSTALLINE AGGREGATES DURING INTRACELLULAR DEVELOPMENT OF A STREPTOCOCCAL BACTERIOPHAGE. Virology. 1965 Jul;26:509–511. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(65)90015-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRAWFORD L. V. Nucleic acid metabolism in Escherichia coli infected with phage T5. Virology. 1959 Apr;7(4):359–374. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(59)90065-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Waard A., Paul A. V., Lehman I. R. The structural gene for deoxyribonucleic acid polymerase in bacteriophages T4 and T5. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Oct;54(4):1241–1248. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.4.1241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards M. R., Brown J. P. Crystalline aggregates of a bacteriophage in Lactobacillus planarum. J Virol. 1968 Dec;2(12):1479–1481. doi: 10.1128/jvi.2.12.1479-1481.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOSS W. A., DEITZ W. H., COOK T. M. MECHANISM OF ACTION OF NALIDIXIC ACID ON ESCHERICHIA COLI.II. INHIBITION OF DEOXYRIBONUCLEIC ACID SYNTHESIS. J Bacteriol. 1965 Apr;89:1068–1074. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.4.1068-1074.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendrickson H. E., McCorquodale D. J. Genetic and physiological studies of bacteriophage T5. 2. The relationship between phage DNA synthesis and protein synthesis in T5-infected cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 May 21;43(4):735–740. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90677-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendrickson H. E., McCorquodale D. J. Genetic and physiological studies of bacteriophage t5 I. An expanded genetic map of t5. J Virol. 1971 May;7(5):612–618. doi: 10.1128/jvi.7.5.612-618.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KELLENBERGER E., RYTER A., SECHAUD J. Electron microscope study of DNA-containing plasms. II. Vegetative and mature phage DNA as compared with normal bacterial nucleoids in different physiological states. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1958 Nov 25;4(6):671–678. doi: 10.1083/jcb.4.6.671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KELLENBERGER E. Vegetative bacteriophage and the maturation of the virus particles. Adv Virus Res. 1961;8:1–61. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3527(08)60682-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karnovsky M. J. The ultrastructural basis of capillary permeability studied with peroxidase as a tracer. J Cell Biol. 1967 Oct;35(1):213–236. doi: 10.1083/jcb.35.1.213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kellenberger E., Eiserling F. A., Boy de la Tour E. Studies on the morphopoiesis of the head of phage T-even. 3. The cores of head-related structures. J Ultrastruct Res. 1967 Dec 12;21(3):335–360. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(67)80099-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANNI Y. T. Infection by bacteriophage T5 and its intracellular growth; a study by complement fixation. J Bacteriol. 1954 Jun;67(6):640–650. doi: 10.1128/jb.67.6.640-650.1954. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANNI Y. T. Invasion by bacteriophage T5. I. Some basic kinetic features. Virology. 1960 Apr;10:501–513. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(60)90132-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANNI Y. T. Lysis inhibition with a mutant of bacteriophage T5. Virology. 1958 Jun;5(3):481–501. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(58)90041-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANNI Y. T., MCCORQUODALE D. J., WILSON C. M. MOLECULAR ASPECTS OF DNA TRANSFER FROM PHAGE T5 TO HOST CELLS. II. ORIGIN OF FIRST-STEP-TRANSFER DNA FRAGMENTS. J Mol Biol. 1964 Oct;10:19–27. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(64)80024-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUFT J. H. Improvements in epoxy resin embedding methods. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1961 Feb;9:409–414. doi: 10.1083/jcb.9.2.409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LURIA S. E., HUMAN M. L. Chromatin staining of bacteria during bacteriophage infection. J Bacteriol. 1950 Apr;59(4):551–560. doi: 10.1128/jb.59.4.551-560.1950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanni Y. T. DNA transfer from phage T5 to host cells: dependence on intercurrent protein synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 May;53(5):969–973. doi: 10.1073/pnas.53.5.969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanni Y. Functions of two genes in the first-step-transfer DNA of bacteriophage T5. J Mol Biol. 1969 Aug 28;44(1):173–183. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90412-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy J. A., Huebner R. J., Kern J., Gilden R. V. High titre T antigen with minimal amounts of structural antigen in adenovirus-infected cells treated with hydroxyurea. Nature. 1968 Feb 24;217(5130):744–745. doi: 10.1038/217744a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liljemark W. F., Anderson D. L. Morphology and physiology of the intracellular development of Bacillus subtilis bacteriophage phi25. J Virol. 1970 Jul;6(1):114–124. doi: 10.1128/jvi.6.1.114-124.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lunt M. R., Kay D. The conversion of viral heads to T5 phage in vivo. J Gen Virol. 1968 Dec;3(3):459–463. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-3-3-459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCCORQUODALE D. J., LANNI Y. T. MOLECULAR ASPECTS OF DNA TRANSFER FROM PHAGE T5 TO HOST CELLS. I. CHARACTERIZATION OF FIRST-STEP-TRANSFER MATERIAL. J Mol Biol. 1964 Oct;10:10–18. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(64)80023-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MURRAY R. G., WHITFIELD J. F. Cytological effects of infection with T5 and some related phages. J Bacteriol. 1953 Jun;65(6):715–726. doi: 10.1128/jb.65.6.715-726.1953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margaretten W., Morgan C., Rosenkranz H. S., Rose H. M. Effect of hydroxyurea on virus development. I. Electron microscopic study of the effect on the development of bacteriophage T4. J Bacteriol. 1966 Feb;91(2):823–833. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.2.823-833.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathews C. K. Evidence that bacteriophage-induced dihydrofolate reductase in a viral gene product. J Biol Chem. 1967 Sep 25;242(18):4083–4086. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCorquodale D. J., Buchanan J. M. Patterns of protein synthesis in T5-infected Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1968 May 25;243(10):2550–2559. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moyer R. W., Buchanan J. M. Patterns of RNA synthesis in T5-infected cells. I. As studied by the technique of DNA-RNA hybridization-competition. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Dec;64(4):1249–1256. doi: 10.1073/pnas.64.4.1249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nii S., Rosenkranz H. S., Morgan C., Rose H. M. Electron microscopy of herpes simplex virus. 3. Effect of hydroxyurea. J Virol. 1968 Oct;2(10):1163–1171. doi: 10.1128/jvi.2.10.1163-1171.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordenskjöld A., Krakoff I. H. Effects of hydroxyurea on polyoma virus replication. Cancer Res. 1968 Sep;28(9):1686–1691. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orr C. W., Herriott S. T., Bessman M. J. The enzymology of virus-infected bacteria. VII. A new deoxyribonucleic acid polymerase induced by bacteriophage T5. J Biol Chem. 1965 Dec;240(12):4652–4658. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PFEFFERKORN E., AMOS H. Deoxyribonucleic acid breakdown and resynthesis in T5 bacteriophage infection. Virology. 1958 Aug;6(1):299–301. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(58)90083-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pispa J. P., Sirbasku D. A., Buchanan J. M. Patterns of ribonucleic acid synthesis in T5-infected Escherichia coli. IV. Examination of the role of deoxyribonucleic acid replication. J Biol Chem. 1971 Mar 25;246(6):1658–1664. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pogo B. G., Dales S. Regulation of the synthesis of nucleotide phosphohydrolase and neutral deoxyribonuclease: two activities present within purified vaccina virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Aug;63(4):1297–1303. doi: 10.1073/pnas.63.4.1297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYNOLDS E. S. The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1963 Apr;17:208–212. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.1.208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSENKRANZ H. S., LEVY J. A. HYDROXYUREA: A SPECIFIC INHIBITOR OF DEOXYRIBONUCLEIC ACID SYNTHESIS. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Jan 11;95:181–183. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(65)90225-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riva S., Cascino A., Geiduschek E. P. Coupling of late transcription to viral replication in bacteriophage T4 development. J Mol Biol. 1970 Nov 28;54(1):85–102. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90447-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenkranz H. S., Garro A. J., Levy J. A., Carr H. S. Studies with hydroxyurea. I. The reversible inhibition of bacterial DNA synthesis and the effect of hydroxyurea on the bactericidal action of streptomycin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Mar 21;114(3):501–515. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenkranz H. S., Pollak R. D., Schmidt R. M. Biologic effects of isohydroxyurea. Cancer Res. 1969 Jan;29(1):209–218. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenkranz H. S., Rose H. M., Morgan C., Hsu K. C. The effect of hydroxyurea on virus development. II. Vaccinia virus. Virology. 1966 Apr;28(4):510–519. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(66)90235-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenkranz S., Carr H. S., Pollak R. D. Studies with hydroxyurea. VI. Effects of hydroxyurea on the metabolism of sensitive and resistant strains of Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Nov 21;149(1):228–245. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(67)90704-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SABATINI D. D., BENSCH K., BARRNETT R. J. Cytochemistry and electron microscopy. The preservation of cellular ultrastructure and enzymatic activity by aldehyde fixation. J Cell Biol. 1963 Apr;17:19–58. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.1.19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHWARTZ F. M., ZINDER N. D. CRYSTALLINE AGGREGATES IN BACTERIAL CELLS INFECTED WITH THE RNA BACTERIOPHAGE F2. Virology. 1963 Oct;21:276–278. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(63)90272-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sauerbier W., räutigam A. R. Control of gene function in baceriophage T4. II. Synthes of messenger ribonucleiccid and proei after interrupting deoxyribonucleic acid replication and glucosylation. J Virol. 1970 Feb;5(2):179–187. doi: 10.1128/jvi.5.2.179-187.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sirbasku D. A., Buchanan J. M. Patterns of ribonucleic acid synthesis in T5-infected Escherichia coli. II. Separation of high molecular weight ribonucleic acid species by disc electrophoresis on acrylamide gel columns. J Biol Chem. 1970 May 25;245(10):2679–2692. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Maizel J. V., Jr T7-directed protein synthesis. Virology. 1969 Nov;39(3):575–586. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90105-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valentine A. F., Chapman G. B. Fine structure and host-virus relationship of a marine bacterium and its bacteriophage. J Bacteriol. 1966 Nov;92(5):1535–1554. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.5.1535-1554.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winshell E. B., Rosenkranz H. S. Nalidixic Acid and the Metabolism of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1970 Dec;104(3):1168–1175. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.3.1168-1175.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]