Abstract
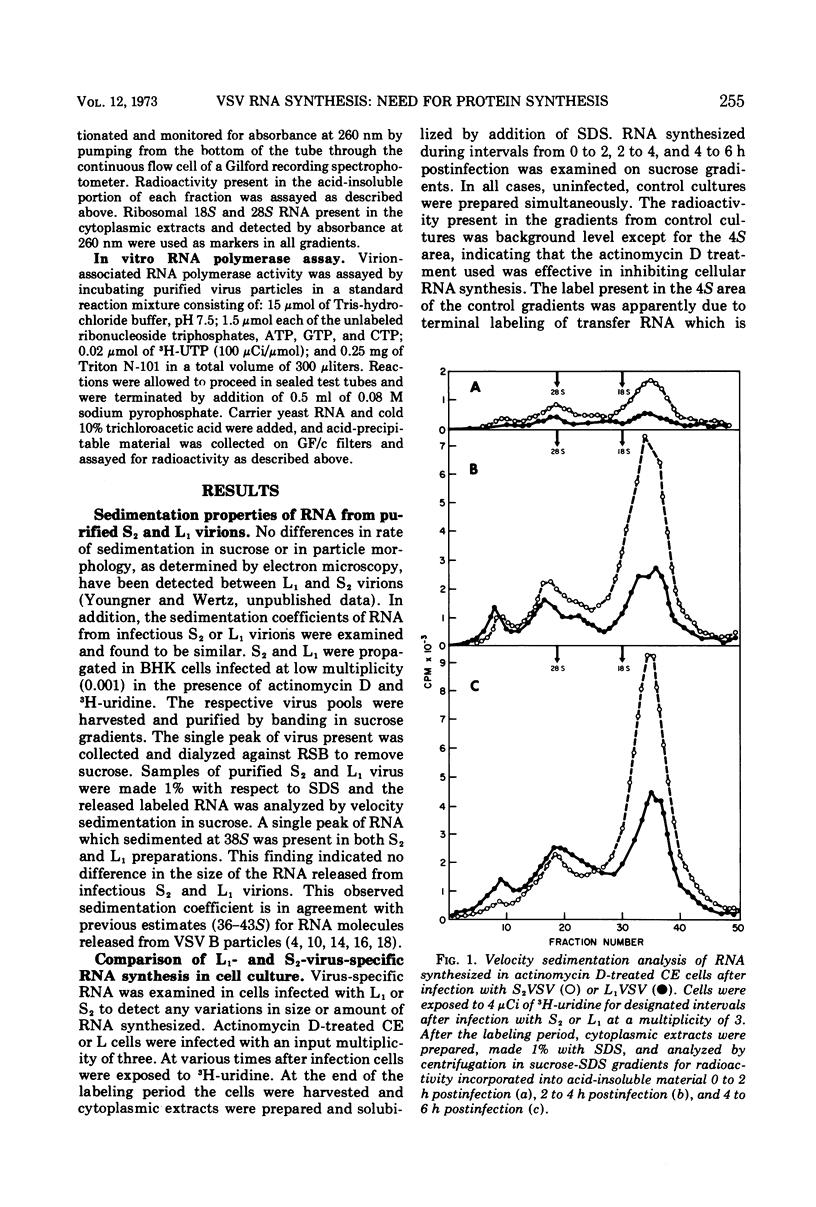
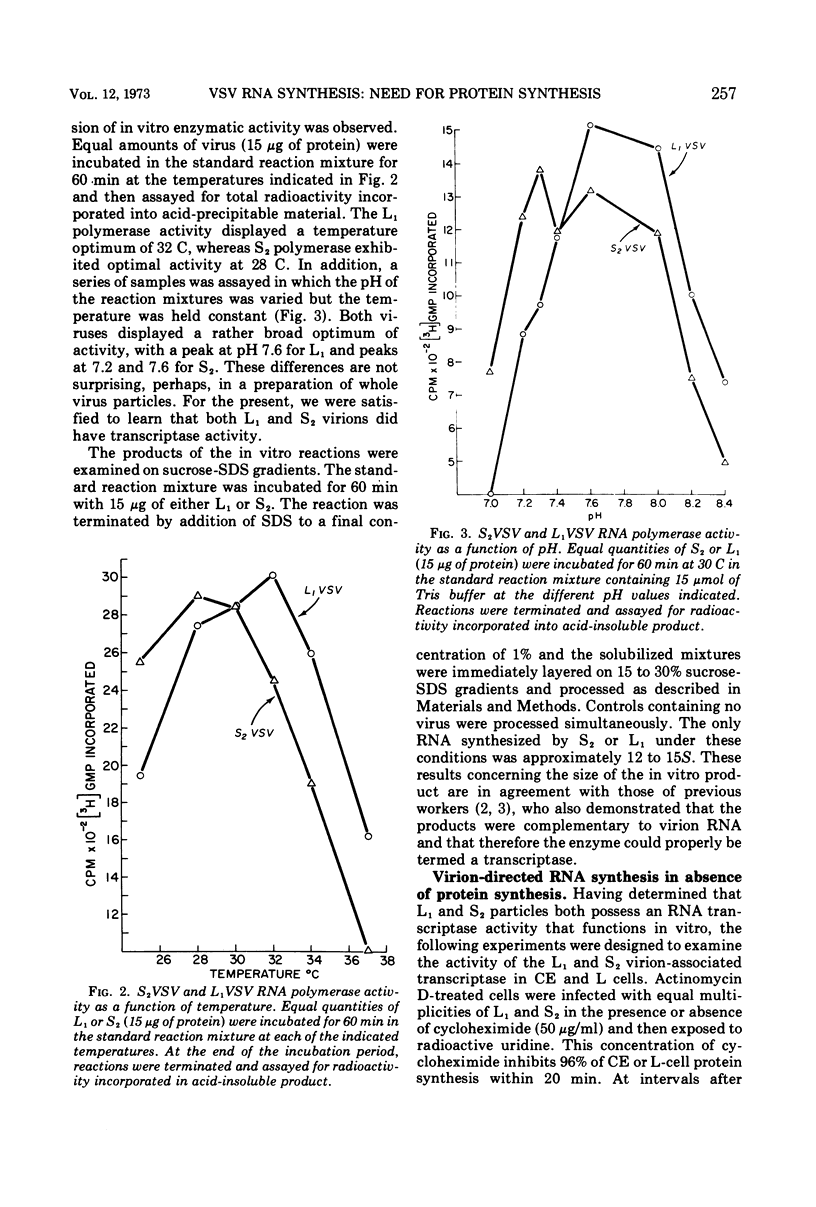
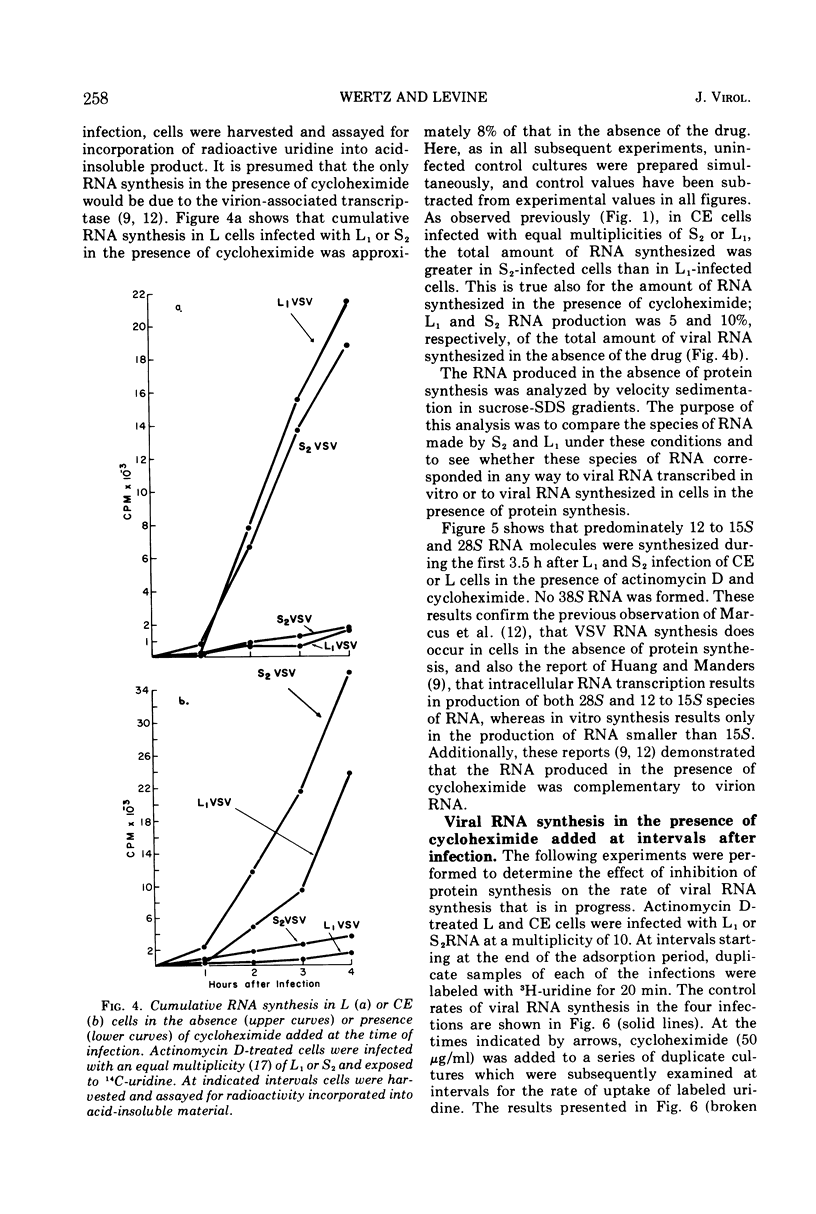
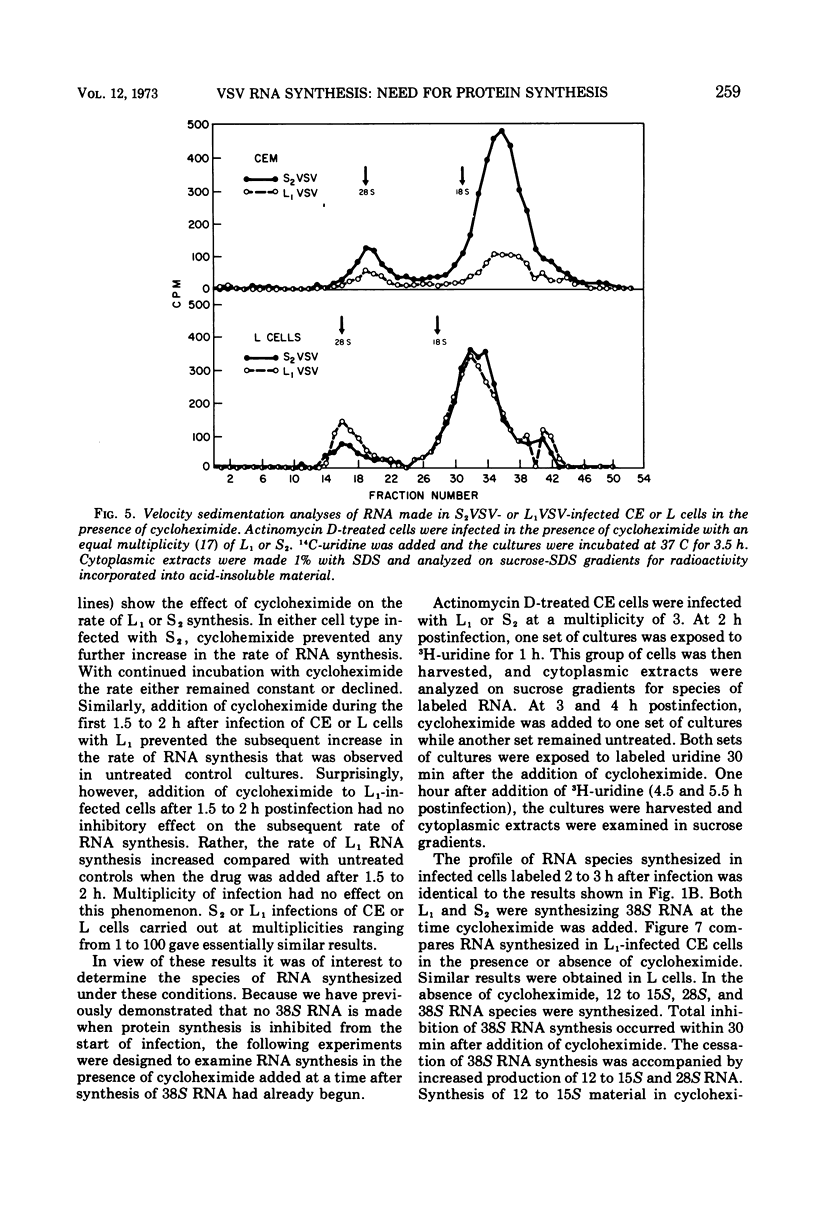
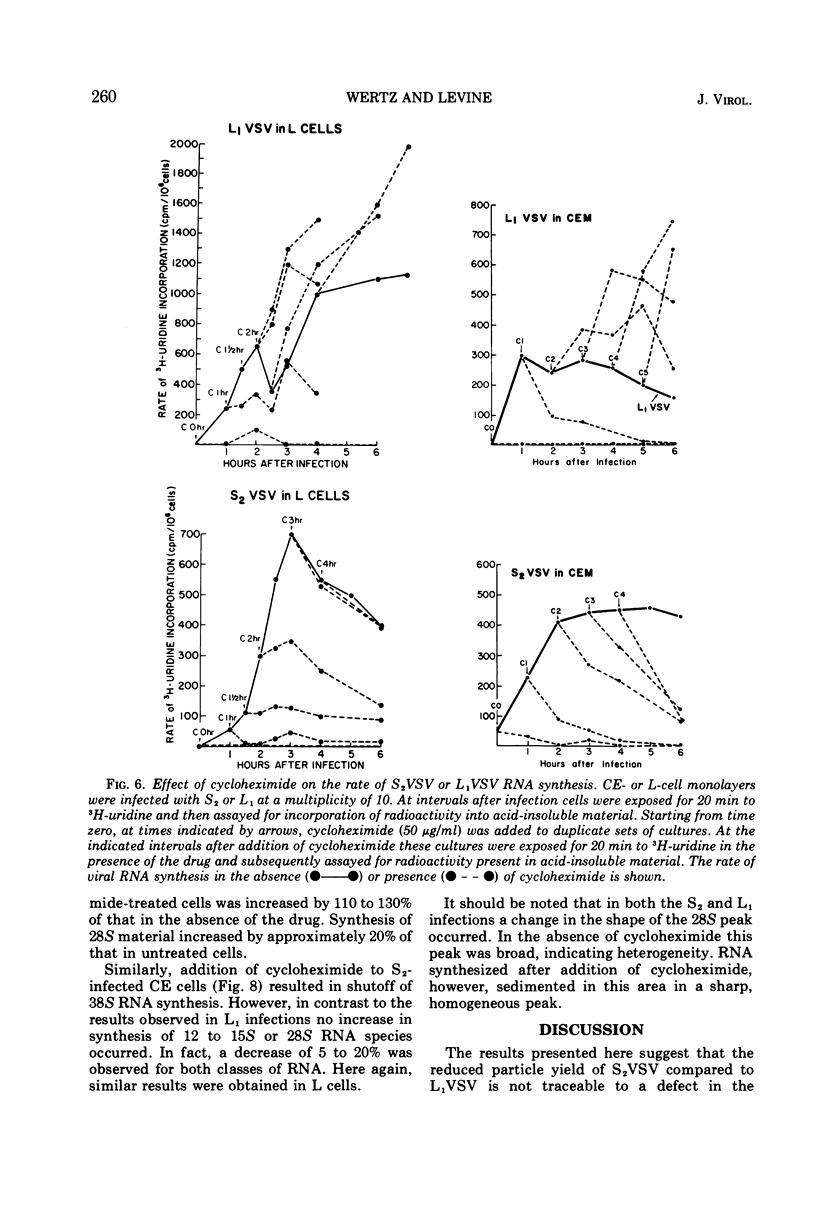
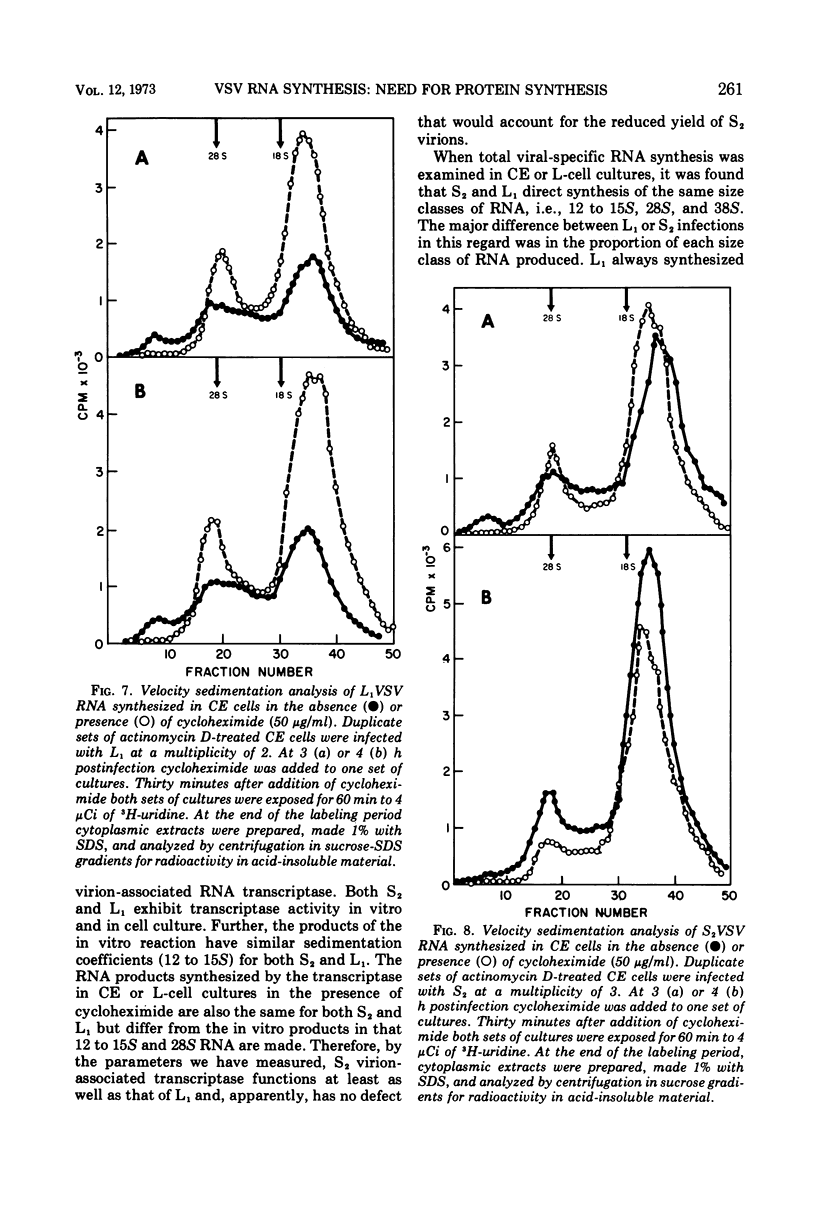
The synthesis of viral RNA by wild-type vesicular stomatitis virus (L1VSV) and a small, plaque-size mutant (S2VSV) was studied in vitro and in chicken embryo (CE) and mouse L-cell cultures. Virus-specific RNA synthesized in CE or L cells infected with either L1 or S2VSV at low multiplicity was of the same size classes, 12 to 15S, 28S, and 38S. The major differences were in the proportion of RNA produced of each size class. L1VSV always synthesized larger proportions of 38S RNA, and S2VSV produced larger proportions of 12 to 15S RNA. Both S2 and L1VSV exhibited RNA transcriptase activity in vitro and in cell culture. The products of the in vitro reaction were the same, 12 to 15S for both. The products of the virion-associated transcriptase in CE or L-cell cultures in the presence of cycloheximide were also the same for both viruses but differed from the in vitro products in that 28S and 12 to 15S RNA were made. The effects of addition of cycloheximide at various times after infection demonstrated that new protein synthesis is required early (0-2 h) for both S2 and L1VSV to initiate and maintain the normal rate of viral RNA synthesis. However, the overall rate of RNA synthesis in L1VSV infections became independent of protein synthesis after 2 h whereas the rate in S2VSV infections did not. With either virus, synthesis of 38S RNA did not occur in the absence of protein synthesis. Moreover, continuous 38S RNA production required continuous protein synthesis. Production of 38S RNA ceased within 30 min after addition of cycloheximide to S2− or L1VSV-infected CE or L cells that had already begun to synthesize the 38S form. The cycloheximide-induced cessation of 38S RNA synthesis was accompanied by a marked increase in production of 12 to 15S and 28S RNA in L1VSV-infected cells, but no increase in synthesis of small RNA species occurred in S2VSV-infected cells.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baltimore D., Huang A. S., Stampfer M. Ribonucleic acid synthesis of vesicular stomatitis virus, II. An RNA polymerase in the virion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Jun;66(2):572–576. doi: 10.1073/pnas.66.2.572. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop D. H. Complete transcription by the transcriptase of vesicular stomatitis virus. J Virol. 1971 Apr;7(4):486–490. doi: 10.1128/jvi.7.4.486-490.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop D. H., Roy P. Kinetics of RNA synthesis by vesicular stomatitis virus particles. J Mol Biol. 1971 May 14;57(3):513–527. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90106-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown F., Martin S. J., Cartwright B., Crick J. The ribonucleic acids of the infective and interfering components of vesicular stomatitis virus. J Gen Virol. 1967 Oct;1(4):479–486. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-1-4-479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANKLIN R. M. THE INHIBITION OF RIBONUCLEIC ACID SYNTHESIS IN MAMMALIAN CELLS BY ACTINOMYCIN D. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Aug 20;72:555–565. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hackett A. J., Schaffer F. L., Madin S. H. The separation of infectious and autointerfering particles in vesicular stomatitis virus preparations. Virology. 1967 Jan;31(1):114–119. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(67)90014-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang A. S., Baltimore D., Stampfer M. Ribonucleic acid synthesis of vesicular stomatitis virus. 3. Multiple complementary messenger RNA molecules. Virology. 1970 Dec;42(4):946–957. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90343-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang A. S., Greenawalt J. W., Wagner R. R. Defective T particles of vesicular stomatitis virus. I. Preparation, morphology, and some biologic properties. Virology. 1966 Oct;30(2):161–172. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(66)90092-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang A. S., Manders E. K. Ribonucleic acid synthesis of vesicular stomatitis virus. IV. Transcription by standard virus in the presence of defective interfering particles. J Virol. 1972 Jun;9(6):909–916. doi: 10.1128/jvi.9.6.909-916.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang A. S., Wagner R. R. Comparative sedimentation coefficients of RNA extracted from plaque-forming and defective particles of vesicular stomatitis virus. J Mol Biol. 1966 Dec 28;22(2):381–384. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(66)90143-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiley M. P., Wagner R. R. Ribonucleic acid species of intracellular nucleocapsids and released virions of vesicular stomatitis virus. J Virol. 1972 Aug;10(2):244–255. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.2.244-255.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcus P. I., Engelhardt D. L., Hunt J. M., Sekellick M. J. Interferon action: inhibition of vesicular stomatitis virus RNA synthesis induced by virion-bound polymerase. Science. 1971 Nov 5;174(4009):593–598. doi: 10.1126/science.174.4009.593. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mudd J. A., Summers D. F. Polysomal ribonucleic acid of vesicular stomatitis virus-infected HeLa cells. Virology. 1970 Dec;42(4):958–968. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90344-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petric M., Prevec L. Vesicular stomatitis virus--a new interfering particle, intracellular structures, and virus-specific RNA. Virology. 1970 Aug;41(4):615–630. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90427-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schincariol A. L., Howatson A. F. Replication of vesicular stomatitis virus. I. Viral specific RNA and nucleoprotein in infected L cells. Virology. 1970 Nov;42(3):732–743. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90319-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schincariol A. L., Howatson A. F. Replication of vesicular stomatitis virus. II. Separation and characterization of virus-specific RNA species. Virology. 1972 Sep;49(3):766–783. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90533-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stampfer M., Baltimore D., Huang A. S. Ribonucleic acid synthesis of vesicular stomatitis virus. I. Species of ribonucleic acid found in Chinese hamster ovary cells infected with plaque-forming and defective particles. J Virol. 1969 Aug;4(2):154–161. doi: 10.1128/jvi.4.2.154-161.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner R. R., Kiley M. P., Snyder R. M., Schnaitman C. A. Cytoplasmic compartmentalization of the protein and ribonucleic acid species of vesicular stomatitis virus. J Virol. 1972 Apr;9(4):672–683. doi: 10.1128/jvi.9.4.672-683.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wertz G. W., Youngner J. S. Inhibition of protein synthesis in L cells infected with vesicular stomatitis virus. J Virol. 1972 Jan;9(1):85–89. doi: 10.1128/jvi.9.1.85-89.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wertz G. W., Youngner J. S. Interferon production and inhibition of host synthesis in cells infected with vesicular stomatitis virus. J Virol. 1970 Oct;6(4):476–484. doi: 10.1128/jvi.6.4.476-484.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wild T. F. Replication of vesicular stomatitis virus: characterization of the virus-induced RNA. J Gen Virol. 1971 Nov;13(2):295–310. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-13-2-295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youngner J. S., Wertz G. Interferon production in mice by vesicular stomatitis virus. J Virol. 1968 Nov;2(11):1360–1361. doi: 10.1128/jvi.2.11.1360-1361.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



