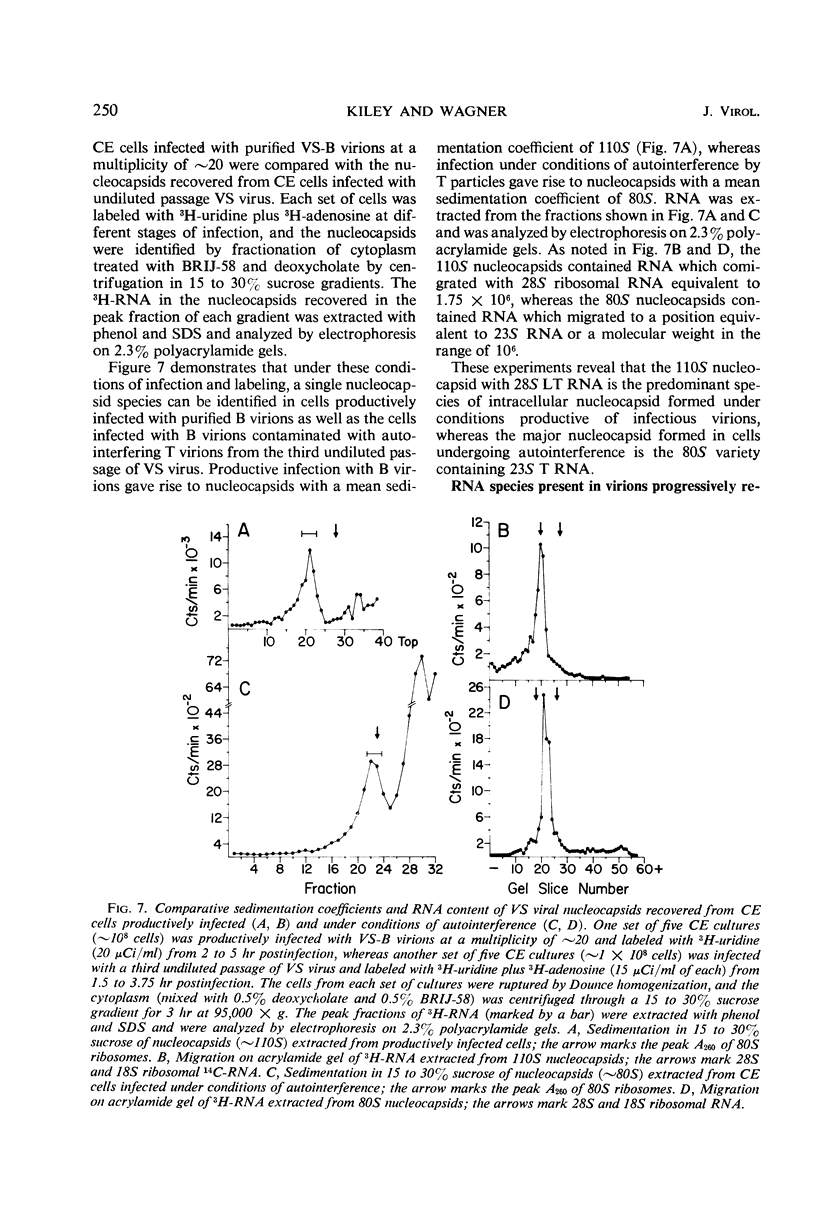
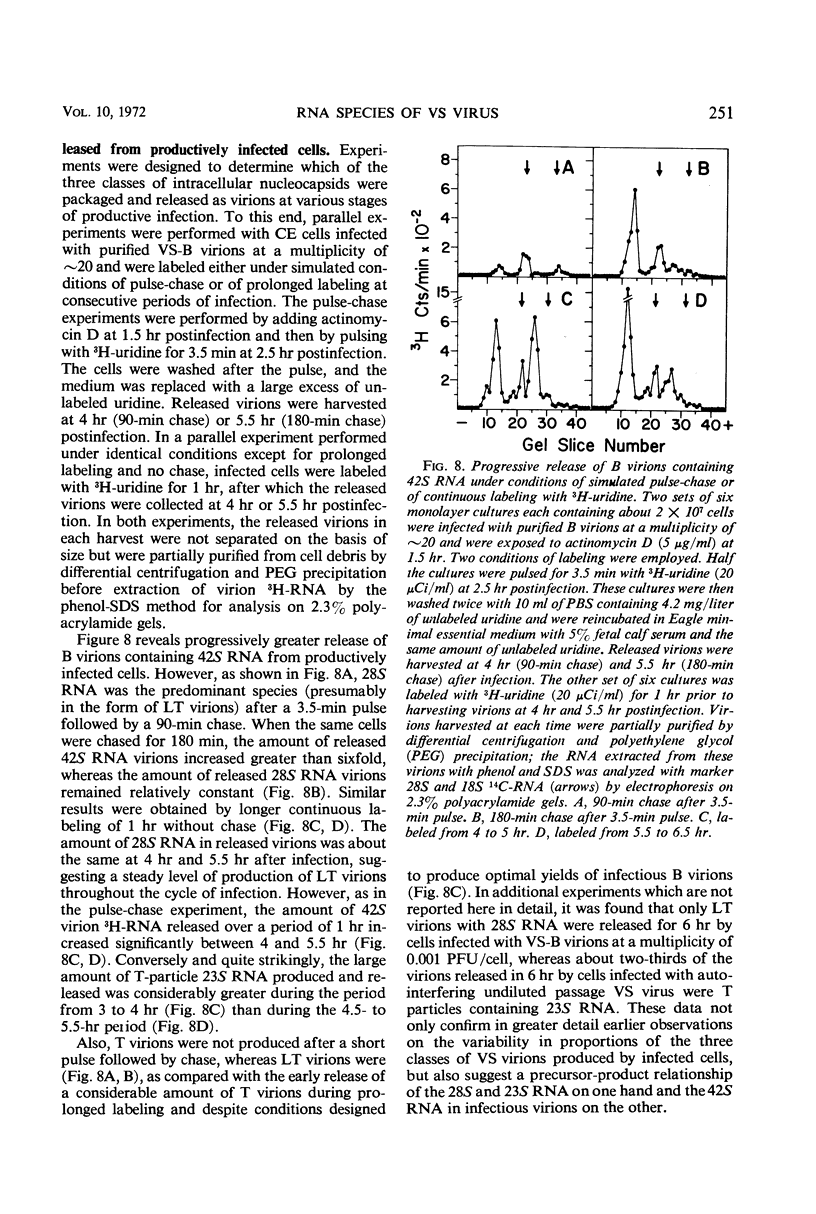
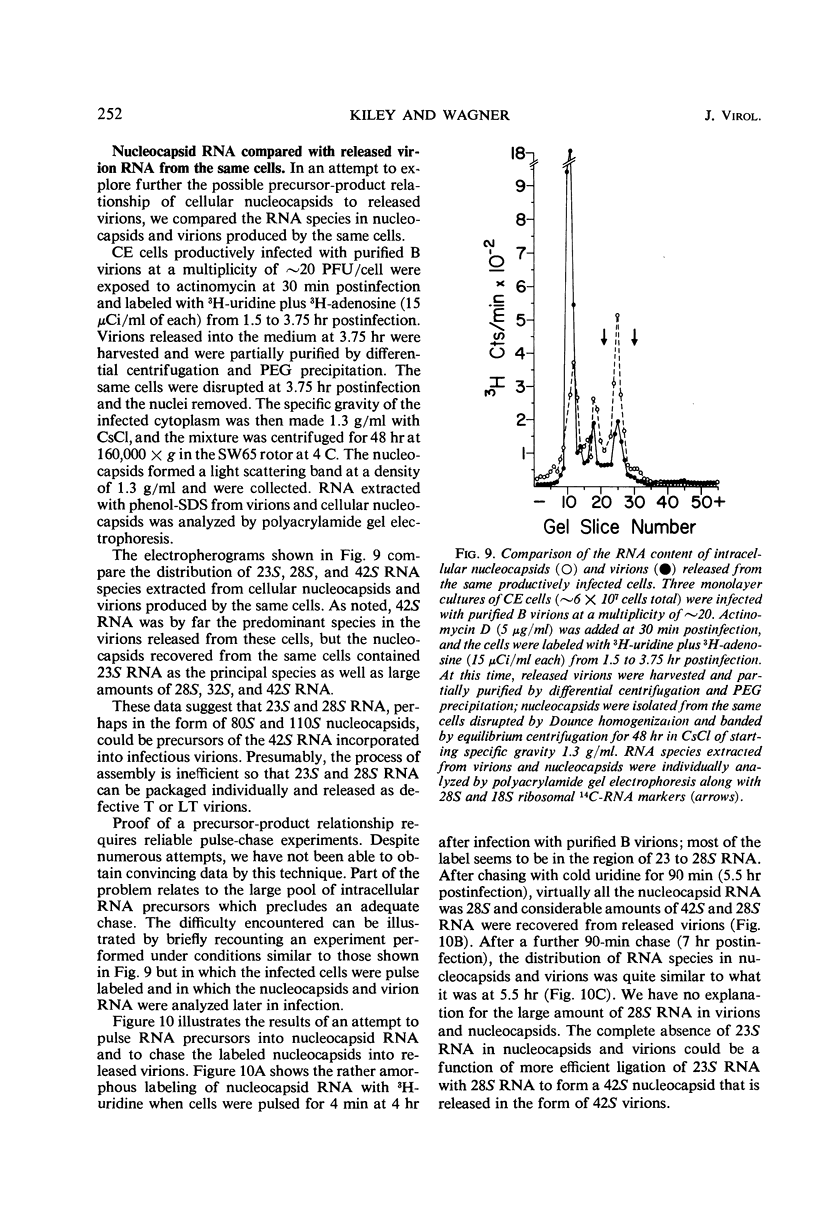
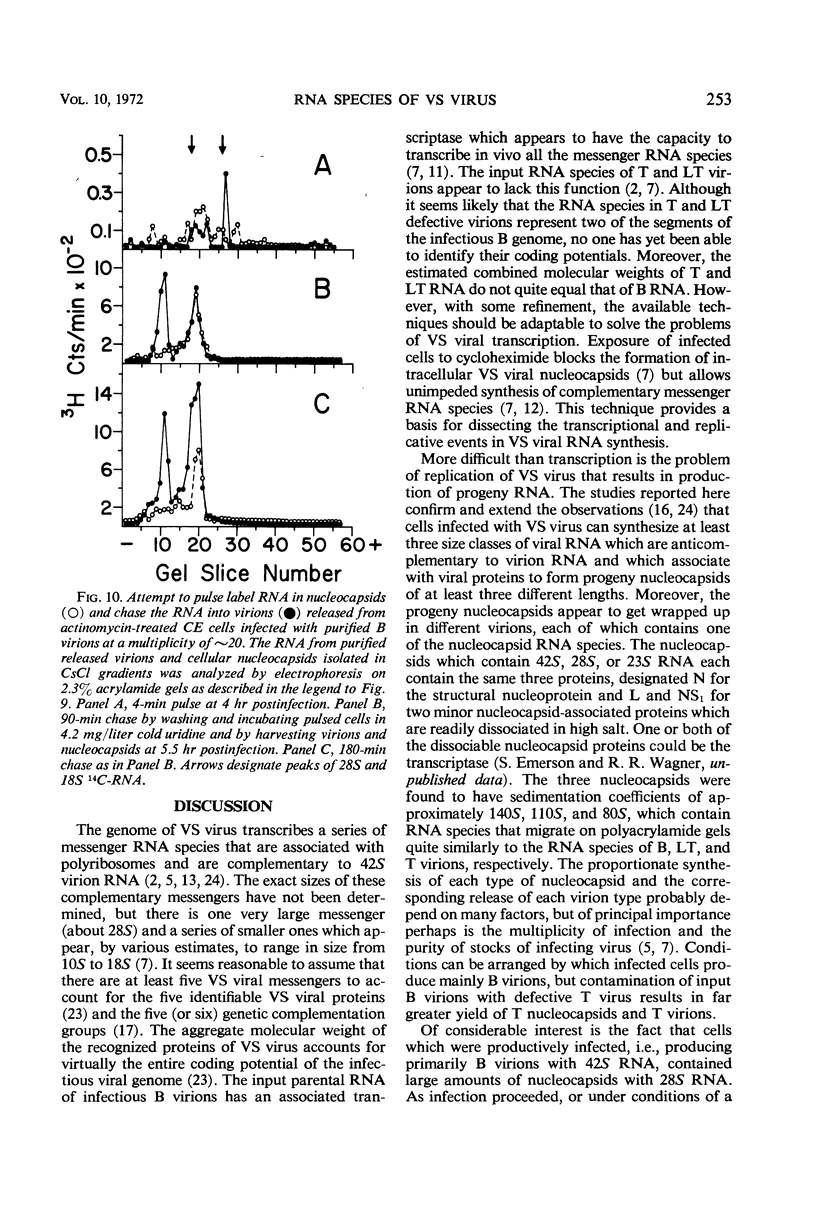
Abstract
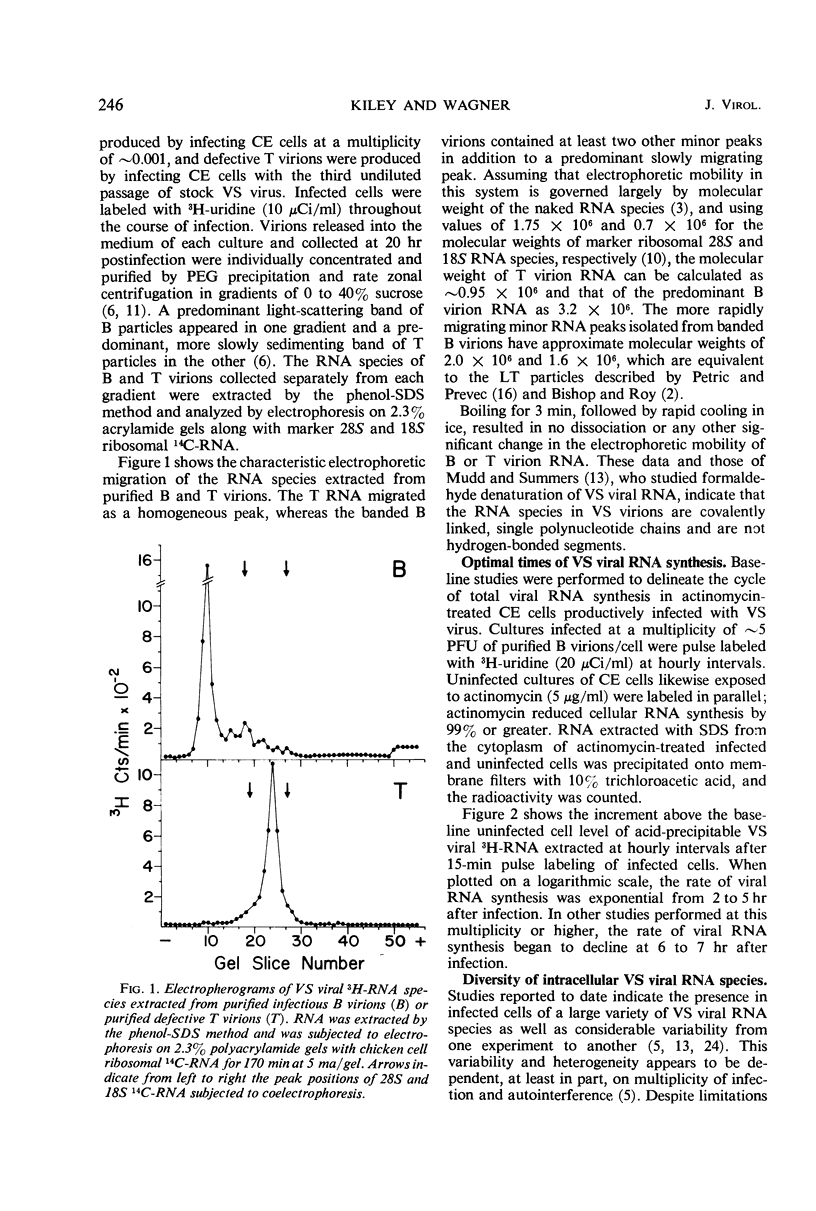
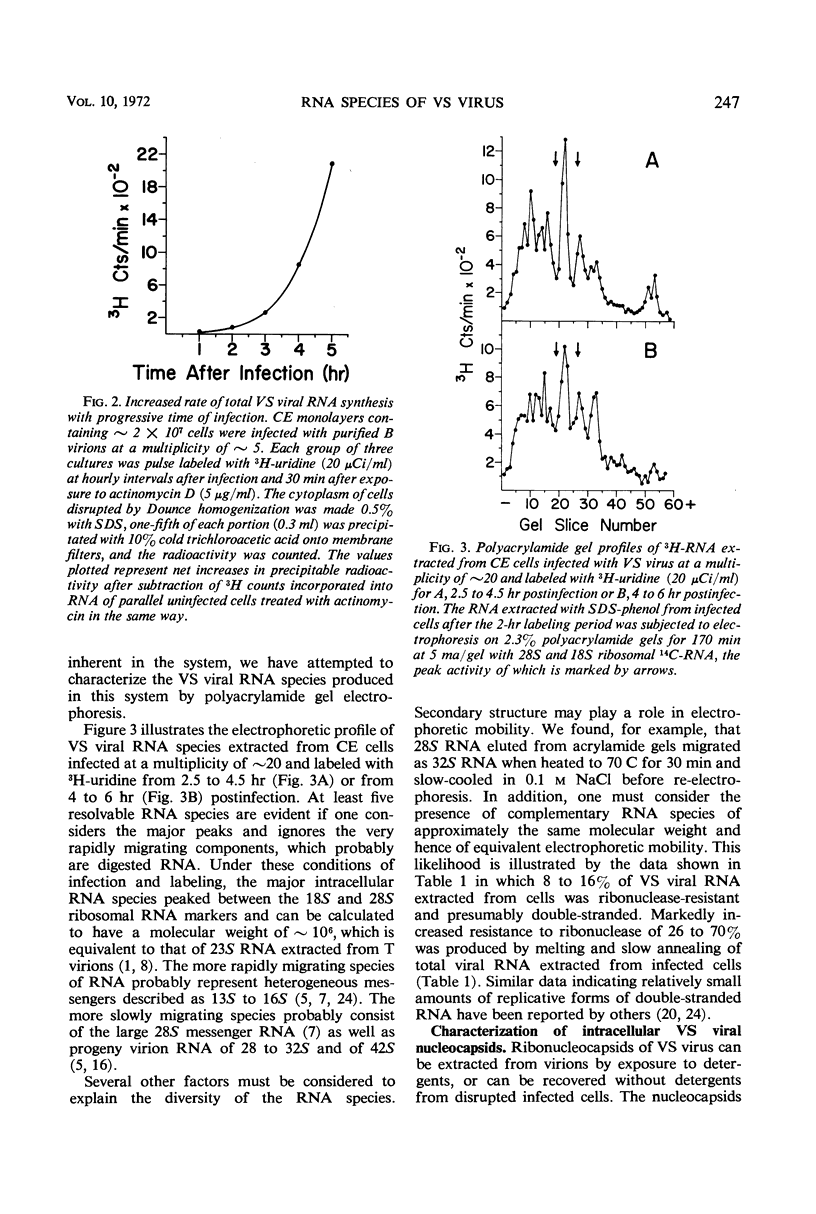
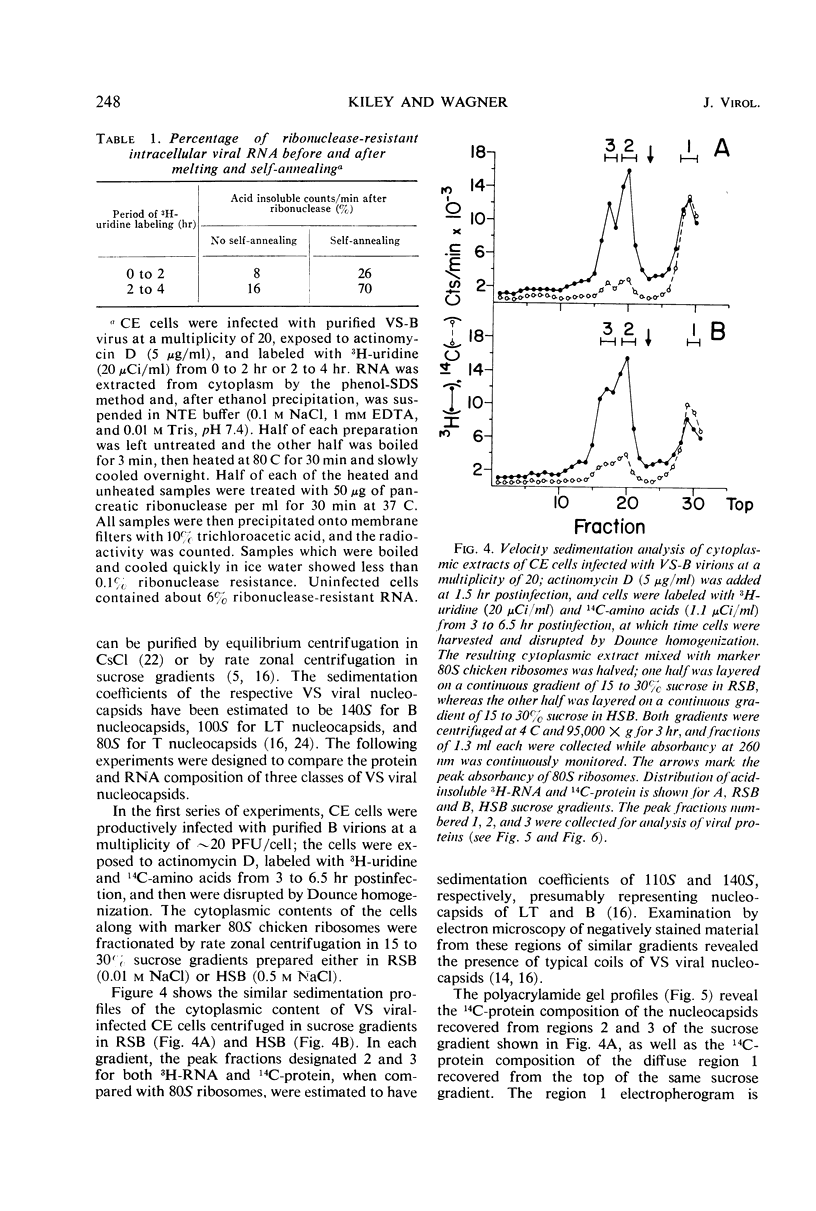
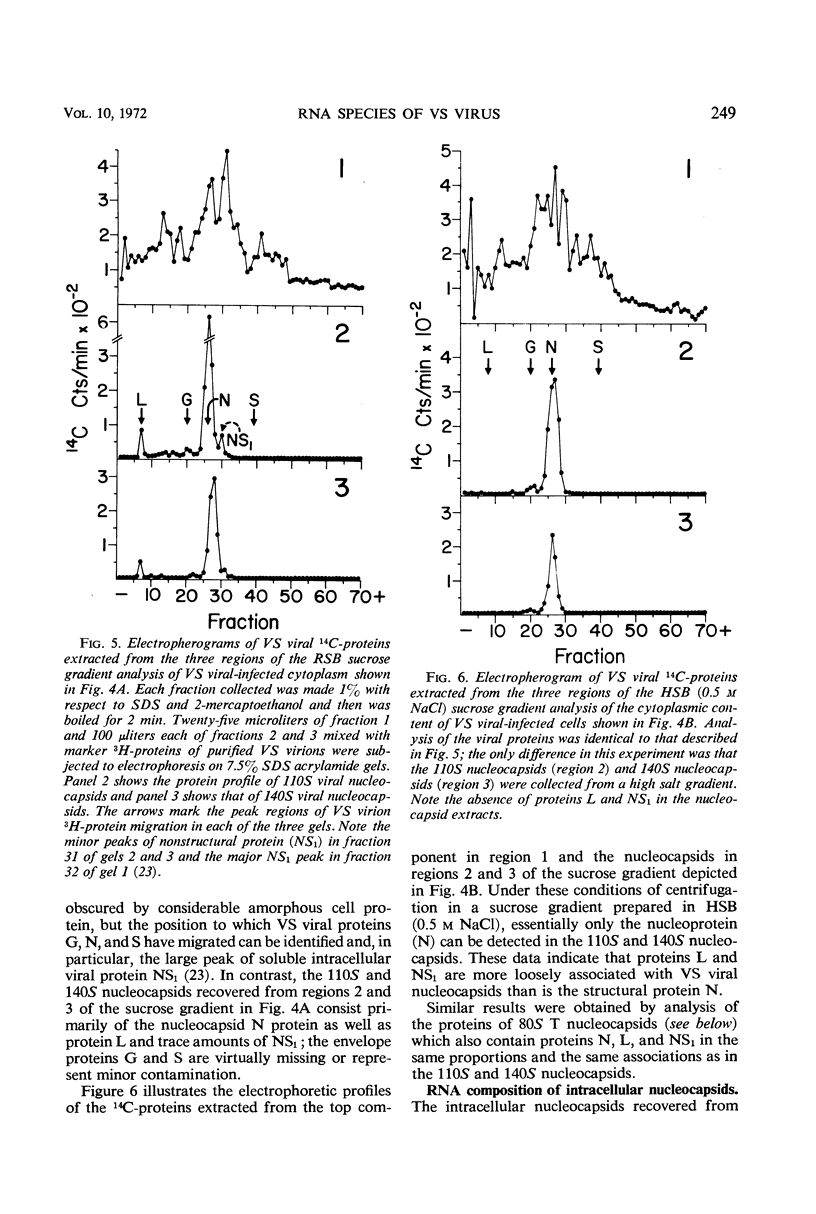
Infection of chicken embryo cells with vesicular stomatitis (VS) virus resulted in variable production of three classes of intracellular viral ribonucleocapsids with sedimentation coefficients of approximately 140S, 110S, and 80S, as well as three corresponding classes of released virions designated B, LT, and T. Intracellular nucleocapsids of each class contained three proteins of which the major N protein was firmly bound, and the minor L and NS1 proteins were readily dissociated with 0.5 m NaCl. The ribonucleic acid (RNA) species extracted from B, LT, and T virions, and from corresponding intracellular nucleocapsids, contained RNA species with approximate molecular weights of 3.2 × 106, 2.0 × 106, and 106, respectively, as determined by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. These values are roughly equivalent to sedimentation coefficients of 42S, 28S, and 23S for each of the virion and nucleocapsid RNA species. Cells infected at high multiplicity with undiluted passage VS virus gave rise primarily to virions and nucleocapsids containing 23S RNA, whereas cells productively infected with purified B virions produced predominantly B and LT virions and nucleocapsids. At late stages in the productive cycle of infection, more virions containing 42S RNA were produced, but the intracellular pool of nucleocapsids containing 28S and 23S RNA remained relatively constant. Additional studies by more refined techniques are required to test the hypothesis that nucleocapsids containing 28S and 23S RNA are precursors of the 42S RNA in infectious VS-B virions and that production of defective T and LT virions results from failure of ligation of the RNA precursors.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bishop D. H., Claybrook J. R., Spiegelman S. Electrophoretic separation of viral nucleic acids on polyacrylamide gels. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 28;26(3):373–387. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90310-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop D. H., Roy P. Kinetics of RNA synthesis by vesicular stomatitis virus particles. J Mol Biol. 1971 May 14;57(3):513–527. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90106-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop D. H., Roy P. Properties of the product synthesized by vesicular stomatitis virus particles. J Mol Biol. 1971 Jun 28;58(3):799–814. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90041-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang A. S., Baltimore D. Defective viral particles and viral disease processes. Nature. 1970 Apr 25;226(5243):325–327. doi: 10.1038/226325a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang A. S., Baltimore D., Stampfer M. Ribonucleic acid synthesis of vesicular stomatitis virus. 3. Multiple complementary messenger RNA molecules. Virology. 1970 Dec;42(4):946–957. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90343-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang A. S., Greenawalt J. W., Wagner R. R. Defective T particles of vesicular stomatitis virus. I. Preparation, morphology, and some biologic properties. Virology. 1966 Oct;30(2):161–172. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(66)90092-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang A. S., Manders E. K. Ribonucleic acid synthesis of vesicular stomatitis virus. IV. Transcription by standard virus in the presence of defective interfering particles. J Virol. 1972 Jun;9(6):909–916. doi: 10.1128/jvi.9.6.909-916.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang A. S., Wagner R. R. Comparative sedimentation coefficients of RNA extracted from plaque-forming and defective particles of vesicular stomatitis virus. J Mol Biol. 1966 Dec 28;22(2):381–384. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(66)90143-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kang C. Y., Prevec L. Proteins of vesicular stomatitis virus. I. Polyacrylamide gel analysis of viral antigens. J Virol. 1969 Apr;3(4):404–413. doi: 10.1128/jvi.3.4.404-413.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loening U. E. Molecular weights of ribosomal RNA in relation to evolution. J Mol Biol. 1968 Dec;38(3):355–365. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90391-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcus P. I., Engelhardt D. L., Hunt J. M., Sekellick M. J. Interferon action: inhibition of vesicular stomatitis virus RNA synthesis induced by virion-bound polymerase. Science. 1971 Nov 5;174(4009):593–598. doi: 10.1126/science.174.4009.593. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McSharry J., Benzinger R. Concentration and purification of vesicular stomatitis virus by polyethylene glycol "precipitation". Virology. 1970 Mar;40(3):745–746. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90219-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mudd J. A., Summers D. F. Polysomal ribonucleic acid of vesicular stomatitis virus-infected HeLa cells. Virology. 1970 Dec;42(4):958–968. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90344-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakai T., Howatson A. F. The fine structure of vesicular stomatitis virus. Virology. 1968 Jun;35(2):268–281. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(68)90267-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penman S., Scherrer K., Becker Y., Darnell J. E. POLYRIBOSOMES IN NORMAL AND POLIOVIRUS-INFECTED HELA CELLS AND THEIR RELATIONSHIP TO MESSENGER-RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 May;49(5):654–662. doi: 10.1073/pnas.49.5.654. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petric M., Prevec L. Vesicular stomatitis virus--a new interfering particle, intracellular structures, and virus-specific RNA. Virology. 1970 Aug;41(4):615–630. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90427-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pringle C. R., Duncan I. B., Stevenson M. Isolation and characterization of temperature-sensitive mutants of vesicular stomatitis virus, New Jersey serotype. J Virol. 1971 Dec;8(6):836–841. doi: 10.1128/jvi.8.6.836-841.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reichmann M. E., Pringle C. R., Follett E. A. Defective particles in BHK cells infected with temperature-sensitive mutants of vesicular stomatitis virus. J Virol. 1971 Aug;8(2):154–160. doi: 10.1128/jvi.8.2.154-160.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaffer F. L., Soergel M. E., Tegtmeier G., Schechmeister I. L. Unusual molecular size of RNA from a long-rod mutant of vesicular stomatitis virus. Virology. 1972 Jan;47(1):236–238. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90255-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schincariol A. L., Howatson A. F. Replication of vesicular stomatitis virus. I. Viral specific RNA and nucleoprotein in infected L cells. Virology. 1970 Nov;42(3):732–743. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90319-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner R. R., Schnaitman T. C., Snyder R. M., Schnaitman C. A. Protein composition of the structural components of vesicular stomatitis virus. J Virol. 1969 Jun;3(6):611–618. doi: 10.1128/jvi.3.6.611-618.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner R. R., Snyder R. M., Yamazaki S. Proteins of vesicular stomatitis virus: kinetics and cellular sites of synthesis. J Virol. 1970 May;5(5):548–558. doi: 10.1128/jvi.5.5.548-558.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wild T. F. Replication of vesicular stomatitis virus: characterization of the virus-induced RNA. J Gen Virol. 1971 Nov;13(2):295–310. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-13-2-295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



