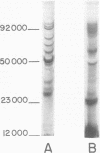
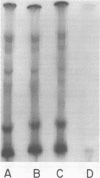
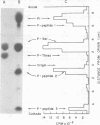
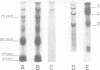
Abstract
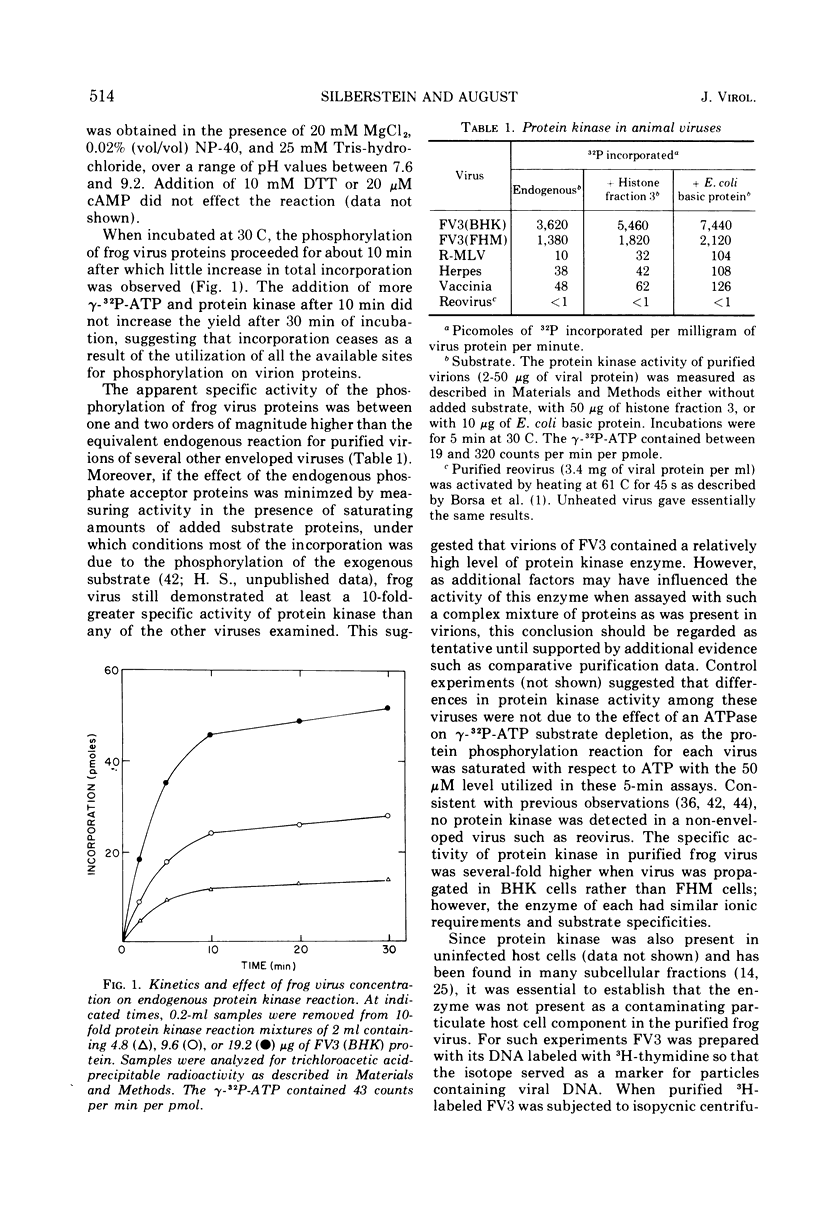
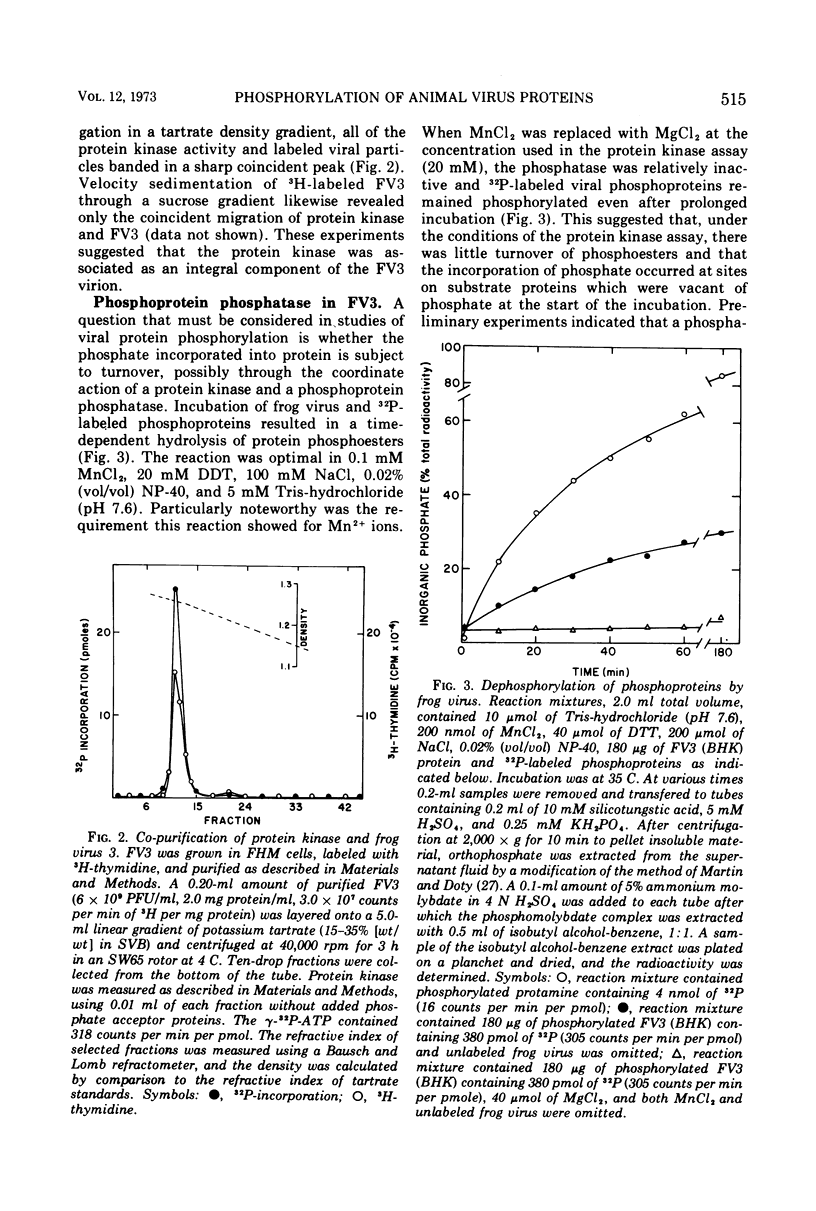
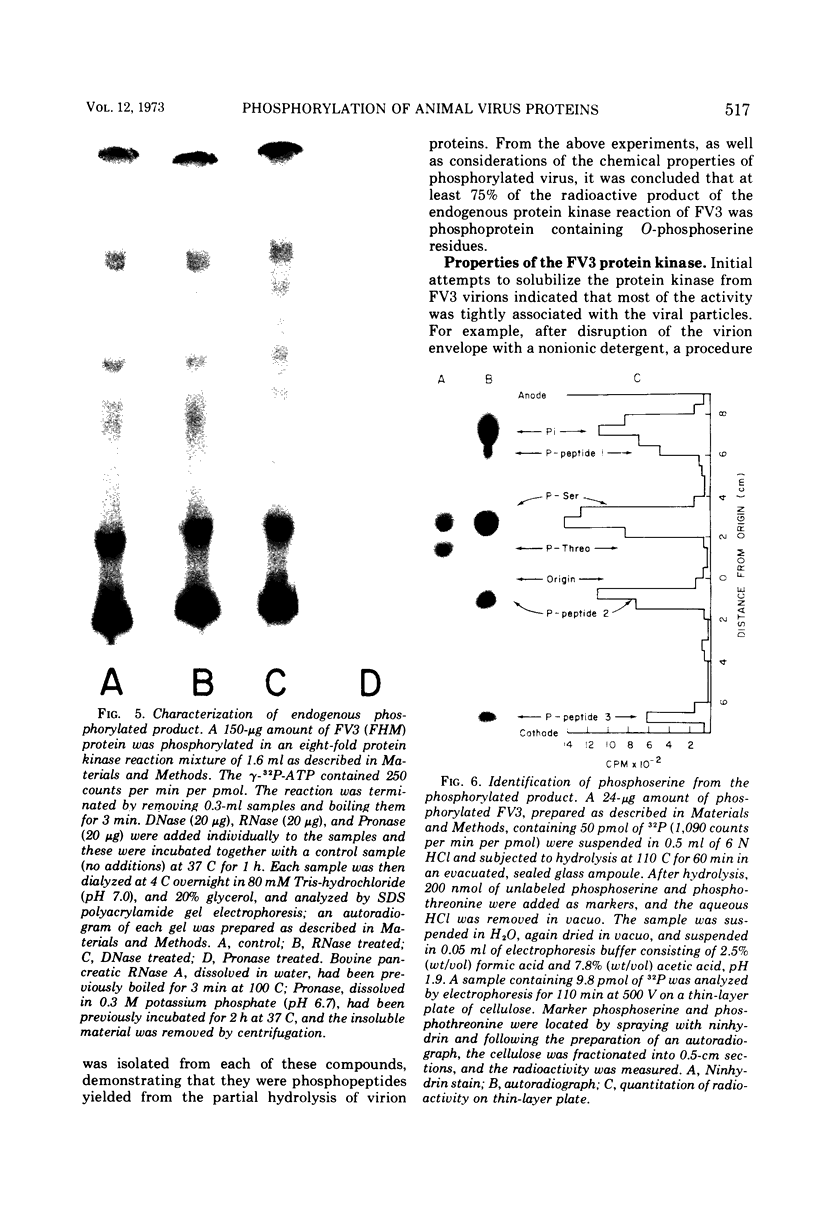
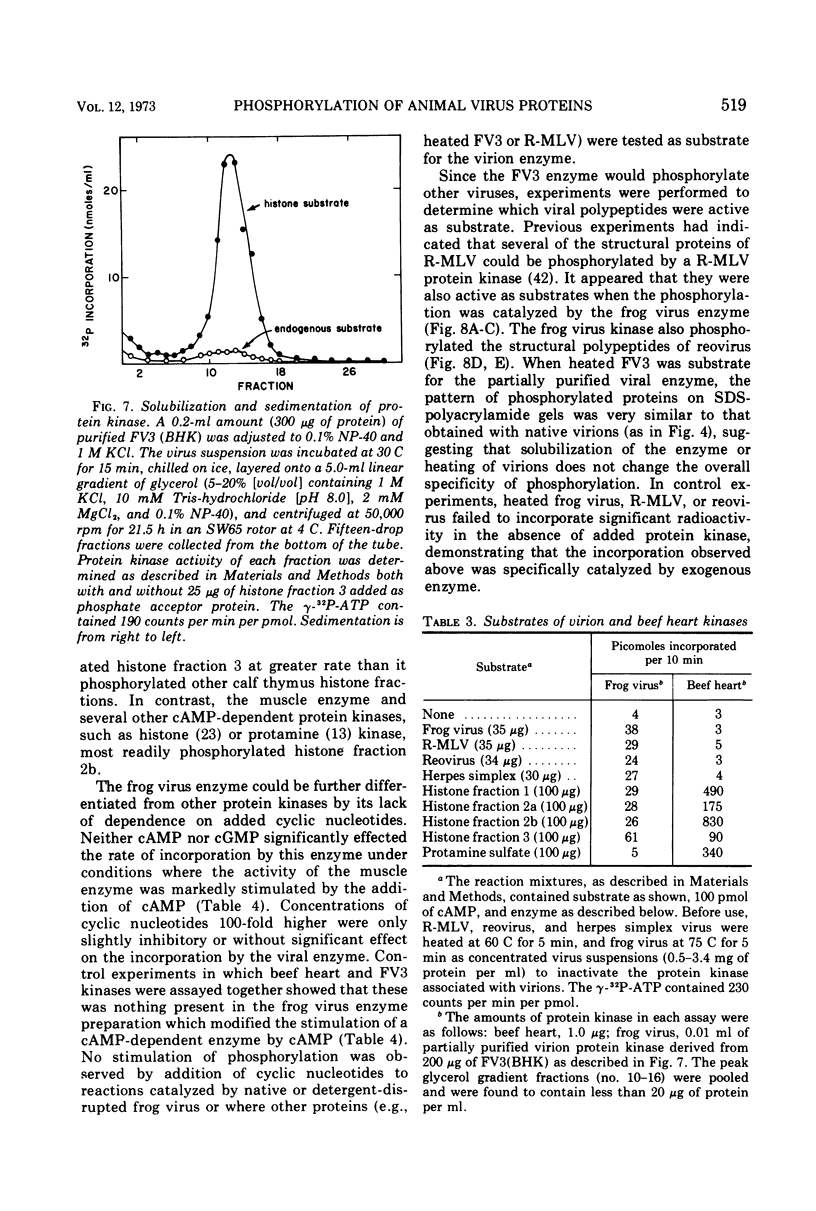
Compared with several other enveloped viruses, purified virions of frog virus 3 contained a relatively high activity of a protein kinase which catalyzed the phosphorylation of endogenous polypeptides or added substrate proteins. Virions also contained a phosphoprotein phosphatase activity which released phosphate covalently linked to proteins. It was possible to select reaction conditions where turnover of protein phosphoesters was minimal, as the phosphatase required Mn2+ ions for activity whereas the protein kinase was active in the presence of Mg2+ ions. Electrophoretic studies in polyacrylamide gels containing sodium dodecyl sulfate indicated that at least 10 of the virion polypeptides were phosphorylated in the in vitro protein kinase reaction. Characterization of these phosphoproteins demonstrated that the phosphate was incorporated predominantly in a phosphoester linkage with serine residues. The protein kinase was solubilized by disrupting purified virions with a nonionic detergent in a high-ionic-strength buffer and was separated from many of the virion substrate proteins by zonal centrifugation in glycerol gradients. The partially purified protein kinase would phosphorylate polypeptides of many different animal viruses, and maximal activity was not dependent on added cyclic nucleotides. These properties distinguished the virion protein kinase from a well characterized cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase which phosphorylated viral proteins only to a small extent.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BURNETT G., KENNEDY E. P. The enzymatic phosphorylation of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1954 Dec;211(2):969–980. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borsa J., Grover J., Chapman J. D. Presence of nucleoside triphosphate phosphohydrolase activity in purified virions of reovirus. J Virol. 1970 Sep;6(3):295–302. doi: 10.1128/jvi.6.3.295-302.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eagle H. Buffer combinations for mammalian cell culture. Science. 1971 Oct 29;174(4008):500–503. doi: 10.1126/science.174.4008.500. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erlichman J., Hirsch A. H., Rosen O. M. Interconversion of cyclic nucleotide-activated and cyclic nucleotide-independent forms of a protein kinase from beef heart. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Apr;68(4):731–735. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.4.731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairbanks G., Jr, Levinthal C., Reeder R. H. Analysis of C14-labeled proteins by disc electrophoresis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1965 Aug 16;20(4):393–399. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(65)90589-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fields B. N., Joklik W. K. Isolation and preliminary genetic and biochemical characterization of temperature-sensitive mutants of reovirus. Virology. 1969 Mar;37(3):335–342. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90217-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill G. N., Garren L. D. Role of the receptor in the mechanism of action of adenosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Apr;68(4):786–790. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.4.786. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granoff A., Came P. E., Breeze D. C. Viruses and renal carcinoma of Rana pipiens. I. The isolation and properties of virus from normal and tumor tissue. Virology. 1966 May;29(1):133–148. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(66)90203-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gravell M., Cromeans T. L. Viron-associated protein kinase and its involvement in nongenetic reactivation of frog polyhedral cytoplasmic deoxyribovirus. Virology. 1972 Jun;48(3):847–851. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90167-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gravell M., Malsberger R. G. A permanent cell line from the fathead minnow (Pimephales promelas). Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1965 Aug 10;126(1):555–565. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1965.tb14302.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatanaka M., Twiddy E., Gilden R. V. Protein kinase associated with RNA tumor viruses and other budding RNA viruses. Virology. 1972 Feb;47(2):536–538. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90297-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOKLIK W. K. The preparation and characteristics of highly purified radioactively labelled poxvirus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Aug 20;61:290–301. doi: 10.1016/0926-6550(62)90091-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOKLIK W. K. The purification fo four strains of poxvirus. Virology. 1962 Sep;18:9–18. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(62)90172-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jergil B., Dixon G. H. Protamine kinase from rainbow trout testis. Partial purification and characterization. J Biol Chem. 1970 Jan 25;245(2):425–434. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jergil B. Protein kinase from rainbow-trout-testis ribosomes. Partial purification and characterization. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Aug 4;28(4):546–554. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb01943.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson E. M., Maeno H., Greengard P. Phosphorylation of endogenous protein of rat brain by cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1971 Dec 25;246(24):7731–7739. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kabat D. Phosphorylation of ribosomal proteins in rabbit reticulocytes. A cell-free system with ribosomal protein kinase activity. Biochemistry. 1971 Jan 19;10(2):197–203. doi: 10.1021/bi00778a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krishna G., Weiss B., Brodie B. B. A simple, sensitive method for the assay of adenyl cyclase. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1968 Oct;163(2):379–385. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo C. H., August J. T. Histone or bacterial basic protein required for replication of bacteriophage RNA. Nat New Biol. 1972 May 24;237(73):105–108. doi: 10.1038/newbio237105a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo J. F., Greengard P. Cyclic nucleotide-dependent protein kinases. IV. Widespread occurrence of adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinase in various tissues and phyla of the animal kingdom. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Dec;64(4):1349–1355. doi: 10.1073/pnas.64.4.1349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langan T. A. Action of adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate-dependent histone kinase in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1969 Oct 25;244(20):5763–5765. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langan T. A. Histone phosphorylation: stimulation by adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate. Science. 1968 Nov 1;162(3853):579–580. doi: 10.1126/science.162.3853.579. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemaire S., Pelletier G., Labrie F. Adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinase from bovine anterior pituitary gland. II. Subcellular distribution. J Biol Chem. 1971 Dec 10;246(23):7303–7310. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meisler M. H., Langan T. A. Characterization of a phosphatase specific for phosphorylated histones and protamine. J Biol Chem. 1969 Sep 25;244(18):4961–4968. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyamoto E., Kuo J. F., Greengard P. Cyclic nucleotide-dependent protein kinases. 3. Purification and properties of adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinase from bovine brain. J Biol Chem. 1969 Dec 10;244(23):6395–6402. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paoletti E., Moss B. Protein kinase and specific phosphate acceptor proteins associated with vaccinia virus cores. J Virol. 1972 Sep;10(3):417–424. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.3.417-424.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RABINOWITZ M., LIPMANN F. Reversible phosphate transfer between yolk phosphoprotein and adenosine triphosphate. J Biol Chem. 1960 Apr;235:1043–1050. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randall C. C., Rogers H. W., Downer D. N., Gentry G. A. Protein kinase activity in equine herpesvirus. J Virol. 1972 Feb;9(2):216–222. doi: 10.1128/jvi.9.2.216-222.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reimann E. M., Walsh D. A., Krebs E. G. Purification and properties of rabbit skeletal muscle adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinases. J Biol Chem. 1971 Apr 10;246(7):1986–1995. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubenstein A. S., Gravell M., Darlington R. Protein kinase in enveloped herpes simplex virions. Virology. 1972 Oct;50(1):287–290. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90374-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin C. S., Erlichman J., Rosen O. M. Cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinase of human erythrocyte membranes. J Biol Chem. 1972 Oct 10;247(19):6135–6139. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin C. S., Erlichman J., Rosen O. M. Molecular forms and subunit composition of a cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinase purified from bovine heart muscle. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jan 10;247(1):36–44. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruddon R. W., Anderson S. L. Presence of multiple protein kinase activities in rat liver nuclei. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Feb 25;46(4):1499–1508. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90777-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STOKER M., MACPHERSON I. SYRIAN HAMSTER FIBROBLAST CELL LINE BHK21 AND ITS DERIVATIVES. Nature. 1964 Sep 26;203:1355–1357. doi: 10.1038/2031355a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. E., Zweerink H. J., Joklik W. K. Polypeptide components of virions, top component and cores of reovirus type 3. Virology. 1969 Dec;39(4):791–810. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90017-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sokol F., Clark H. F. Phosphoproteins, structural components of rhabdoviruses. Virology. 1973 Mar;52(1):246–263. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90413-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spear P. G., Roizman B. Proteins specified by herpes simplex virus. V. Purification and structural proteins of the herpesvirion. J Virol. 1972 Jan;9(1):143–159. doi: 10.1128/jvi.9.1.143-159.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strand M., August J. T. Protein kinase and phosphate acceptor proteins in Rauscher murine leukaemia virus. Nat New Biol. 1971 Sep 29;233(39):137–140. doi: 10.1038/newbio233137a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan K. B., McAuslan B. R. Proteins of polyhedral cytoplasmic deoxyviruses. I. The structural polypeptides of FV 3 . Virology. 1971 Jul;45(1):200–207. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90127-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan K. B., Sokol F. Structural proteins of simian virus 40: phosphoproteins. J Virol. 1972 Nov;10(5):985–994. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.5.985-994.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tao M., Salas M. L., Lipmann F. Mechanism of activation by adenosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate of a protein phosphokinase from rabbit reticulocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Sep;67(1):408–414. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.1.408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walton G. M., Gill G. N., Abrass I. B., Garren L. D. Phosphorylation of ribosome-associated protein by an adenosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate-dependent protein kinase: location of the microsomal receptor and protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 May;68(5):880–884. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.5.880. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weller M., Rodnight R. Stimulation by cyclic AMP of intrinsic protein kinase activity in ox brain membrane preparations. Nature. 1970 Jan 10;225(5228):187–188. doi: 10.1038/225187a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]