Abstract
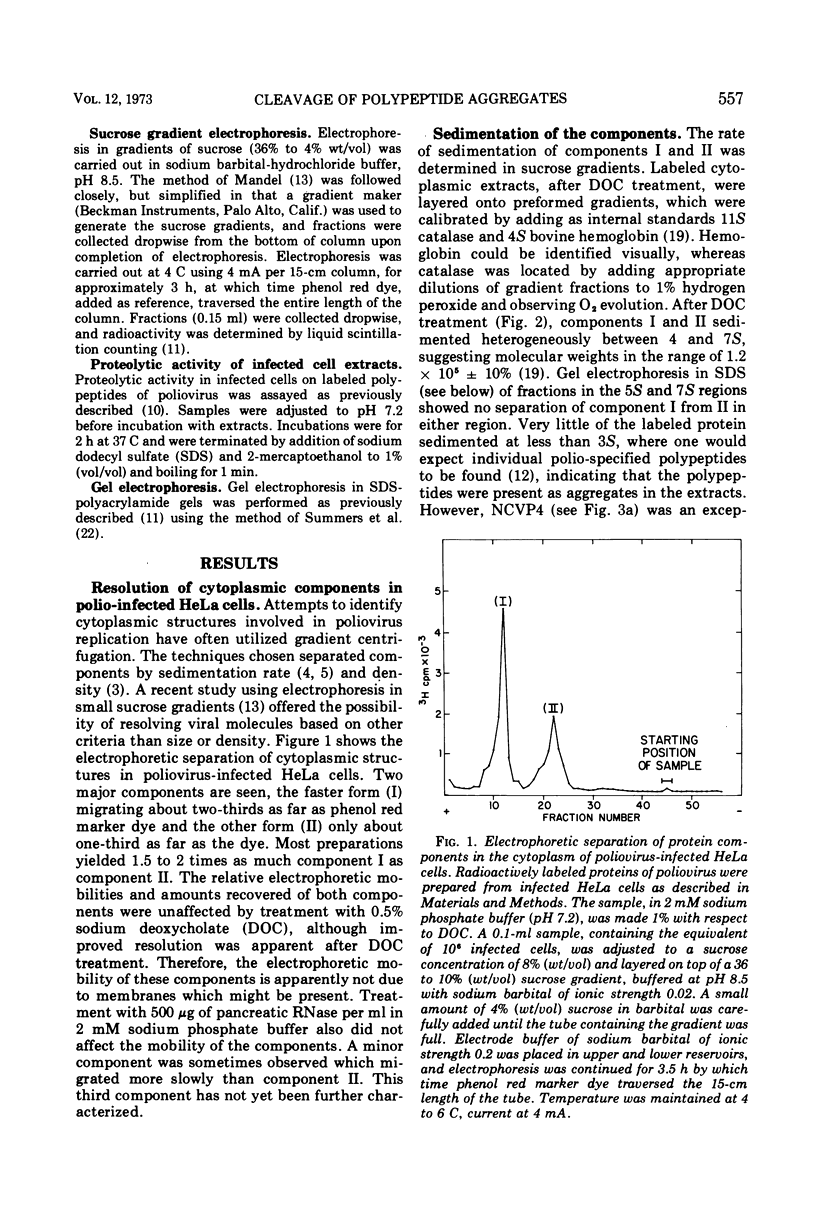
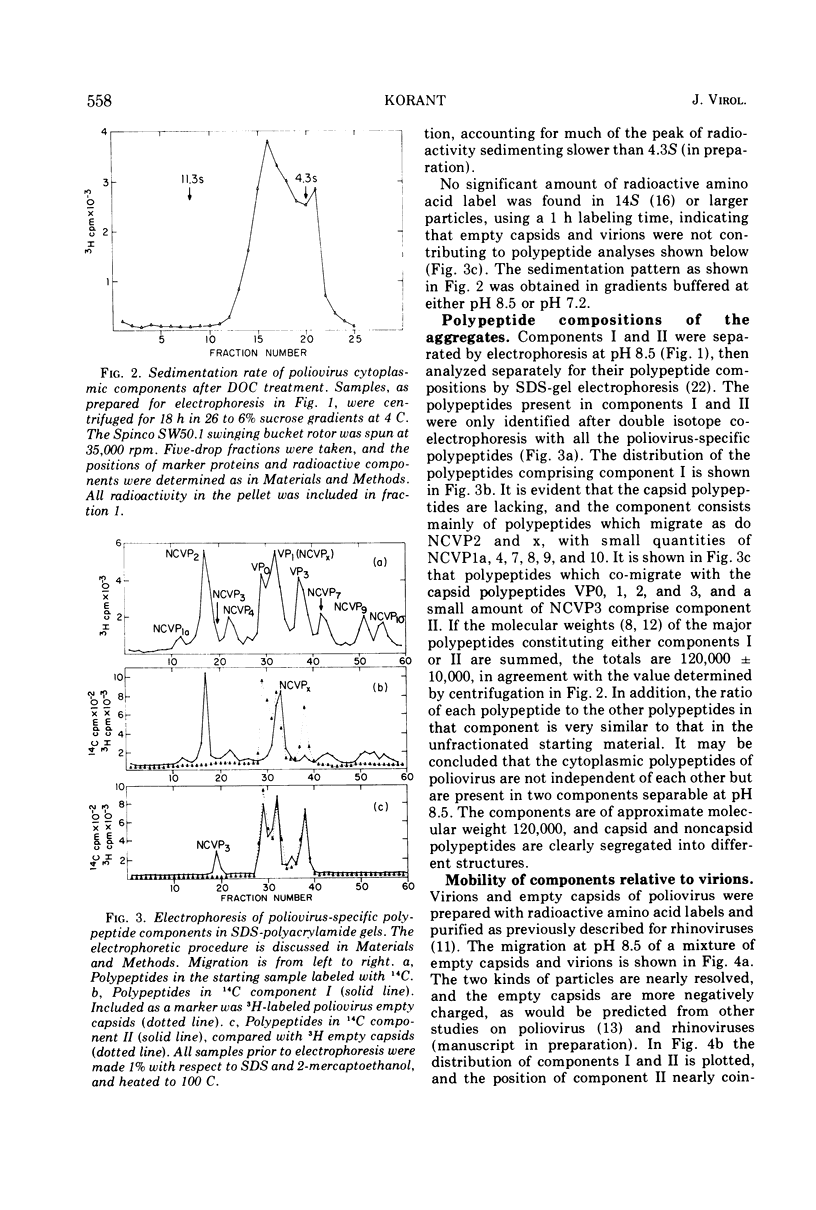
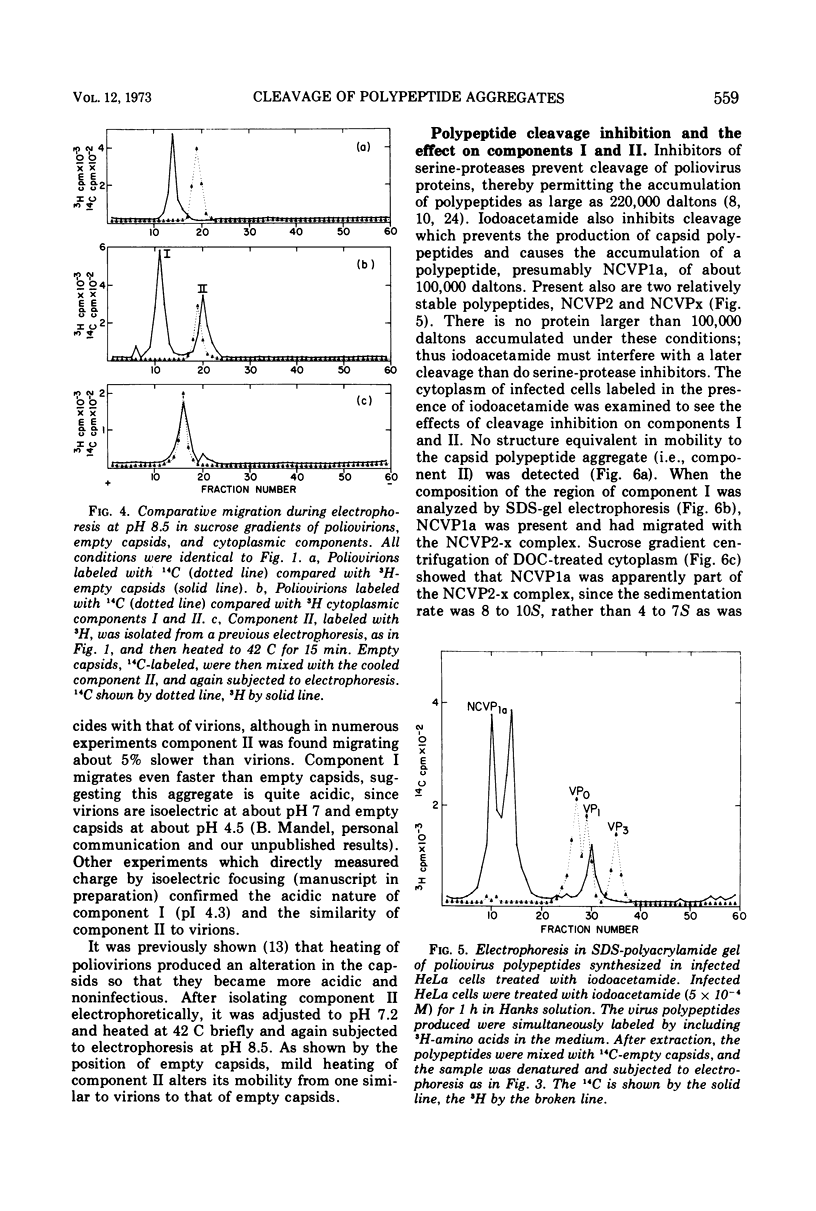
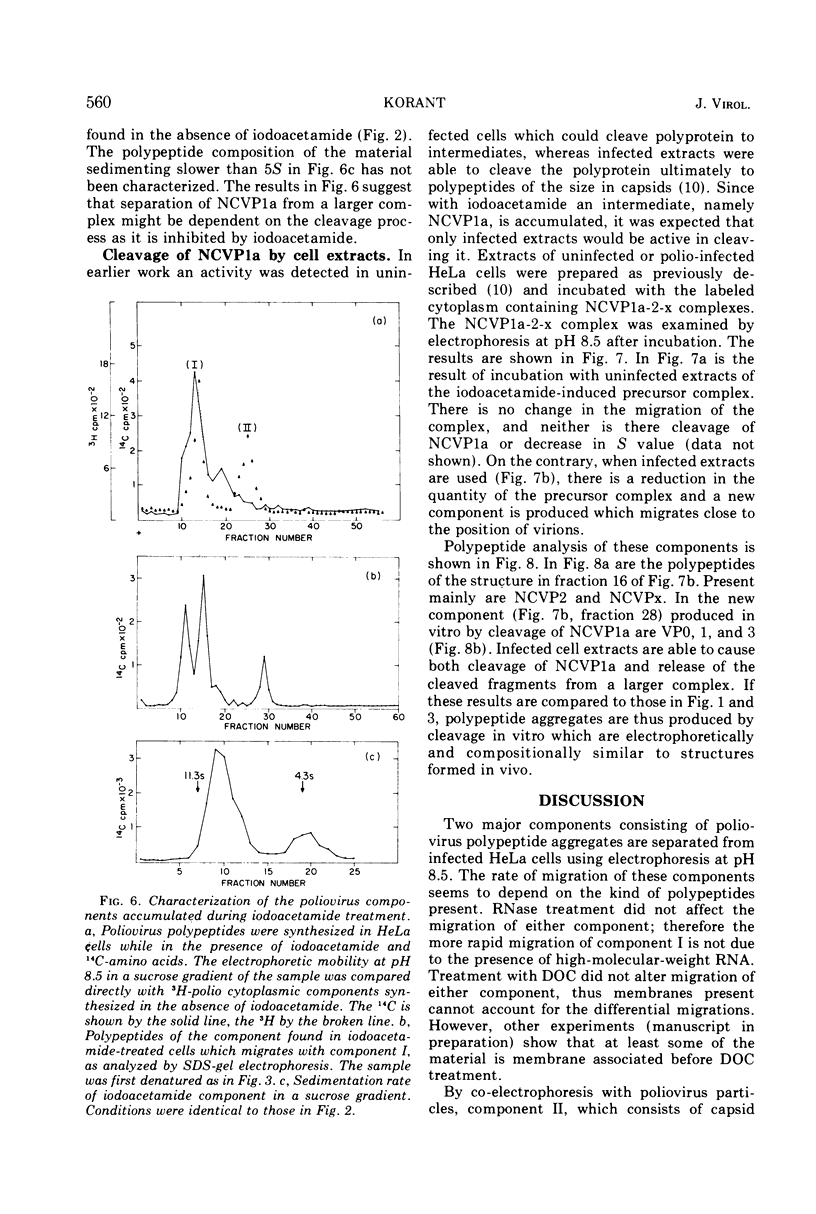
Zonal electrophoresis resolves two aggregates of poliovirus type 2 cytoplasmic polypeptides. The more negatively charged aggregate contains mainly noncapsid viral-specific polypeptides (NCVP) 2 and x, whereas the other consists of the capsid polypeptides (VP) 0, 1, 2, and 3 (VP0, VP1, VP2, VP3). After treatment with sodium deoxycholate (DOC), the aggregates sediment at 5 to 6S. Their electrophoretic mobilities are unaffected by DOC or RNase. The capsid polypeptide aggregate is similar in mobility to virions but can be converted to a faster electrophoretic form, resembling empty capsids, by heating. If infected HeLa cells are allowed to synthesize poliovirus polypeptides in the presence of iodoacetamide, no capsid polypeptides are produced, but rather NCVP1a (the precursor to capsid polypeptides) is accumulated, along with NCVP2 and NCVPx. When analyzed by electrophoresis and centrifugation, uncleaved NCVP1a migrates with the NCVP2-x aggregate. NCVP1a can be cleaved to capsid-like polypeptides in vitro by using extracts of infected cells, but not uninfected cells, indicating either a virus-specified protease or a cellular enzyme activated during infection. After cleavage of NCVP1a by infected cell extracts, the capsid polypeptides which are produced dissociate from the NCVP2-x complex.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baltimore D. Viral genetic systems. Trans N Y Acad Sci. 1971 Mar;33(3):327–332. doi: 10.1111/j.2164-0947.1971.tb02600.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butterworth B. E., Hall L., Stoltzfus C. M., Rueckert R. R. Virus-specific proteins synthesized in encephalomyocarditis virus-infected HeLa cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Dec;68(12):3083–3087. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.12.3083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caliguiri L. A., Mosser A. G. Proteins associated with the poliovirus RNA replication complex. Virology. 1971 Nov;46(2):375–386. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90039-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper P. D., Geissler E., Scotti P. D., Tannock G. A. Further characterization of the genetic map of poliovirus temperature-sensitive mutants. In: strategy of the viral genome. Ciba Found Symp. 1971:75–100. doi: 10.1002/9780470719824.ch5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrenfeld E., Maizel J. V., Summers D. F. Soluble RNA polymerase complex from poliovirus-infected HeLa cells. Virology. 1970 Apr;40(4):840–846. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90129-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghendon Y. Z., Yakobson E. A. Antigenic specificity of poliovirus-related particles. J Virol. 1971 Oct;8(4):589–590. doi: 10.1128/jvi.8.4.589-590.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland J. J., Kiehn E. D. Specific cleavage of viral proteins as steps in the synthesis and maturation of enteroviruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Jul;60(3):1015–1022. doi: 10.1073/pnas.60.3.1015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson M. F., Asso J., Baltimore D. Further evidence on the formation of poliovirus proteins. J Mol Biol. 1970 May 14;49(3):657–669. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90289-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson M. F., Baltimore D. Polypeptide cleavages in the formation of poliovirus proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Sep;61(1):77–84. doi: 10.1073/pnas.61.1.77. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korant B. D. Cleavage of viral precursor proteins in vivo and in vitro. J Virol. 1972 Oct;10(4):751–759. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.4.751-759.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korant B. D., Lonberg-Holm K., Noble J., Stasny J. T. Naturally occurring and artificially produced components of three rhinoviruses. Virology. 1972 Apr;48(1):71–86. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90115-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maizel J. V., Jr, Summers D. F. Evidence for differences in size and composition of the poliovirus-specific polypeptides in infected HeLa cells. Virology. 1968 Sep;36(1):48–54. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(68)90115-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel B. Characterization of type 1 poliovirus by electrophoretic analysis. Virology. 1971 Jun;44(3):554–568. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90369-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POLSON A., SELZER G., VAN DEN ENDE M. The electrophoretic mobilities of adapted MEF1 poliomyelitis virus and its soluble antigen. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1957 Jun;24(3):600–603. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(57)90253-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips B. A., Summers D. F., Maizel J. V., Jr In vitro assembly of poliovirus-related particles. Virology. 1968 Jun;35(2):216–226. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(68)90262-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHARFF M. D., MAIZEL J. V., Jr, LEVINTOW L. PHYSICAL AND IMMUNOLOGICAL PROPERTIES OF A SOLUBLE PRECURSOR OF THE POLIOVIRUS CAPSID. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Feb;51:329–337. doi: 10.1073/pnas.51.2.329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugiyama T., Korant B. D., Lonberg-Holm K. K. RNA virus gene expression and its control. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1972;26:467–502. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.26.100172.002343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers D. F., Maizel J. V., Jr, Darnell J. E., Jr Evidence for virus-specific noncapsid proteins in poliovirus-infected HeLa cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Aug;54(2):505–513. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.2.505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers D. F., Maizel J. V., Jr Evidence for large precursor proteins in poliovirus synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Mar;59(3):966–971. doi: 10.1073/pnas.59.3.966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers D. F., Roumiantzeff M., Maizel J. V. The translation and processing of poliovirus proteins. In: strategy of the viral genome. Ciba Found Symp. 1971:111–140. doi: 10.1002/9780470719824.ch7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers D. F., Shaw E. N., Stewart M. L., Maizel J. V., Jr Inhibition of cleavage of large poliovirus-specific precursor proteins in infected HeLa cells by inhibitors of proteolytic enzymes. J Virol. 1972 Oct;10(4):880–884. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.4.880-884.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WATANABE Y., WATANABE K., HINUMA Y. Synthesis of poliovirus-specific proteins in HeLa cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Dec 31;61:976–977. doi: 10.1016/0926-6550(62)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


