Abstract
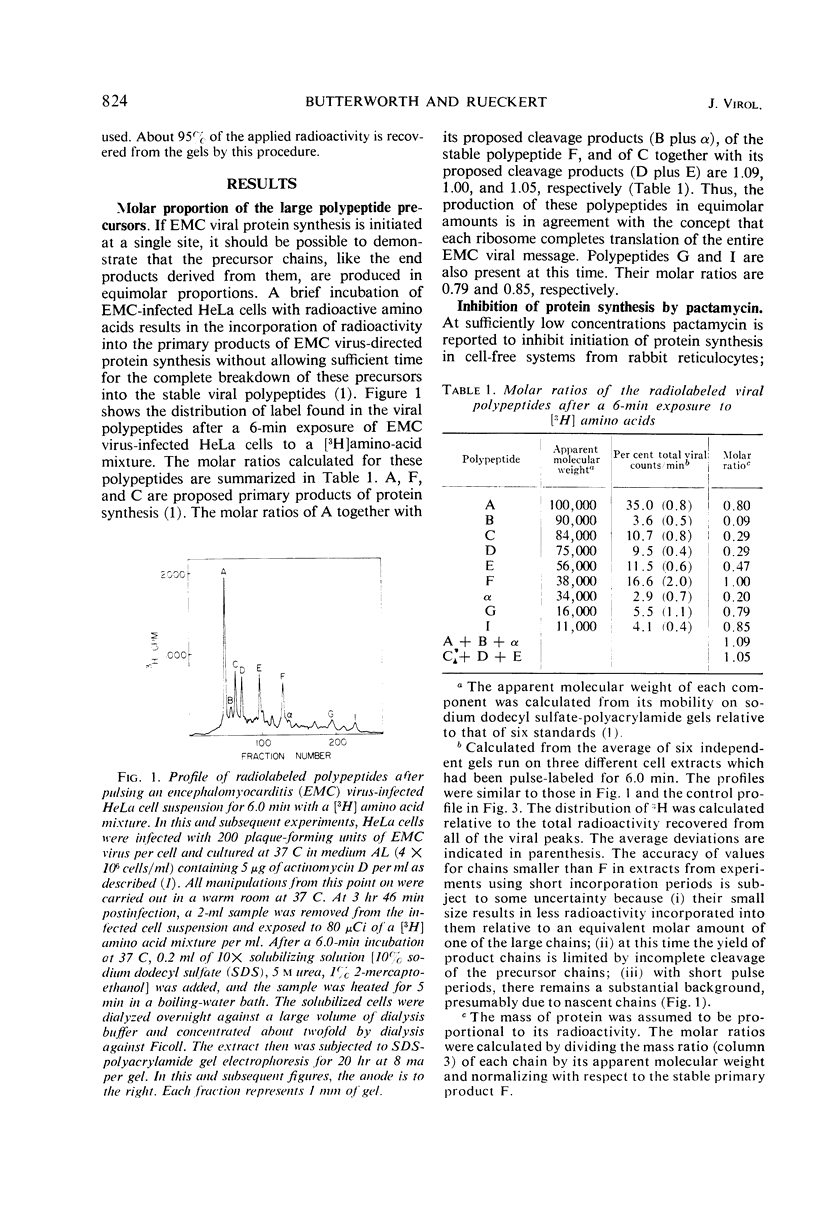
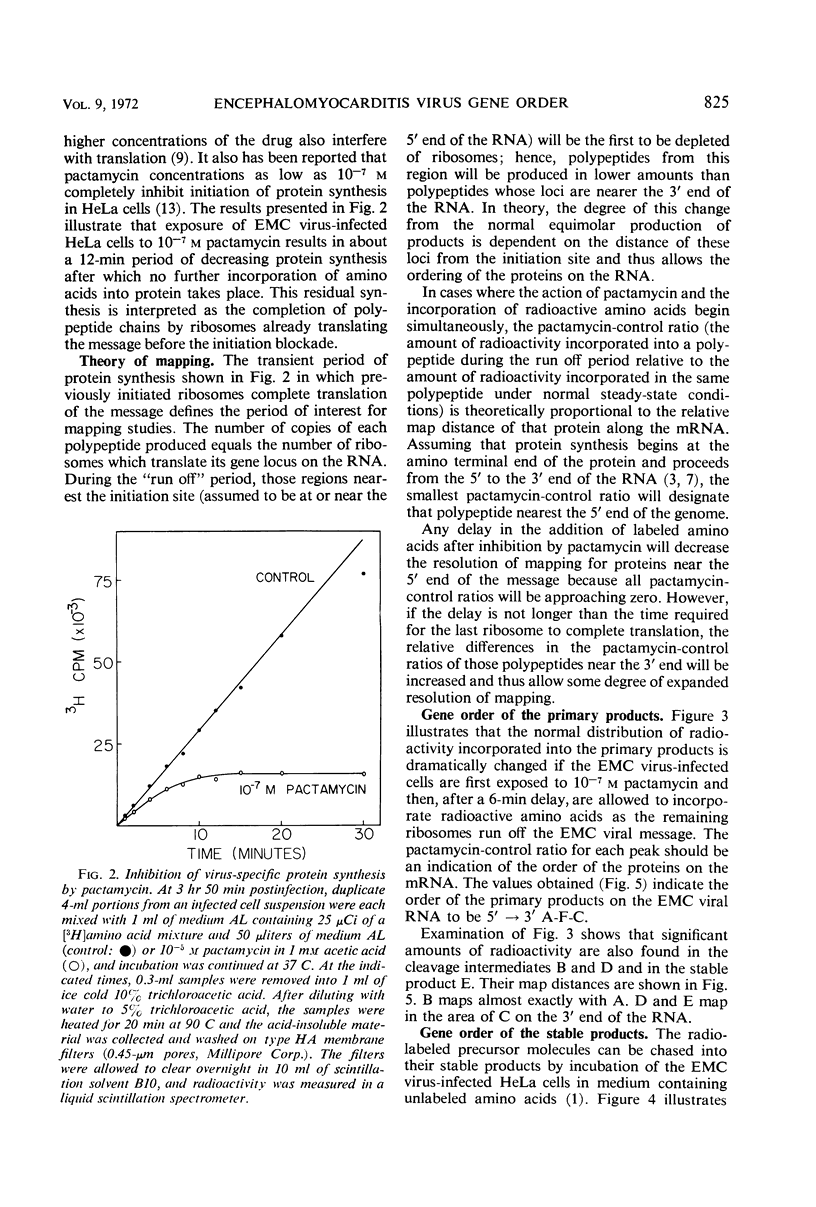
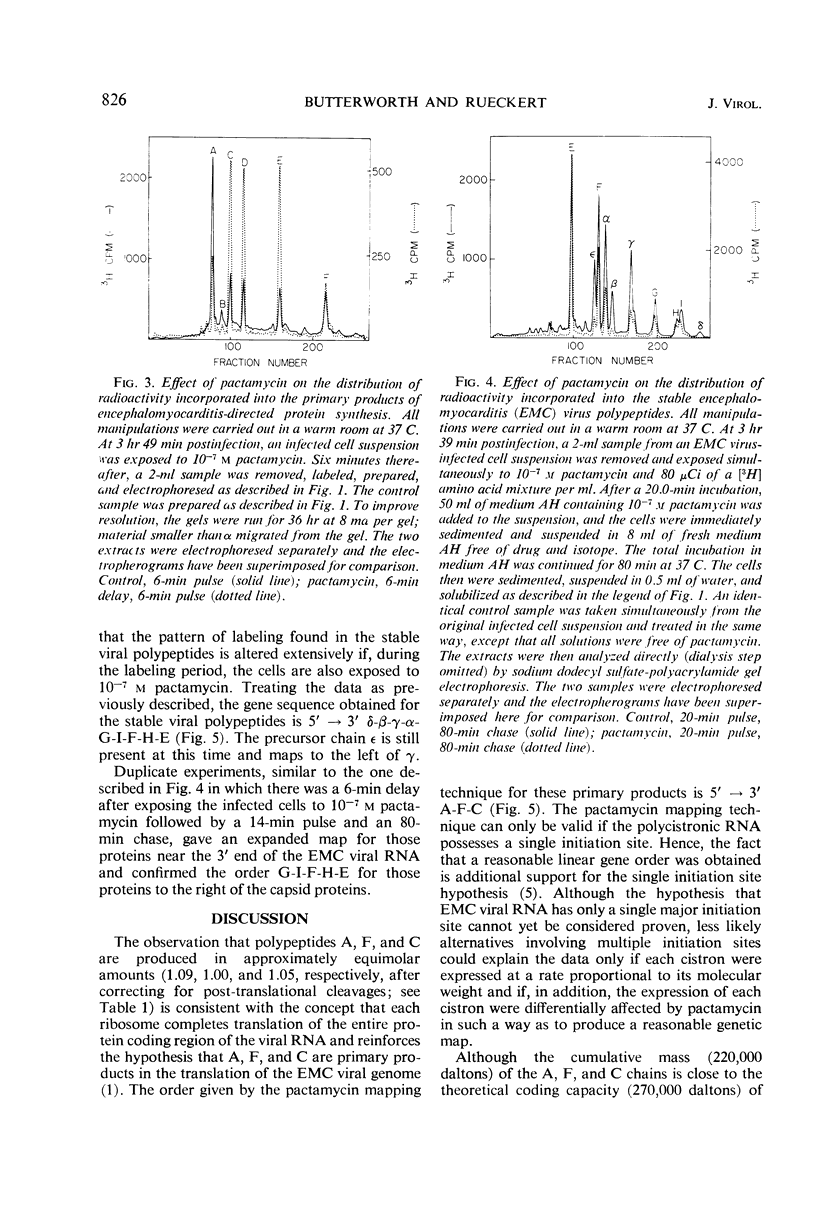
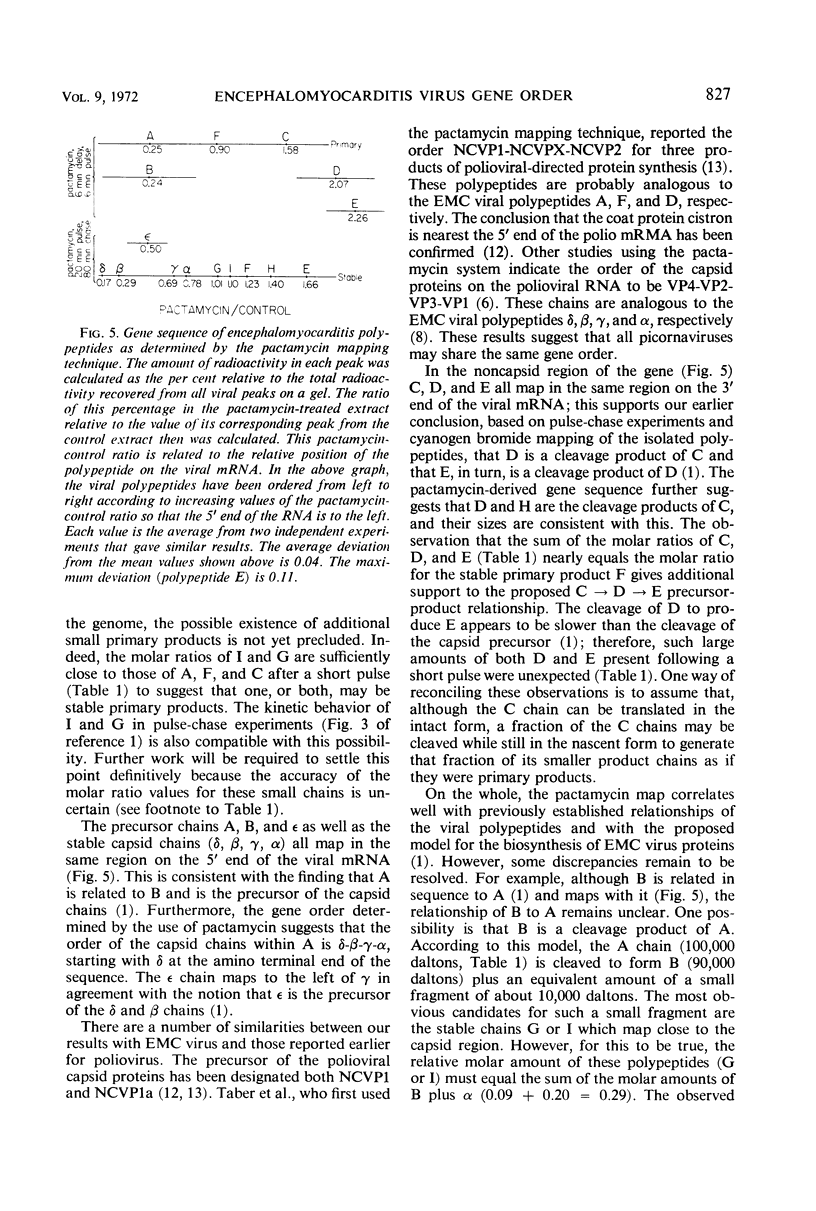
Previous work has shown that translation of the encephalomyocarditis (EMC) viral ribonucleic acid (RNA) generates at least three primary products, polypeptides A, F, and C. The A and C polypeptides then undergo post-translational cleavages to complete the production of the stable viral polypeptides (δ, β, γ, α, G, I, F, H, and E). In this communication we show that A, F, and C are produced in equimolar amounts giving further support to the theory that the RNA of picornaviruses has only a single site for the initiation of protein synthesis. The biosynthesis of viral proteins in EMC virus-infected HeLa cells was studied in the presence of pactamycin at concentrations which preferentially inhibit the initiation of protein synthesis. The amount of each polypeptide formed during the residual period of protein synthesis observed after the addition of pactamycin was used as a criterion for ordering the genes on the viral RNA. The results obtained indicate that the primary gene products are ordered on the EMC viral RNA 5′ → 3′ A-F-C and that the stable products are ordered δ-β-γ-α-G-I-F-H-E. Moreover, the intermediate chains B and ε map in the capsid region, whereas the intermediate chain D maps in the E region. This order is largely consistent with previously established relationships of the viral polypeptides and thus indicates that pactamycin is a valid tool for “genetic” mapping of polycistronic RNA molecules with single initiation sites.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Butterworth B. E., Hall L., Stoltzfus C. M., Rueckert R. R. Virus-specific proteins synthesized in encephalomyocarditis virus-infected HeLa cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Dec;68(12):3083–3087. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.12.3083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole C. N., Smoler D., Wimmer E., Baltimore D. Defective interfering particles of poliovirus. I. Isolation and physical properties. J Virol. 1971 Apr;7(4):478–485. doi: 10.1128/jvi.7.4.478-485.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DINTZIS H. M. Assembly of the peptide chains of hemoglobin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1961 Mar 15;47:247–261. doi: 10.1073/pnas.47.3.247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson M. F., Asso J., Baltimore D. Further evidence on the formation of poliovirus proteins. J Mol Biol. 1970 May 14;49(3):657–669. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90289-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson M. F., Baltimore D. Polypeptide cleavages in the formation of poliovirus proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Sep;61(1):77–84. doi: 10.1073/pnas.61.1.77. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rekosh D. Gene order of the poliovirus capsid proteins. J Virol. 1972 Mar;9(3):479–487. doi: 10.1128/jvi.9.3.479-487.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson W. E., Frist R. H., Kaesberg P. Genetic coding: oligonucleotide coding for first six amino acid residues of the coat protein of R17 bacteriophage. Science. 1969 Dec 5;166(3910):1291–1293. doi: 10.1126/science.166.3910.1291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart-Blair M. L., Yanowitz I. S., Goldberg I. H. Inhibition of synthesis of new globin chains in reticulocyte lysates by pactamycin. Biochemistry. 1971 Nov;10(23):4198–4206. doi: 10.1021/bi00799a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers D. F., Levintow L. Constitution and function of polyribosomes of poliovirus-infected HeLa cells. Virology. 1965 Sep;27(1):44–53. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(65)90142-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers D. F., Maizel J. V., Jr Determination of the gene sequence of poliovirus with pactamycin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Nov;68(11):2852–2856. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.11.2852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers D. F., Maizel J. V., Jr Evidence for large precursor proteins in poliovirus synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Mar;59(3):966–971. doi: 10.1073/pnas.59.3.966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taber R., Rekosh D., Baltimore D. Effect of pactamycin on synthesis of poliovirus proteins: a method for genetic mapping. J Virol. 1971 Oct;8(4):395–401. doi: 10.1128/jvi.8.4.395-401.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



