Abstract
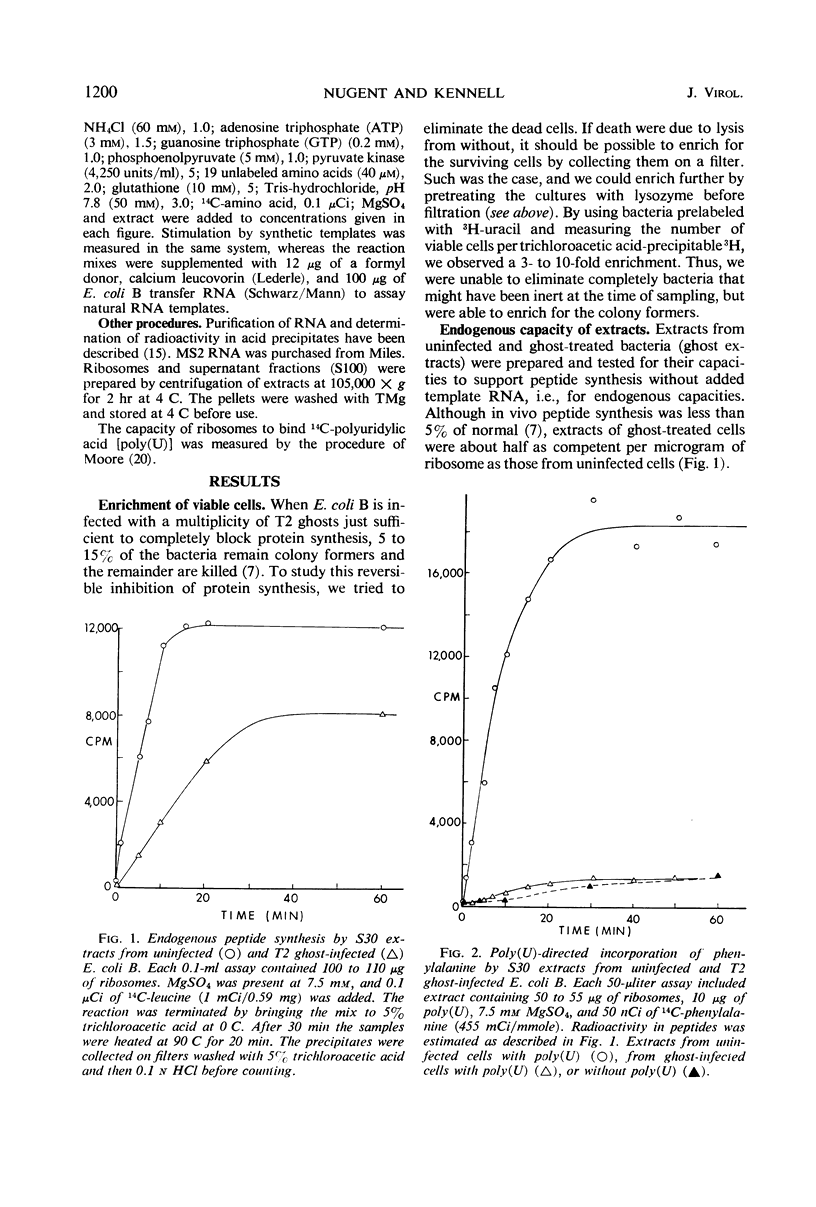
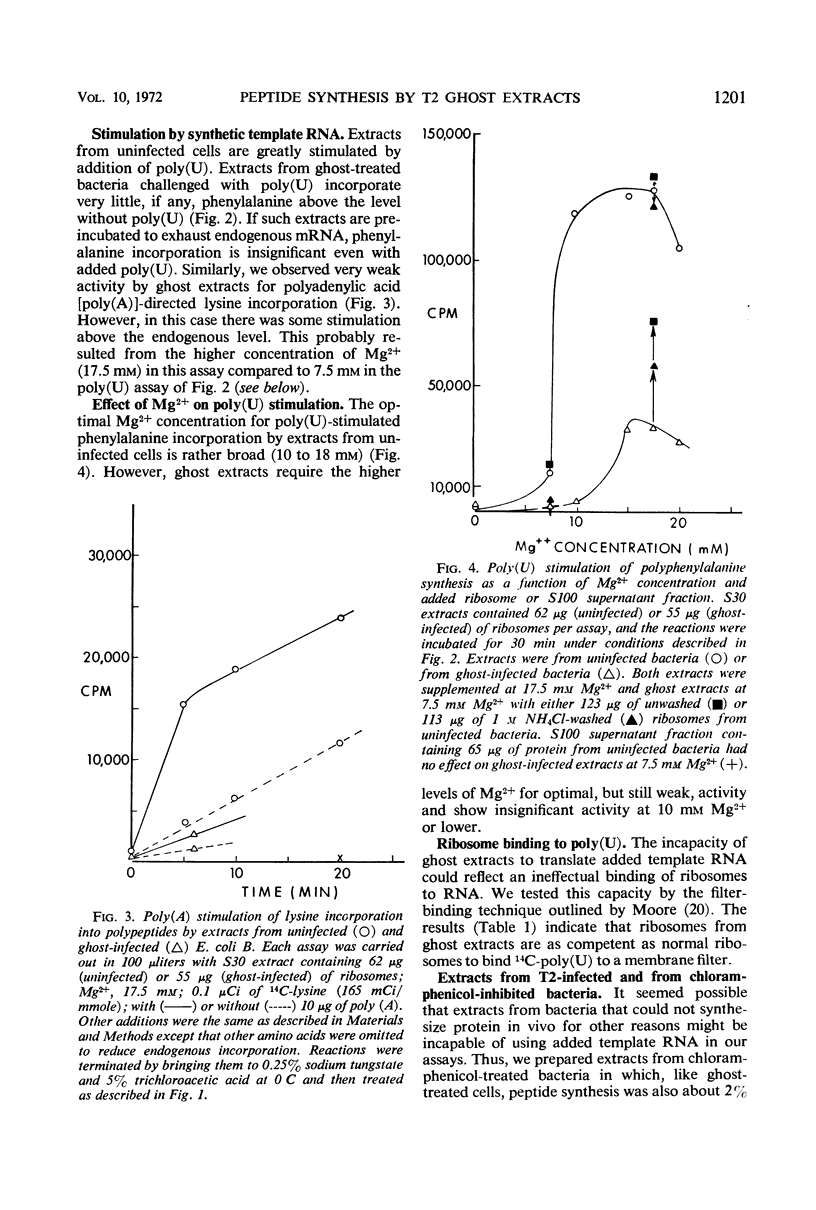
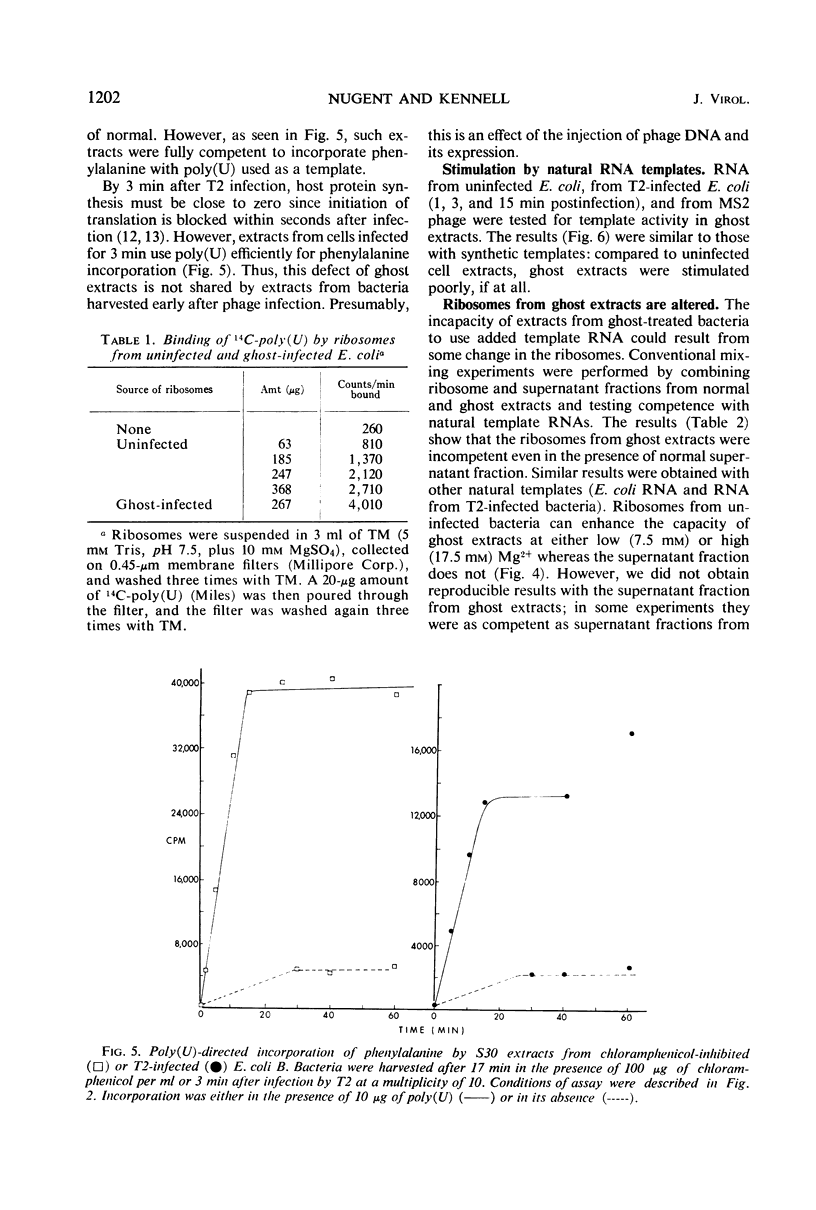
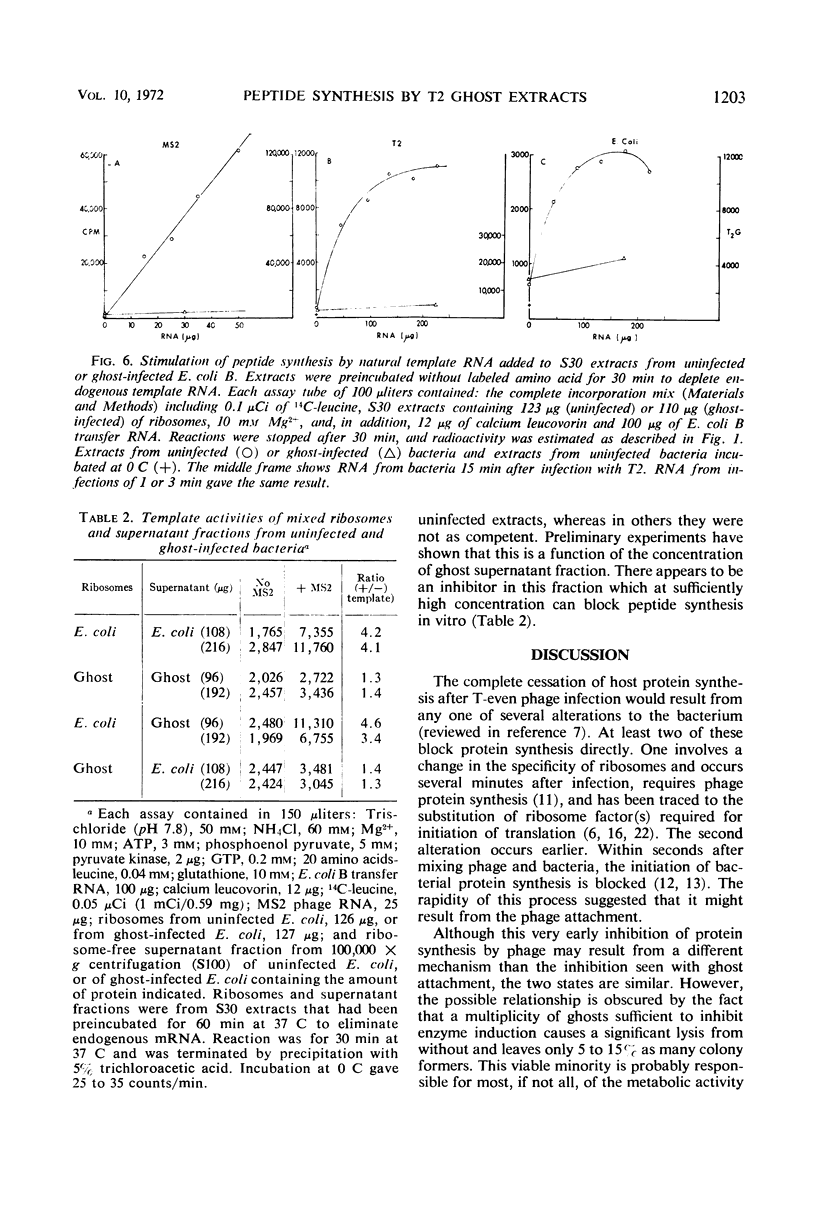
Infection of Escherichia coli B in inorganic salts-glycerol with a multiplicity of deoxyribonucleic acid-less T2 “ghosts” just sufficient to block all protein synthesis results in both viable and killed bacteria. We enriched for the viable cells by a combination of lysozyme treatment and filtration and measured the in vitro capacity of their extracts to synthesize polypeptides. Without added template ribonucleic acid (RNA), such “ghost extracts” incorporate amino acids (endogenous synthesis) at approximately one-half the rate as do extracts from uninfected bacteria. However, they are unable to use added synthetic or natural template RNAs for peptide synthesis. Some activity can be observed but only at high concentrations of Mg2+. These results suggest that ghost infection may result in a blockage of ribosomes during translation. Mixing experiments show that the incapacity of ghost extracts to translate added template RNA is due to a defect in the ribosomes.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson E. H. Growth Requirements of Virus-Resistant Mutants of Escherichia Coli Strain "B". Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1946 May;32(5):120–128. doi: 10.1073/pnas.32.5.120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BENZER S. Induced synthesis of enzymes in bacteria analyzed at the cellular level. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1953 Jul;11(3):383–395. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(53)90057-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BONIFAS V., KELLENBERGER E. Etude de l'action des membranes du bactériophage T2 sur Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1955 Mar;16(3):330–338. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(55)90234-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bilezikian J. P., Kaempfer R. O., Magasanik B. Mechanism of tryptophanase induction in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1967 Aug 14;27(3):495–506. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90054-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capecchi M. R. Initiation of E. coli proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Jun;55(6):1517–1524. doi: 10.1073/pnas.55.6.1517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dube S. K., Rudland P. S. Control of translation by T4 phage: altered binding of disfavoured messengers. Nature. 1970 May 30;226(5248):820–823. doi: 10.1038/226820a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRENCH R. C., SIMINOVITCH L. The action of T2 bacteriophage ghosts on Escherichia coli B. Can J Microbiol. 1955 Dec;1(9):757–774. doi: 10.1139/m55-090. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabricant R., Kennell D. Exclusion of bacteriophages by T2 ghosts. J Virol. 1972 Oct;10(4):872–874. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.4.872-874.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabricant R., Kennell D. Inhibition of host protein synthesis during infection of Escherichi coli by bacteriophage T4. 3. Inhibition by ghosts. J Virol. 1970 Dec;6(6):772–781. doi: 10.1128/jvi.6.6.772-781.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HERRIOTT R. M., BARLOW J. L. The protein coats or ghosts of coli phage T2. II. The biological functions. J Gen Physiol. 1957 Nov 20;41(2):307–331. doi: 10.1085/jgp.41.2.307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu W. T., Weiss S. B. Selective translation of T4 template RNA by ribosomes from T4-infected Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Sep;64(1):345–351. doi: 10.1073/pnas.64.1.345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaempfer R. O., Magasanik B. Mechanism of beta-galactosidase induction in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1967 Aug 14;27(3):475–494. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90053-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennell D. Inhibition of host protein synthesis during infection of Escherichia coli by bacteriophage T4. I. Continued synthesis of host ribonucleic acid. J Virol. 1968 Nov;2(11):1262–1271. doi: 10.1128/jvi.2.11.1262-1271.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennell D. Inhibition of host protein synthesis during infection of Escherichia coli by bacteriophage T4. II. Induction of host messenger ribonucleic acid and its exclusion from polysomes. J Virol. 1970 Aug;6(2):208–217. doi: 10.1128/jvi.6.2.208-217.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennell D., Kotoulas A. Magnesium starvation of Aerobacter aerogenes. I. Changes in nucleic acid composition. J Bacteriol. 1967 Jan;93(1):334–344. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.1.334-344.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klem E. B., Hsu W. T., Weiss S. B. The selective inhibition of protein initiation by T4 phage-induced factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Oct;67(2):696–701. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.2.696. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVIN A. P., BURTON K. Inhibition of enzyme formation following infection of Escherichia coli with phage T2r. J Gen Microbiol. 1961 Jun;25:307–314. doi: 10.1099/00221287-25-2-307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landy A., Spiegelman S. Exhaustive hybridization and its application to an analysis of the ribonucleic acid synthesized in T4-infected cells. Biochemistry. 1968 Feb;7(2):585–591. doi: 10.1021/bi00842a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore P. B. Polynucleotide attachment to ribosomes. J Mol Biol. 1966 Jun;18(1):8–20. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80072-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHER I. H., MALLETTE M. F. The adaptive nature of the formation of lysine decarboxylase in Escherichia coli B. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1954 Oct;52(2):331–339. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(54)90131-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steitz J. A., Dube S. K., Rudland P. S. Control of translation of T4 phage: altered ribosome binding at R17 initiation sites. Nature. 1970 May 30;226(5248):824–827. doi: 10.1038/226824a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



