Abstract
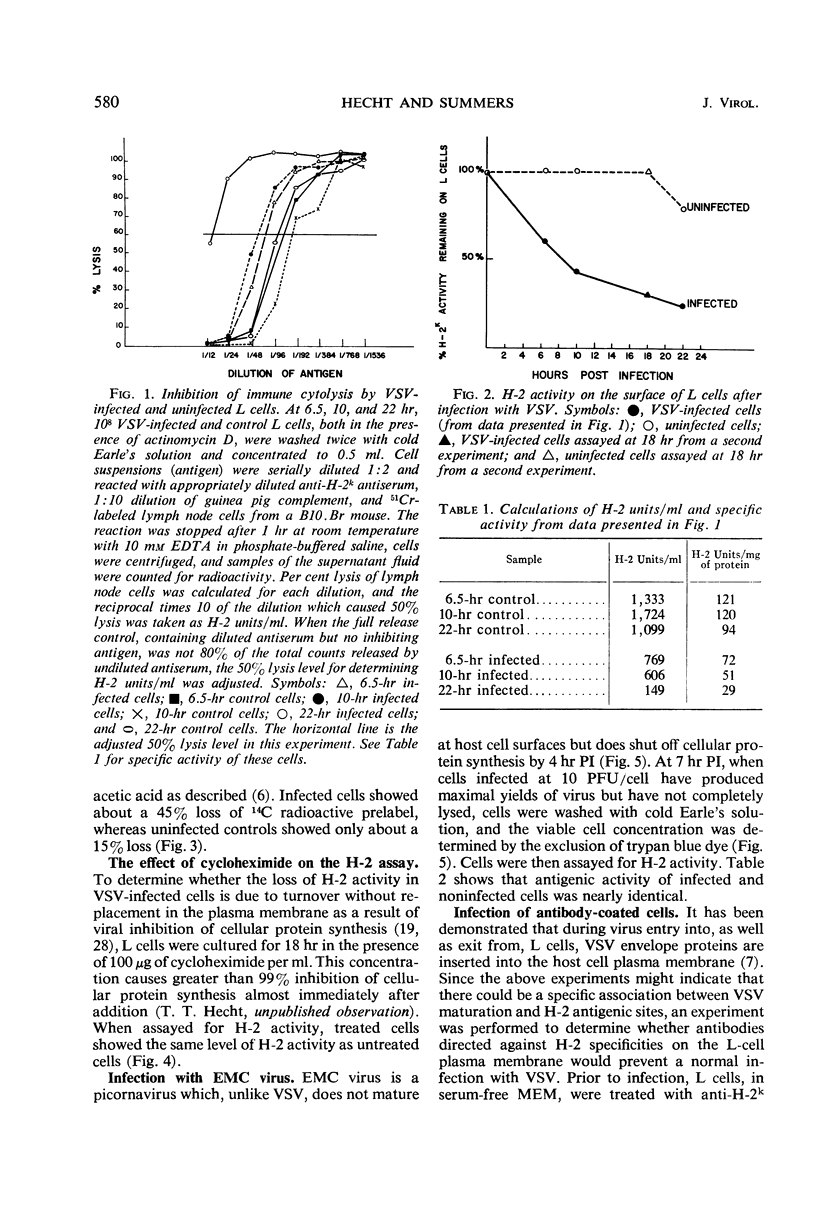
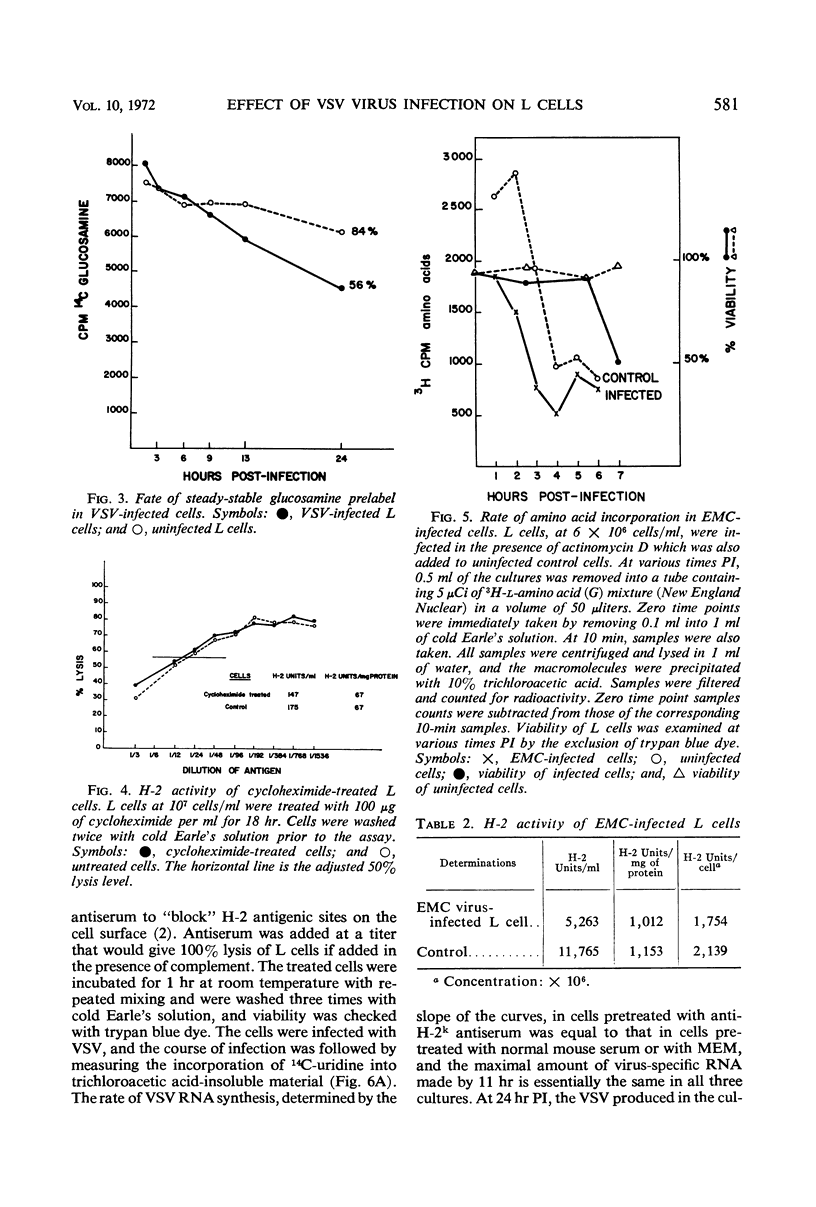
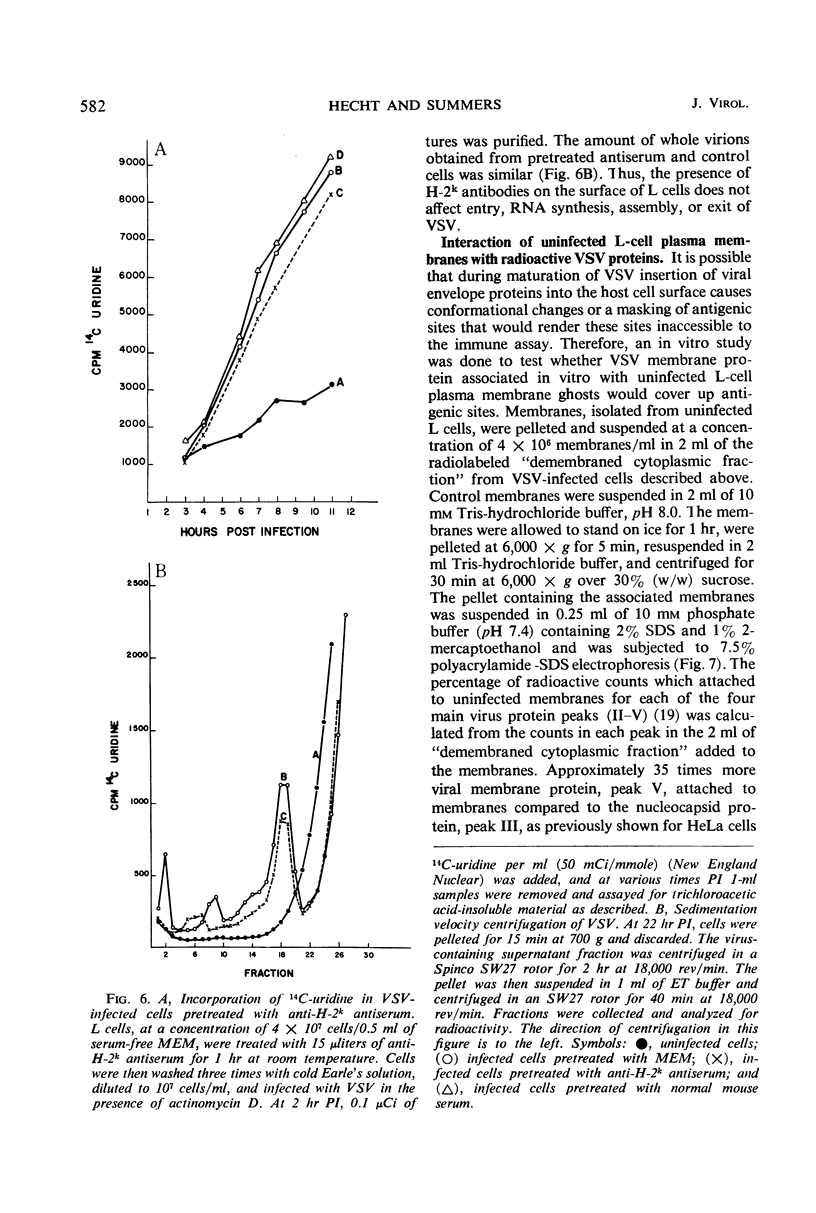
When mouse L cells are infected for 22 hr with vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV), a ribonucleic acid-containing enveloped virus, greater than 70% of the major histocompatibility antigen (H-2), is no longer detectable by the method of inhibition of immune cytolysis. Infected cells prelabeled with 14C-glucosamine also show a correspondingly greater loss of trichloroacetic acid-insoluble radioactivity than uninfected cells. The loss of H-2 antigenic activity is not due to the viral inhibition of host cell protein synthesis since cells cultured for 18 hr in the presence of cycloheximide have the same amount of H-2 activity as untreated controls. Also, cells infected with encephalomyocarditis virus, a picornavirus, show no loss of H-2 activity at a time when host cell protein synthesis is completely inhibited. VSV structural proteins associated in vitro with uninfected L-cell plasma membranes do not render H-2 sites inaccessible to the assay. Although antibodies may not combine with all the H-2 antigenic sites on the plasma membrane, anti-H-2 serum reacted with L cells before infection does not prevent a normal infection with VSV. H-2 activity can be detected in virus samples purified from the medium of infected L cells; this virus purified after being mixed with L-cell homogenates shows greater H-2 activity than virus purified after being mixed with HeLa cell homogenates. However, VSV made in HeLa cells shows no H-2 activity when mixed with L-cell homogenates.
Full text
PDF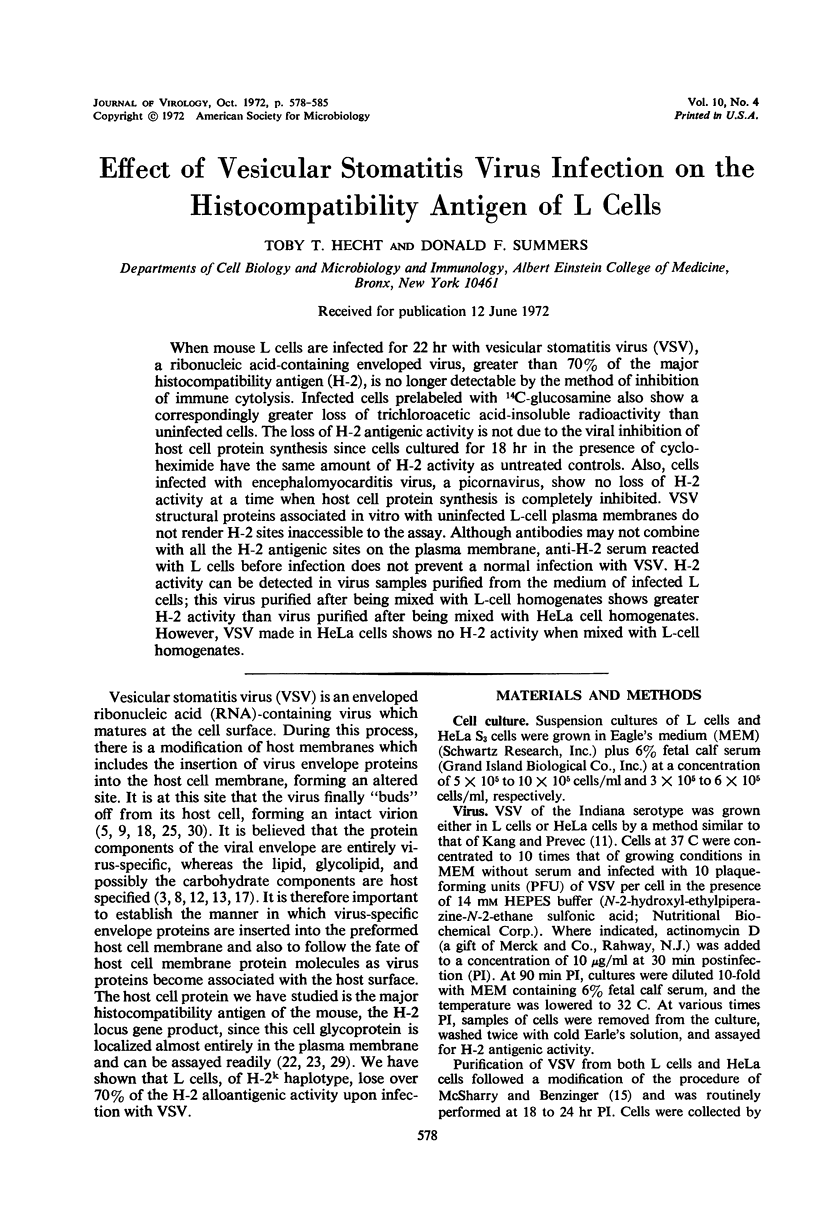

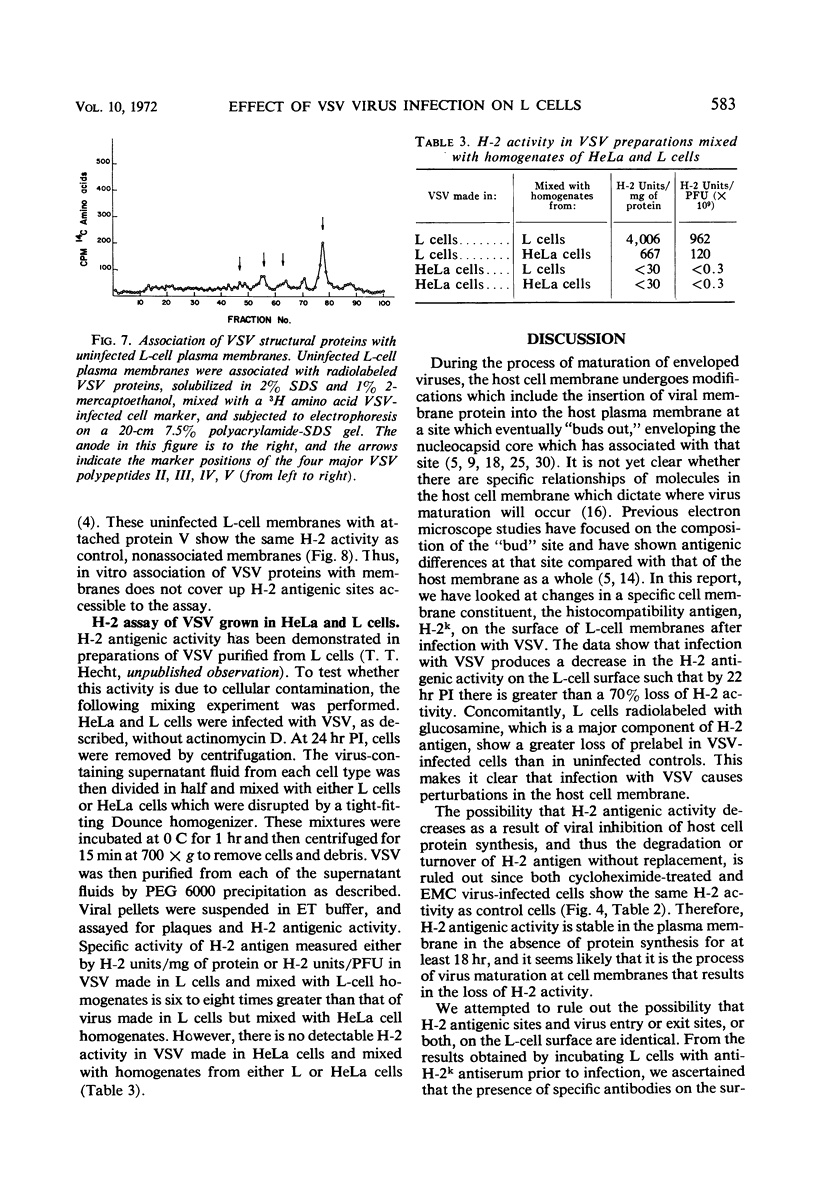
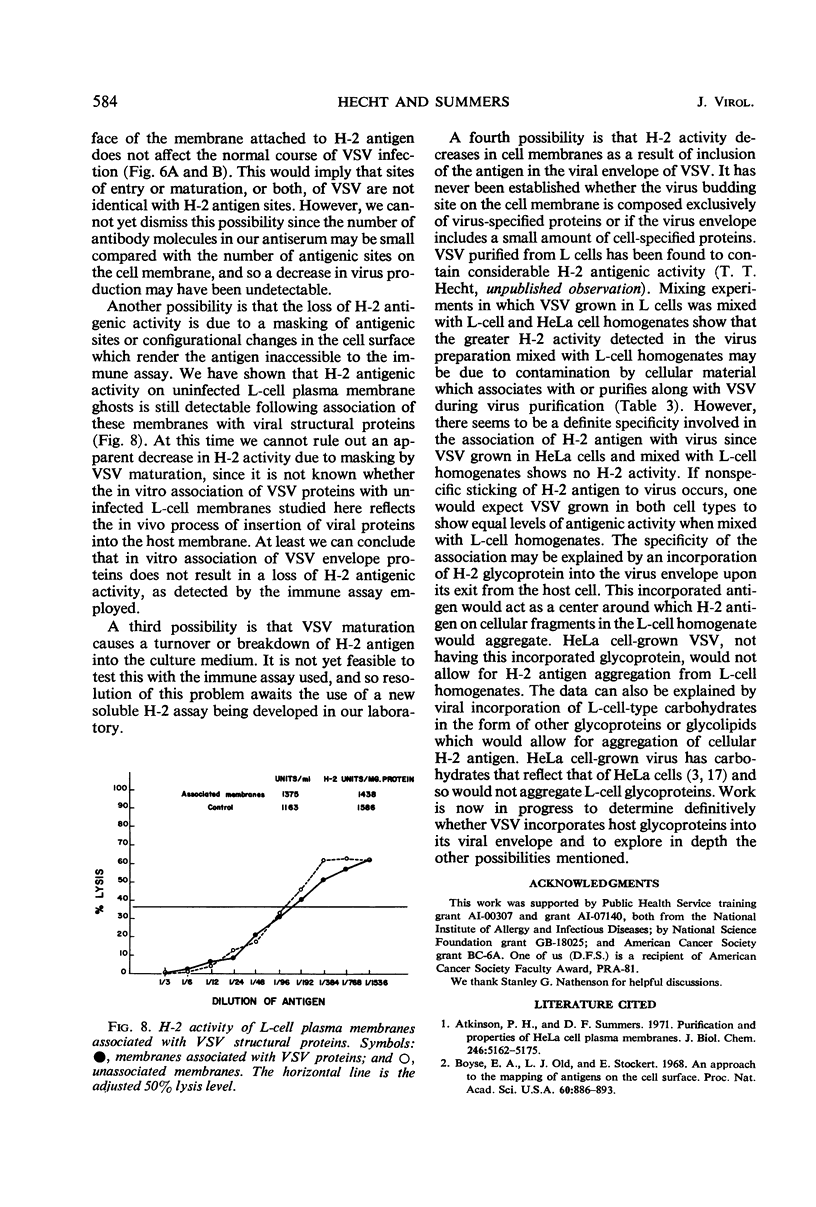

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atkinson P. H., Summers D. F. Purification and properties of HeLa cell plasma membranes. J Biol Chem. 1971 Aug 25;246(16):5162–5175. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyse E. A., Old L. J., Stockert E. An approach to the mapping of antigens on the cell surface. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Jul;60(3):886–893. doi: 10.1073/pnas.60.3.886. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burge B. W., Huang A. S. Comparison of membrane protein glycopeptides of Sindbis virus and vesicular stomatitis virus. J Virol. 1970 Aug;6(2):176–182. doi: 10.1128/jvi.6.2.176-182.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen G. H., Atkinson P. H., Summers D. F. Interactions of vesicular stomatitis virus structural proteins with HeLa plasma membranes. Nat New Biol. 1971 May 26;231(21):121–123. doi: 10.1038/newbio231121a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOWATSON A. F., WHITMORE G. F. The development and structure of vesicular stomatitis virus. Virology. 1962 Apr;16:466–478. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(62)90228-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hecht T. T., Summers D. F. The effect of phleomycin on poliovirus RNA replication. Virology. 1970 Mar;40(3):441–447. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90187-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heine J. W., Schnaitman C. A. Entry of vesicular stomatitis virus into L cells. J Virol. 1971 Nov;8(5):786–795. doi: 10.1128/jvi.8.5.786-795.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland J. J., Kiehn E. D. Influenza virus effects on cell membrane proteins. Science. 1970 Jan 9;167(3915):202–205. doi: 10.1126/science.167.3915.202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kang C. Y., Prevec L. Proteins of vesicular stomatitis virus. I. Polyacrylamide gel analysis of viral antigens. J Virol. 1969 Apr;3(4):404–413. doi: 10.1128/jvi.3.4.404-413.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klenk H. D., Choppin P. W. Glycosphingolipids of plasma membranes of cultured cells and an enveloped virus (SV5) grown in these cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 May;66(1):57–64. doi: 10.1073/pnas.66.1.57. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klenk H. D., Choppin P. W. Lipids of plasma membranes of monkey and hamster kidney cells and of parainfluenza virions grown in these cells. Virology. 1969 Jun;38(2):255–268. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90367-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klenk H. D., Compans R. W., Choppin W. P. An electron microscopic study of the presence or absence of neuraminic acid in enveloped viruses. Virology. 1970 Dec;42(4):1158–1162. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90368-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McSharry J. J., Compans R. W., Choppin P. W. Proteins of vesicular stomatitis virus and of phenotypically mixed vesicular stomatitis virus-simian virus 5 virions. J Virol. 1971 Nov;8(5):722–729. doi: 10.1128/jvi.8.5.722-729.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McSharry J. J., Wagner R. R. Carbohydrate composition of vesicular stomatitis virus. J Virol. 1971 Mar;7(3):412–415. doi: 10.1128/jvi.7.3.412-415.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McSharry J., Benzinger R. Concentration and purification of vesicular stomatitis virus by polyethylene glycol "precipitation". Virology. 1970 Mar;40(3):745–746. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90219-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mudd J. A., Summers D. F. Protein synthesis in vesicular stomatitis virus-infected HeLa cells. Virology. 1970 Oct;42(2):328–340. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90277-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muramatsu T., Nathenson S. G. Studies on the carbohydrate portion of membrane-located mouse H-2 alloantigens. Biochemistry. 1970 Dec 8;9(25):4875–4883. doi: 10.1021/bi00827a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathenson S. G. Biochemical properties of histocompatibility antigens. Annu Rev Genet. 1970;4(0):69–90. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.04.120170.000441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathenson S. G., Davies D. A. Solubilization and partial purification of mouse histocompatibility antigens from a membranous lipoprotein fraction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Aug;56(2):476–483. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.2.476. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SANDERSON A. R. CYTOTOXIC REACTIONS OF MOUSE ISO-ANTISERA: PRELIMINARY CONSIDERATIONS. Br J Exp Pathol. 1964 Aug;45:398–408. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro A. L., Viñuela E., Maizel J. V., Jr Molecular weight estimation of polypeptide chains by electrophoresis in SDS-polyacrylamide gels. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1967 Sep 7;28(5):815–820. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(67)90391-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WIGZELL H. QUANTITATIVE TITRATIONS OF MOUSE H-2 ANTIBODIES USING CR-51-LABELLED TARGET CELLS. Transplantation. 1965 May;3:423–431. doi: 10.1097/00007890-196505000-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner R. R., Kiley M. P., Snyder R. M., Schnaitman C. A. Cytoplasmic compartmentalization of the protein and ribonucleic acid species of vesicular stomatitis virus. J Virol. 1972 Apr;9(4):672–683. doi: 10.1128/jvi.9.4.672-683.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallis C., Melnick J. L. Stabilization of enveloped viruses by dimethyl sulfoxide. J Virol. 1968 Sep;2(9):953–954. doi: 10.1128/jvi.2.9.953-954.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wertz G. W., Youngner J. S. Inhibition of protein synthesis in L cells infected with vesicular stomatitis virus. J Virol. 1972 Jan;9(1):85–89. doi: 10.1128/jvi.9.1.85-89.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zee Y. C., Hackett A. J., Talens L. Vesicular stomatitis virus maturation sites in six different host cells. J Gen Virol. 1970;7(2):95–102. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-7-2-95. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


