Abstract
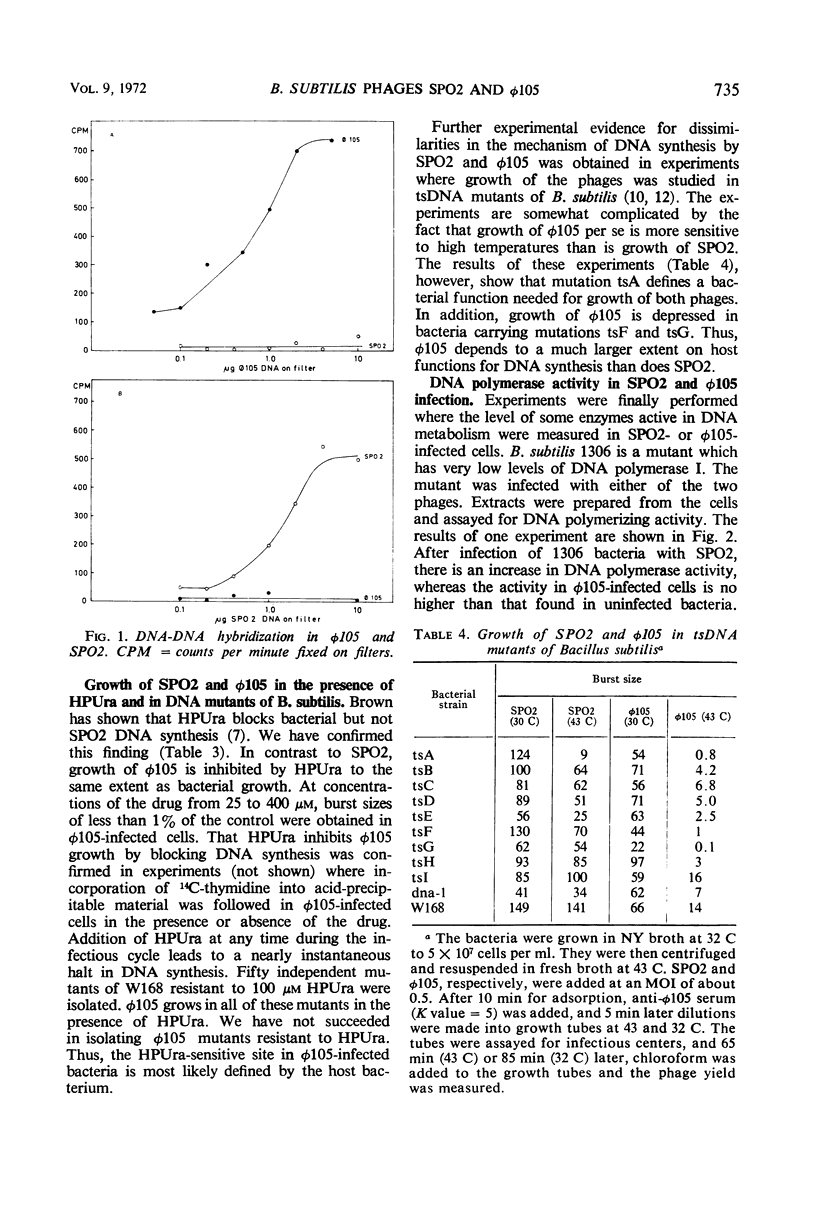
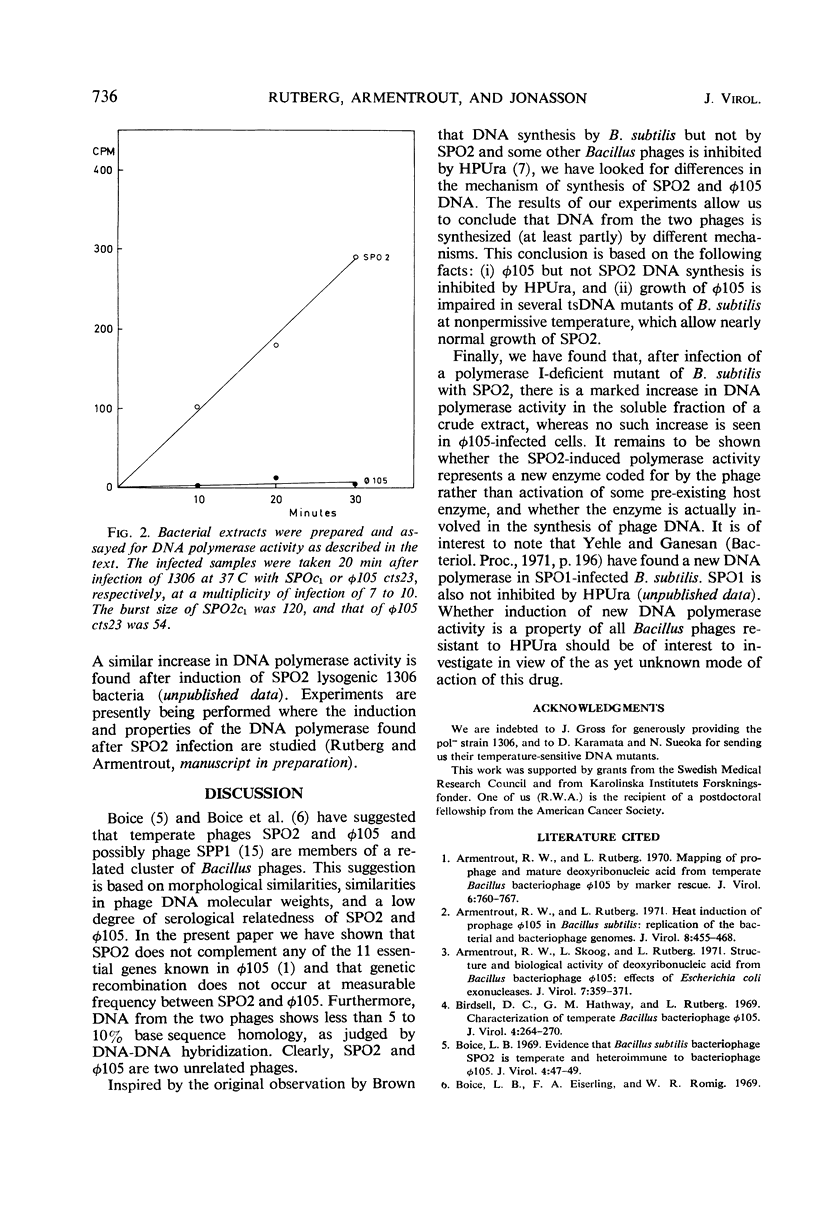
SPO2 and φ105 are temperate Bacillus subtilis bacteriophages which have been suggested to belong to a cluster of related bacteriophages. In the present work, we show that SPO2 does not complement any of the 11 essential genes known in φ105 and that the phages do not recombine. Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA)-DNA hybridization shows less than 10% homology between SPO2 and φ105 DNA. DNA synthesis in φ105 shows a greater dependence on host functions than does SPO2 DNA synthesis. Growth of φ105 but not of SPO2 is inhibited by the uracil analogue 6-(p-hydroxyphenylazo)-uracil. Infection of a DNA polymerase-deficient strain of B. subtilis with SPO2 leads to an increase in DNA polymerase activity in crude extracts, whereas no such increase is found after infection of this strain with φ105. It is concluded that SPO2 and φ105 are unrelated bacteriophages.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armentrout R. W., Rutberg L. Heat induction of prophage phi 105 in Bacillus subtilis: replication of the bacterial and bacteriophage genomes. J Virol. 1971 Oct;8(4):455–468. doi: 10.1128/jvi.8.4.455-468.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armentrout R. W., Rutberg L. Mapping of prophage and mature deoxyribonucleic acid from temperate Bacillus bacteriophage phi 105 by marker rescue. J Virol. 1970 Dec;6(6):760–767. doi: 10.1128/jvi.6.6.760-767.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armentrout R. W., Skoog L., Rutberg L. Structure and biological activity of deoxyribonucleic acid from Bacillus bacteriophage phi 105: effects of Escherichia coli exonucleases. J Virol. 1971 Mar;7(3):359–371. doi: 10.1128/jvi.7.3.359-371.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birdsell D. C., Hathaway G. M., Rutberg L. Characterization of Temperate Bacillus Bacteriophage phi105. J Virol. 1969 Sep;4(3):264–270. doi: 10.1128/jvi.4.3.264-270.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boice L. B. Evidence that Bacillus subtilis bacteriophage SP02 is temperate and heteroimmune to bacteriophage phi-105. J Virol. 1969 Jul;4(1):47–49. doi: 10.1128/jvi.4.1.47-49.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boice L., Eiserling F. A., Romig W. R. Structure of bacillus subtilis phage SPO2 and its DNA: similarity of Bacillus subtilis phages SPO2, phi 1O5 and SPP1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1969 Feb 21;34(4):398–403. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(69)90395-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown N. C. 6-(p-hydroxyphenylazo)-uracil: a selective inhibitor of host DNA replication in phage-infected Bacillus subtilis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Nov;67(3):1454–1461. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.3.1454. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown N. C. Inhibition of bacterial DNA replication by 6-(p-hydroxyphenylazo)-uracil: differential effect on repair and semi-conservative synthesis in Bacillus subtilis. J Mol Biol. 1971 Jul 14;59(1):1–16. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90409-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inselburg J. W., Eremenko-Volpe T., Greenwald L., Meadow W. L., Marmur J. Physical and genetic mapping of the SPO2 prophage on the chromosome of Bacillus subtilis 168. J Virol. 1969 Jun;3(6):627–628. doi: 10.1128/jvi.3.6.627-628.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karamata D., Gross J. D. Isolation and genetic analysis of temperature-sensitive mutants of B. subtilis defective in DNA synthesis. Mol Gen Genet. 1970;108(3):277–287. doi: 10.1007/BF00283358. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsushita T., White K. P., Sueoka N. Chromosom replication in toluenized Bacillus subtilis cells. Nat New Biol. 1971 Jul 28;232(30):111–114. doi: 10.1038/newbio232111a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okubo S., Romig W. R. Impaired transformability of Bacillus subtilis mutant sensitive to mitomycin C and ultraviolet radiation. J Mol Biol. 1966 Feb;15(2):440–454. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80120-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards O. C. Hybridization of Euglena gracilis chloroplast and nuclear DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Jan;57(1):156–163. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.1.156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riva S., Polsinelli M., Falaschi A. A new phage of Bacillus subtilis with infectious DNA having separable strands. J Mol Biol. 1968 Jul 28;35(2):347–356. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(68)80029-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutberg L. Mapping of a temperate bacteriophage active on Bacillus subtilis. J Virol. 1969 Jan;3(1):38–44. doi: 10.1128/jvi.3.1.38-44.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



