Abstract
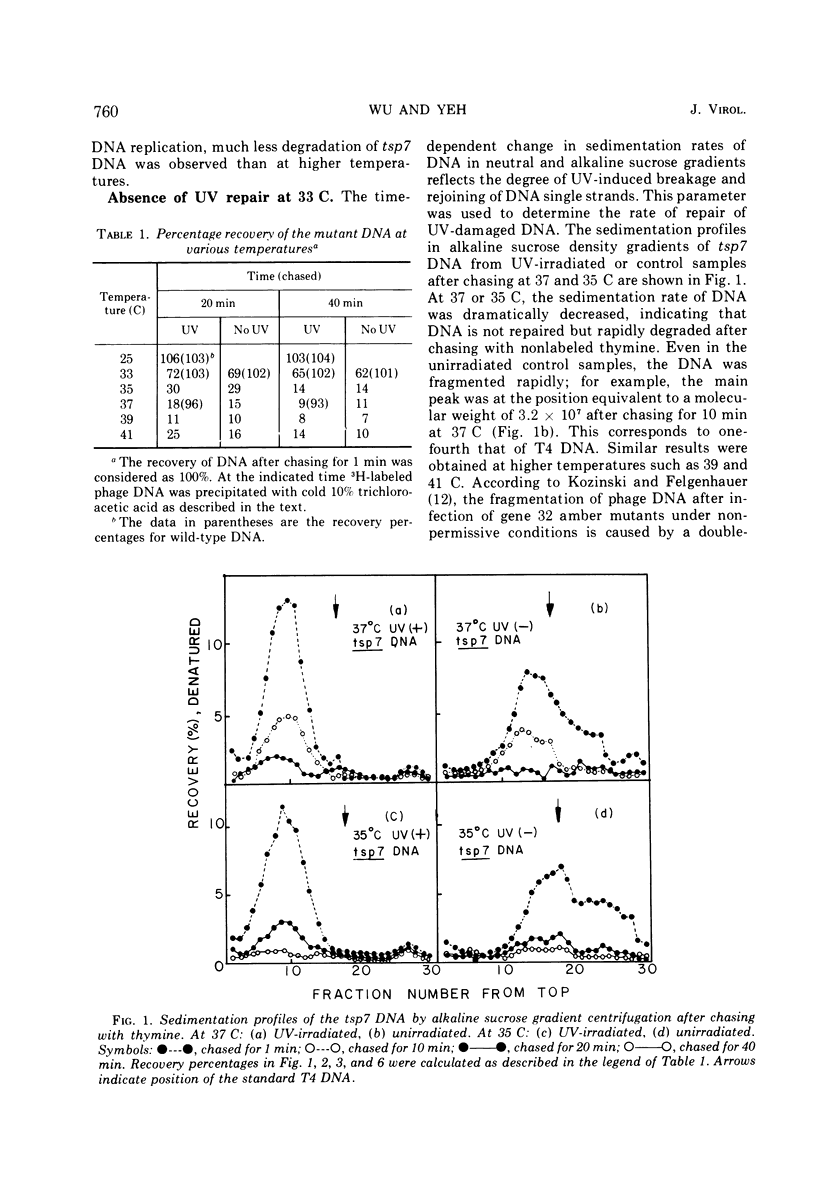
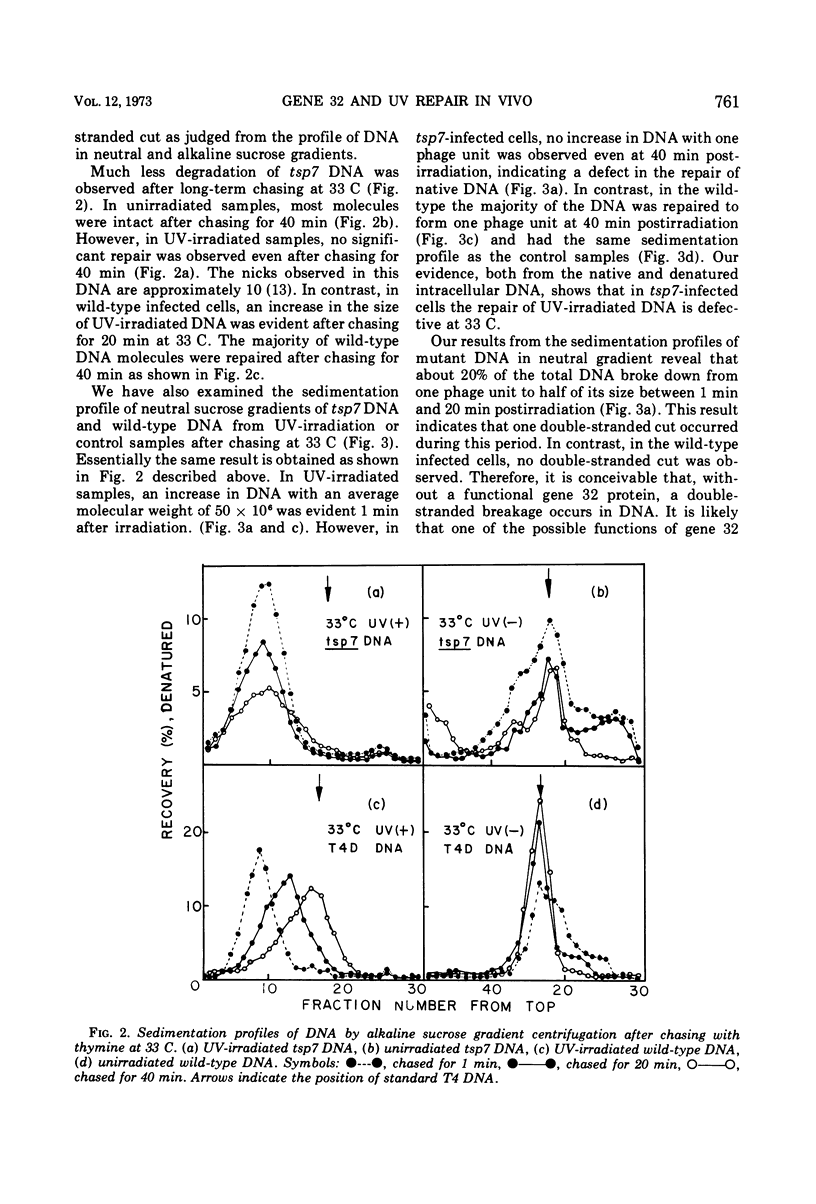
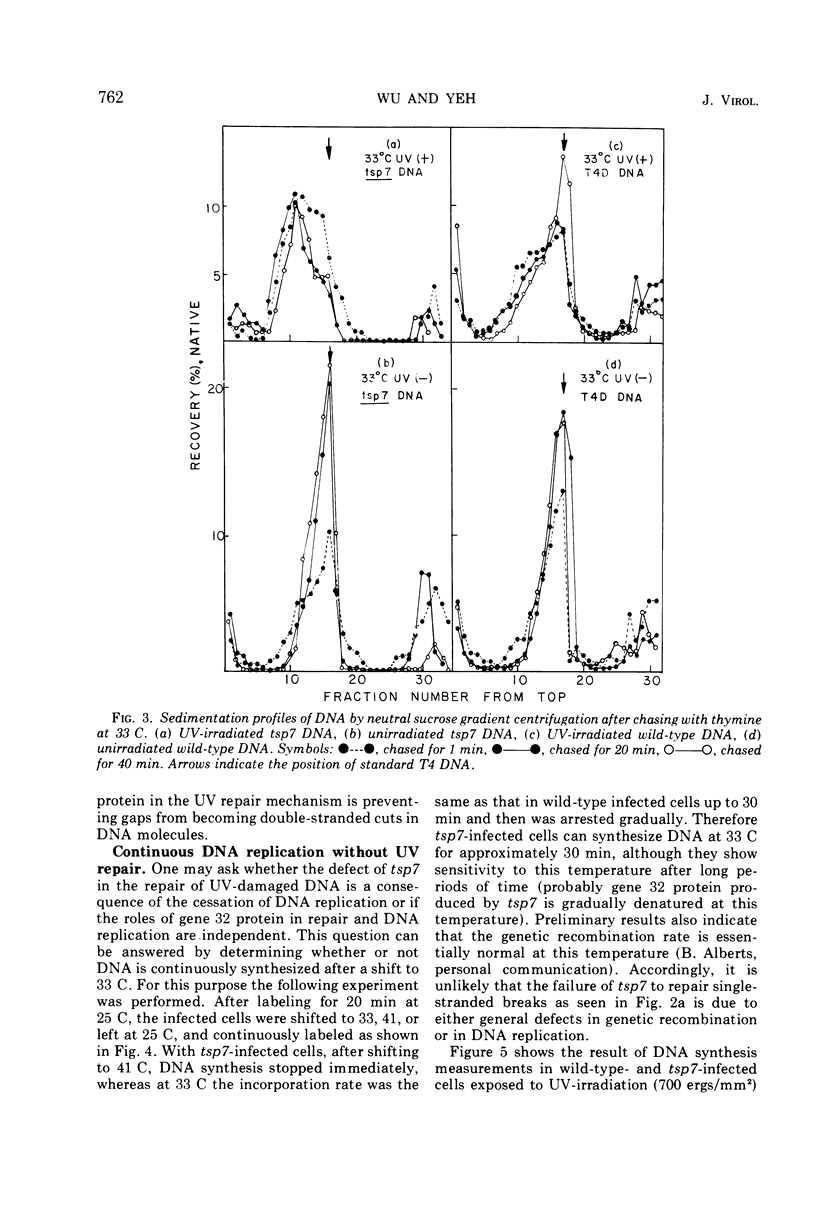
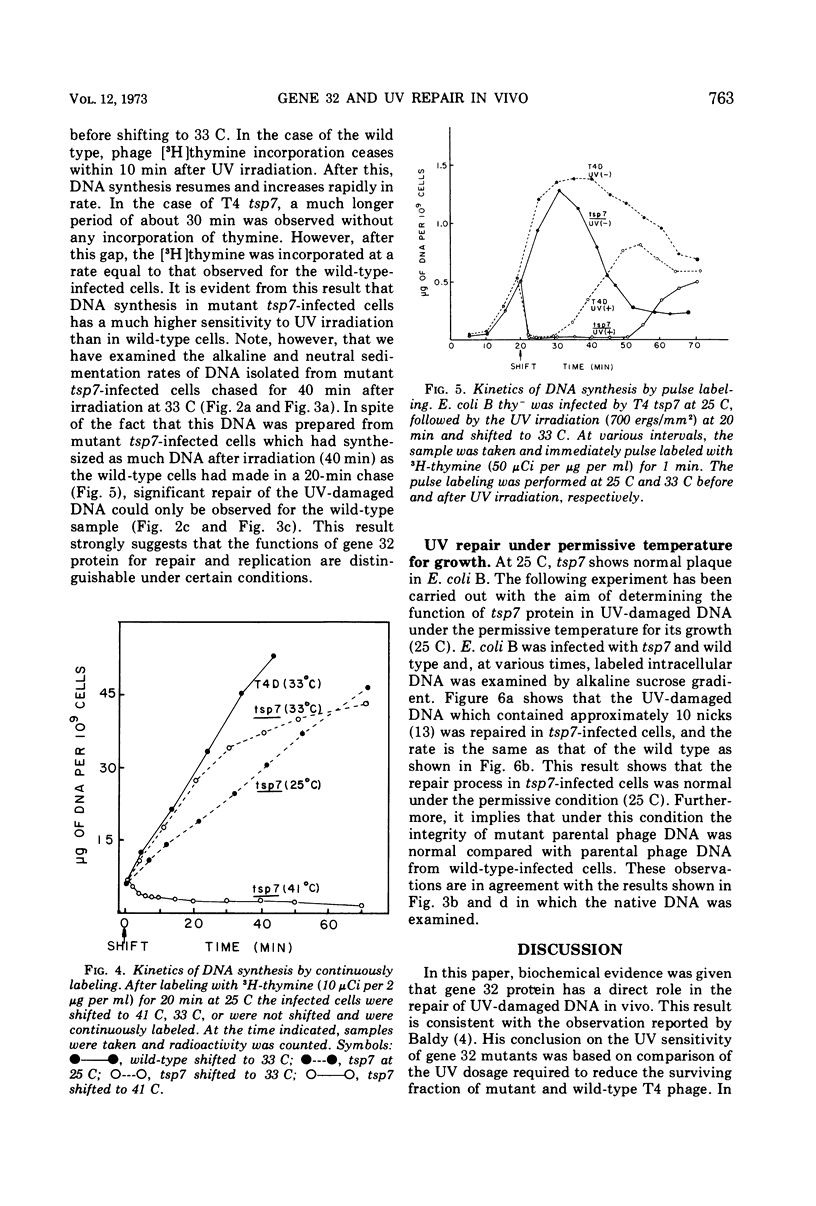
A temperature-sensitive mutation in gene 32 was used to study the role of gene 32 protein in the repair of UV-damaged DNA of bacteriophage T4. It was possible to distinguish between repair and replication of DNA at 33 C. At this temperature, DNA replication continued, and the intracellular DNA was stable. In contrast, no significant repair of UV-damaged DNA was observed even 40 min after the irradiation. Therefore, it was concluded that the defect in the repair mechanism at this temperature is not a simple consequence of the defect in DNA replication but that gene 32 apparently has an independent role for DNA repair. It was reported previously that gene 32 product is required for both T4 DNA replication and genetic recombination. In addition to these findings, this study has given direct evidence that, in vivo, this protein is also essential for the UV repair mechanism.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alberts B. M., Frey L. T4 bacteriophage gene 32: a structural protein in the replication and recombination of DNA. Nature. 1970 Sep 26;227(5265):1313–1318. doi: 10.1038/2271313a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURGI E., HERSHEY A. D. Sedimentation rate as a measure of molecular weight of DNA. Biophys J. 1963 Jul;3:309–321. doi: 10.1016/s0006-3495(63)86823-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldy M. W. The UV sensitivity of some early-function temperature-sensitive mutants of phage T4. Virology. 1970 Feb;40(2):272–287. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90403-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frankel F. R. Evidence for long DNA strands in the replicating pool after T4 infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Jan;59(1):131–138. doi: 10.1073/pnas.59.1.131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frankel F. R. Studies on the nature of replicating DNA in T4-infected Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1966 Jun;18(1):127–143. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80081-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedberg E. C., King J. J. Dark repair of ultraviolet-irradiated deoxyribonucleic acid by bacteriophage T4: purification and characterization of a dimer-specific phage-induced endonuclease. J Bacteriol. 1971 May;106(2):500–507. doi: 10.1128/jb.106.2.500-507.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray H. B., Jr, Hearst J. E. Flexibility of native DNA from the sedimentation behavior as a function of molecular weight and temperature. J Mol Biol. 1968 Jul 14;35(1):111–129. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(68)80041-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huberman J. A., Kornberg A., Alberts B. M. Stimulation of T4 bacteriophage DNA polymerase by the protein product of T4 gene 32. J Mol Biol. 1971 Nov 28;62(1):39–52. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90129-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozinski A. W., Felgenhauer Z. Z. Molecular recombination in T4 bacteriophage deoxyribonucleic acid. II. Single-strand breaks and exposure of uncomplemented areas as a prerequisite for recombination. J Virol. 1967 Dec;1(6):1193–1202. doi: 10.1128/jvi.1.6.1193-1202.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Litwin S., Shahn E., Kozinski A. W. Interpretation of sucrose gradient sedimentation pattern of deoxyribonucleic acid fragments resulting from random breaks. J Virol. 1969 Jul;4(1):24–30. doi: 10.1128/jvi.4.1.24-30.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. C., Kozinski A. W., Litwin S. Molecular Recombination in T4 Bacteriophage Deoxyribonucleic Acid: III. Formation of Long Single Strands During Recombination. J Virol. 1970 Mar;5(3):368–380. doi: 10.1128/jvi.5.3.368-380.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mortelmans K., Friedberg E. C. Deoxyribonucleic acid repair in bacteriophage T4: observations on the roles of the x and v genes and of host factors. J Virol. 1972 Oct;10(4):730–736. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.4.730-736.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prashad N., Hosoda J. Role of genes 46 and 47 in bacteriophage T4 reproduction. II. Formation of gaps on parental DNA of polynucleotide ligase defective mutants. J Mol Biol. 1972 Oct 14;70(3):617–635. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90562-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riva S., Cascino A., Geiduschek E. P. Coupling of late transcription to viral replication in bacteriophage T4 development. J Mol Biol. 1970 Nov 28;54(1):85–102. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90447-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snustad D. P. Dominance interactions in Escherichia coli cells mixedly infected with bacteriophage T4D wild-type and amber mutants and their possible implications as to type of gene-product function: catalytic vs. stoichiometric. Virology. 1968 Aug;35(4):550–563. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(68)90285-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomizawa J. I., Anraku N., Iwama Y. Molecular mechanisms of genetic recombination in bacteriophage. VI. A mutant defective in the joining of DNA molecules. J Mol Biol. 1966 Nov 14;21(2):247–253. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(66)90095-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


